Abstract
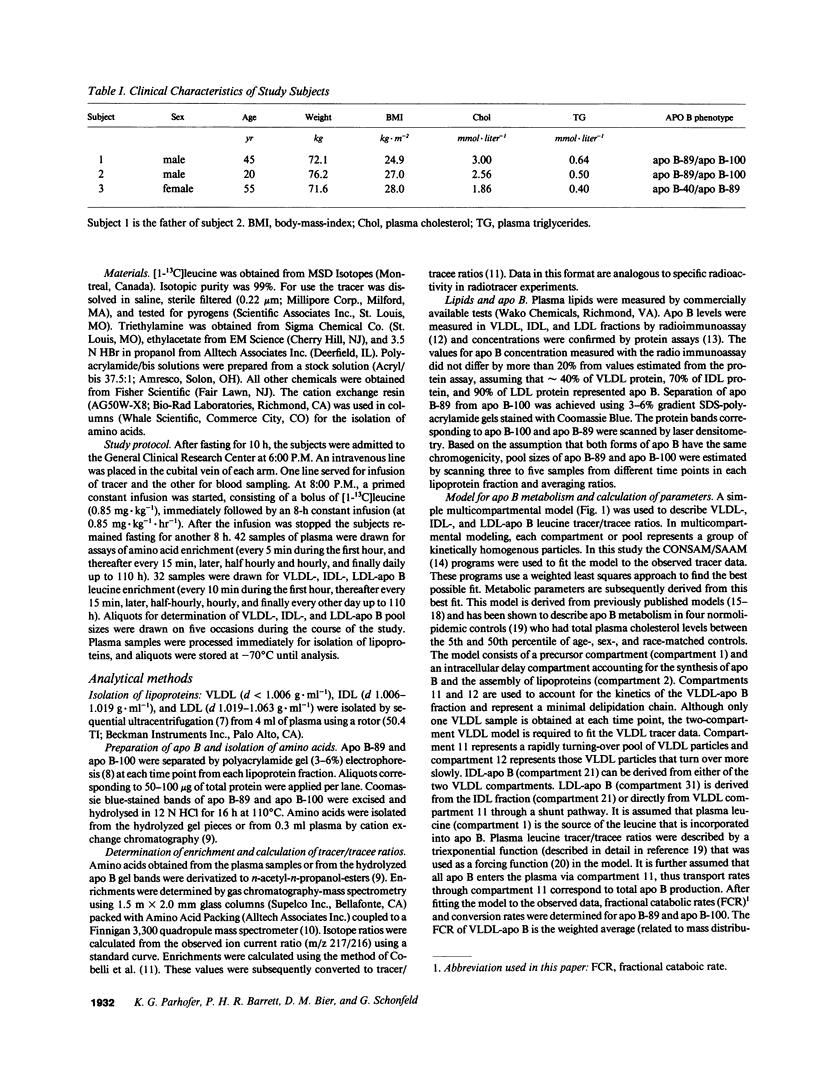
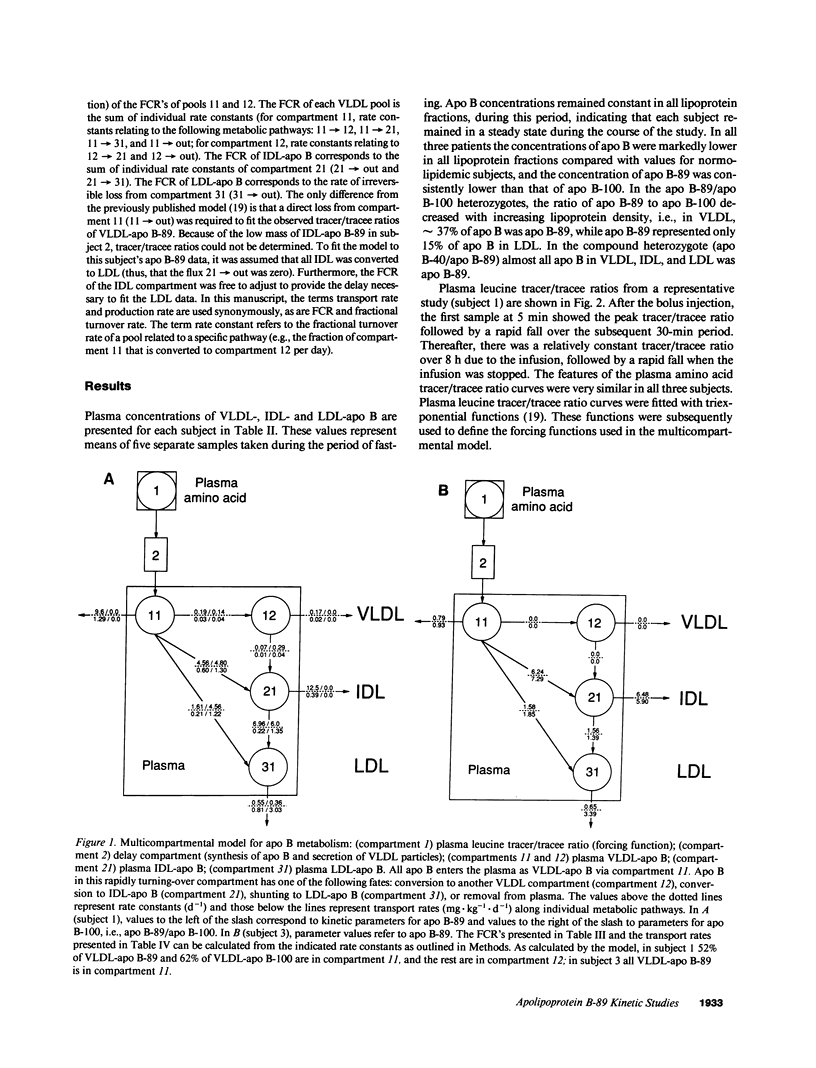
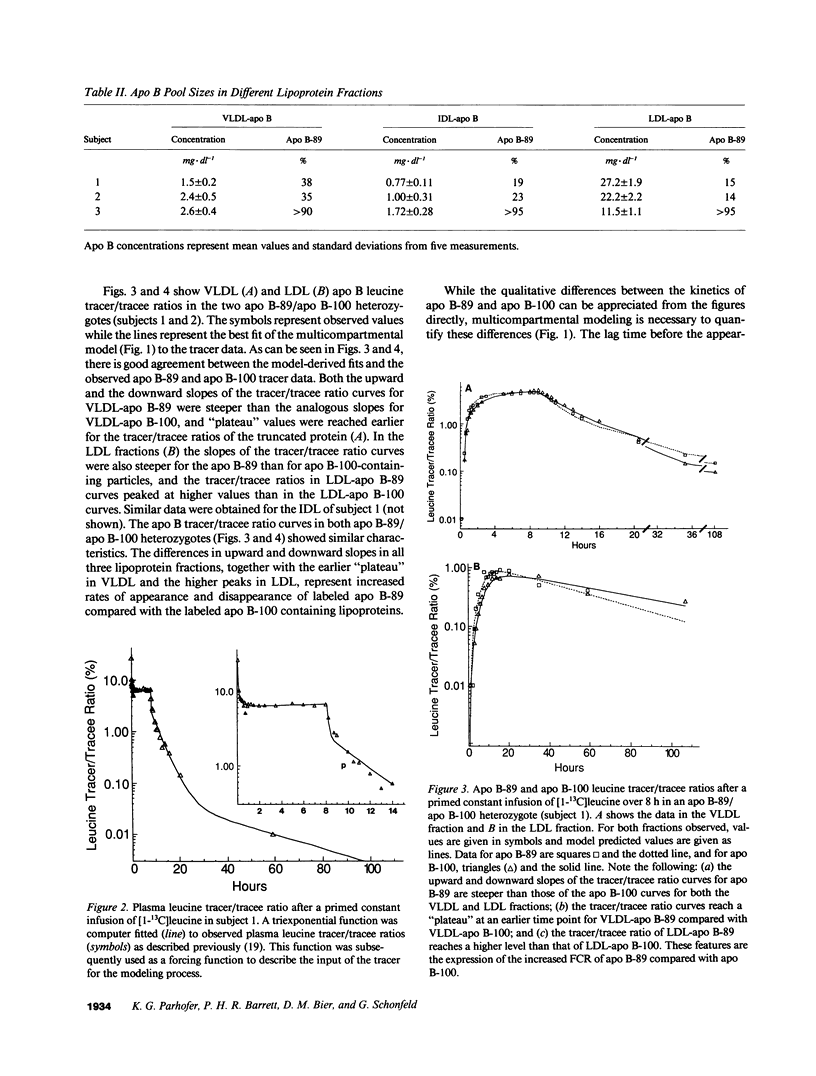
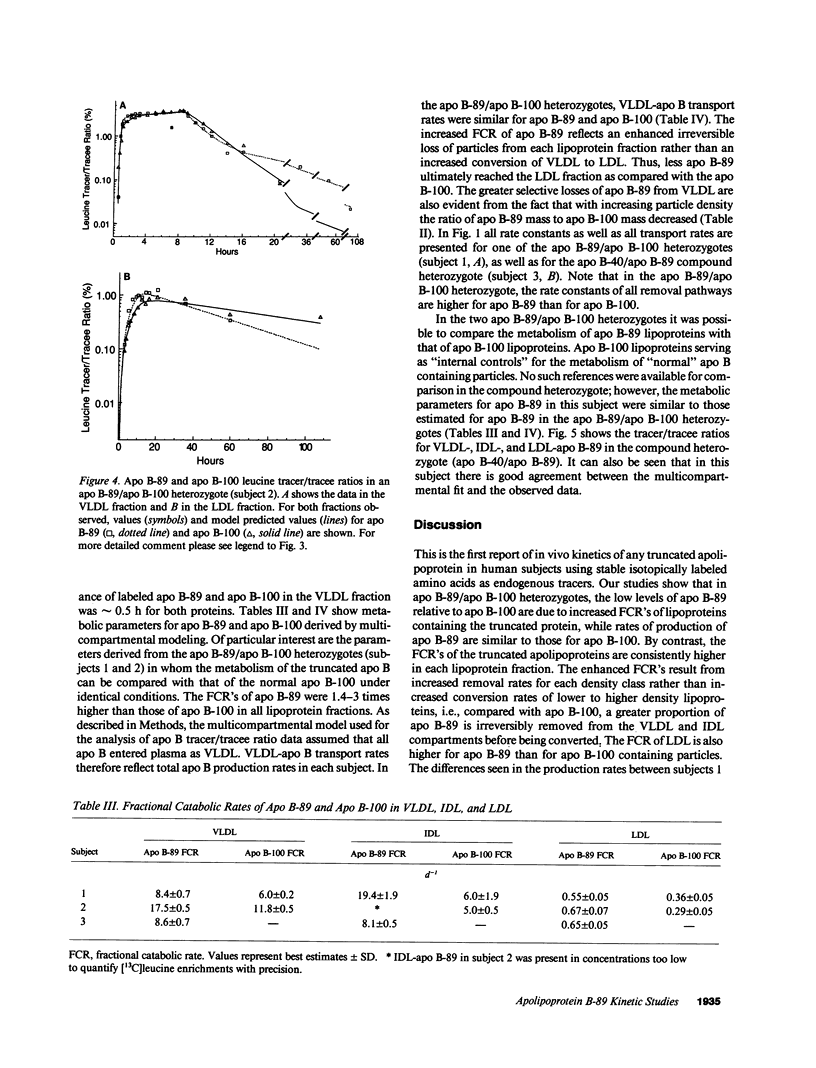
We have reported previously on two truncations of apolipoprotein B (apo B-40 and apo B-89) in a kindred with hypobetalipoproteinemia. Premature stop codons were found to be responsible for both apo B-40 and apo B-89, but the physiologic mechanisms accounting for the reduced plasma concentrations of these proteins have not been determined in vivo. This study investigates the metabolism of apo B-89 in two subjects heterozygous for apo B-89/apo B-100 and in one apo B-40/apo B-89 compound heterozygote. In both heterozygotes total apo B concentration is approximately 30% of normal and apo B-89 is present in lower concentrations in plasma than apo B-100. After the administration of [1-13C]leucine as a primed constant infusion over 8 h, 13C enrichments of plasma leucine as well as enrichments of VLDL-, IDL-, and LDL-apo B-89 leucine and VLDL-, IDL-, and LDL-apo B-100 leucine were measured over 110 h. Enrichment values were subsequently converted to tracer/tracee ratios and a multicompartmental model was used to estimate metabolic parameters. In both apo B-89/apo B-100 heterozygotes apo B-89 and apo B-100 were produced at similar rates. Respective transport rates of apo B-89 and apo B-100 for subject 1 were 2.13 +/- 0.18 and 2.56 +/- 0.13 mg.kg-1.d-1, and for subject 2, 6.59 +/- 0.18 and 8.23 +/- 0.39 mg.kg-1.d-1. However, fractional catabolic rates of VLDL, IDL, and LDL particles containing apo B-89 were 1.4-3 times higher than the rates for corresponding apo B-100-containing particles. Metabolic parameters of apo B-89 in the apo B-40/apo B-89 compound heterozygote compared favorably with those established for apo B-89 in apo B-89/apo B-100 heterozygotes. Thus, the enhanced catabolism of VLDL, IDL, and LDL particles containing the truncated apolipoprotein is responsible for the relatively low levels of apo B-89 seen in these subjects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. F. Determination of amino acid profiles in biological samples by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1974 Aug 14;95(2):189–212. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)84078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltz W. F., Kesäniemi Y. A., Howard B. V., Grundy S. M. Development of an integrated model for analysis of the kinetics of apolipoprotein B in plasma very low density lipoproteins, intermediate density lipoproteins, and low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):575–585. doi: 10.1172/JCI112009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltz W. F., Kesäniemi Y. A., Miller N. H., Fisher W. R., Grundy S. M., Zech L. A. Studies on the metabolism of apolipoprotein B in hypertriglyceridemic subjects using simultaneous administration of tritiated leucine and radioiodinated very low density lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):361–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M., Hall M., 3rd, Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Phair R. D., Goebel R. H. Metabolsim of apoB and apoC lipoproteins in man: kinetic studies in normal and hyperlipoproteininemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):38–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobelli C., Toffolo G., Bier D. M., Nosadini R. Models to interpret kinetic data in stable isotope tracer studies. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):E551–E564. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.5.E551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. S., Wagner D. A., Cohn S. D., Millar J. S., Schaefer E. J. Measurement of very low density and low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein (Apo) B-100 and high density lipoprotein Apo A-I production in human subjects using deuterated leucine. Effect of fasting and feeding. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):804–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI114507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Matsushima T., Marsh J. B., Yudkoff M., Coates P. M., Cortner J. A. Direct measurement of apolipoprotein B synthesis in human very low density lipoprotein using stable isotopes and mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1986 May;27(5):508–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keidar S., Goldberg A. C., Cook K., Bateman J., Schonfeld G. A high carbohydrate-fat free diet alters the proportion of heparin-bound VLDL in plasma and the expression of VLDL-apoB-100 epitopes. Metabolism. 1990 Mar;39(3):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90048-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krul E. S., Kinoshita M., Talmud P., Humphries S. E., Turner S., Goldberg A. C., Cook K., Boerwinkle E., Schonfeld G. Two distinct truncated apolipoprotein B species in a kindred with hypobetalipoproteinemia. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Nov-Dec;9(6):856–868. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A. H., Cohn J. S., Hachey D. L., Millar J. S., Ordovas J. M., Schaefer E. J. Comparison of deuterated leucine, valine, and lysine in the measurement of human apolipoprotein A-I and B-100 kinetics. J Lipid Res. 1990 Sep;31(9):1693–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. E., Ben-Galim E., Bier D. M. Determination of stable isotopic enrichment in individual plasma amino acids by chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1979 Jan;51(1):80–84. doi: 10.1021/ac50037a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard C. J., Munro A., Lorimer A. R., Gotto A. M., Shepherd J. Metabolism of apolipoprotein B in large triglyceride-rich very low density lipoproteins of normal and hypertriglyceridemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2178–2192. doi: 10.1172/JCI111644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parhofer K. G., Daugherty A., Kinoshita M., Schonfeld G. Enhanced clearance from plasma of low density lipoproteins containing a truncated apolipoprotein, apoB-89. J Lipid Res. 1990 Nov;31(11):2001–2007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poapst M., Uffelman K., Steiner G. The chromogenicity and quantitation of apoB-100 and apoB-48 of human plasma lipoproteins on analytical SDS gel electrophoresis. Atherosclerosis. 1987 May;65(1-2):75–88. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Lees R. S., George P. K., Pfleger B. Assay of total plasma apolipoprotein B concentration in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1458–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI107694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmud P., King-Underwood L., Krul E., Schonfeld G., Humphries S. The molecular basis of truncated forms of apolipoprotein B in a kindred with compound heterozygous hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1989 Nov;30(11):1773–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. D., Krul E. S., Tang J., Parhofer K. G., Garlock K., Talmud P., Schonfeld G. ApoB-54.8, a truncated apolipoprotein found primarily in VLDL, is associated with a nonsense mutation in the apoB gene and hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jun;32(6):1001–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. D., Krul E. S., Tang J., Parhofer K. G., Garlock K., Talmud P., Schonfeld G. ApoB-54.8, a truncated apolipoprotein found primarily in VLDL, is associated with a nonsense mutation in the apoB gene and hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jun;32(6):1001–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welty F. K., Hubl S. T., Pierotti V. R., Young S. G. A truncated species of apolipoprotein B (B67) in a kindred with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1748–1754. doi: 10.1172/JCI115193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G. Recent progress in understanding apolipoprotein B. Circulation. 1990 Nov;82(5):1574–1594. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.5.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


