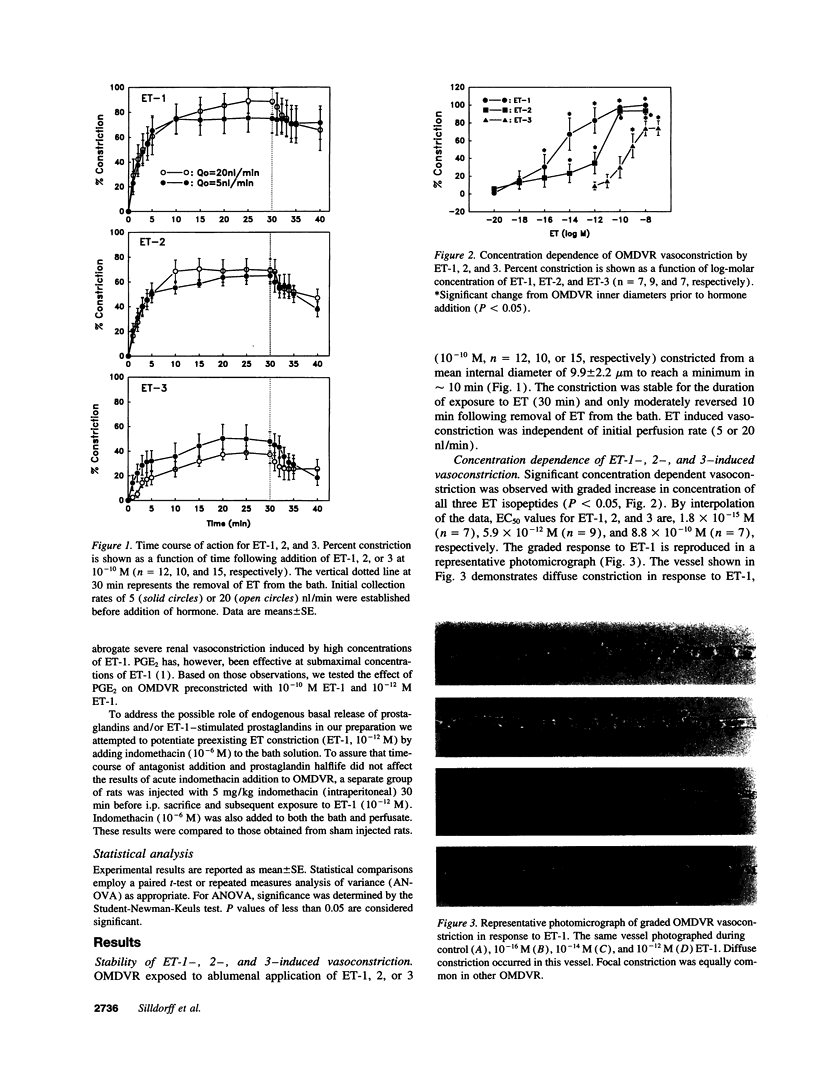
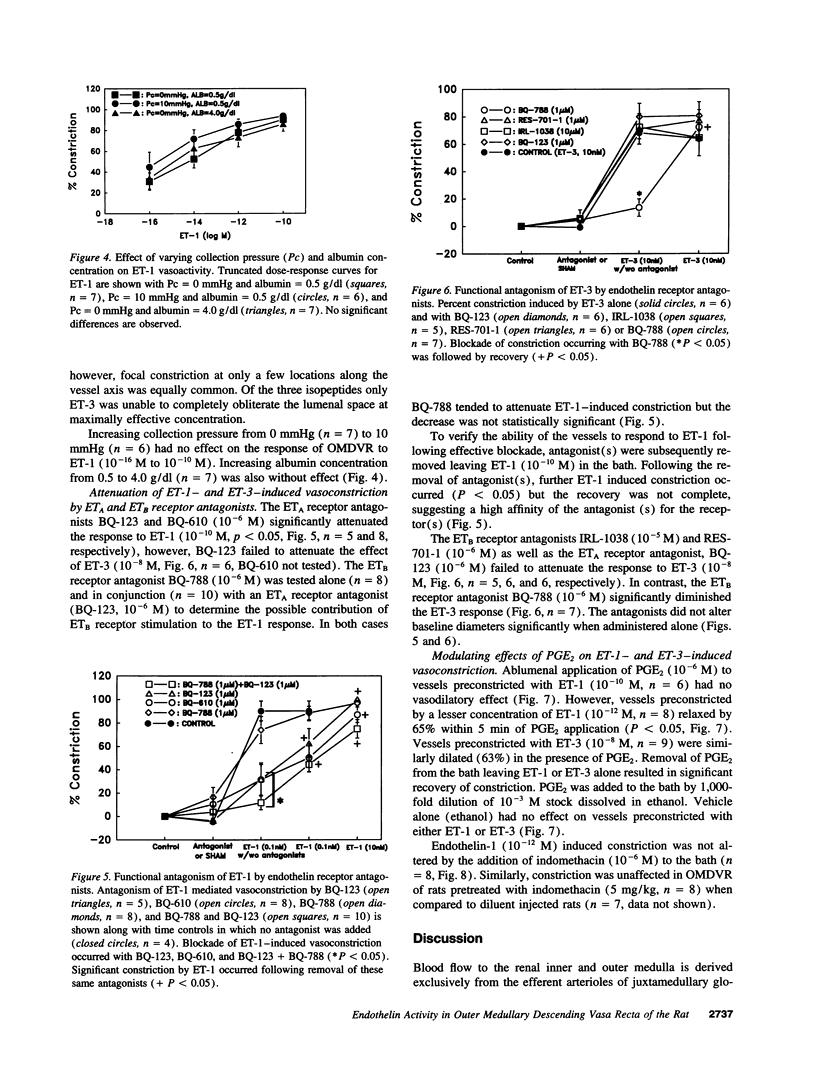
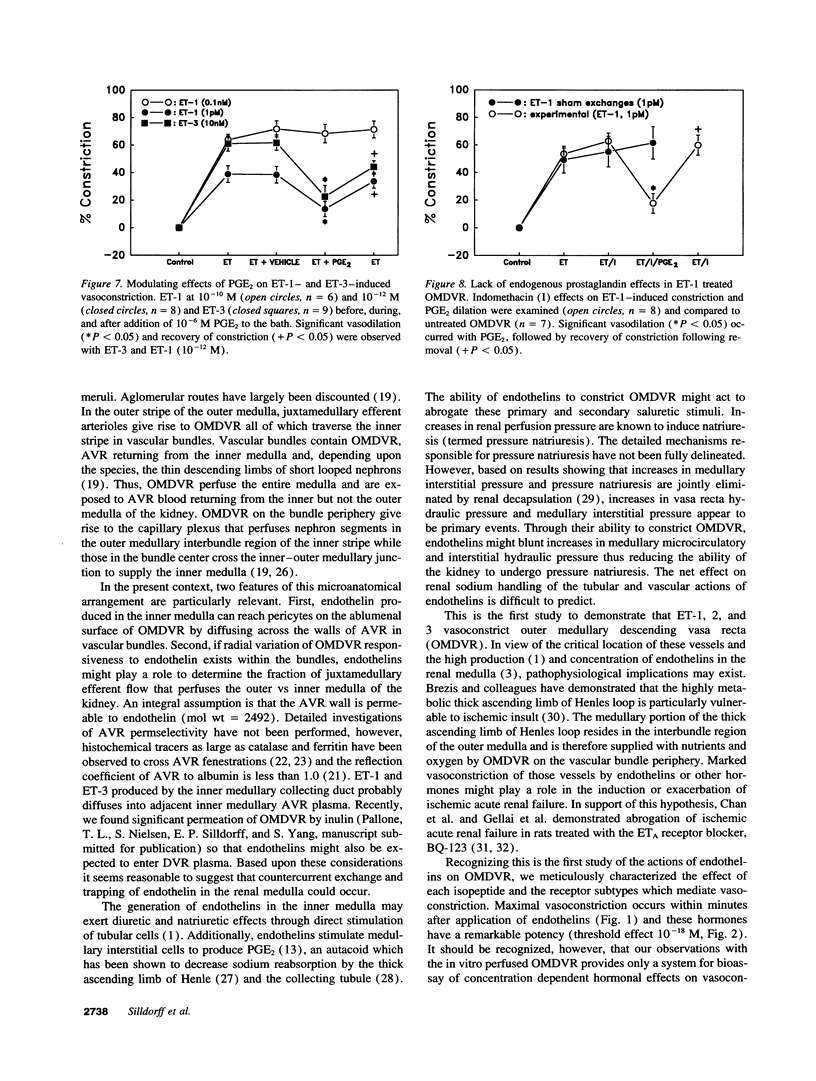
Abstract
Endothelins (ET) and prostaglandin E2 are synthesized in the inner medulla by collecting duct epithelium and interstitial cells, respectively. All ascending vasa recta (AVR) blood returns from the inner medulla to the cortex in outer medullary vascular bundles. We reasoned that hormones might influence medullary blood flow by diffusing across AVR fenestrations to modulate vasoconstriction of outer medullary descending vasa recta (OMDVR). To investigate this possibility, OMDVR dissected from vascular bundles were exposed to ET-1, 2, or 3. Each endothelin isoform induced stable vasoconstriction with potency, ET-1 > ET-2 > ET-3 (EC50, 1.8 x 10(-15), 5.9 x 10(-12), and 8.8 x 10(-10) M, respectively). The ETA receptor antagonist BQ-123 and BQ-610 (10(-6) M), as well as an ETA and ETB receptor antagonist combination, attenuated vasoconstriction due to ET-1 (10(-12) M). BQ-123 had no effect on the response to ET-3 (10(-8) M). The ETB receptor antagonist BQ-788 (10(-6) M) attenuated the response to ET-3 (10(-10) M), but not that to ET-1 (10(-12) M). Finally, PGE2 (10(-6) M) reversibly dilated OMDVR preconstricted with ET-1 (10(-12) M) or ET-3 (10(-8) M) but not ET-1 (10(-10) M). We conclude that ET-1,2, and 3 are potent constrictors of OMDVR and the response to ET-1 is mainly ETA receptor subtype mediated, while ET-3 acts via the ETB. PGE2 modulates ET induced constriction. These findings are consistent with interactive feedback and control of medullary perfusion by locally synthesized hormones.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom I. T., Bentley F. R., Wilson M. A., Garrison R. N. In vivo effects of endothelin on the renal microcirculation. J Surg Res. 1993 Apr;54(4):274–280. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1993.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezis M., Rosen S., Silva P., Epstein F. H. Selective vulnerability of the medullary thick ascending limb to anoxia in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):182–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B. Perfusion of isolated renal tubules. Yale J Biol Med. 1972 Jun-Aug;45(3-4):321–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Chittinandana A., Shapiro J. I., Shanley P. F., Schrier R. W. Effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist on ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 2):F135–F138. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.1.F135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. M., Trizna W., Ohlstein E. H. Renal microvascular effects of endothelin. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):F217–F221. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretschner M., Endlich K., Gulbins E., Lang R. E., Schlottmann K., Steinhausen M. Effects of endothelin on the renal microcirculation of the split hydronephrotic rat kidney. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1991 May-Jun;14(3):112–127. doi: 10.1159/000173394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellai M., Jugus M., Fletcher T., DeWolf R., Nambi P. Reversal of postischemic acute renal failure with a selective endothelinA receptor antagonist in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):900–906. doi: 10.1172/JCI117046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasinath B. S., Fried T. A., Davalath S., Marsden P. A. Glomerular epithelial cells synthesize endothelin peptides. Am J Pathol. 1992 Aug;141(2):279–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E. Endothelins in the kidney: physiology and pathophysiology. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993 Oct;22(4):493–510. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80920-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E., Fiedorek F. T., Jr Endothelin synthesis by rat inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Aug;2(2):150–155. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V22150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E. Production of endothelin-1 by rat mesangial cells: regulation by tumor necrosis factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 May;119(5):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemley K. V., Kriz W. Cycles and separations: the histotopography of the urinary concentrating process. Kidney Int. 1987 Feb;31(2):538–548. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemley K. V., Schmitt S. L., Holliger C., Dunn M. J., Robertson C. R., Jamison R. L. Prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors and vasa recta erythrocyte velocities in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 2):F562–F567. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.4.F562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loutzenhiser R., Epstein M., Hayashi K., Horton C. Direct visualization of effects of endothelin on the renal microvasculature. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):F61–F68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.1.F61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L. Molecular sieving of albumin by the ascending vasa recta wall. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):30–34. doi: 10.1172/JCI115852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L., Robertson C. R., Jamison R. L. Renal medullary microcirculation. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):885–920. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L. Vasoconstriction of outer medullary vasa recta by angiotensin II is modulated by prostaglandin E2. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 2):F850–F857. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.6.F850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone T. L., Work J., Myers R. L., Jamison R. L. Transport of sodium and urea in outer medullary descending vasa recta. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):212–222. doi: 10.1172/JCI116948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perico N., Cornejo R. P., Benigni A., Malanchini B., Ladny J. R., Remuzzi G. Endothelin induces diuresis and natriuresis in the rat by acting on proximal tubular cells through a mechanism mediated by lipoxygenase products. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Jul;2(1):57–69. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V2157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R. J., Zou A. P. Influence of the renal medullary circulation on the control of sodium excretion. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 2):R963–R973. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.265.5.R963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. M., Karnovsky M. J., Vehkatachalam M. A. Ultrastructural differences between rat inner medullary descending and ascending vasa recta;. Lab Invest. 1976 Aug;35(2):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T., Morrison A. B. Vascular permeability of the renal medullary vessels in the mouse and rat. Am J Pathol. 1973 May;71(2):155–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S. Endothelins: multifunctional renal peptides. Physiol Rev. 1993 Apr;73(2):375–411. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S., Wann S., Mené P., Dubyak G. R., Kester M., Nakazato Y., Sedor J. R., Dunn M. J. Endothelin stimulates phospholipase C, Na+/H+ exchange, c-fos expression, and mitogenesis in rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):708–712. doi: 10.1172/JCI113935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solez K., Fox J. A., Miller M., Heptinstall R. H. Effects of indomethacin on renal inner medullary plasma flow. Prostaglandins. 1974 Jul 25;7(2):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Effect of prostaglandin E2 on chloride transport across the rabbit thick ascending limb of Henle. Selective inhibitions of the medullary portion. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):495–502. doi: 10.1172/JCI109487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Kokko J. P. Inhibition of sodium transport by prostaglandin E2 across the isolated, perfused rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1172/JCI108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner M. J., Cannon T. R., Mundin J. W., White D. G., Watts I. S. Endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediate vascular smooth muscle contraction. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):858–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Different localization of two types of endothelin receptor mRNA in microdissected rat nephron segments using reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction assay. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):107–112. doi: 10.1172/JCI115822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Takemoto F., Ogata E., Kurokawa K. Detection of endothelin-1 mRNA by RT-PCR in isolated rat renal tubules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):108–113. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ujiie K., Terada Y., Nonoguchi H., Shinohara M., Tomita K., Marumo F. Messenger RNA expression and synthesis of endothelin-1 along rat nephron segments. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1043–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI115918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urade Y., Fujitani Y., Oda K., Watakabe T., Umemura I., Takai M., Okada T., Sakata K., Karaki H. An endothelin B receptor-selective antagonist: IRL 1038, [Cys11- Cys15]-endothelin-1(11-21) FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 28;342(1):103–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80593-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Karnovsky M. J. Extravascular protein in the kidney. An ultrastructural study of its relation to renal peritubular capillary permeability using protein tracers. Lab Invest. 1972 Nov;27(5):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes B. M., Ruston A. S., Mento P., Girardi E., Hart D., Vander Molen M., Barnett R., Nord E. P. Characterization of endothelin 1 receptor and signal transduction mechanisms in rat medullary interstitial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 2):F579–F589. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.4.F579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Thomas R., D'Orleans-Juste P., Antunes E., Walder C., Warner T. D., Vane J. R. Pressor effects of circulating endothelin are limited by its removal in the pulmonary circulation and by the release of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9797–9800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



