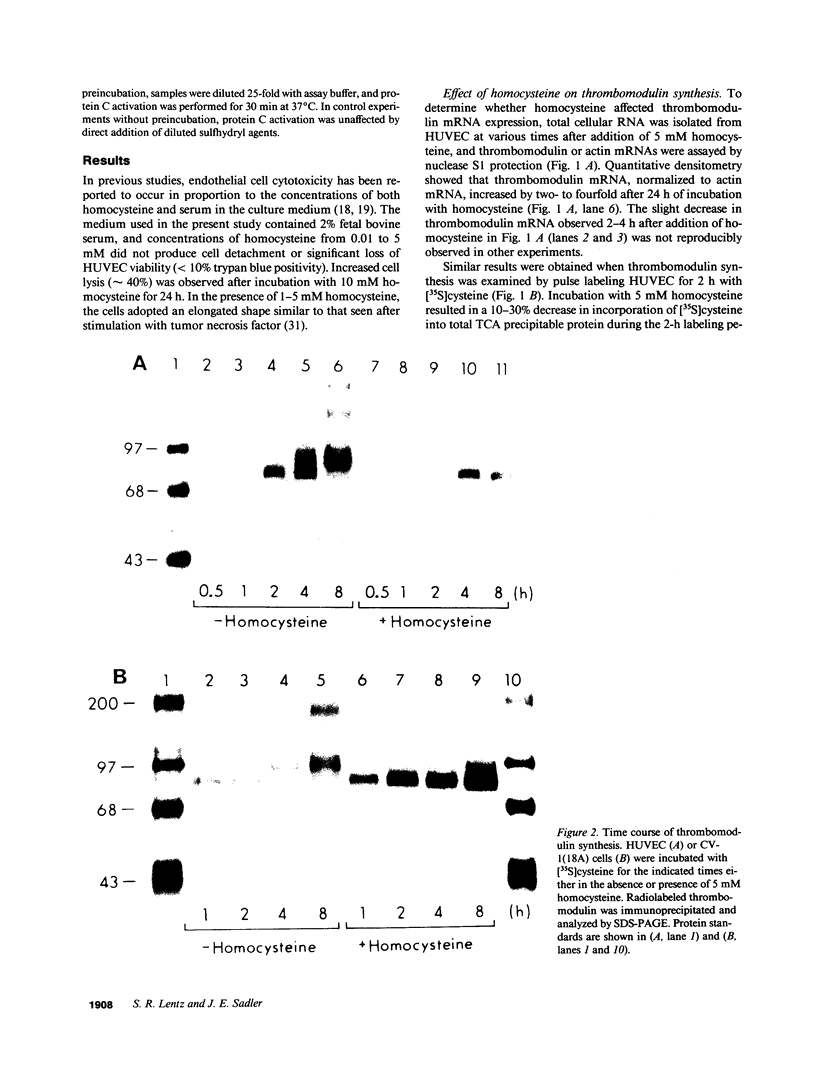
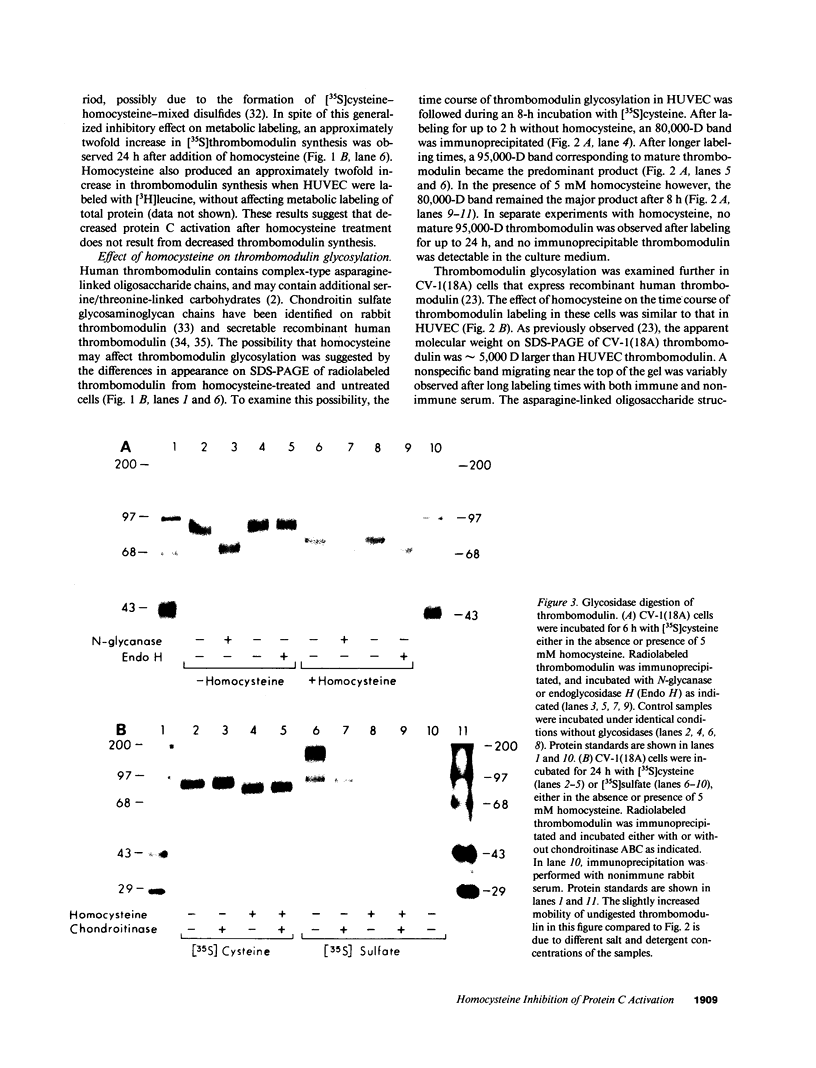
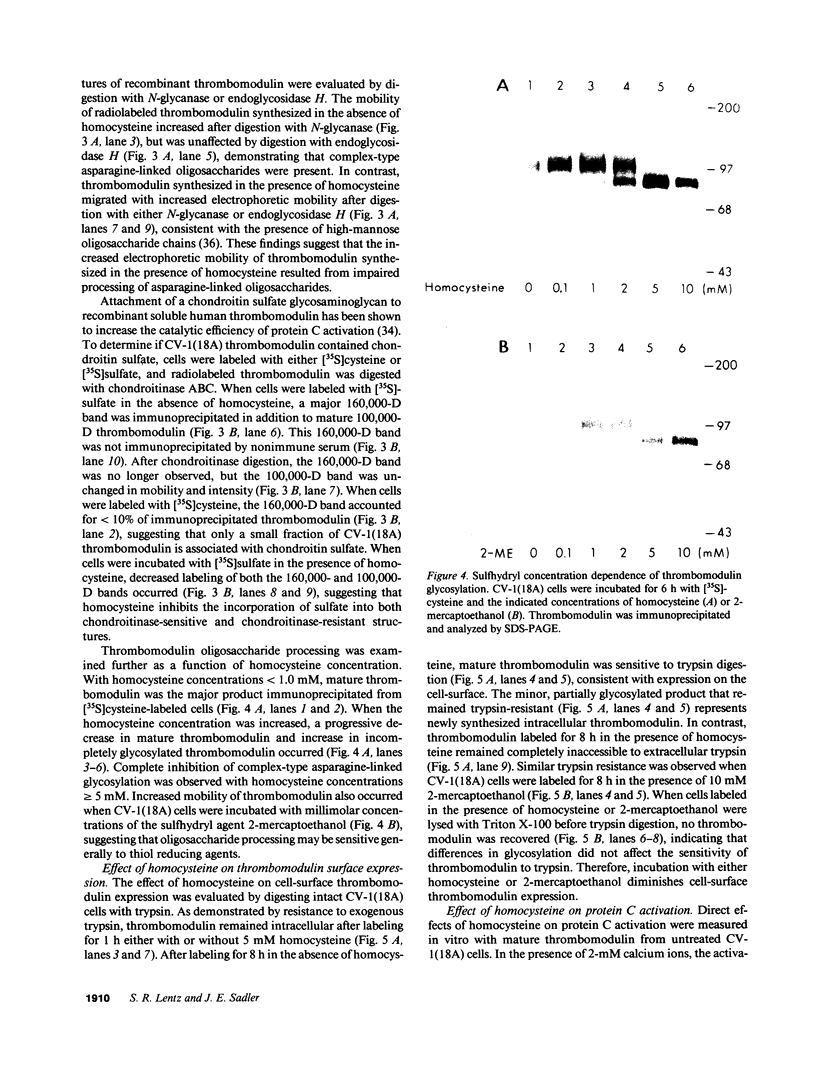
Abstract
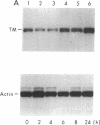
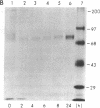
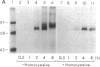
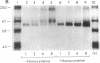
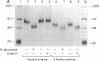
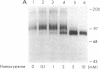
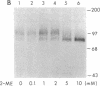
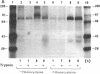
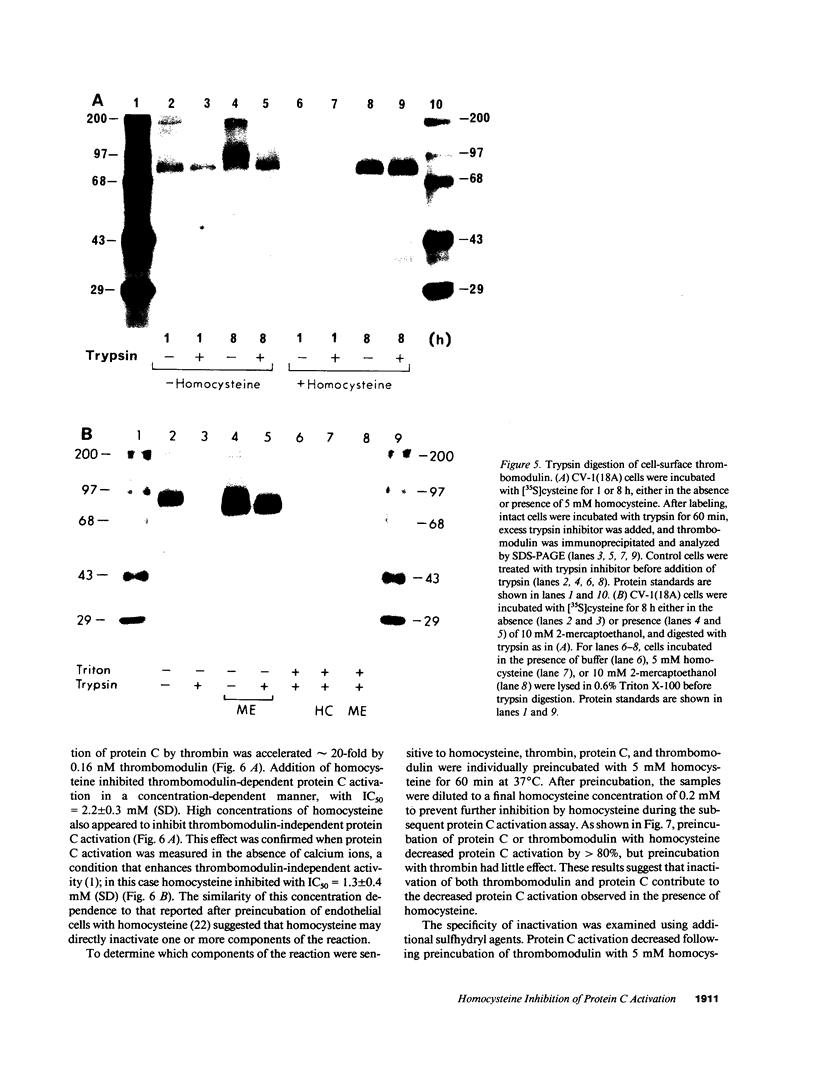
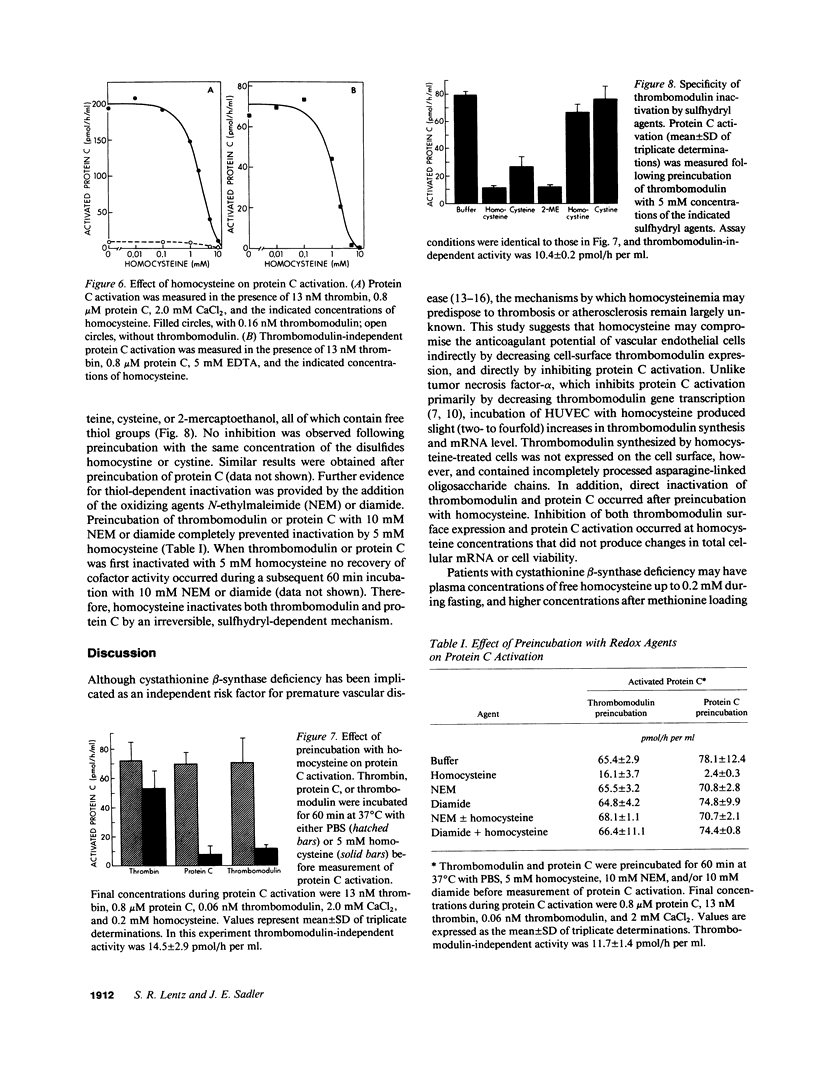
Elevated levels of plasma homocysteine are associated with both venous and arterial thrombosis. Homocysteine inhibits the function of thrombomodulin, an anticoagulant glycoprotein on the endothelial surface that serves as a cofactor for the activation of protein C by thrombin. The effects of homocysteine on thrombomodulin expression and protein C activation were investigated in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and CV-1(18A) cells that express recombinant human thrombomodulin. Addition of 5 mM homocysteine to endothelial cells produced slight increases in thrombomodulin mRNA and thrombomodulin synthesis without affecting cell viability. In both cell types, thrombomodulin synthesized in the presence of homocysteine remained sensitive to digestion with endoglycosidase H and failed to appear on the cell surface, suggesting impaired transit along the secretory pathway. In a cell-free protein C activation assay, homocysteine irreversibly inactivated both thrombomodulin and protein C in a process that required free thiol groups and was inhibited by the oxidizing agents diamide or N-ethylmaleimide. By inhibiting both thrombomodulin surface expression and protein C activation, homocysteine may contribute to the development of thrombosis in patients with cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberini C. M., Bet P., Milstein C., Sitia R. Secretion of immunoglobulin M assembly intermediates in the presence of reducing agents. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):485–487. doi: 10.1038/347485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers G. H., Smals A. G., Trijbels F. J., Fowler B., Bakkeren J. A., Schoonderwaldt H. C., Kleijer W. J., Kloppenborg P. W. Heterozygosity for homocystinuria in premature peripheral and cerebral occlusive arterial disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Sep 19;313(12):709–715. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198509193131201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourin M. C., Lundgren-Akerlund E., Lindahl U. Isolation and characterization of the glycosaminoglycan component of rabbit thrombomodulin proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15424–15431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R., Daly L., Robinson K., Naughten E., Cahalane S., Fowler B., Graham I. Hyperhomocysteinemia: an independent risk factor for vascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 25;324(17):1149–1155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104253241701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway E. M., Rosenberg R. D. Tumor necrosis factor suppresses transcription of the thrombomodulin gene in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5588–5592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Kumada T., Sadler J. E., Majerus P. W. The structure and function of mouse thrombomodulin. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates degradation and synthesis of thrombomodulin without affecting mRNA levels in hemangioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15815–15822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Majerus P. W. Structure and function of thrombomodulin: a natural anticoagulant. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.3029867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Slichter S. J., Scott C. R., Ross R. Homocystinemia. Vascular injury and arterial thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 12;291(11):537–543. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409122911101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Oxidation-reduction and the molecular mechanism of a regulatory RNA-protein interaction. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.2711187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelsson B., Brattström L. E., Hultberg B. L. Homocysteine and myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Jun;71(2-3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz S. R., Tsiang M., Sadler J. E. Regulation of thrombomodulin by tumor necrosis factor-alpha: comparison of transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):542–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Transport of secretory and membrane glycoproteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. A rate-limiting step in protein maturation and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2107–2110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow M. R., Kang S. S., Taylor L. M., Wong P. W., Coull B., Inahara T., Mukerjee D., Sexton G., Upson B. Prevalence of hyperhomocyst(e)inemia in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Circulation. 1989 Jun;79(6):1180–1188. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.6.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Beta protein C is not glycosylated at asparagine 329. The rate of translation may influence the frequency of usage at asparagine-X-cysteine sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11397–11404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. L., Andreoli S. P., Esmon N. L., Esmon C. T., Bang N. U. Endotoxin enhances tissue factor and suppresses thrombomodulin expression of human vascular endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):124–130. doi: 10.1172/JCI112772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. L., Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L. Tumor necrosis factor leads to the internalization and degradation of thrombomodulin from the surface of bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S. H., Skovby F., Levy H. L., Pettigrew K. D., Wilcken B., Pyeritz R. E., Andria G., Boers G. H., Bromberg I. L., Cerone R. The natural history of homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;37(1):1–31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa K., Sakano K., Fujiwara H., Sato Y., Sugiyama N., Teruuchi T., Iwamoto M., Marumoto Y. Presence and function of chondroitin-4-sulfate on recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Handley D. A., Esmon C. T., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszewski A. J., Szostak W. B. Homocysteine content of plasma proteins in ischemic heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Feb;69(2-3):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. F., Grinnell B. W., Moore R. E., Hoskins J., Vlahos C. J., Bang N. U. Stable expression of a secretable deletion mutant of recombinant human thrombomodulin in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12602–12610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Conn M. T. Homocysteine, an atherogenic stimulus, reduces protein C activation by arterial and venous endothelial cells. Blood. 1990 Feb 15;75(4):895–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Kane W. H. Activation of endogenous factor V by a homocysteine-induced vascular endothelial cell activator. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1909–1916. doi: 10.1172/JCI112519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Goto T., Haranaka K., Satomi N., Nariuchi H., Mano-Hirano Y., Sawasaki Y. Actions of tumor necrosis factor on cultured vascular endothelial cells: morphologic modulation, growth inhibition, and cytotoxicity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Jun;76(6):1113–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpati E. M., Sadler J. E. Regulation of endothelial cell coagulant properties. Modulation of tissue factor, plasminogen activator inhibitors, and thrombomodulin by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20705–20713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkebaum G., Harlan J. M. Endothelial cell injury due to copper-catalyzed hydrogen peroxide generation from homocysteine. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1370–1376. doi: 10.1172/JCI112442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns D. J., Kurosawa S., Esmon C. T. Microthrombomodulin. Residues 310-486 from the epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain of thrombomodulin will accelerate protein C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3352–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugumaran G., Silbert J. E. Subfractionation of chick embryo epiphyseal cartilage Golgi. Localization of enzymes involved in the synthesis of the polysaccharide portion of proteochondroitin sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9565–9569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Lentz S. R., Dittman W. A., Wen D., Scarpati E. M., Sadler J. E. Equilibrium binding of thrombin to recombinant human thrombomodulin: effect of hirudin, fibrinogen, factor Va, and peptide analogues. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10602–10612. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. T., Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Striker G. E. Homocysteine-induced endothelial cell injury in vitro: a model for the study of vascular injury. Thromb Res. 1980 Apr 1;18(1-2):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]