Abstract
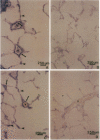
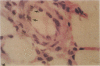
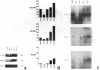
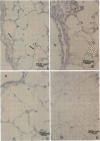
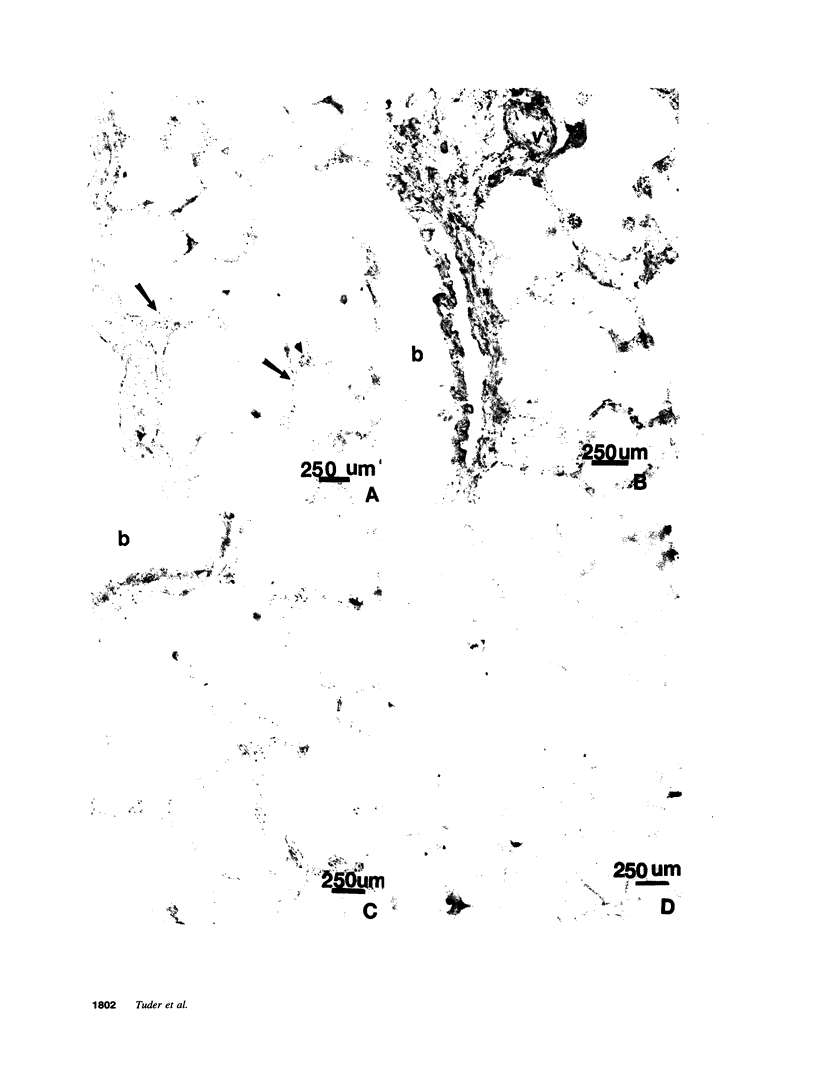
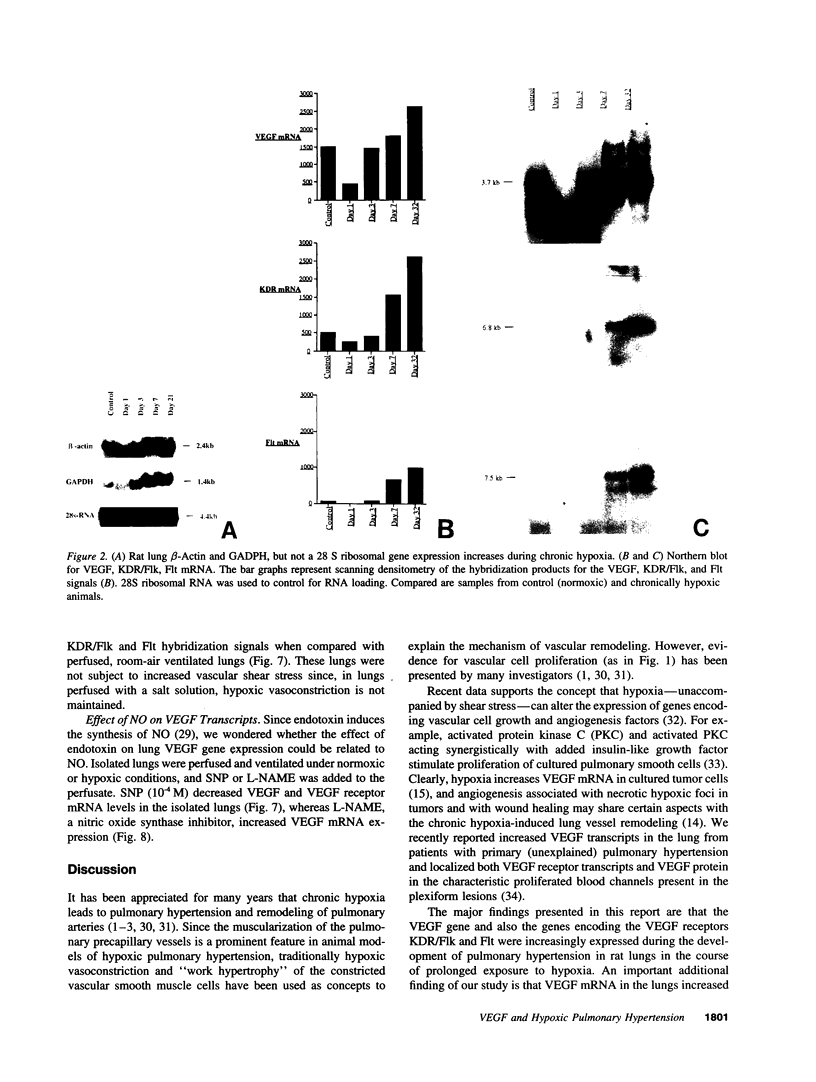
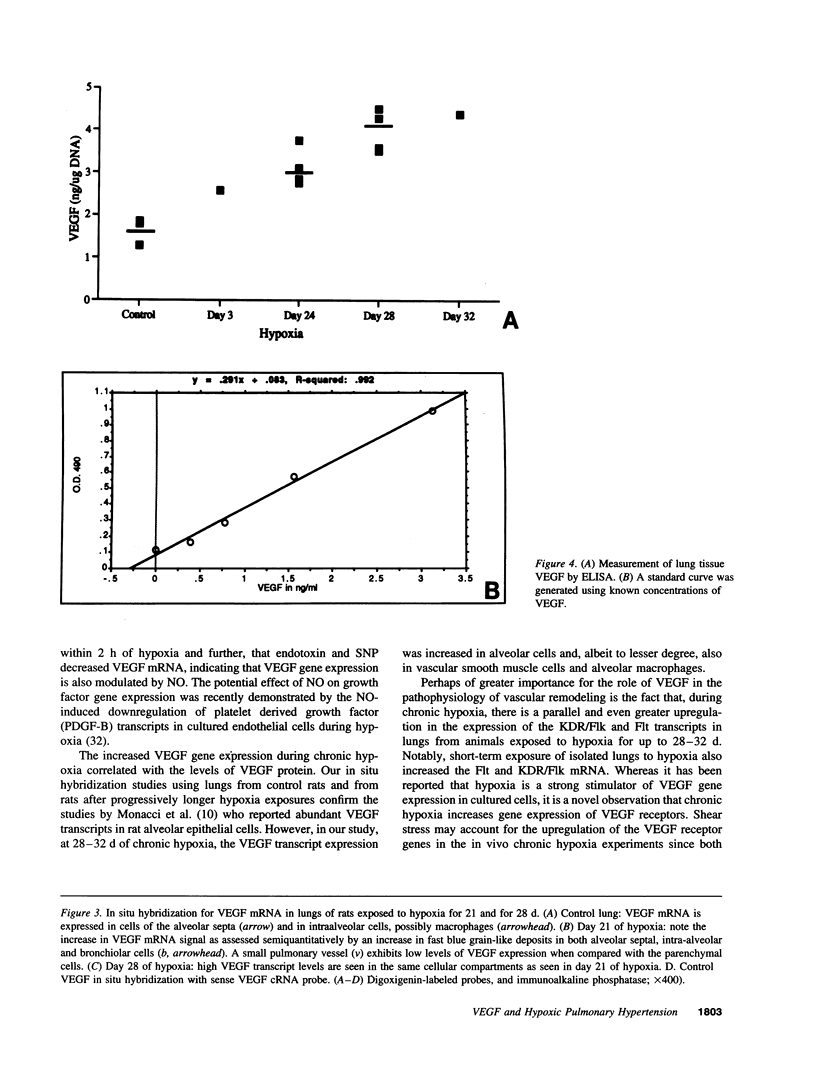
Endothelial cells constitute an essential integrator of factors that effect blood vessel remodeling induced by chronic hypoxia. We hypothesized that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) may participate in the lung response to acute and to chronic hypoxia. We found that ex vivo perfusion of isolated lungs under hypoxic conditions (when compared with normoxia) caused an increase in lung tissue mRNA of VEGF and of the VEGF receptors KDR/Flk and Flt. Chronic hypobaric hypoxia also increased lung tissue mRNA levels of VEGF, KDR/Flk, and Flt and the amount of VEGF protein. In situ hybridization studies demonstrated increased VEGF and KDR/flk hybridization signals in lungs from chronically hypoxic rats. Since endotoxin treatment of rats decreased lung VEGF mRNA, we postulated that nitric oxide (NO) or an NO-related metabolite might be involved in lung VEGF gene expression. Indeed, sodium nitroprusside, a NO donor, decreased and L-NAME (N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester), an inhibitor of NO-synthesis, increased both VEGF and VEGF receptor transcripts. We conclude that VEGF in the isolated perfused lung acts as an early gene in response to hypoxia and that lung VEGF and VEGF receptor mRNA levels are influenced by hypoxia and NO-dependent mechanisms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barer G., Emery C., Stewart A., Bee D., Howard P. Endothelial control of the pulmonary circulation in normal and chronically hypoxic rats. J Physiol. 1993 Apr;463:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berse B., Brown L. F., Van de Water L., Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):211–220. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Albrecht U., Sterrer S., Risau W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992 Feb;114(2):521–532. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauss M., Gerlach M., Gerlach H., Brett J., Wang F., Familletti P. C., Pan Y. C., Olander J. V., Connolly D. T., Stern D. Vascular permeability factor: a tumor-derived polypeptide that induces endothelial cell and monocyte procoagulant activity, and promotes monocyte migration. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1535–1545. