Abstract
Lymphocytes enter lymph nodes by first adhering to high endothelial venules, an adhesive event mediated by a lectinlike lymphocyte receptor (L-selectin). Previously, it was shown with an in vitro assay that lymphocytes preferentially adhere to myelin-rich regions in brain sections. Here, using a recombinant form of L-selectin as an immunohistochemical reagent, we demonstrate potential ligands for L-selectin in myelinated regions of the central but not the peripheral nervous system. Using several antibodies and phorbol ester downmodulation of the receptor, we establish that L-selectin on human lymphocytes has a primary involvement in lymphocyte adherence to the myelinated regions. On mouse lymphocytes, the contribution of L-selectin appears to be partial. These findings raise the possibility that leukocyte targeting to myelin-rich regions, via a L-selectin dependent mechanism, may be a factor in the pathogenesis of certain central nervous system demyelinating diseases.
Full text
PDF



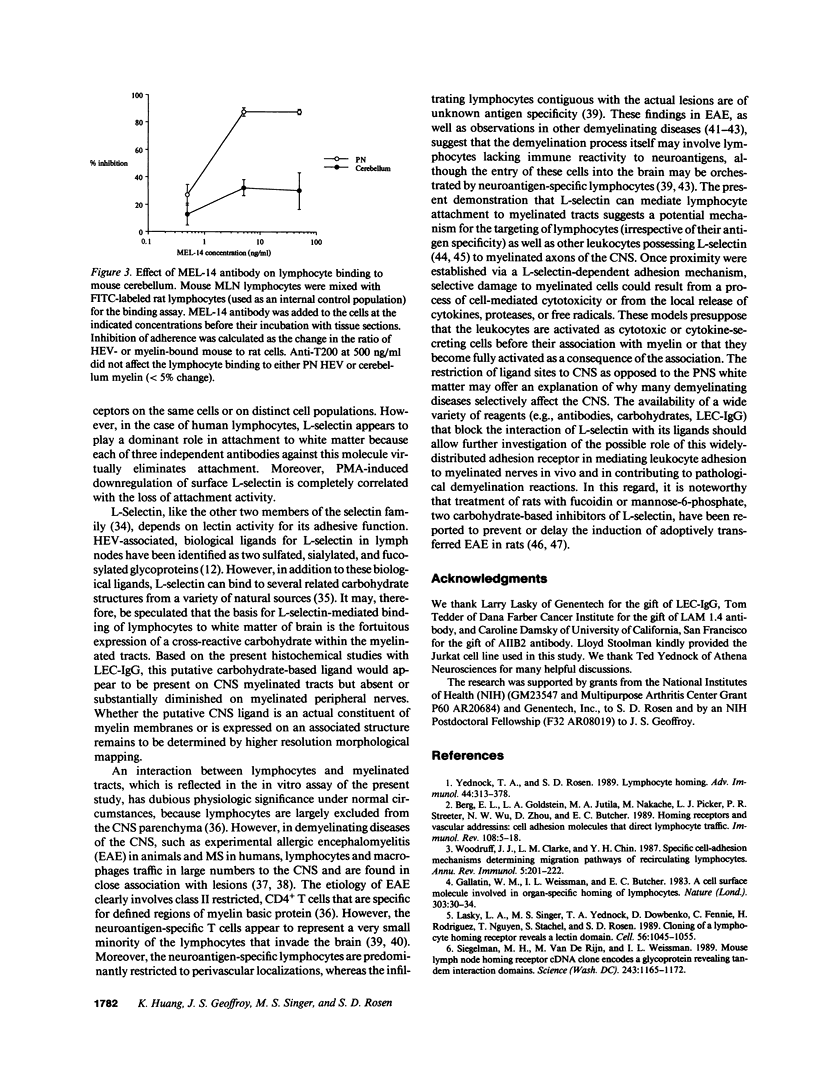

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg E. L., Goldstein L. A., Jutila M. A., Nakache M., Picker L. J., Streeter P. R., Wu N. W., Zhou D., Butcher E. C. Homing receptors and vascular addressins: cell adhesion molecules that direct lymphocyte traffic. Immunol Rev. 1989 Apr;108:5–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg E. L., Robinson M. K., Warnock R. A., Butcher E. C. The human peripheral lymph node vascular addressin is a ligand for LECAM-1, the peripheral lymph node homing receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):343–349. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B. R., Nguyen T., Lasky L. A. Characterization of a human homologue of the murine peripheral lymph node homing receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):421–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Lymphocyte adherence to high endothelial venules: characterization of a modified in vitro assay, and examination of the binding of syngeneic and allogeneic lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):1996–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C. The regulation of lymphocyte traffic. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;128:85–122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71272-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini D., James S. P., Stamenkovic I., Seed B. Leu-8/TQ1 is the human equivalent of the Mel-14 lymph node homing receptor. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):78–82. doi: 10.1038/342078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin Y. H., Rasmussen R. A., Woodruff J. J., Easton T. G. A monoclonal anti-HEBFPP antibody with specificity for lymphocyte surface molecules mediating adhesion to Peyer's patch high endothelium of the rat. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2556–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. H., Cannella B., Brosnan C. F., Raine C. S. Homing to central nervous system vasculature by antigen-specific lymphocytes. I. Localization of 14C-labeled cells during acute, chronic, and relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Lab Invest. 1990 Aug;63(2):162–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore-Duffy P., Goertz V., Rothman B. L. Lymphocyte adherence to myelinated tissue in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):843–846. doi: 10.1172/JCI109922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Munro J. M., Rice G. E., Bevilacqua M. P., Morimoto C., McIntyre B. W., Rhynhart K., Pober J. S., Nadler L. M. Adhesion of human B cells to germinal centers in vitro involves VLA-4 and INCAM-110. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1030–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.1697696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy J. S., Rosen S. D. Demonstration that a lectin-like receptor (gp90MEL) directly mediates adhesion of lymphocytes to high endothelial venules of lymph nodes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2463–2469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. E., Reichardt L. F., Crowley E., Holley B., Moezzi H., Sonnenberg A., Damsky C. H. The alpha 1/beta 1 and alpha 6/beta 1 integrin heterodimers mediate cell attachment to distinct sites on laminin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2175–2184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann B., McIntyre B. W., Weissman I. L. Identification of a murine Peyer's patch--specific lymphocyte homing receptor as an integrin molecule with an alpha chain homologous to human VLA-4 alpha. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90981-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., Singer M. S., Fennie C., Lasky L. A., Rosen S. D. Identification of a carbohydrate-based endothelial ligand for a lymphocyte homing receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1213–1221. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., True D. D., Singer M. S., Rosen S. D. Direct demonstration of the lectin activity of gp90MEL, a lymphocyte homing receptor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1225–1232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Bargatze R. F., de los Toyos J., Butcher E. C. Lymphocyte recognition of high endothelium: antibodies to distinct epitopes of an 85-95-kD glycoprotein antigen differentially inhibit lymphocyte binding to lymph node, mucosal, or synovial endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):983–990. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Steere A. C., Fox R. I., Butcher E. C. A distinct endothelial cell recognition system that controls lymphocyte traffic into inflamed synovium. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):556–558. doi: 10.1126/science.3726548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Jutila M. A., Butcher E. C. Identification of a human peripheral lymph node homing receptor: a rapidly down-regulated adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2244–2248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuttner B. J., Woodruff J. J. Selective adherence of lymphocytes to myelinated areas of rat brain. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1666–1671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Singer M. S., Yednock T. A., Dowbenko D., Fennie C., Rodriguez H., Nguyen T., Stachel S., Rosen S. D. Cloning of a lymphocyte homing receptor reveals a lectin domain. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1045–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90637-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewinsohn D. M., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: evidence of a common molecular mechanism shared by neutrophils, lymphocytes, and other leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4313–4321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley K., Gaehtgens P., Fennie C., Singer M. S., Lasky L. A., Rosen S. D. Lectin-like cell adhesion molecule 1 mediates leukocyte rolling in mesenteric venules in vivo. Blood. 1991 Jun 15;77(12):2553–2555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Clatch R. J., Pevear D. C., Trotter J. L., Lipton H. L. Class II-restricted T cell responses in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV)-induced demyelinating disease. I. Cross-specificity among TMEV substrains and related picornaviruses, but not myelin proteins. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3776–3784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ord D. C., Ernst T. J., Zhou L. J., Rambaldi A., Spertini O., Griffin J., Tedder T. F. Structure of the gene encoding the human leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (TQ1, Leu-8) of lymphocytes and neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7760–7767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M. H., Cheng I. C., Weissman I. L., Wakeland E. K. The mouse lymph node homing receptor is identical with the lymphocyte cell surface marker Ly-22: role of the EGF domain in endothelial binding. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):611–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90473-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M. H., van de Rijn M., Weissman I. L. Mouse lymph node homing receptor cDNA clone encodes a glycoprotein revealing tandem interaction domains. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1165–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.2646713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Lasky L. A. Cell adhesion. Sticky sugars for selectins. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):196–197. doi: 10.1038/349196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamper H. B., Jr, Woodruff J. J. Lymphocyte homing into lymph nodes: in vitro demonstration of the selective affinity of recirculating lymphocytes for high-endothelial venules. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):828–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolman L. M. Adhesion molecules controlling lymphocyte migration. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):907–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolman L. M., Tenforde T. S., Rosen S. D. Phosphomannosyl receptors may participate in the adhesive interaction between lymphocytes and high endothelial venules. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1535–1540. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanborg R. H. Horror Autotoxicus and homing: implications for autoimmunity. Lab Invest. 1990 Aug;63(2):141–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Isaacs C. M., Ernst T. J., Demetri G. D., Adler D. A., Disteche C. M. Isolation and chromosomal localization of cDNAs encoding a novel human lymphocyte cell surface molecule, LAM-1. Homology with the mouse lymphocyte homing receptor and other human adhesion proteins. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):123–133. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Penta A. C., Levine H. B., Freedman A. S. Expression of the human leukocyte adhesion molecule, LAM1. Identity with the TQ1 and Leu-8 differentiation antigens. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):532–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S. Immunopathology of the lesion in chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1986 May;99(2):395–410. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Reinherz E. L., Raine C. S. Multiple sclerosis: distribution of T cell subsets within active chronic lesions. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.6217550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. R., Imai Y., Fennie C., Geoffroy J. S., Rosen S. D., Lasky L. A. A homing receptor-IgG chimera as a probe for adhesive ligands of lymph node high endothelial venules. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2221–2229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdelin O., McCluskey R. T. The nature and the specificity of mononuclear cells in experimental autoimmune inflammations and the mechanisms leading to their accumulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1242–1263. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willenborg D. O., Parish C. R., Cowden W. B. Phosphosugars are potent inhibitors of central nervous system inflammation. FASEB J. 1989 Jun;3(8):1968–1971. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.8.2721857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willenborg D. O., Parish C. R. Inhibition of allergic encephalomyelitis in rats by treatment with sulfated polysaccharides. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3401–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Bloom B. R. Primary demyelination as a nonspecific consequence of a cell-mediated immune reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):346–359. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. J., Clarke L. M., Chin Y. H. Specific cell-adhesion mechanisms determining migration pathways of recirculating lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:201–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. J., Katz M., Lucas L. E., Stamper H. B., Jr An in vitro model of lymphocyte homing. II. Membrane and cytoplasmic events involved in lymphocyte adherence to specialized high-endothelial venules of lymph nodes. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1603–1610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yednock T. A., Rosen S. D. Lymphocyte homing. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:313–378. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60645-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yednock T. A., Stoolman L. M., Rosen S. D. Phosphomannosyl-derivatized beads detect a receptor involved in lymphocyte homing. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):713–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Steinman L. The T lymphocyte in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:579–621. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





