Abstract
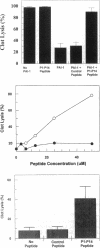
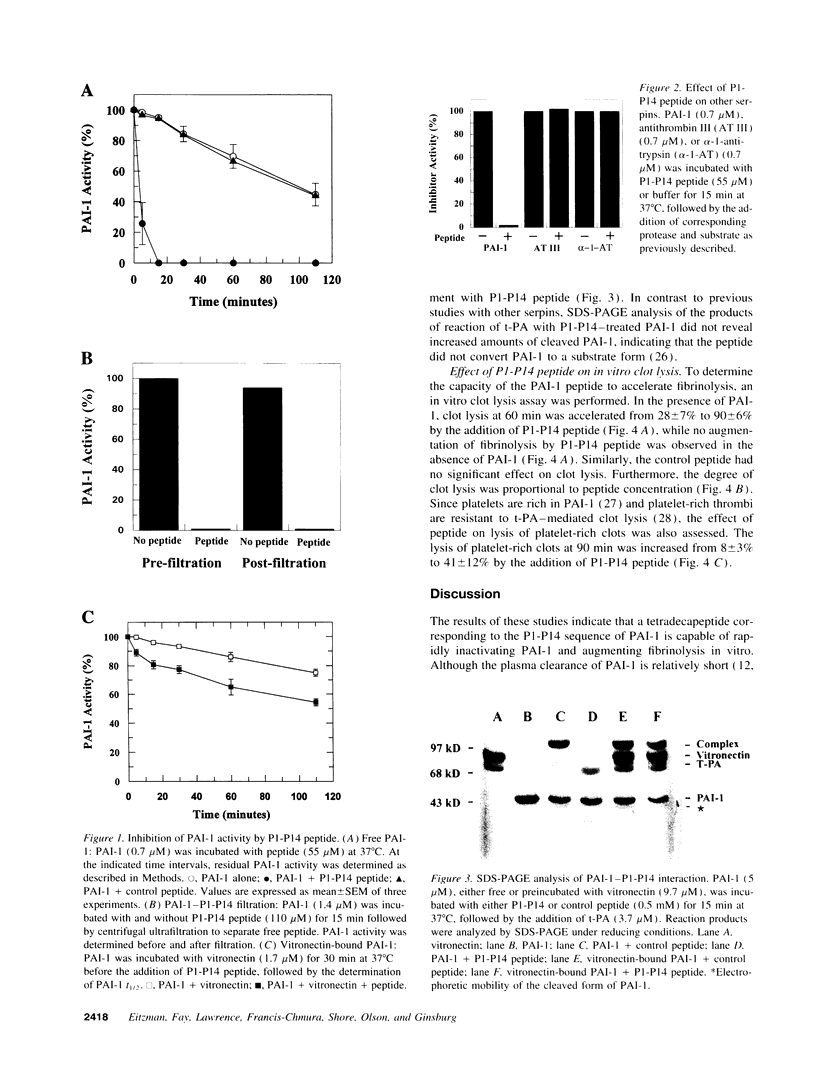
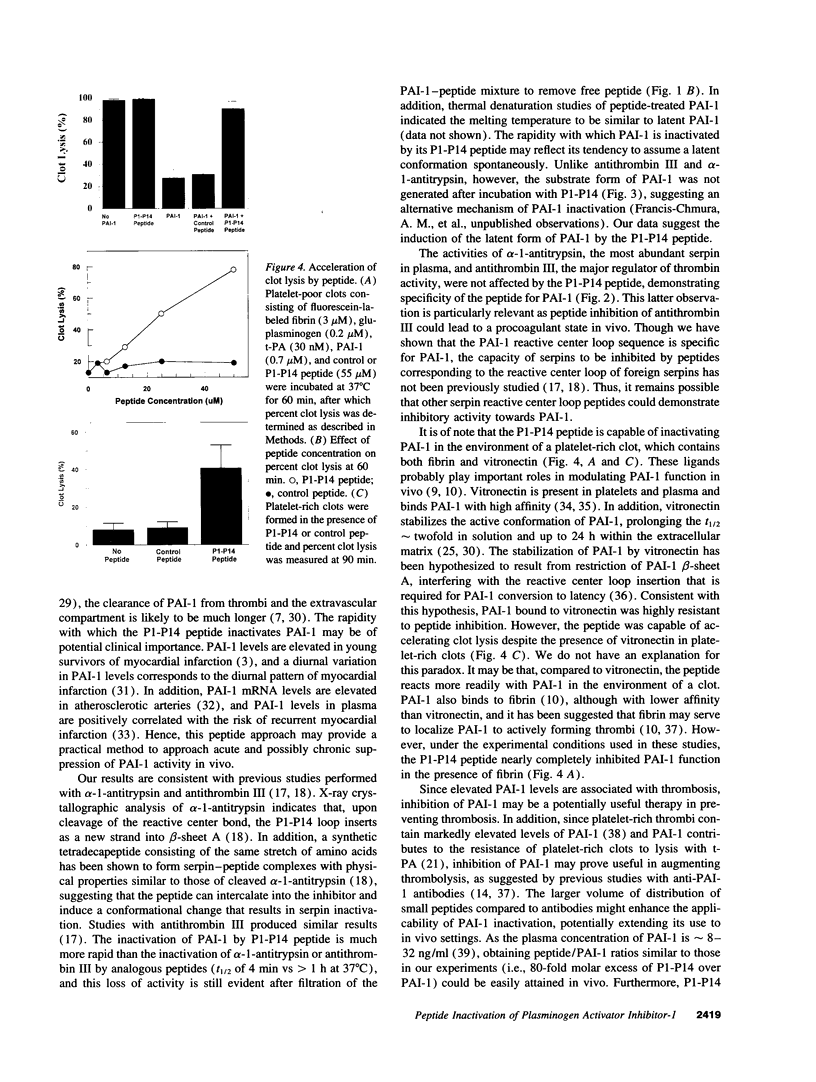
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), the primary inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) and urokinase plasminogen activator, is an important regulator of the blood fibrinolytic system. Elevated plasma levels of PAI-1 are associated with thrombosis, and high levels of PAI-1 within platelet-rich clots contribute to their resistance to lysis by t-PA. Consequently, strategies aimed at inhibition of PAI-1 may prove clinically useful. This study was designed to test the hypothesis that a 14-amino acid peptide, corresponding to the PAI-1 reactive center loop (residues 333-346), can rapidly inhibit PAI-1 function. PAI-1 (0.7 microM) was incubated with peptide (55 microM) at 37 degrees C. At timed intervals, residual PAI-1 activity was determined by addition of reaction mixture samples to t-PA and chromogenic substrate. The T1/2 of PAI-1 activity in the presence of peptide was 4 +/- 3 min compared to a control T1/2 of 98 +/- 18 min. The peptide also inhibited complex formation between PAI-1 and t-PA as demonstrated by SDS-PAGE analysis. However, the capacity of the peptide to inhibit PAI-1 bound to vitronectin, a plasma protein that stabilizes PAI-1 activity, was markedly attenuated. Finally, the peptide significantly enhanced in vitro lysis of platelet-rich clots and platelet-poor clots containing recombinant PAI-1. These results indicate that a 14-amino acid peptide can rapidly inactivate PAI-1 and accelerate fibrinolysis in vitro. These studies also demonstrate that PAI-1 function can be directly attenuated in a physiologic setting and suggest a novel approach for augmenting fibrinolysis in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angleton P., Chandler W. L., Schmer G. Diurnal variation of tissue-type plasminogen activator and its rapid inhibitor (PAI-1). Circulation. 1989 Jan;79(1):101–106. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Ylinenjärvi K., Olson S. T., Bock P. E. Conversion of antithrombin from an inhibitor of thrombin to a substrate with reduced heparin affinity and enhanced conformational stability by binding of a tetradecapeptide corresponding to the P1 to P14 region of the putative reactive bond loop of the inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1976–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth N. A., Simpson A. J., Croll A., Bennett B., MacGregor I. R. Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) in plasma and platelets. Br J Haematol. 1988 Nov;70(3):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braaten J. V., Handt S., Jerome W. G., Kirkpatrick J., Lewis J. C., Hantgan R. R. Regulation of fibrinolysis by platelet-released plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: light scattering and ultrastructural examination of lysis of a model platelet-fibrin thrombus. Blood. 1993 Mar 1;81(5):1290–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet P., Stassen J. M., Schoonjans L., Ream B., van den Oord J. J., De Mol M., Mulligan R. C., Collen D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene-deficient mice. II. Effects on hemostasis, thrombosis, and thrombolysis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2756–2760. doi: 10.1172/JCI116893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Evans D. L., Stein P. E. Mobile reactive centre of serpins and the control of thrombosis. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):576–578. doi: 10.1038/353576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Paramo J. A., Collen D. Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):818–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI111777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declerck P. J., De Mol M., Alessi M. C., Baudner S., Pâques E. P., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Collen D. Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 binding protein from human plasma. Identification as a multimeric form of S protein (vitronectin). J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15454–15461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declerck P. J., De Mol M., Vaughan D. E., Collen D. Identification of a conformationally distinct form of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, acting as a noninhibitory substrate for tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11693–11696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eitzman D. T., Chi L., Saggin L., Schwartz R. S., Lucchesi B. R., Fay W. P. Heparin neutralization by platelet-rich thrombi. Role of platelet factor 4. Circulation. 1994 Apr;89(4):1523–1529. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.4.1523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. A., Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. The primary plasminogen-activator inhibitors in endothelial cells, platelets, serum, and plasma are immunologically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8710–8714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay W. P., Eitzman D. T., Shapiro A. D., Madison E. L., Ginsburg D. Platelets inhibit fibrinolysis in vitro by both plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Blood. 1994 Jan 15;83(2):351–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay W. P., Shapiro A. D., Shih J. L., Schleef R. R., Ginsburg D. Brief report: complete deficiency of plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 due to a frame-shift mutation. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 10;327(24):1729–1733. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212103272406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelehrter T. D., Sznycer-Laszuk R. Thrombin induction of plasminogen activator-inhibitor in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):165–169. doi: 10.1172/JCI112271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., Wiman B., de Faire U., Blombäck M. Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1557–1563. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., de Faire U., Walldius G., Dahlén G., Szamosi A., Landou C., Blombäck M., Wiman B. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma: risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1987 Jul 4;2(8549):3–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)93050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Carrell R. W. Implications of the three-dimensional structure of alpha 1-antitrypsin for structure and function of serpins. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):8951–8966. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang I. K., Gold H. K., Ziskind A. A., Fallon J. T., Holt R. E., Leinbach R. C., May J. W., Collen D. Differential sensitivity of erythrocyte-rich and platelet-rich arterial thrombi to lysis with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. A possible explanation for resistance to coronary thrombolysis. Circulation. 1989 Apr;79(4):920–928. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.4.920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keijer J., Ehrlich H. J., Linders M., Preissner K. T., Pannekoek H. Vitronectin governs the interaction between plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10700–10707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Berkenpas M. B., Palaniappan S., Ginsburg D. Localization of vitronectin binding domain in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):15223–15228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Inactivation of plasminogen activator inhibitor by oxidants. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6351–6355. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Olson S. T., Palaniappan S., Ginsburg D. Engineering plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 mutants with increased functional stability. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 29;33(12):3643–3648. doi: 10.1021/bi00178a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi M., Biemond B. J., van Zonneveld A. J., ten Cate J. W., Pannekoek H. Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity results in promotion of endogenous thrombolysis and inhibition of thrombus extension in models of experimental thrombosis. Circulation. 1992 Jan;85(1):305–312. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.1.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Sawdey M., Mimuro J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:87–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J. Inhibiting the inhibitor. Circulation. 1992 Jan;85(1):386–387. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.1.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of a protein from bovine plasma that binds to type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and prevents its interaction with extracellular matrix. Evidence that the protein is vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):936–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottonen J., Strand A., Symersky J., Sweet R. M., Danley D. E., Geoghegan K. F., Gerard R. D., Goldsmith E. J. Structural basis of latency in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):270–273. doi: 10.1038/355270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter van Loon B. J., Rijken D. C., Brommer E. J., van der Maas A. P. The amount of plasminogen, tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in human thrombi and the relation to ex-vivo lysibility. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jan 23;67(1):101–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Holzhüter S., Justus C., Müller-Berghaus G. Identification of and partial characterization of platelet vitronectin: evidence for complex formation with platelet-derived plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1989–1996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F., Hutzelmann J. E. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 binds to fibrin and inhibits tissue-type plasminogen activator-mediated fibrin dissolution. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17128–17135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman J., Sawdey M. S., Keeton M. R., Bordin G. M., Bernstein E. F., Dilley R. B., Loskutoff D. J. Increased type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in atherosclerotic human arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6998–7002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze A. J., Baumann U., Knof S., Jaeger E., Huber R., Laurell C. B. Structural transition of alpha 1-antitrypsin by a peptide sequentially similar to beta-strand s4A. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):51–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Loskutoff D. J. Kinetic analysis of the interaction between type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and vitronectin and evidence that the bovine inhibitor binds to a thrombin-derived amino-terminal fragment of bovine vitronectin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 30;1078(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90087-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. M., Lawrence D. A., Yang A. Y., Vandenberg E. T., Paielli D., Olson S. T., Shore J. D., Ginsburg D. Saturation mutagenesis of the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 reactive center. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7588–7595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. E., Declerck P. J., Van Houtte E., De Mol M., Collen D. Studies of recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in rabbits. Pharmacokinetics and evidence for reactivation of latent plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in vivo. Circ Res. 1990 Nov;67(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.5.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Hamsten A. The fibrinolytic enzyme system and its role in the etiology of thromboembolic disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1990 Jul;16(3):207–216. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]