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Olander J. V., Heuvelman D., Nelson R., Monsell R., Siegel N., Haymore B. L., Leimgruber R., Feder J. Human vascular permeability factor. Isolation from U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20017–20024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey E. C., Stenmark K. R., McMurtry I. F., O'Brien R. F., Voelkel N. F., Badesch D. B. Insulin-like growth factor I and protein kinase C activation stimulate pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation through separate but synergistic pathways. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):159–165. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddahibi S., Adnot S., Carville C., Blouquit Y., Raffestin B. L-arginine restores endothelium-dependent relaxation in pulmonary circulation of chronically hypoxic rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):L194–L200. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.2.L194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Henzel W. J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbower A. C., Mason R. J., Abman S. H., Tuder R. M. Agarose infiltration improves morphology of cryostat sections of lung. Lab Invest. 1994 Jul;71(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosang M. Suramin binds to platelet-derived growth factor and inhibits its biological activity. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(3):265–273. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Harris P. K., Foellmi L. A. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a "housekeeping" enzyme subject to tissue-specific regulation by hormones, nutrients, and oxidant stress. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):174–181. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.2.8119488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourembanas S., McQuillan L. P., Leung G. K., Faller D. V. Nitric oxide regulates the expression of vasoconstrictors and growth factors by vascular endothelium under both normoxia and hypoxia. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):99–104. doi: 10.1172/JCI116604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. The effect of continued hypoxia on rat pulmonary arterial circulation. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(2):188–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millauer B., Shawver L. K., Plate K. H., Risau W., Ullrich A. Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature. 