Abstract
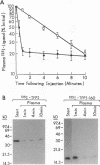
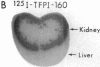
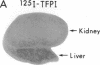
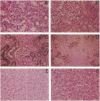
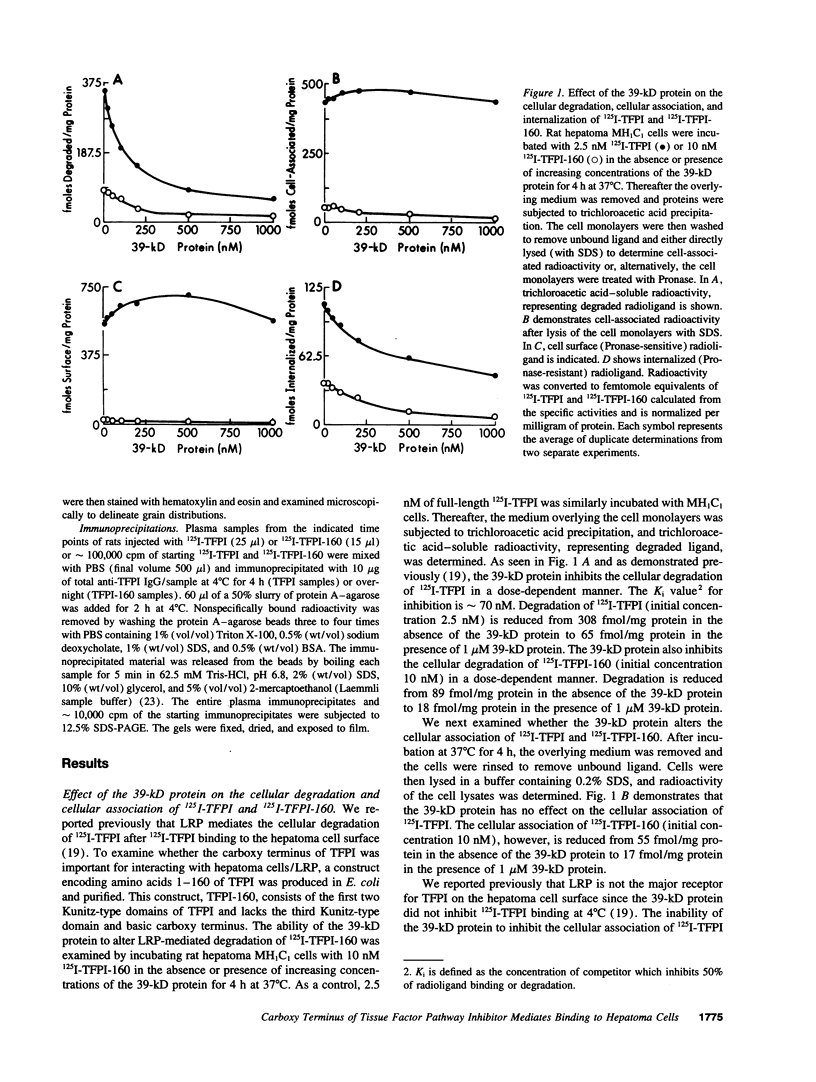
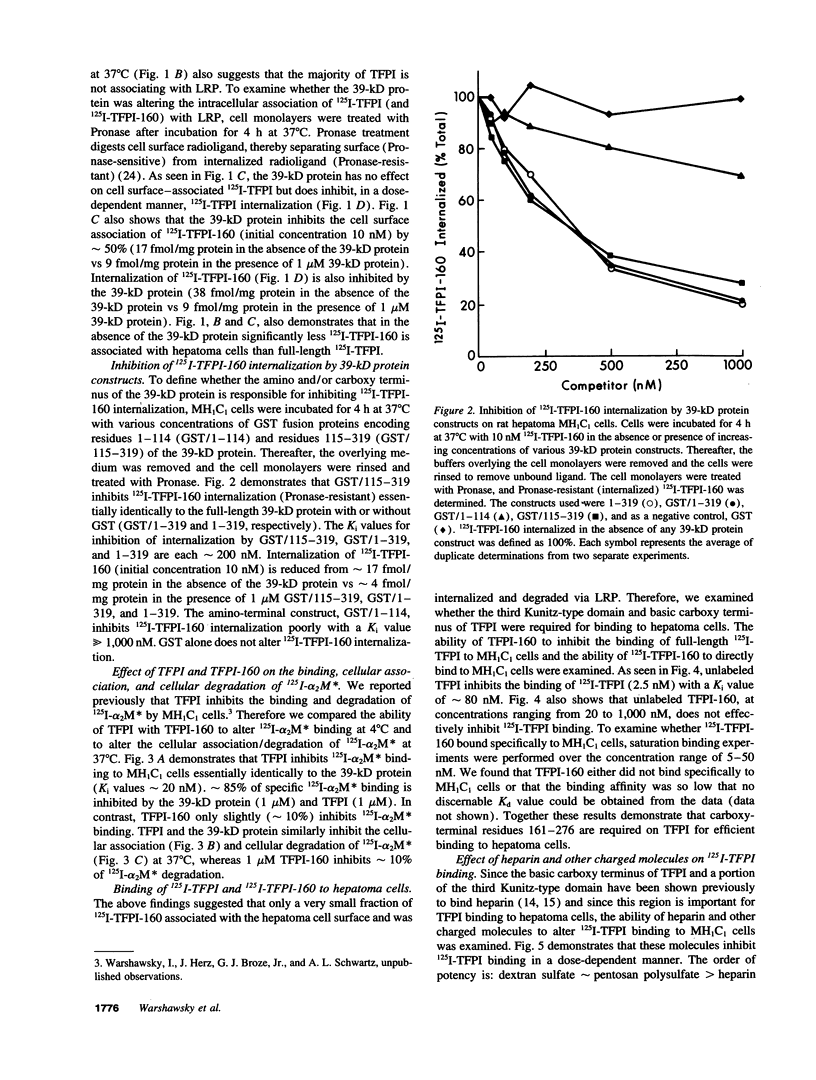
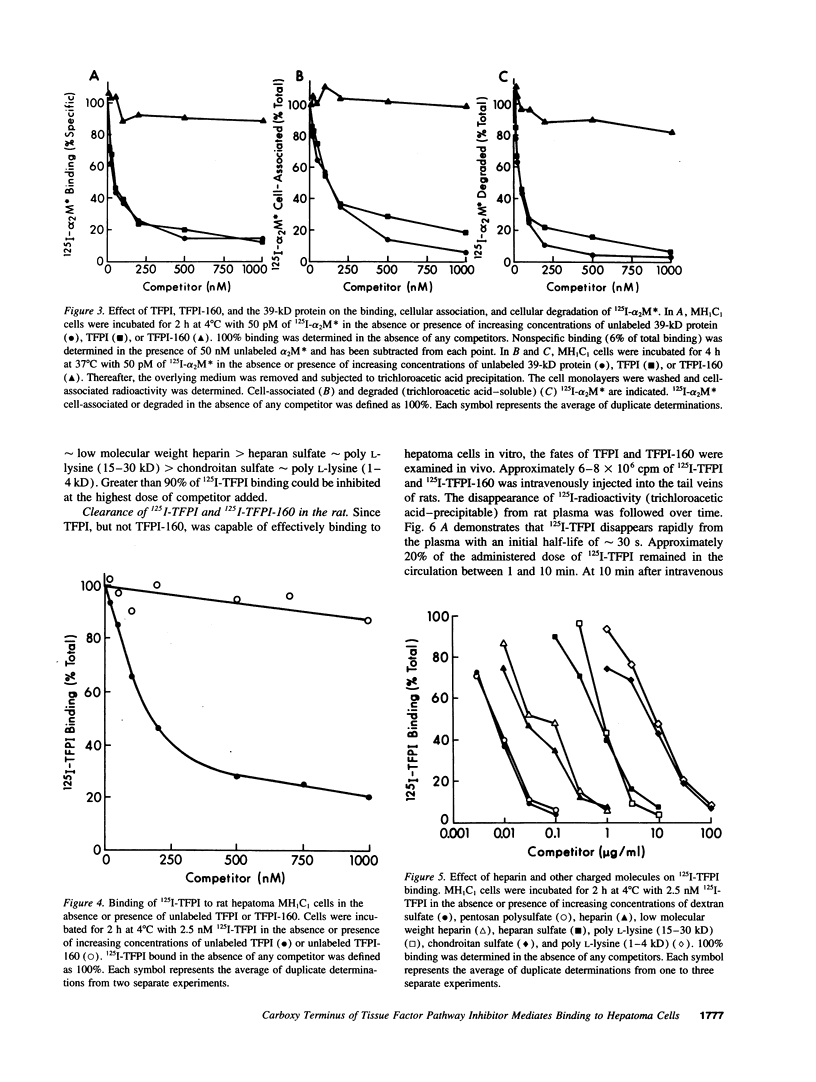
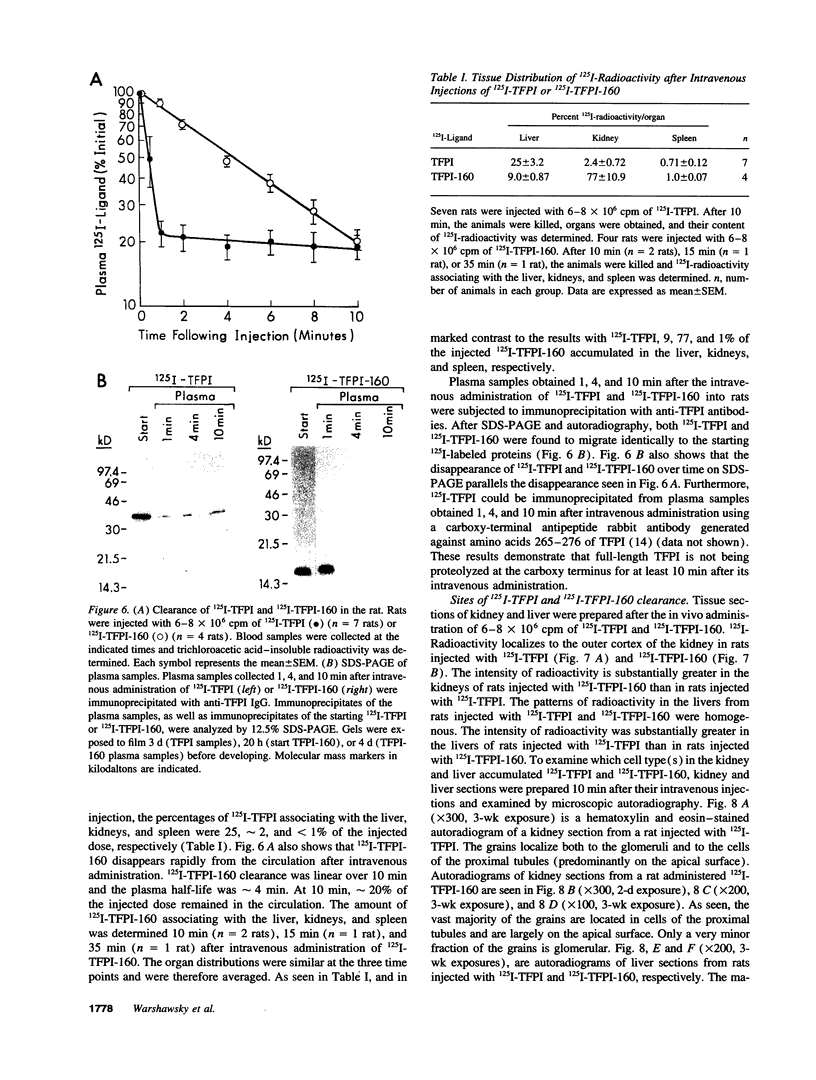
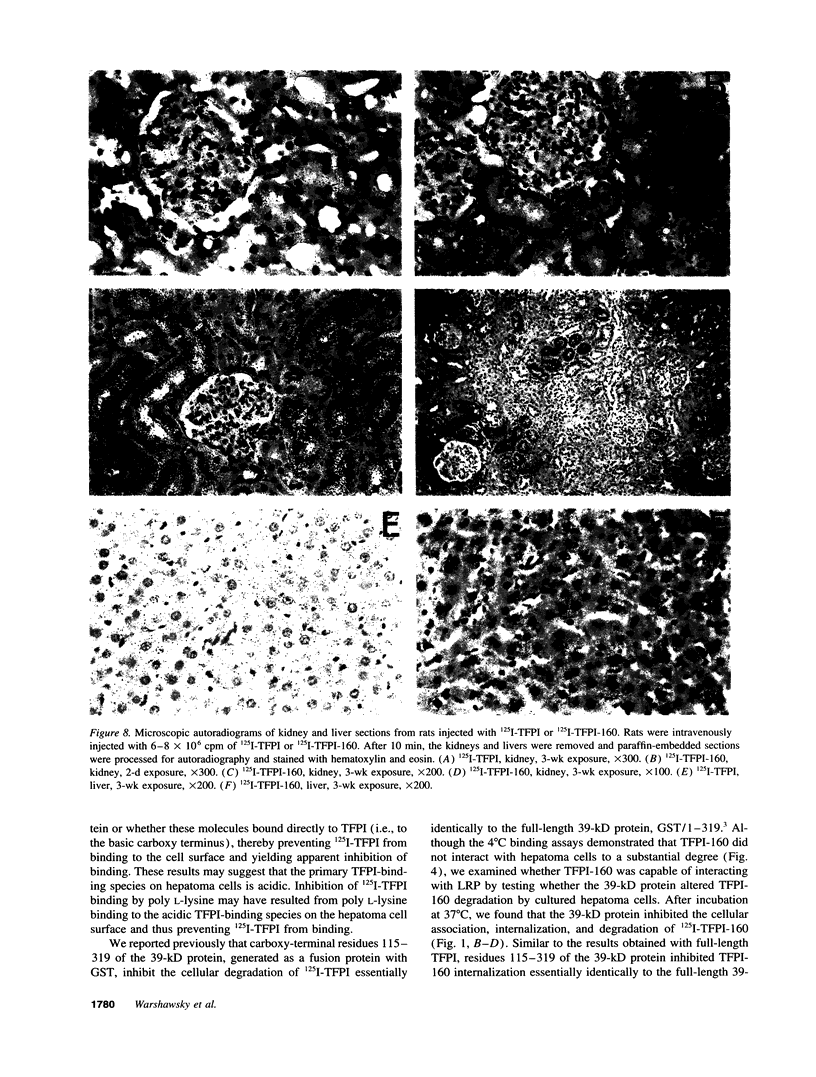
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is a plasma Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor that directly inhibits coagulation Factor Xa and also inhibits tissue factor-initiated coagulation. Normal human plasma TFPI exists both as the full-length molecule and as variably carboxy-terminal truncated forms. We reported recently that the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates the cellular degradation of TFPI after TFPI binding to the hepatoma cell surface. To examine whether the carboxy terminus of TFPI was required for interacting with hepatoma cells, a mutant of TFPI lacking the third Kunitz-type domain and basic carboxy terminus was generated. We found that this mutant, TFPI-160, did not compete with full-length 125I-TFPI-160 for binding to hepatoma cells. We were also unable to demonstrate specific binding of 125I-TFPI-160 to hepatoma cells at 4 degrees C. At 37 degrees C, significantly less 125I-TFPI-160 was internalized and degraded via low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein than full-length 125I-TFPI. Full-length 125I-TFPI binding to hepatoma cells could be inhibited > 90% by heparin and other highly charged molecules. Since TFPI, but not TFPI-160, was capable of effectively binding to cultured hepatoma cells, the fates of TFPI and TFPI-160 in vivo were examined. Both 125I-TFPI and 125I-TFPI-160 disappeared rapidly from the circulation after their intravenous administration into rats. The initial plasma half-life of 125I-TFPI was approximately 30 s whereas the half-life of 125I-TFPI-160 was approximately 4 min. 125I-TFPI was cleared predominantly by the liver. In contrast, 125I-TFPI-160 accumulated in the outer cortex of the kidney. Using microscopic autoradiography, we demonstrate that 