Abstract
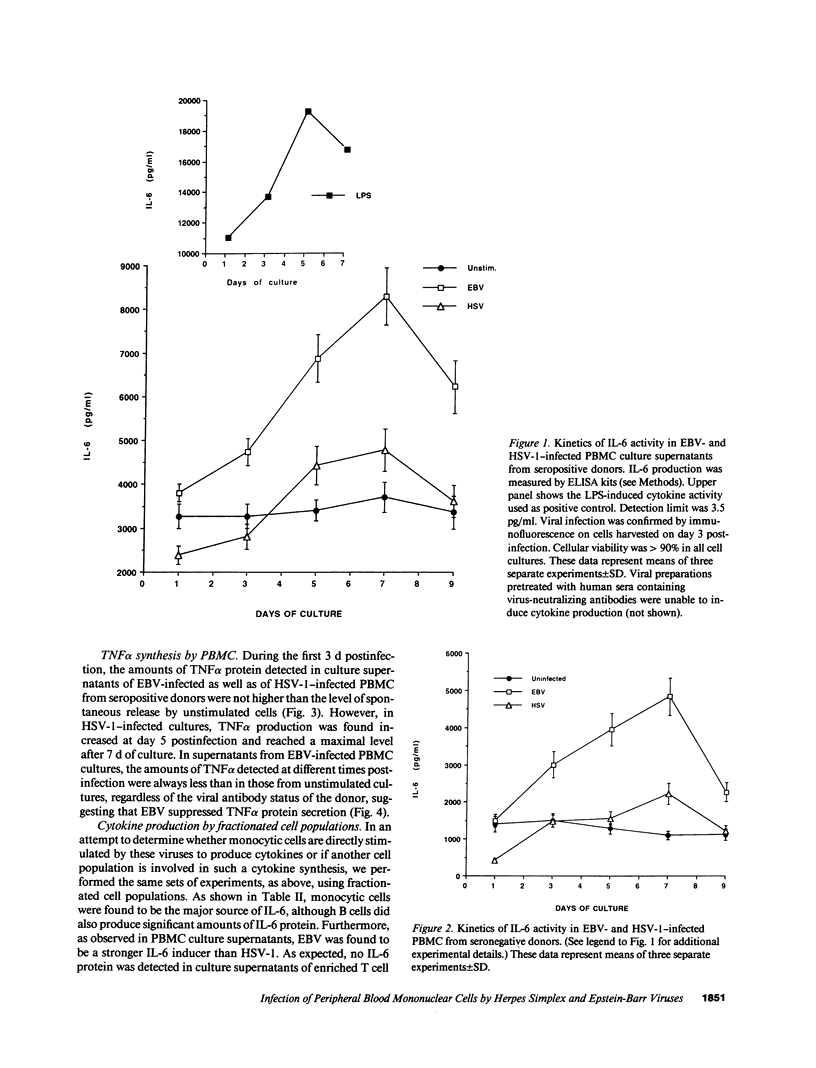
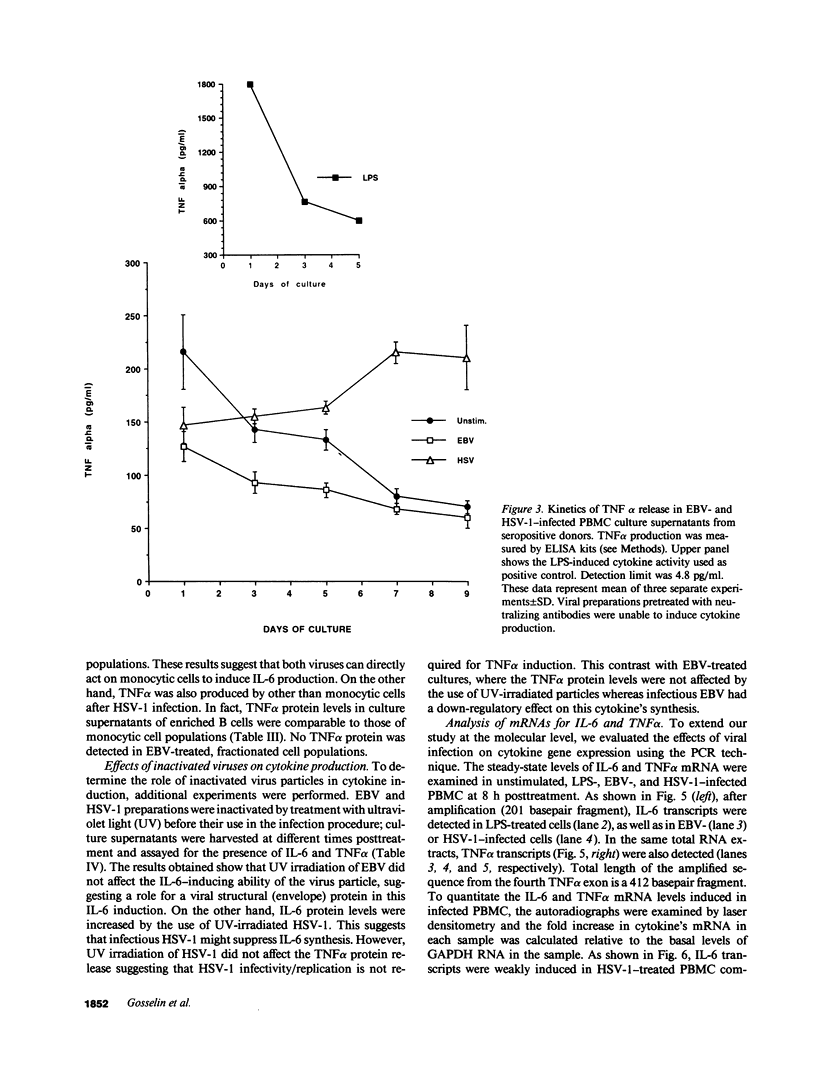
Infection by herpesviruses can result in profound immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory effects. However, no significant information is available on the effect of such infections on the production of immunoregulatory cytokines. We studied the kinetics of production of two monocyte-derived cytokines, interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha), induced by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) in peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures and in fractionated cell populations. We observed that, when compared to HSV-1, EBV is a stronger inducer of IL-6. In EBV-infected cultures, IL-6 protein was detected at day 1 postinfection and gradually increased with time. In contrast, lower amounts of IL-6 were detected 5 d postinfection in HSV-1-infected cultures. HSV-1-infected cultures secreted significant amounts of TNF alpha protein after 5 d of culture and reached a maximal level of production at day 7, whereas EBV inhibited TNF alpha production. In fractionated cell populations, monocytic cells were found to be the main source of IL-6 synthesis after EBV or HSV-1 infection. However, TNF alpha synthesis in HSV-1-infected cultures was from both B and monocytic cells. By using the polymerase chain reaction technique we show that, after infection by these two herpesviruses, differences in cytokine gene products are also observed at the transcriptional level. These observations demonstrate that EBV and HSV-1 exert differential effects on IL-6 and TNF alpha gene transcription and on the resulting protein secretion in human mononuclear blood cells.
Full text
PDF

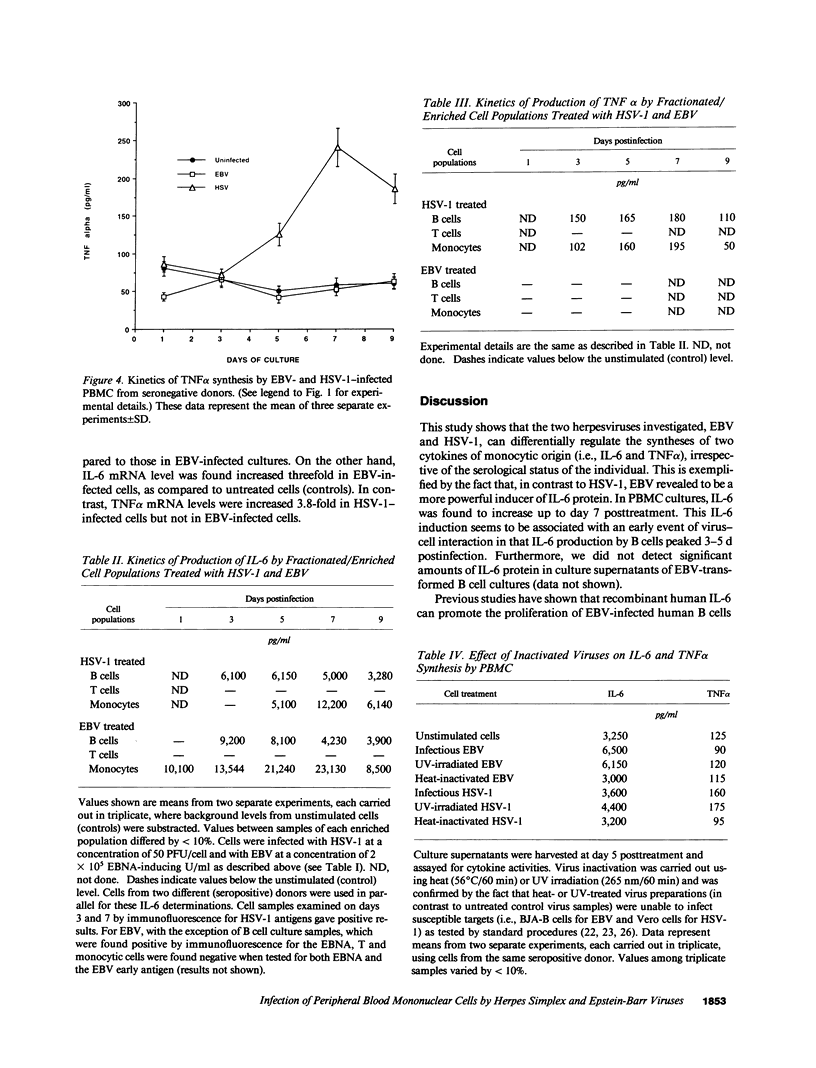
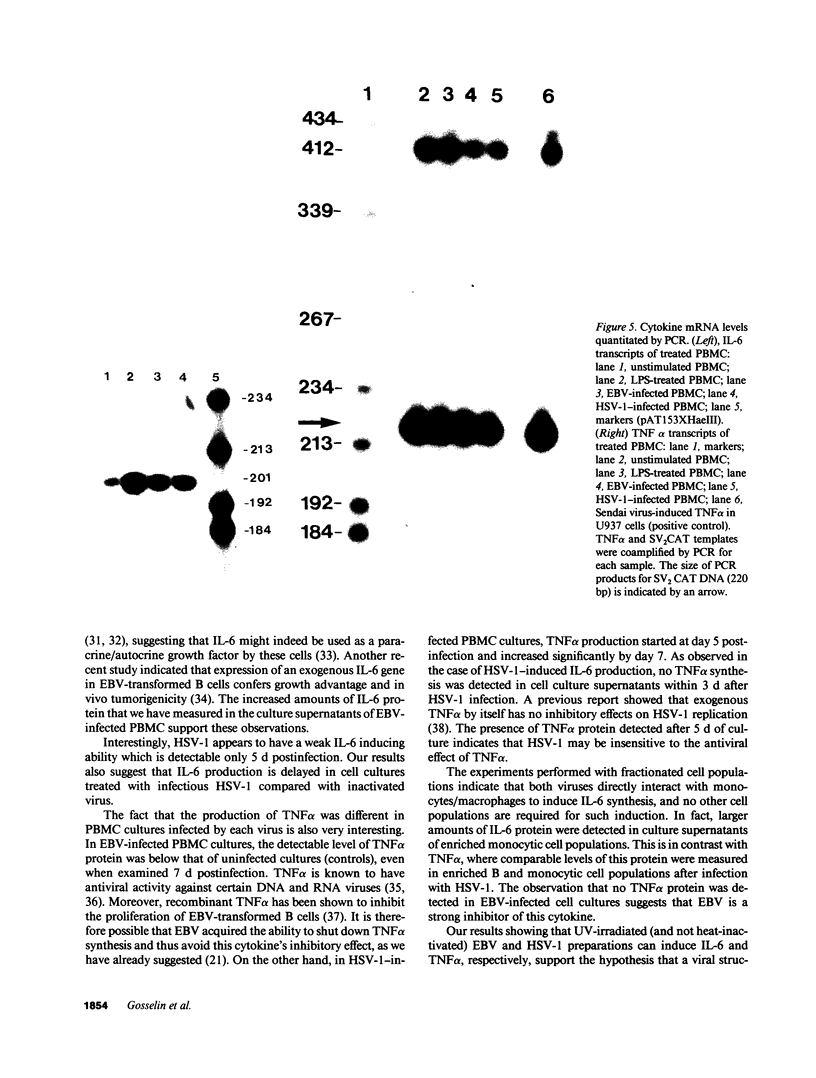
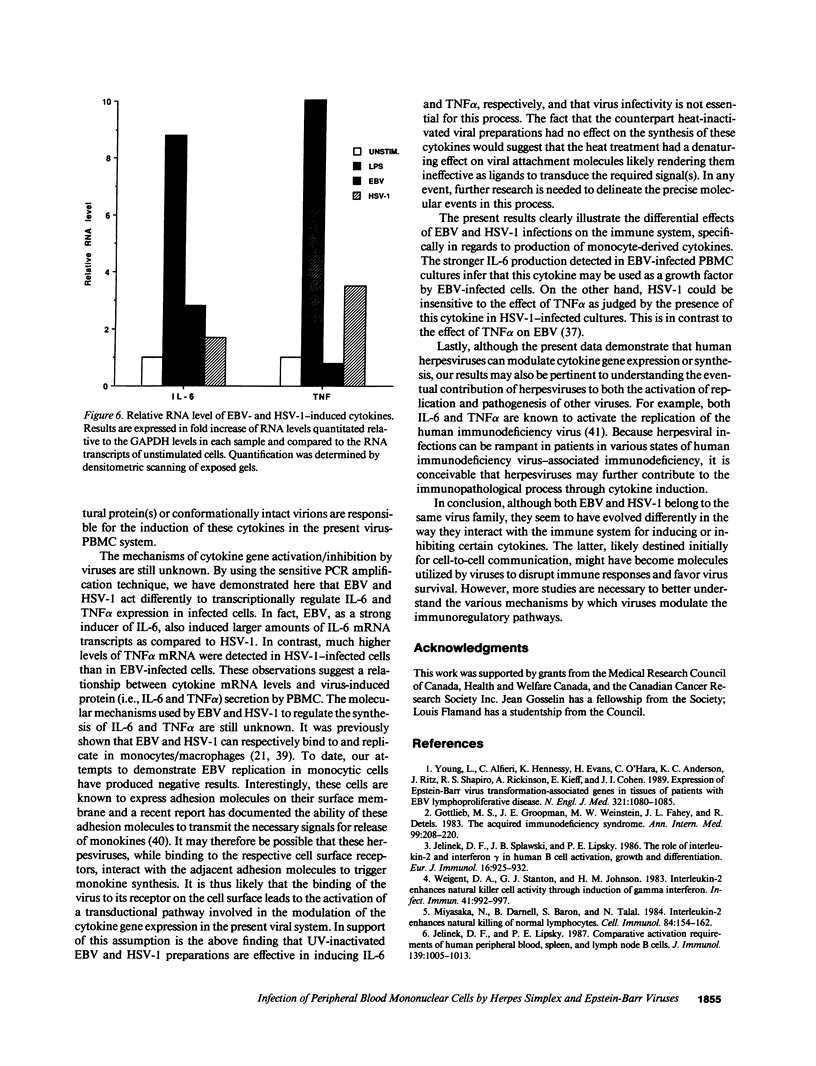

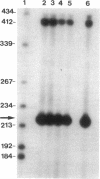
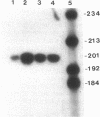
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcari P., Martinelli R., Salvatore F. The complete sequence of a full length cDNA for human liver glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: evidence for multiple mRNA species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):9179–9189. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.9179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. W., Teute H. K., Kirchner H., Munk K. Replication of herpes simplex virus in human T lymphocytes: characterization of the viral target cell. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):914–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Addario M., Roulston A., Wainberg M. A., Hiscott J. Coordinate enhancement of cytokine gene expression in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected promonocytic cells. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6080–6089. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6080-6089.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feduchi E., Alonso M. A., Carrasco L. Human gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor exert a synergistic blockade on the replication of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1354–1359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1354-1359.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinman R., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Tsujimoto M., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor is an important mediator of tumor cell killing by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):635–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin J., Menezes J., D'Addario M., Hiscott J., Flamand L., Lamoureux G., Oth D. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha transcription by Epstein-Barr virus. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jan;21(1):203–208. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin J., Menezes J., Mercier G., Lamoureux G., Oth D. Differential interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma production by human lymphocyte cultures exceptionally resistant to Epstein-Barr virus immortalization. Cell Immunol. 1989 Sep;122(2):440–449. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin J., Menezes J., Mercier G., Lamoureux G., Oth D. Peripheral blood lymphocytes resistant to Epstein-Barr virus immortalization manifest high natural killer (NK) type activity against NK-resistant target cells. Viral Immunol. 1990 Spring;3(1):55–65. doi: 10.1089/vim.1990.3.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Groopman J. E., Weinstein W. M., Fahey J. L., Detels R. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):208–220. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-2-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Y., Muraguchi A., Suematsu S., Matsuda T., Yoshizaki K., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Regulation of BSF-2/IL-6 production by human mononuclear cells. Macrophage-dependent synthesis of BSF-2/IL-6 by T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1529–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen O., Kabelitz D. Tumor necrosis factor selectively inhibits activation of human B cells by Epstein-Barr virus. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Comparative activation requirements of human peripheral blood, spleen, and lymph node B cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1005–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Splawski J. B., Lipsky P. E. The roles of interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma in human B cell activation, growth and differentiation. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(8):925–932. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasparian S. S., Menezes J. CD8+ suppressor cells inhibit staphylococcal protein A-induced gamma interferon production by CD4+ lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 1991 Jan;27(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90240-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Miller A., Fauci A. S. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on mitogen-activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):786–791. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Cox P. A., Loo L. S. Defective production of antibody to herpes simplex virus in neonates: defective production of T helper lymphokine and induction of suppression. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1179–1187. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Loo L. S., Drath D. B., Cox P. Interleukin-2 protects neonatal mice from lethal herpes simplex virus infection: a macrophage-mediated, gamma interferon-induced mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):239–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Summers W. C. Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection of isogenic Epstein-Barr virus genome-negative and -positive Burkitt's lymphoma-derived cell lines. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.248-254.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Tsoukas C. D., Fong S., Dinarello C. A., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Release of lymphokines after Epstein Barr virus infection in vitro. I. Sources of and kinetics of production of interferons and interleukins in normal humans. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3636–3642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Bourkas A. E. Herpesvirus-lymphoid cell interactions: comparative studies on the biology of herpes simplex virus-induced Fc receptors in B, T, and "null" lymphoid cell lines. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):115–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.115-122.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Jondal M., Leibold W., Dorval G. Epstein-Barr virus interactions with human lymphocyte subpopulations: virus adsorption, kinetics of expression of Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen, and lymphocyte transformation. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):303–310. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.303-310.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G. Biological differences between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) strains with regard to lymphocyte transforming ability, superinfection and antigen induction. Exp Cell Res. 1975 May;92(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestan J., Digel W., Mittnacht S., Hillen H., Blohm D., Möller A., Jacobsen H., Kirchner H. Antiviral effects of recombinant tumour necrosis factor in vitro. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):816–819. doi: 10.1038/323816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka N., Darnell B., Baron S., Talal N. Interleukin 2 enhances natural killing of normal lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1984 Mar;84(1):154–162. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro S., Debili N., Bernaudin J. F., Vainchenker W., Doly J. Regulation of the expression of IL-6 in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4339–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason L. H., Mathieson B. J., Liang S. M., Flick D. A., Herberman R. B. Mediation of mouse natural cytotoxic activity by tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):700–702. doi: 10.1038/321700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P., Menezes J. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-lymphoid cell interactions. I. Quantification of EBV particles required for the membrane immunofluorescence assay and the comparative expression of EBV receptors on different human B, T and null cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Z. F., Fauci A. S. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection: cytokine induction of HIV expression. Immunol Today. 