Abstract
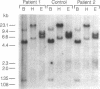
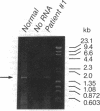
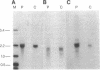
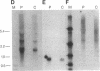
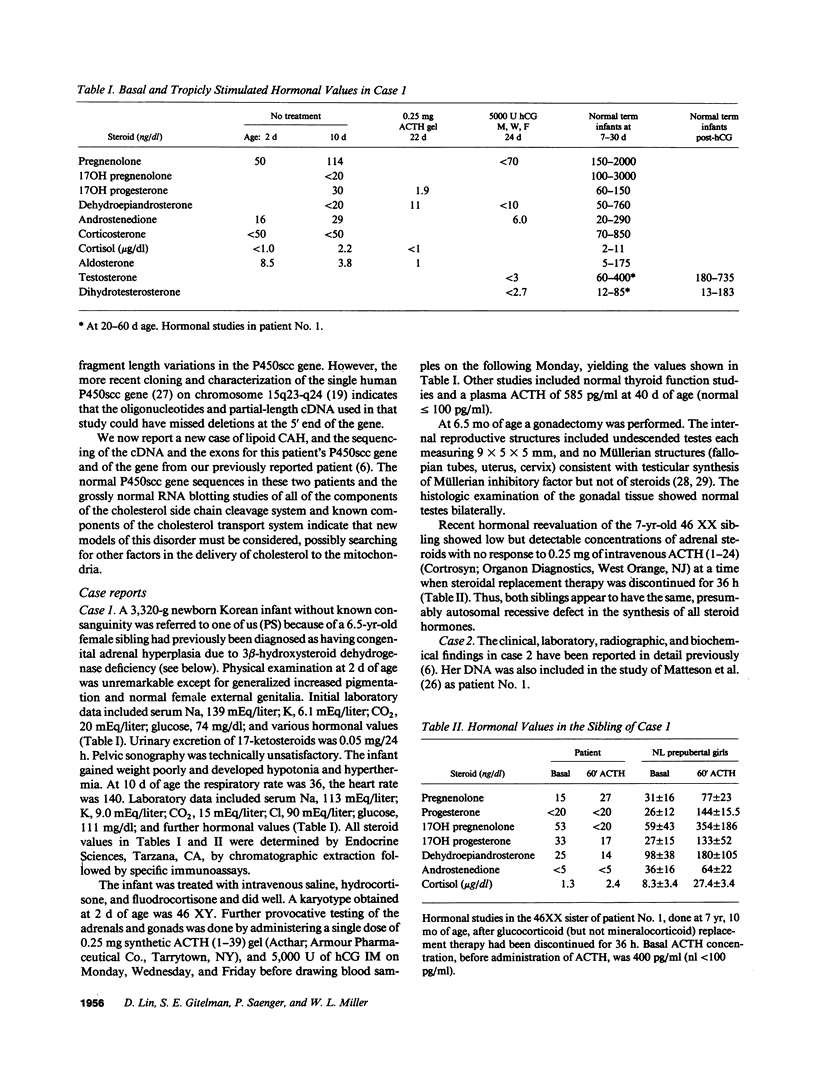
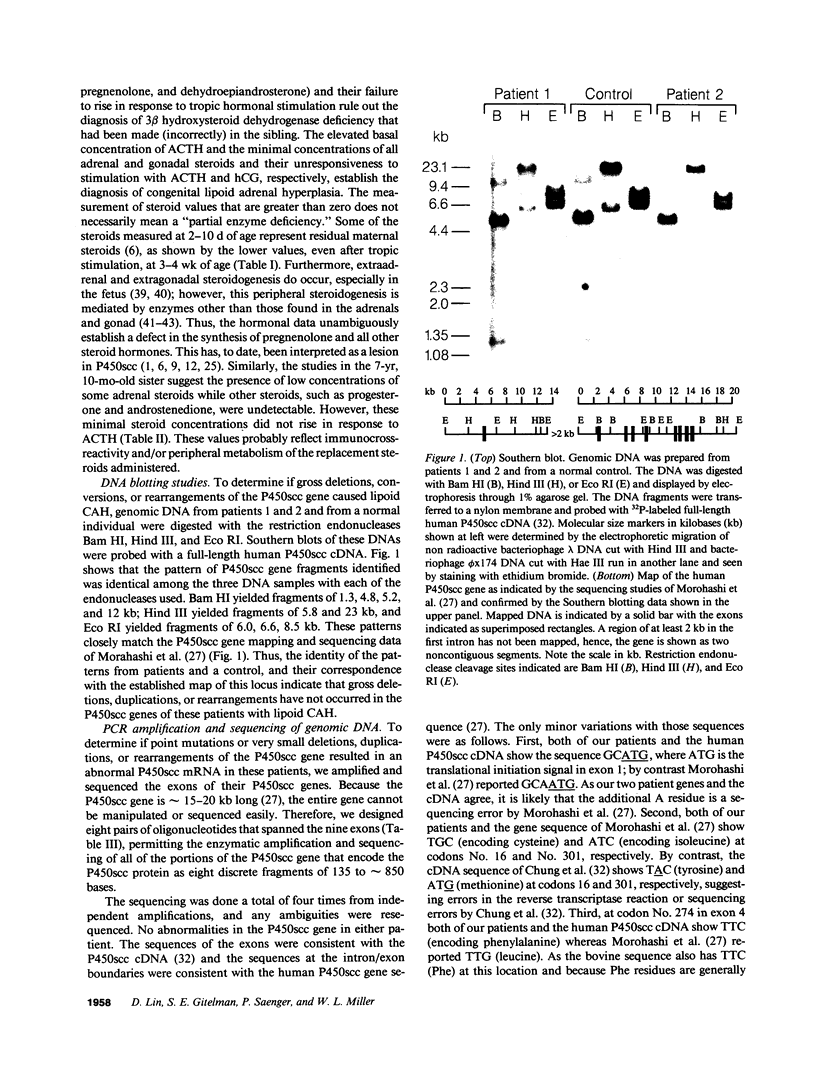
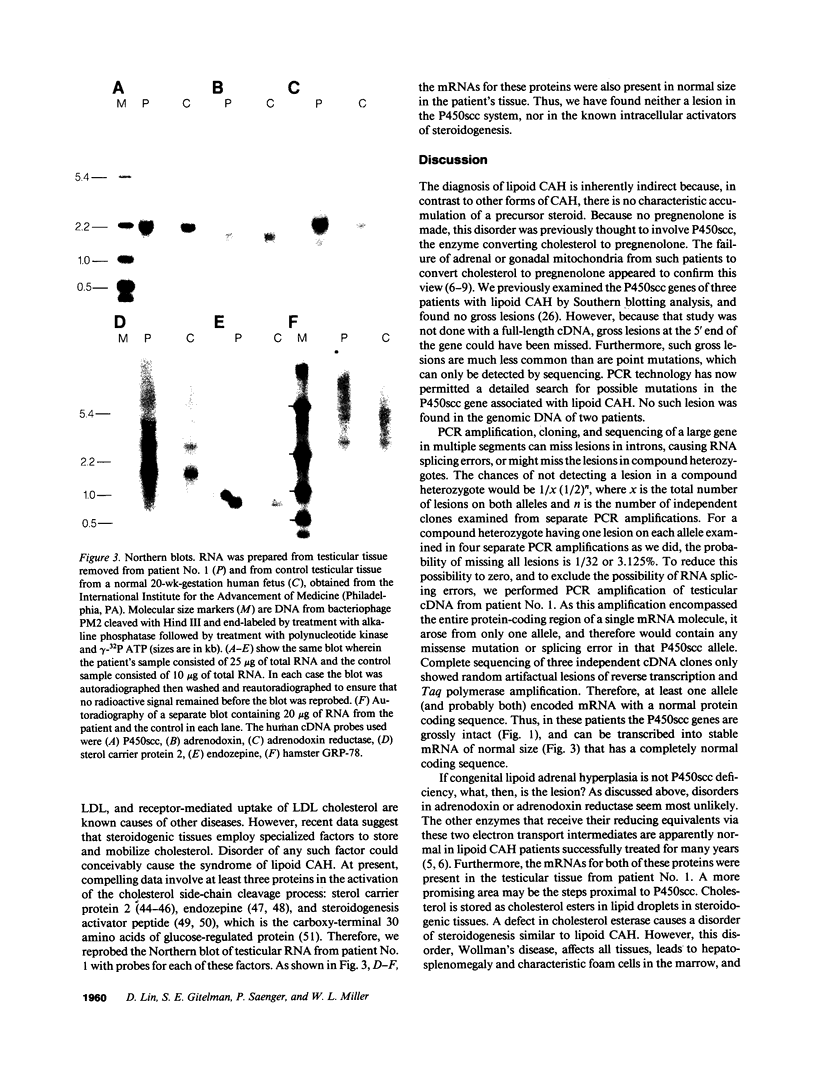
Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia is the most severe form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Affected individuals can synthesize no steroid hormones, and hence are all phenotypic females with a severe salt-losing syndrome that is fatal if not treated in early infancy. All previous studies have suggested that the disorder is in the cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme (P450scc), which converts cholesterol to pregnenolone. A newborn patient was diagnosed by the lack of significant concentrations of adrenal or gonadal steroids either before or after stimulation with corticotropin (ACTH) or gonadotropin (hCG). The P450scc gene in this patient and in a previously described patient were grossly intact, as evidenced by Southern blotting patterns. Enzymatic (polymerase chain reaction) amplification and sequencing of the coding regions of their P450scc genes showed these were identical to the previously cloned human P450scc cDNA and gene sequences. Undetected compound heterozygosity was ruled out in the new patient by sequencing P450scc cDNA enzymatically amplified from gonadal RNA. Northern blots of gonadal RNA from this patient contained normal sized mRNAs for P450scc and also for adrenodoxin reductase, adrenodoxin, sterol carrier protein 2, endozepine, and GRP-78 (the precursor to steroidogenesis activator peptide). These studies show that lipoid CAH is not caused by lesions in the P450scc gene, and suggest that another unidentified factor is required for the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone, and is disordered in congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besman M. J., Yanagibashi K., Lee T. D., Kawamura M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Identification of des-(Gly-Ile)-endozepine as an effector of corticotropin-dependent adrenal steroidogenesis: stimulation of cholesterol delivery is mediated by the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Holmberg I., Oftebro H., Pedersen J. I. Properties of a reconstituted vitamin D3 25-hydroxylase from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5244–5249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A. M., Kowarski A., Migeon C. J., Brough A. J. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to a deficiency of one of the enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of pregnenolone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Feb;28(2):153–161. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-2-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey M. L., MacDonald P. C. Extraadrenal formation of a mineralocorticosteroid: deoxycorticosterone and deoxycorticosterone sulfate biosynthesis and metabolism. Endocr Rev. 1982 Fall;3(4):396–403. doi: 10.1210/edrv-3-4-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey M. L., Winkel C. A., MacDonald P. C. Conversion of progesterone to deoxycorticosterone in the human fetus: steroid 21-hydroxylase activity in fetal tissues. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Apr;18(4):449–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanderbhan R., Noland B. J., Scallen T. J., Vahouny G. V. Sterol carrier protein2. Delivery of cholesterol from adrenal lipid droplets to mitochondria for pregnenolone synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8928–8934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. Y., Wu D. A., Lai C. C., Miller W. L., Chung B. C. Cloning and structure of the human adrenodoxin gene. DNA. 1988 Nov;7(9):609–615. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. Y., Wu D. A., Mohandas T. K., Chung B. C. Structure, sequence, chromosomal location, and evolution of the human ferredoxin gene family. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;9(3):205–212. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Voutilainen R., Mohandas T. K., Miller W. L. Human cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc: cDNA cloning, assignment of the gene to chromosome 15, and expression in the placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8962–8966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupp J. R., Vickery L. E. Identification of free and [Fe2S2]-bound cysteine residues of adrenodoxin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17418–17421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degenhart H. J., Visser H. K., Boon H., O'Doherty N. J. Evidence for deficient 20 -cholesterol-hydroxylase activity in adrenal tissue of a patient with lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Nov;71(3):512–518. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0710512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauffa B. P., Miller W. L., Grumbach M. M., Conte F. A., Kaplan S. L. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to deficient cholesterol side-chain cleavage activity (20, 22-desmolase) in a patient treated for 18 years. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1985 Nov;23(5):481–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1985.tb01107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T. ACTH stimulation on cholesterol side chain cleavage activity of adrenocortical mitochondria. Transfer of the stimulus from plasma membrane to mitochondria. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Apr 27;36(2):105–122. doi: 10.1007/BF02354909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland R. T., Kirkland J. L., Johnson C. M., Horning M. G., Librik L., Clayton G. W. Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia in an eight-year-old phenotypic female. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Mar;36(3):488–496. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-3-488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Kyoya S., Miyawaki T. M., Kidani H., Funabashi T. Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme activity and cytochrome P-450 content in adrenal mitochondria of a patient with congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia (Prader disease). Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Jun 15;77(3):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. S., Delegeane A., Scharff D. Highly conserved glucose-regulated protein in hamster and chicken cells: preliminary characterization of its cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4922–4925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. A., Warren D. W., Gregoire J., Pedersen R. C., Lee A. S. The rat 78,000 dalton glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) as a precursor for the rat steroidogenesis-activator polypeptide (SAP): the SAP coding sequence is homologous with the terminal end of GRP78. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1944–1952. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-12-1944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D., Shi Y. F., Miller W. L. Cloning and sequence of the human adrenodoxin reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8516–8520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson K. J., Chung B. C., Urdea M. S., Miller W. L. Study of cholesterol side-chain cleavage (20,22 desmolase) deficiency causing congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia using bovine-sequence P450scc oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1296–1305. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Miller W. L. Extraadrenal steroid 21-hydroxylation is not mediated by P450c21. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1497–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI114325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Immunoassays for human müllerian inhibitory factor (MIF): new insights into the physiology of MIF. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jan;70(1):8–10. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Levine L. S. Molecular and clinical advances in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;111(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Molecular biology of steroid hormone synthesis. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):295–318. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Regulation of mRNAs for human steroidogenic enzymes. Endocr Res. 1989;15(1-2):1–16. doi: 10.1080/07435808909039085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. C., Brentano S. T., Miller W. L. Human P450scc gene transcription is induced by cyclic AMP and repressed by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and A23187 through independent cis elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6013–6023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., David M., Forest M. G., Betuel H., Hauptman G., Andre J., Bertrand J., Miller W. L. Gene conversions and rearrangements cause discordance between inheritance of forms of 21-hydroxylase deficiency and HLA types. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Mar;68(3):592–599. doi: 10.1210/jcem-68-3-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., Picado-Leonard J., Wu D. A., Chang C. Y., Mohandas T. K., Chung B. C., Miller W. L. Assignment of the functional gene for human adrenodoxin to chromosome 11q13----qter and of adrenodoxin pseudogenes to chromosome 20cen----q13.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):52–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Sogawa K., Omura T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of human cytochrome P-450(SCC), cholesterol desmolase. J Biochem. 1987 Apr;101(4):879–887. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRADER A., SIEBENMANN R. E. Nebennierenisuffizienz bei kongenitaler Lipoid hyperplasie der Nebennieren. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1957 Dec;12(6):569–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen R. C., Brownie A. C. Cholesterol side-chain cleavage in the rat adrenal cortex: isolation of a cycloheximide-sensitive activator peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1882–1886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen R. C., Brownie A. C. Steroidogenesis-activator polypeptide isolated from a rat Leydig cell tumor. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.3563495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Voutilainen R., Kao L. C., Chung B. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin: cloning of three cDNAs and cycloheximide enhancement in JEG-3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3240–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDISON A. T. A form of lipoidosis of the adrenal cortex in an infant. Arch Dis Child. 1955 Dec;30(154):538–541. doi: 10.1136/adc.30.154.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saenger P. Abnormal sex differentiation. J Pediatr. 1984 Jan;104(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80581-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R. Cholesterol side-chain cleavage, cytochrome P450, and the control of steroidogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Mar;13(3):213–227. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solish S. B., Picado-Leonard J., Morel Y., Kuhn R. W., Mohandas T. K., Hanukoglu I., Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin reductase: two mRNAs encoded by a single gene on chromosome 17cen----q25 are expressed in steroidogenic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Klisak I., Miller W. L. Regional mapping of genes encoding human steroidogenic enzymes: P450scc to 15q23-q24, adrenodoxin to 11q22; adrenodoxin reductase to 17q24-q25; and P450c17 to 10q24-q25. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):359–365. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su P., Rennert H., Shayiq R. M., Yamamoto R., Zheng Y. M., Addya S., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Avadhani N. G. A cDNA encoding a rat mitochondrial cytochrome P450 catalyzing both the 26-hydroxylation of cholesterol and 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D3: gonadotropic regulation of the cognate mRNA in ovaries. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;9(9):657–667. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahouny G. V., Chanderbhan R., Noland B. J., Irwin D., Dennis P., Lambeth J. D., Scallen T. J. Sterol carrier protein2. Identification of adrenal sterol carrier protein2 and site of action for mitochondrial cholesterol utilization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11731–11737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb N. R., Rose T. M., Malik N., Marquardt H., Shoyab M., Todaro G. J., Lee D. C. Bovine and human cDNA sequences encoding a putative benzodiazepine receptor ligand. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):71–79. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikvall K. Hydroxylations in biosynthesis of bile acids. Isolation of a cytochrome P-450 from rabbit liver mitochondria catalyzing 26-hydroxylation of C27-steroids. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3800–3804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto R., Kallen C. B., Babalola G. O., Rennert H., Billheimer J. T., Strauss J. F., 3rd Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding human sterol carrier protein 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):463–467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Ohno Y., Kawamura M., Hall P. F. The regulation of intracellular transport of cholesterol in bovine adrenal cells: purification of a novel protein. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):2075–2082. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-2075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]