Abstract
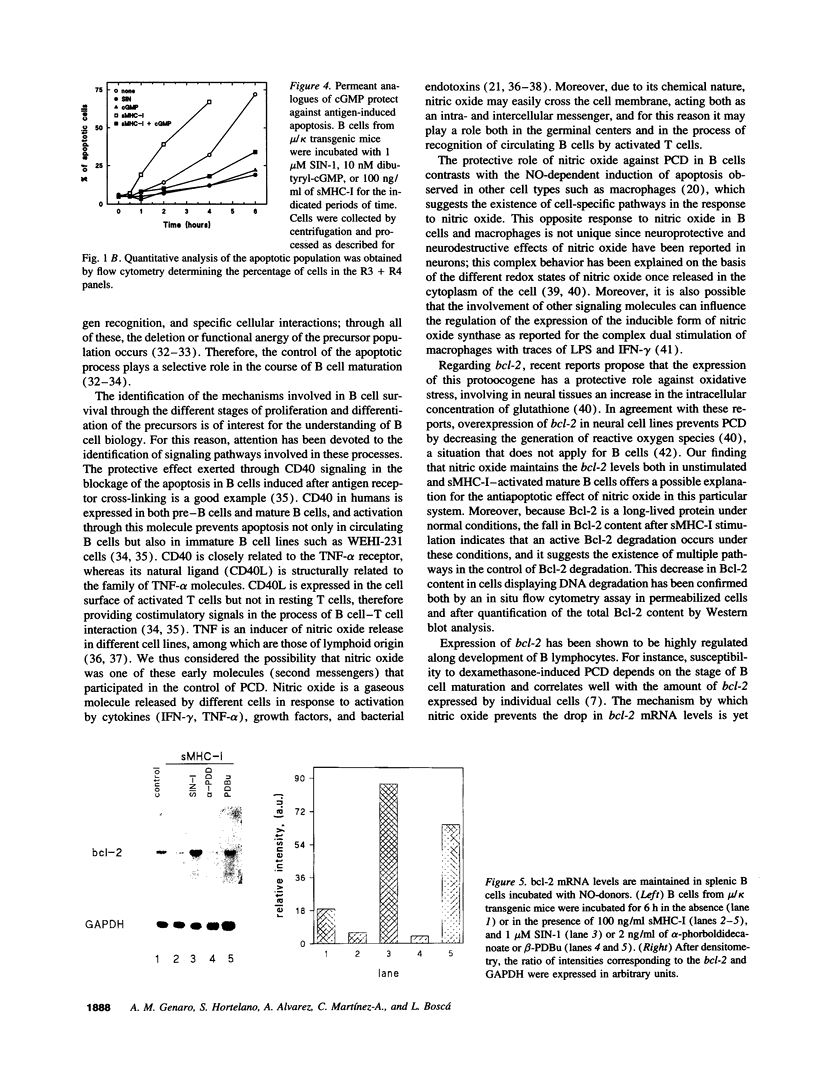
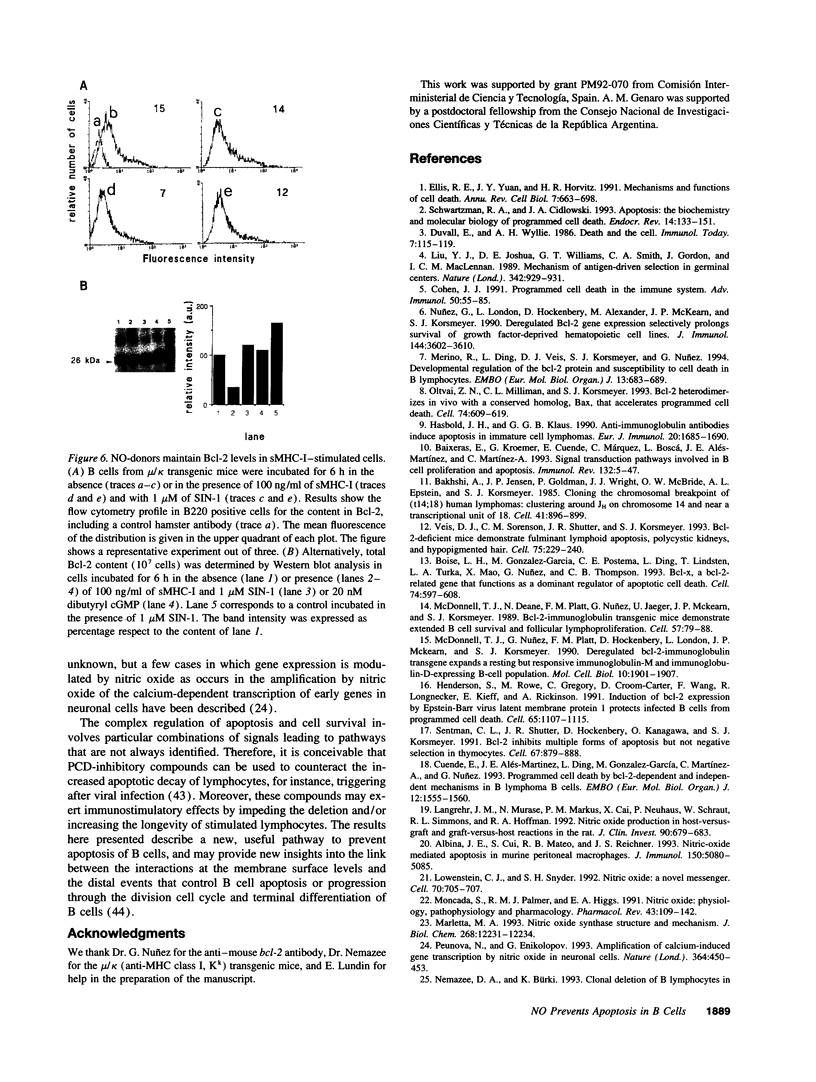
Incubation of ex vivo cultured mature B cells in the presence of nitric oxide or nitric oxide-donor substances delays programmed cell death as determined by the appearance of DNA laddering in agarose gel electrophoresis or by flow-cytometry analysis of DNA. Nitric oxide also rescues B cells from antigen-induced apoptosis but fails to provide a co-stimulatory signal that converts the signal elicited by the antigen into a proliferative response. The protective effects of nitric oxide against programmed cell death can be reproduced by treatment of the cells with permeant analogues of cyclic GMP. Regarding the mechanisms by which nitric oxide prevents apoptosis in B cells, we have observed that nitric oxide release prevents the drop in the expression of the protooncogene bcl-2, both at the mRNA and protein levels, suggesting the existence of an unknown pathway that links nitric oxide signaling with Bcl-2 expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albina J. E., Cui S., Mateo R. B., Reichner J. S. Nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):5080–5085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baixeras E., Bosca L., Stauber C., Gonzalez A., Carrera A. C., Gonzalo J. A., Martinez C. From apoptosis to autoimmunity: insights from the signaling pathways leading to proliferation or to programmed cell death. Immunol Rev. 1994 Dec;142:53–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baixeras E., Kroemer G., Cuende E., Márquez C., Boscá L., Alés Martínez J. E., Martínez C. Signal transduction pathways involved in B-cell induction. Immunol Rev. 1993 Apr;132:5–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb00836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi A., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Wright J. J., McBride O. W., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):899–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Vodovotz Y., Paik J., Xie Q. W., Nathan C. Traces of bacterial lipopolysaccharide suppress IFN-gamma-induced nitric oxide synthase gene expression in primary mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):301–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boise L. H., González-García M., Postema C. E., Ding L., Lindsten T., Turka L. A., Mao X., Nuñez G., Thompson C. B. bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90508-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. How B and T cells talk to each other. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):425–428. doi: 10.1038/367425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J. Programmed cell death in the immune system. Adv Immunol. 1991;50:55–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuende E., Alés-Martínez J. E., Ding L., Gónzalez-García M., Martínez C., Nunez G. Programmed cell death by bcl-2-dependent and independent mechanisms in B lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1555–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genaro A. M., Boscá L. Early signals in alloantigen induced B-cell proliferation. Comparison between B-cell triggering by intact allogeneic cells and solubilized alloantigen. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):1832–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalo J. A., González-García A., Kalland T., Hedlung G., Martínez C., Kroemer G. Linomide inhibits programmed cell death of peripheral T cells in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):48–52. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalo J. A., Moreno de Alborán I., Alés-Martínez J. E., Martínez C., Kroemer G. Expansion and clonal deletion of peripheral T cells induced by bacterial superantigen is independent of the interleukin-2 pathway. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Apr;22(4):1007–1011. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasbold J., Klaus G. G. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies induce apoptosis in immature B cell lymphomas. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D. M., Oltvai Z. N., Yin X. M., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80066-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane D. J., Sarafian T. A., Anton R., Hahn H., Gralla E. B., Valentine J. S., Ord T., Bredesen D. E. Bcl-2 inhibition of neural death: decreased generation of reactive oxygen species. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1274–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.8235659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Merrett M., Salter M., Moncada S. Differential induction of brain, lung and liver nitric oxide synthase by endotoxin in the rat. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 15;270(3):833–836. doi: 10.1042/bj2700833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langrehr J. M., Murase N., Markus P. M., Cai X., Neuhaus P., Schraut W., Simmons R. L., Hoffman R. A. Nitric oxide production in host-versus-graft and graft-versus-host reactions in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):679–683. doi: 10.1172/JCI115911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Choi Y. B., Pan Z. H., Lei S. Z., Chen H. S., Sucher N. J., Loscalzo J., Singel D. J., Stamler J. S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):626–632. doi: 10.1038/364626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. J., Johnson G. D., Gordon J., MacLennan I. C. Germinal centres in T-cell-dependent antibody responses. Immunol Today. 1992 Jan;13(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90199-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. J., Joshua D. E., Williams G. T., Smith C. A., Gordon J., MacLennan I. C. Mechanism of antigen-driven selection in germinal centres. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):929–931. doi: 10.1038/342929a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):705–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90301-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons A. B., Samuel K., Sanderson A., Maddy A. H. Simultaneous analysis of immunophenotype and apoptosis of murine thymocytes by single laser flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992;13(8):809–821. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase structure and mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12231–12234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Deane N., Platt F. M., Nunez G., Jaeger U., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Nunez G., Platt F. M., Hockenberry D., London L., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. Deregulated Bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgene expands a resting but responsive immunoglobulin M and D-expressing B-cell population. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1901–1907. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino R., Ding L., Veis D. J., Korsmeyer S. J., Nuñez G. Developmental regulation of the Bcl-2 protein and susceptibility to cell death in B lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):683–691. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S. The 1991 Ulf von Euler Lecture. The L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Jul;145(3):201–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez G., London L., Hockenbery D., Alexander M., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. Deregulated Bcl-2 gene expression selectively prolongs survival of growth factor-deprived hemopoietic cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3602–3610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai Z. N., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C. T cell-dependent B cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:331–360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peunova N., Enikolopov G. Amplification of calcium-induced gene transcription by nitric oxide in neuronal cells. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):450–453. doi: 10.1038/364450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H., Ney P., Woditsch I., Schrör K. Cyclic GMP mediates SIN-1-induced inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 3;182(2):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90279-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman R. A., Cidlowski J. A. Apoptosis: the biochemistry and molecular biology of programmed cell death. Endocr Rev. 1993 Apr;14(2):133–151. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentman C. L., Shutter J. R., Hockenbery D., Kanagawa O., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2 inhibits multiple forms of apoptosis but not negative selection in thymocytes. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):879–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubata T., Wu J., Honjo T. B-cell apoptosis induced by antigen receptor crosslinking is blocked by a T-cell signal through CD40. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):645–648. doi: 10.1038/364645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis D. J., Sorenson C. M., Shutter J. R., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2-deficient mice demonstrate fulminant lymphoid apoptosis, polycystic kidneys, and hypopigmented hair. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80065-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]