Abstract
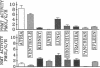
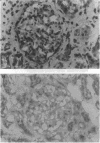
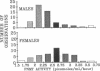
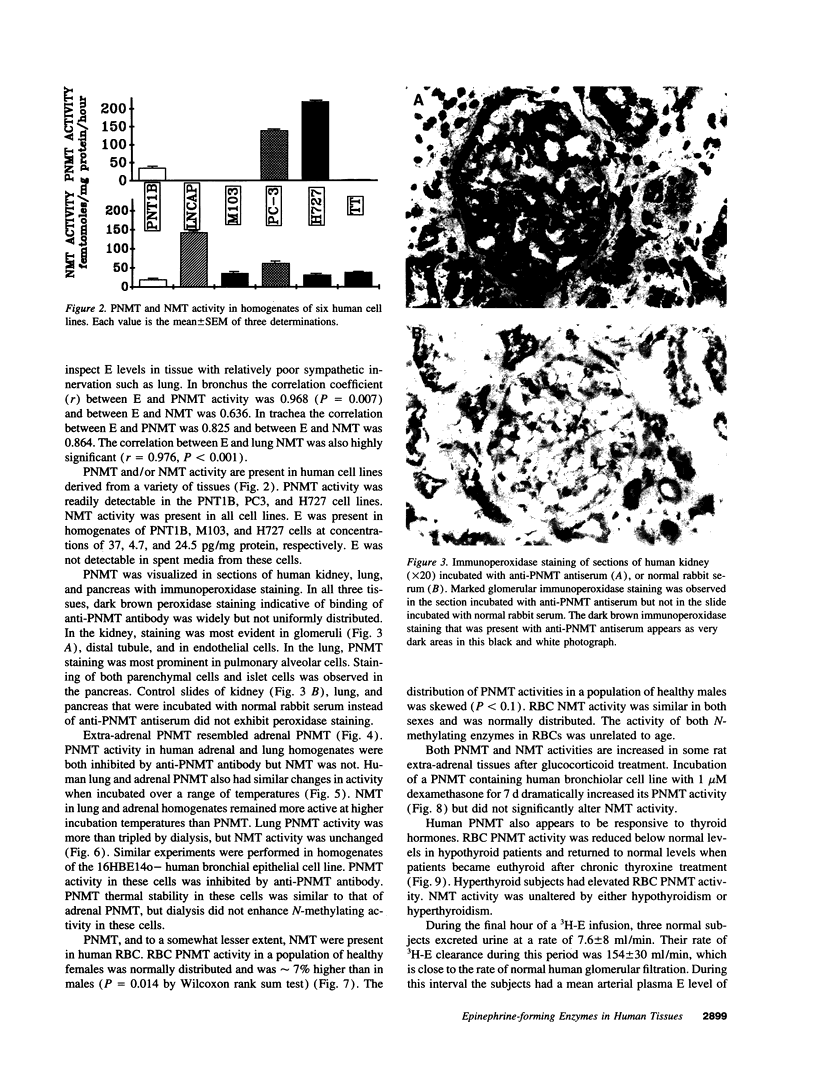
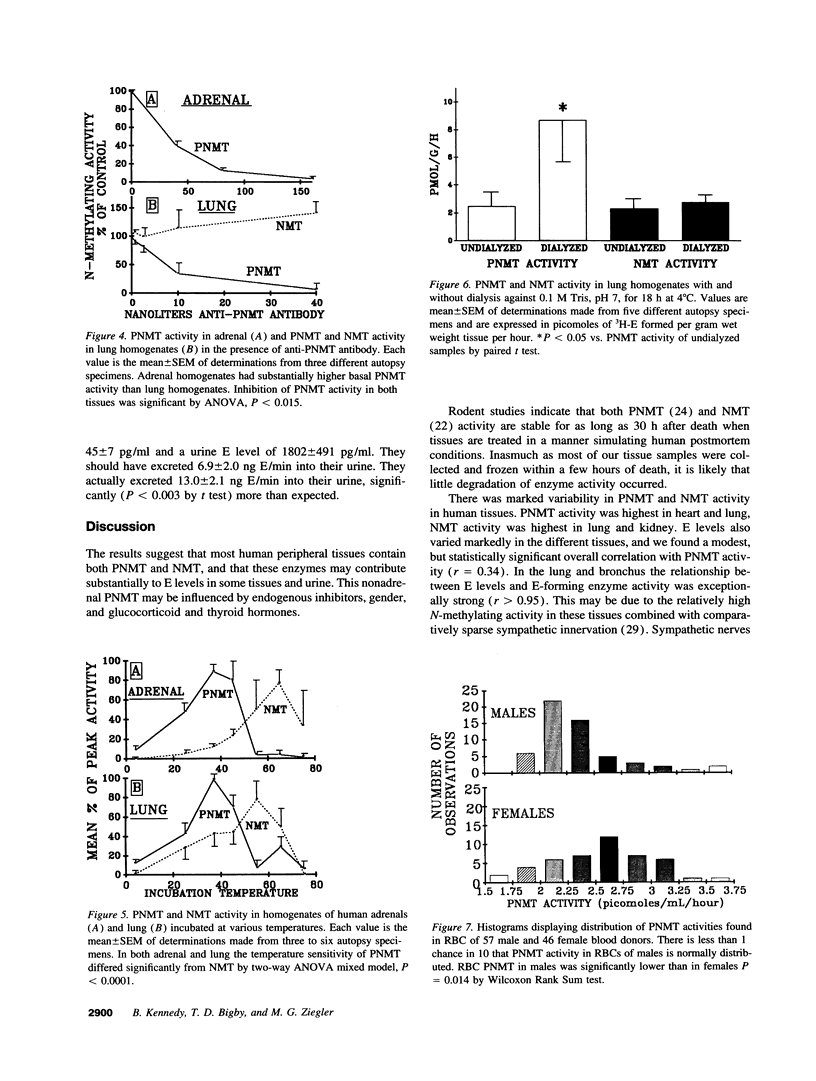
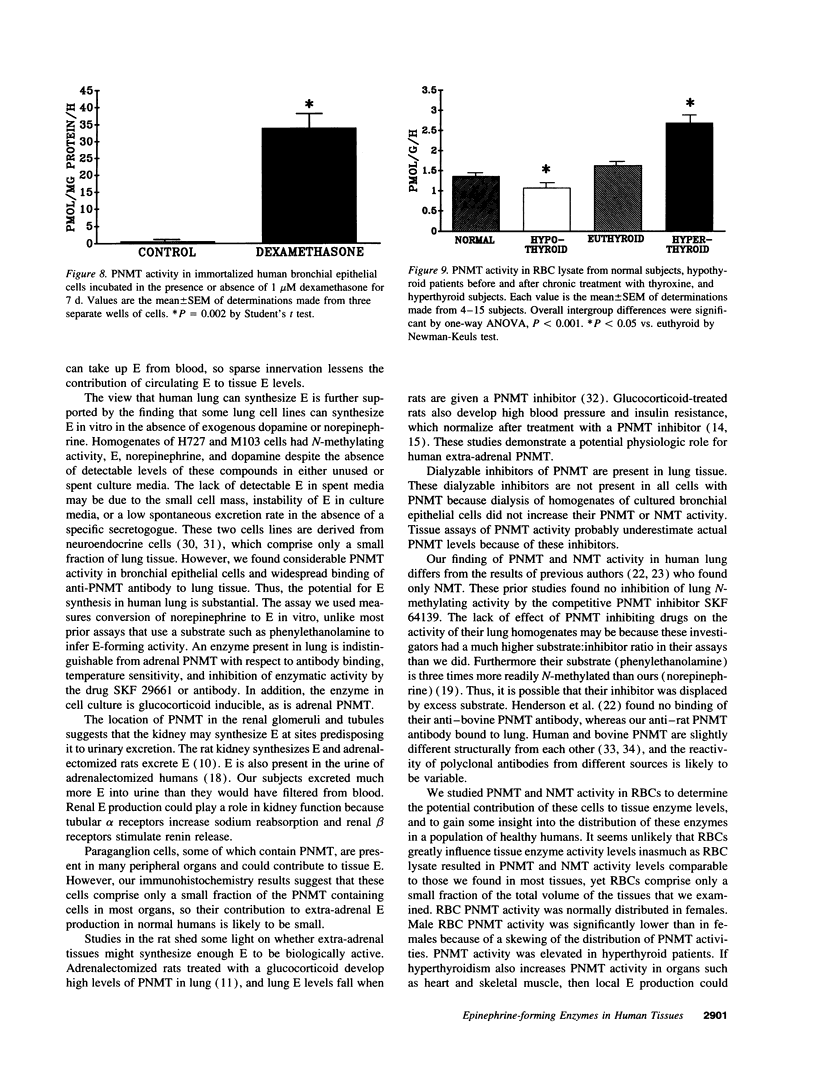
Animal studies indicate that nonadrenal tissues may synthesize epinephrine (E). Here we demonstrate phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) and/or nonspecific N-methyltransferase (NMT) enzymatic activity in human lung, kidney, heart, liver, spleen, and pancreas. There was a significant overall correlation (r = 0.34) between tissue PNMT and E. PNMT and NMT in human tissues differed in substrate and inhibitor specificity, thermal stability, and antigenicity. By these criteria, PNMT in human lung and in human bronchial epithelial cells were indistinguishable from adrenal PNMT. PNMT and/or NMT activity were present in red blood cells (RBCs), and cancer cell lines. Human kidney, lung, and pancreas showed immunohistochemical staining with an antibody to adrenal PNMT. RBC PNMT activity was lower in males than females and was increased in hyperthyroidism and decreased in hypothyroidism. PNMT activity in a human bronchial epithelial