1994 Feb 10;367(6463):576–579. doi: 10.1038/367576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedenzu C., Grasedyck K., Voelkel N. F., Bittmann S., Lindner J. Proliferation of lung cells in chronically hypoxic rats. An autoradiographic and radiochemical study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1981;48(2):185–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00378440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S., Westcott J. Y., Voelkel N. F. PAF antagonists inhibit pulmonary vascular remodeling induced by hypobaric hypoxia in rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Sep;73(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.3.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesenti E., Sola F., Mongelli N., Grandi M., Spreafico F. Suramin prevents neovascularisation and tumour growth through blocking of basic fibroblast growth factor activity. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):367–372. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. P., Peters K. G., De Vries C., Ferrara N., Williams L. T. Fetal liver kinase 1 is a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor and is selectively expressed in vascular endothelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7533–7537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Gamble W., Nadas A. S., Miettinen O. S., Reid L. Rat pulmonary circulation after chronic hypoxia: hemodynamic and structural features. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):H818–H827. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.6.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick N., Collins T., Atkinson W., Bonthron D. T., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Platelet-derived growth factor B chain promoter contains a cis-acting fluid shear-stress-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4591–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Perruzzi C. A., Harvey V. S., Dvorak H. F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Van de Water L., Brown L. F., Nagy J. A., Yeo K. T., Yeo T. K., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Vascular permeability factor (VPF, VEGF) in tumor biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993 Sep;12(3-4):303–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00665960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Yamaguchi S., Yamane A., Ikeda T., Tojo A., Matsushime H., Sato M. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a novel human receptor-type tyrosine kinase gene (flt) closely related to the fms family. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shweiki D., Itin A., Neufeld G., Gitay-Goren H., Keshet E. Patterns of expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF receptors in mice suggest a role in hormonally regulated angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2235–2243. doi: 10.1172/JCI116450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shweiki D., Itin A., Soffer D., Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):843–845. doi: 10.1038/359843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terman B. I., Carrion M. E., Kovacs E., Rasmussen B. A., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B. Identification of a new endothelial cell growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1677–1683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terman B. I., Dougher-Vermazen M., Carrion M. E., Dimitrov D., Armellino D. C., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P. Identification of the KDR tyrosine kinase as a receptor for vascular endothelial cell growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 30;187(3):1579–1586. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuder R. M., Groves B., Badesch D. B., Voelkel N. F. Exuberant endothelial cell growth and elements of inflammation are present in plexiform lesions of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1994 Feb;144(2):275–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisman N., Gospodarowicz D., Neufeld G. Characterization of the receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19461–19466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Völkel N., Wiegers U., Sill V., Trautmann J. A kinetic study of lung DNA-synthesis during simulated chronic high altitude hypoxia. Thorax. 1977 Oct;32(5):578–581. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.5.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. A., Gunning P., Hardeman E., Wallace D. C., Kedes L. Coordinate reciprocal trends in glycolytic and mitochondrial transcript accumulations during the in vitro differentiation of human myoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Mar;142(3):566–573. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries C., Escobedo J. A., Ueno H., Houck K., Ferrara N., Williams L. T. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):989–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1312256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]