Abstract
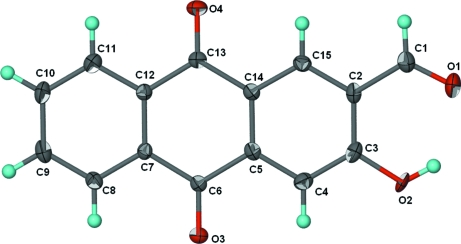
The molecule of the title compound, C15H8O4, is approximately planar. An intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond is observed between the hydroxy and formyl groups. The crystal used was a nonmerohedral twin, with a minor twin component of 15.9%.
Related literature
For antileshmanial and antiplasmodial activities, see: Sittie et al. (1999 ▶). For the treatment of twinned diffraction data, see: Spek (2003 ▶).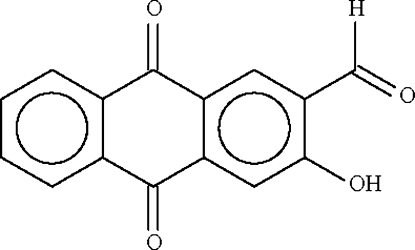
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H8O4
M r = 252.21
Triclinic,
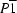
a = 6.9194 (2) Å
b = 8.0650 (2) Å
c = 10.7601 (3) Å
α = 86.250 (2)°
β = 83.214 (2)°
γ = 64.692 (2)°
V = 538.96 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 100 (2) K
0.22 × 0.04 × 0.04 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
4946 measured reflections
2419 independent reflections
1880 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.087
wR(F 2) = 0.343
S = 1.11
2419 reflections
173 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.49 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: X-SEED (Barbour, 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032224/ci2681sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032224/ci2681Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O1 | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.635 (5) | 132 |
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the University of Malaya for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Experimental
Rennellia elliptica Korth from the Rubiaceae family was collected from Kuala Keniam, Pahang, Malaysia. The root was chopped into small pieces and dried. The dried sample (1 kg) was ground and then extracted successively with hexane, dichloromethane and methanol. The dichloromethane extract was concentrated in vacuo to give 27 g crude extract. The crude extract was fractionated by column chromatography. The column (60 cm X 5 cm) was packed with acid-washed silica gel and eluted with hexane, dichloromethane and methanol. Nine fractions were obtained, and 3-hydroxy-2-formyl-9,10-anthraquinone (41.5 mg) was isolated from the third fraction (hexane:dichloromethane, 30:70) by slow evaporation of the solvent mixture. The yellow crystals obtained were washed with acetone.
Refinement
Carbon- and oxygen-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 Å and O—H = 0.84 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with U(H) set to 1.2–1.5Ueq(C,O). The crystal studied was a non-merohedral twin. The TwinRotMat in PLATON (Spek, 2003) gave the twin law as (-1 0 0, 0 - 1 0, -0.343 - 0.049 1), whose inclusion in the refinement lowered the R index from 11.3 to 8.7%. The twin component refined to 18.9%. The refinement is deemed satisfactory although the wR2 value for all reflections is somewhat high. The structure has a long C5–C14 bond; as the anisotropic displacement parameters are normal, the likely reason is localization of the double bonds in the ring. On the other hand, the C13–C14 bond is somewhat short.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 70% probability displacement ellipsoids. H atoms are drawn as spheres of arbitrary radii.