125I-TFPI clearance is largely hepatocellular, whereas 125I-TFPI-160 accumulates mainly in the cells of the kidney proximal tubules. Together our findings demonstrate that the carboxy-terminal region(s) distal to amino acid 160 of TFPI mediates TFPI binding to hepatoma cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bregengaard C., Nordfang O., Ostergaard P., Petersen J. G., Meyn G., Diness V., Svendsen O., Hedner U. Pharmacokinetics of full length and two-domain tissue factor pathway inhibitor in combination with heparin in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Sep 1;70(3):454–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Lange G. W., Duffin K. L., MacPhail L. Heterogeneity of plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1994 Aug;5(4):551–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P. Isolation of the tissue factor inhibitor produced by HepG2 hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1886–1890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in a revised coagulation cascade. Semin Hematol. 1992 Jul;29(3):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Warren L. A., Girard J. J., Miletich J. P. Isolation of the lipoprotein associated coagulation inhibitor produced by HepG2 (human hepatoma) cells using bovine factor Xa affinity chromatography. Thromb Res. 1987 Oct 15;48(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90422-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Warren L. A., Novotny W. F., Higuchi D. A., Girard J. J., Miletich J. P. The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action. Blood. 1988 Feb;71(2):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu G., Morton P. A., Schwartz A. L. Identification and partial characterization by chemical cross-linking of a binding protein for tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) on rat hepatoma cells. A plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1-independent t-PA receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15595–15602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasey A. A., Chang A. C., Feigen L., Wün T. C., Taylor F. B., Jr, Hinshaw L. B. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor reduces mortality from Escherichia coli septic shock. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2850–2860. doi: 10.1172/JCI116529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Collier J. A., Palmier M. O., Kretzmer K. K., Bishop B. F., Combs R. G., Obukowicz M. G., Frazier R. B., Bild G. S., Joy W. D., Hill S. R. Refold and characterization of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor expressed in Escherichia coli. Thromb Haemost. 1994 Mar;71(3):339–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard T. J., Warren L. A., Novotny W. F., Likert K. M., Brown S. G., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Functional significance of the Kunitz-type inhibitory domains of lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):518–520. doi: 10.1038/338518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto T., Yamamoto M., Nordfang O., Petersen J. G., Foster D. C., Kisiel W. Inhibitory properties of full-length and truncated recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). Evidence that the third Kunitz-type domain of TFPI is not essential for the inhibition of factor VIIa-tissue factor complexes on cell surfaces. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8704–8710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Miettinen A., Farquhar M. G. Initial events in the formation of immune deposits in passive Heymann nephritis. gp330-anti-gp330 immune complexes form in epithelial coated pits and rapidly become attached to the glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):109–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounnas M. Z., Chappell D. A., Strickland D. K., Argraves W. S. Glycoprotein 330, a member of the low density lipoprotein receptor family, binds lipoprotein lipase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14176–14181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Nielsen S., Andreasen P., Jørgensen K. E., Nykjaer A., Røigaard H., Gliemann J., Christensen E. I. Epithelial glycoprotein-330 mediates endocytosis of plasminogen