1990 May;11(5):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancéau J., Falcoff R., Zilberstein A., Béranger F., Lebeau J., Revel M., Vaquero C. Interferon-beta 2 (BSF-2) mRNA is expressed in human monocytes. J Interferon Res. 1988 Aug;8(4):473–481. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Quinto I., Ruocco M. R., Arcucci A., Mallardo M., Caretto P., Forni G., Venuta S. Expression of an exogenous interleukin 6 gene in human Epstein Barr virus B cells confers growth advantage and in vivo tumorigenicity. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):61–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Espevik T., Rice G. C., Ammann A. J., Figari I. S., Ranges G. E., Palladino M. A., Jr The involvement of human tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta in the mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):499–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Gerrard T. L., Goldman N. G., Pike S. E. Stimulation of EBV-activated human B cells by monocytes and monocyte products. Role of IFN-beta 2/B cell stimulatory factor 2/IL-6. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4329–4336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Seamon K. B., Goldman N. D., Sehgal P. B., May L. T., Washington G. C., Jones K. D., Pike S. E. Monocyte-derived human B-cell growth factor identified as interferon-beta 2 (BSF-2, IL-6). Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):502–504. doi: 10.1126/science.2829354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Tanner J., Jones K. D., Revel M., Pike S. E. Identification of interleukin-6 as an autocrine growth factor for Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized B cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3033–3041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3033-3041.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. S., Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Shaw S., Gerrard T. L. LFA-3, CD44, and CD45: physiologic triggers of human monocyte TNF and IL-1 release. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1295–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.1697984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Interleukin 2 enhances natural killer cell activity through induction of gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):992–997. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.992-997.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]