Crystal data
| C15H8O4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 252.21 | F(000) = 260 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.554 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.9194 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 1888 reflections |
| b = 8.0650 (2) Å | θ = 3.3–28.3° |
| c = 10.7601 (3) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| α = 86.250 (2)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 83.214 (2)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 64.692 (2)° | 0.22 × 0.04 × 0.04 mm |
| V = 538.96 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII area-detector diffractometer | 1880 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.024 |
| graphite | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| 4946 measured reflections | k = −10→10 |
| 2419 independent reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.087 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.343 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.11 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1778P)2 + 2.2381P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2419 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 173 parameters | Δρmax = 0.49 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.3155 (6) | 0.6486 (5) | 0.0888 (3) | 0.0251 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.2501 (6) | 0.3493 (5) | 0.0941 (3) | 0.0242 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.2611 | 0.4345 | 0.0490 | 0.029* | |
| O3 | 0.2366 (5) | −0.0898 (4) | 0.4383 (3) | 0.0153 (7) | |
| O4 | 0.2779 (5) | 0.4648 (4) | 0.6688 (3) | 0.0172 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.3060 (7) | 0.6395 (6) | 0.2041 (4) | 0.0178 (9) | |
| H1 | 0.3171 | 0.7336 | 0.2474 | 0.021* | |
| C2 | 0.2786 (7) | 0.4901 (6) | 0.2772 (4) | 0.0143 (9) | |
| C3 | 0.2544 (7) | 0.3500 (6) | 0.2187 (4) | 0.0161 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.2356 (7) | 0.2059 (6) | 0.2894 (4) | 0.0152 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.2187 | 0.1116 | 0.2500 | 0.018* | |
| C5 | 0.2419 (6) | 0.2016 (5) | 0.4183 (4) | 0.0123 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.2335 (6) | 0.0406 (5) | 0.4916 (4) | 0.0112 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.2285 (6) | 0.0417 (5) | 0.6299 (4) | 0.0112 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.2117 (7) | −0.1043 (6) | 0.7003 (4) | 0.0139 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.1986 | −0.1999 | 0.6601 | 0.017* | |
| C9 | 0.2144 (7) | −0.1091 (6) | 0.8286 (4) | 0.0179 (9) | |
| H9 | 0.2031 | −0.2083 | 0.8766 | 0.021* | |
| C10 | 0.2336 (7) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.8883 (4) | 0.0188 (9) | |
| H10 | 0.2353 | 0.0269 | 0.9767 | 0.023* | |
| C11 | 0.2503 (7) | 0.1762 (6) | 0.8187 (4) | 0.0173 (9) | |
| H11 | 0.2645 | 0.2709 | 0.8594 | 0.021* | |
| C12 | 0.2462 (6) | 0.1835 (5) | 0.6895 (4) | 0.0113 (8) | |
| C13 | 0.2641 (6) | 0.3403 (6) | 0.6165 (4) | 0.0126 (8) | |
| C14 | 0.2621 (6) | 0.3426 (5) | 0.4787 (4) | 0.0120 (8) | |
| C15 | 0.2815 (7) | 0.4851 (6) | 0.4072 (4) | 0.0133 (8) | |
| H15 | 0.2968 | 0.5801 | 0.4468 | 0.016* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.038 (2) | 0.0258 (18) | 0.0125 (16) | −0.0155 (16) | −0.0033 (13) | 0.0054 (13) |
| O2 | 0.046 (2) | 0.0283 (18) | 0.0063 (15) | −0.0226 (17) | −0.0062 (13) | 0.0020 (12) |
| O3 | 0.0194 (15) | 0.0131 (14) | 0.0147 (15) | −0.0079 (12) | −0.0028 (11) | −0.0009 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0228 (16) | 0.0148 (15) | 0.0165 (15) | −0.0103 (13) | −0.0003 (12) | −0.0039 (11) |
| C1 | 0.021 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.0078 (17) | −0.0040 (16) | 0.0035 (16) |
| C2 | 0.0146 (19) | 0.0149 (19) | 0.0119 (19) | −0.0053 (16) | −0.0011 (14) | 0.0030 (15) |
| C3 | 0.017 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.0103 (19) | −0.0080 (17) | −0.0030 (15) | 0.0010 (15) |
| C4 | 0.016 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.0074 (16) | −0.0007 (15) | −0.0025 (15) |
| C5 | 0.0106 (18) | 0.0107 (18) | 0.0135 (19) | −0.0032 (14) | 0.0010 (14) | 0.0003 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0099 (17) | 0.0105 (18) | 0.0121 (19) | −0.0036 (14) | −0.0001 (14) | −0.0004 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0109 (18) | 0.0114 (18) | 0.0103 (18) | −0.0038 (14) | −0.0025 (13) | 0.0011 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0145 (19) | 0.0118 (18) | 0.015 (2) | −0.0053 (15) | −0.0023 (15) | 0.0013 (14) |
| C9 | 0.019 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.017 (2) | −0.0081 (17) | −0.0012 (16) | 0.0055 (16) |
| C10 | 0.024 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.0110 (19) | −0.0100 (18) | −0.0009 (16) | 0.0026 (16) |
| C11 | 0.021 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.013 (2) | −0.0084 (17) | −0.0008 (16) | −0.0009 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0108 (18) | 0.0112 (18) | 0.0109 (18) | −0.0039 (14) | −0.0002 (14) | −0.0005 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0112 (18) | 0.0125 (19) | 0.0139 (19) | −0.0046 (15) | −0.0015 (14) | −0.0010 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0116 (18) | 0.0112 (18) | 0.0127 (19) | −0.0044 (14) | 0.0001 (14) | −0.0002 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0138 (19) | 0.0112 (18) | 0.014 (2) | −0.0049 (15) | 0.0006 (14) | −0.0017 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.234 (5) | C7—C8 | 1.398 (5) |
