Abstract
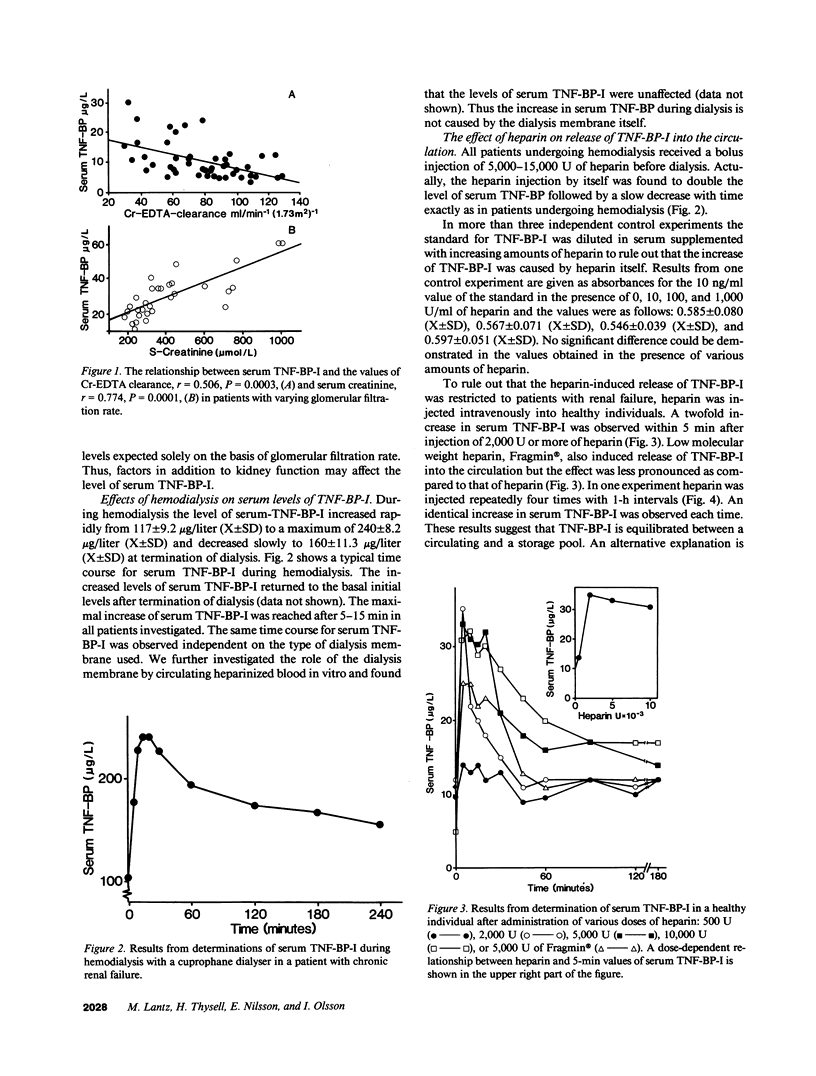
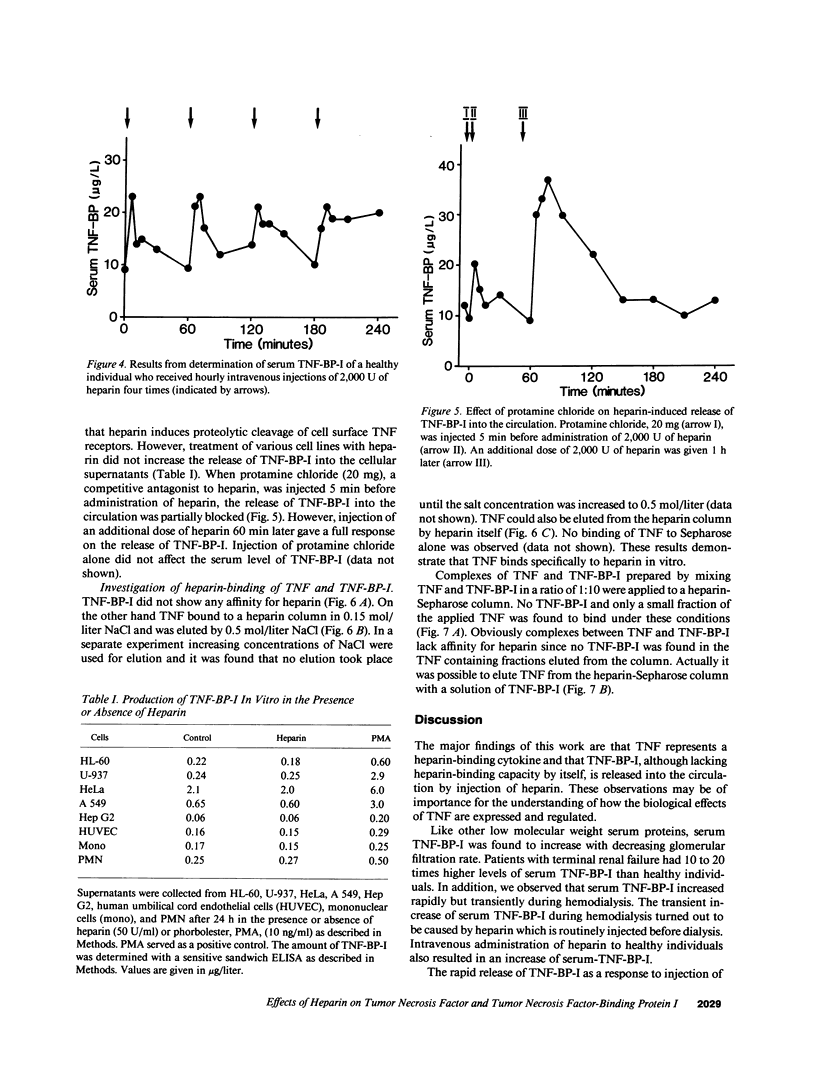
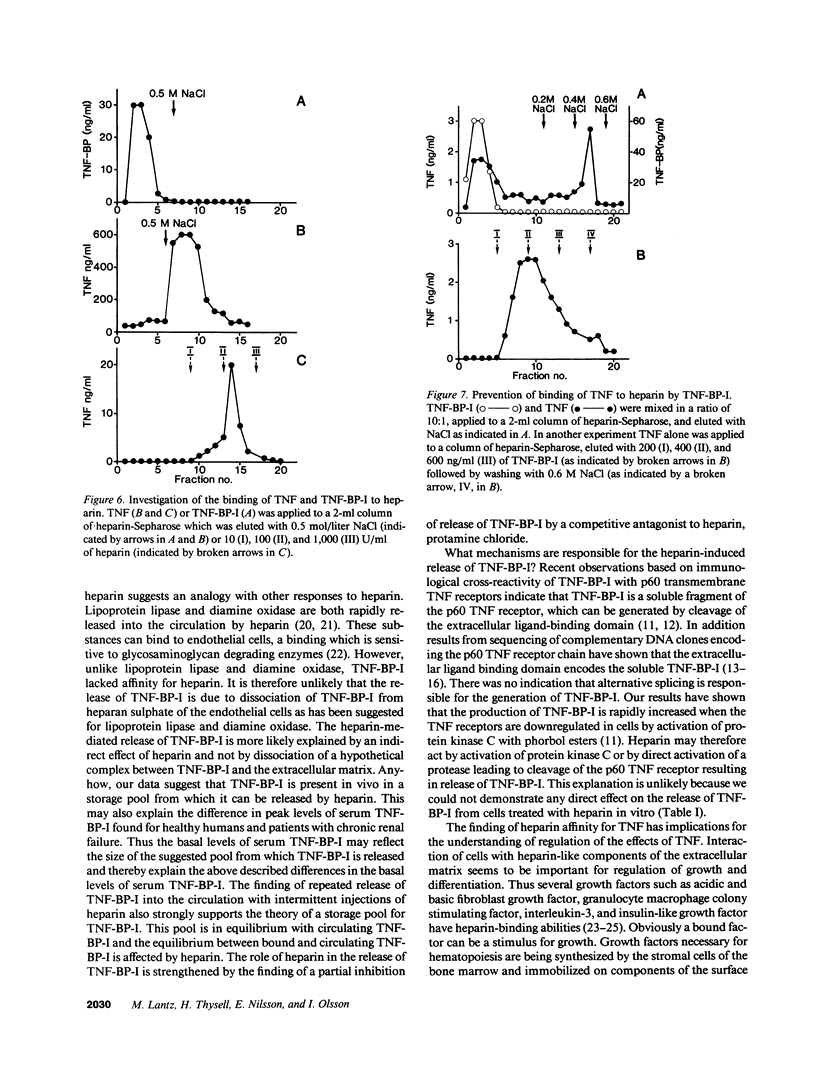
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a protein released by activated macrophages, is a central mediator of the host response to infection and inflammation. The TNF-binding protein I (TNF-BP-I) is a soluble fragment of the p60 transmembrane TNF receptor and an antagonist to TNF. The level of serum TNF-BP-I was found to be increased in patients with renal insufficiency as a result of a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate. During hemodialysis of patients with renal failure there was a rapid but transient increase in serum TNF-BP-I. This increase was found to be caused by heparin given before dialysis and a similar dose-dependent response to heparin was observed also in healthy individuals. The finding of a repeated release of TNF-BP-I into the circulation with intermittent injections of heparin indicates that TNF-BP-I is present both in a storage pool and in a circulating pool. The mechanism for the heparin-mediated release of TNF-BP-I was not explained; TNF-BP did not show affinity for heparin. On the other hand, TNF was found to have affinity for heparin and it could also be dissociated from heparin by TNF-BP-I. It is suggested that heparin-like molecules of the extracellular matrix can retain TNF in physical proximity with target cells and restrict the actions of TNF and protect against systemic harmful manifestations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bröchner-Mortensen J. A simple method for the determination of glomerular filtration rate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Nov;30(3):271–274. doi: 10.3109/00365517209084290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Aderka D., Rubinstein