activator-plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complexes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16564–16570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordfang O., Bjørn S. E., Valentin S., Nielsen L. S., Wildgoose P., Beck T. C., Hedner U. The C-terminus of tissue factor pathway inhibitor is essential to its anticoagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10371–10376. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny W. F., Girard T. J., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Purification and characterization of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18832–18837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny W. F., Palmier M., Wun T. C., Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P. Purification and properties of heparin-releasable lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):394–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny W. F., Palmier M., Wun T. C., Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P. Purification and properties of heparin-releasable lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):394–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owensby D. A., Morton P. A., Schwartz A. L. Quantitative evaluation of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:305–328. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmier M. O., Hall L. J., Reisch C. M., Baldwin M. K., Wilson A. G., Wun T. C. Clearance of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):33–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport S. I. Inhibition of factor VIIa/tissue factor-induced blood coagulation: with particular emphasis upon a factor Xa-dependent inhibitory mechanism. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychowdhury R., Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Smith J. A. Autoimmune target in Heymann nephritis is a glycoprotein with homology to the LDL receptor. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1163–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2786251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandset P. M., Abildgaard U., Larsen M. L. Heparin induces release of extrinsic coagulation pathway inhibitor (EPI). Thromb Res. 1988 Jun 15;50(6):803–813. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Skelton T. P., Fiete D., Dharmesh S. M., Beranek M. C., MacPhail L., Broze G. J., Jr, Baenziger J. U. The asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on tissue factor pathway inhibitor terminate with SO4-4GalNAc beta 1, 4GlcNAc beta 1,2 Mana alpha. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19140–19146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshawsky I., Broze G. J., Jr, Schwartz A. L. The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates the cellular degradation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6664–6668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshawsky I., Bu G., Schwartz A. L. Identification of domains on the 39-kDa protein that inhibit the binding of ligands to the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22046–22054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselschmidt R., Likert K., Girard T., Wun T. C., Broze G. J., Jr Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: the carboxy-terminus is required for optimal inhibition of factor Xa. Blood. 1992 Apr 15;79(8):2004–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselschmidt R., Likert K., Huang Z., MacPhail L., Broze G. J., Jr Structural requirements for tissue factor pathway inhibitor interactions with factor Xa and heparin. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1993 Oct;4(5):661–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Kretzmer K. K., Girard T. J., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Cloning and characterization of a cDNA coding for the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor shows that it consists of three tandem Kunitz-type inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6001–6004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C. Lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor (LACI) is a cofactor for heparin: synergistic anticoagulant action between LACI and sulfated polysaccharides. Blood. 1992 Jan 15;79(2):430–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]