| O2—C3 | 1.345 (5) | C7—C12 | 1.403 (5) |
| O2—H2 | 0.84 | C8—C9 | 1.380 (6) |
| O3—C6 | 1.222 (5) | C8—H8 | 0.95 |
| O4—C13 | 1.226 (5) | C9—C10 | 1.397 (6) |
| C1—C2 | 1.464 (6) | C9—H9 | 0.95 |
| C1—H1 | 0.95 | C10—C11 | 1.388 (6) |
| C2—C15 | 1.400 (6) | C10—H10 | 0.95 |
| C2—C3 | 1.407 (6) | C11—C12 | 1.391 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.391 (6) | C11—H11 | 0.95 |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.487 (5) |
| C4—H4 | 0.95 | C13—C14 | 1.483 (6) |
| C5—C14 | 1.410 (6) | C14—C15 | 1.387 (6) |
| C5—C6 | 1.494 (5) | C15—H15 | 0.95 |
| C6—C7 | 1.485 (5) | ||
| C3—O2—H2 | 120.0 | C9—C8—H8 | 120.1 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 122.8 (4) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.1 |
| O1—C1—H1 | 118.6 | C8—C9—C10 | 120.4 (4) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 118.6 | C8—C9—H9 | 119.8 |
| C15—C2—C3 | 119.7 (4) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.8 |
| C15—C2—C1 | 119.1 (4) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.0 (4) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.2 (4) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| O2—C3—C4 | 117.9 (4) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| O2—C3—C2 | 121.8 (4) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.2 (4) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.3 (4) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.2 (4) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.4 | C11—C12—C7 | 119.6 (4) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.4 | C11—C12—C13 | 119.4 (4) |
| C4—C5—C14 | 121.2 (4) | C7—C12—C13 | 121.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.4 (4) | O4—C13—C14 | 121.0 (4) |
| C14—C5—C6 | 120.3 (4) | O4—C13—C12 | 121.0 (4) |
| O3—C6—C7 | 121.3 (4) | C14—C13—C12 | 118.0 (3) |
| O3—C6—C5 | 120.5 (4) | C15—C14—C5 | 119.0 (4) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 118.1 (3) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.7 (4) |
| C8—C7—C12 | 120.1 (4) | C5—C14—C13 | 121.3 (4) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 118.9 (4) | C14—C15—C2 | 120.5 (4) |
| C12—C7—C6 | 121.0 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.7 (4) | C2—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| O1—C1—C2—C15 | 176.5 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −1.0 (6) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −2.1 (7) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 180.0 (4) |
| C15—C2—C3—O2 | 179.8 (4) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 1.0 (6) |
| C1—C2—C3—O2 | −1.7 (7) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | −177.2 (4) |
| C15—C2—C3—C4 | −0.7 (7) | C8—C7—C12—C13 | −180.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 177.9 (4) | C6—C7—C12—C13 | 1.8 (6) |
| O2—C3—C4—C5 | 179.3 (4) | C11—C12—C13—O4 | −1.5 (6) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.3 (7) | C7—C12—C13—O4 | 179.4 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C14 | 1.4 (6) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 179.2 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −176.7 (4) | C7—C12—C13—C14 | 0.2 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—O3 | 5.1 (6) | C4—C5—C14—C15 | −1.6 (6) |
| C14—C5—C6—O3 | −173.0 (4) | C6—C5—C14—C15 | 176.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −176.8 (4) | C4—C5—C14—C13 | 178.7 (4) |
| C14—C5—C6—C7 | 5.1 (6) | C6—C5—C14—C13 | −3.2 (6) |
| O3—C6—C7—C8 | −4.6 (6) | O4—C13—C14—C15 | 1.6 (6) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 177.4 (4) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −179.1 (4) |
| O3—C6—C7—C12 | 173.7 (4) | O4—C13—C14—C5 | −178.7 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C12 | −4.4 (6) | C12—C13—C14—C5 | 0.6 (6) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.5 (6) | C5—C14—C15—C2 | 0.7 (6) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 177.7 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C2 | −179.6 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.0 (7) | C3—C2—C15—C14 | 0.4 (6) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 (7) | C1—C2—C15—C14 | −178.1 (4) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.5 (7) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O1 | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.635 (5) | 132 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI2681).
References
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem.1, 189–191.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sittie, A. A., Lemnmich, E., Olsen, C. E., Hviid, L., Kharazmi, A., Nkrumah, F. K. & Christensen, S. B. (1999). Planta Med.65, 259–261. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Westrip, S. P. (2008). publCIF In preparation.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032224/ci2681sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808032224/ci2681Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report