M., Rotman D., Wallach D. A tumor necrosis factor-binding protein purified to homogeneity from human urine protects cells from tumor necrosis factor toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11974–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Novick D., Wallach D. Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological cross-reactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Tiderström G. Determination of serum creatinine by a direct colorimetric method. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Feb 12;43(3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Maurer-Fogy I., Krönke M., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K., Lantz M., Olsson I., Hauptmann R., Stratowa C., Adolf G. R. Molecular cloning and expression of human and rat tumor necrosis factor receptor chain (p60) and its soluble derivative, tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;9(10):705–715. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization in vitro of a human tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. A soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1396–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI114853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfberg H., Grubb A. O. Quantitation of gamma-trace in human biological fluids: indications for production in the central nervous system. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1979 Nov;39(7):619–626. doi: 10.3109/00365517909108866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nophar Y., Kemper O., Brakebusch C., Englemann H., Zwang R., Aderka D., Holtmann H., Wallach D. Soluble forms of tumor necrosis factor receptors (TNF-Rs). The cDNA for the type I TNF-R, cloned using amino acid sequence data of its soluble form, encodes both the cell surface and a soluble form of the receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3269–3278. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumour necrosis factor. Polypeptide mediator network. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):330–331. doi: 10.1038/326330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Adolf G. Isolation and characterization of a tumor necrosis factor binding protein from urine. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Mar;42(3):270–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Olsson I. A tumor necrosis factor binding protein is present in human biological fluids. Eur J Haematol. 1988 Nov;41(5):414–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1988.tb00220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R., Gallagher J., Spooncer E., Allen T. D., Bloomfield F., Dexter T. M. Heparan sulphate bound growth factors: a mechanism for stromal cell mediated haemopoiesis. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):376–378. doi: 10.1038/332376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson-White A., Baylin S. B., Olivecrona T., Beaven M. A. Binding of diamine oxidase activity to rat and guinea pig microvascular endothelial cells. Comparisons with lipoprotein lipase binding. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):93–100. doi: 10.1172/JCI111983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. A human inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1511–1516. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Gill P. J., Silbert J. E., Douglas W. H., Fanburg B. L. Involvement of cell surface heparin sulfate in the binding of lipoprotein lipase to cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):995–1002. doi: 10.1172/JCI110354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