cell line was dramatically increased by incubation with dexamethasone. E and 3H-E levels in plasma and urine during an intravenous infusion of 3H-E into humans indicated that kidney may synthesize half of urinary E. We conclude that PNMT and NMT are widely distributed in human tissues, that they may synthesize E in vivo and are influenced by glucocorticoid and thyroid hormones.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD J. Purification and properties of phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1657–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELROD J. The enzymatic N-methylation of serotonin and other amines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Oct;138:28–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchas J. D., Ciaranello R. D., Steinman A. M. Epinephrine formation and metabolism in mammalian brain. Biol Psychiatry. 1969 Jan;1(1):31–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E. Plasma dose-response studies with noradrenaline and adrenaline in man. Prog Biochem Pharmacol. 1980;17:84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Eisenhofer G., Dart A., Chin J., Cox H., Lambert G., Jennings G. Adrenaline release by the human heart. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1991 Feb;18(2):67–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1991.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr N., Kownatzki E. Inhibition of rat kidney histamine-N-methyltransferase by biogenic amines. Pharmacology. 1986;32(2):114–120. doi: 10.1159/000138159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. D., Ruffin R. E., Alpers J. H., Crockett A. J., Schembri D. A., Latimer K. M. Biochemical studies of N-methyltransferase in human and guinea-pig lung: no apparent role in the pathogenesis of asthma. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Jul;75(1):5–11. doi: 10.1042/cs0750005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobel C. J., Parvez H., Parvez S., Lirette M., Papiernik E. Enzymes for epinephrine synthesis and metabolism in the myometrium, endometrium, red blood cells, and plasma of pregnant human subjects. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Dec 15;141(8):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32692-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda N., Ichinose H., Kobayashi K., Oka K., Kishi F., Nakazawa A., Kurosawa Y., Fujita K., Nagatsu T. Molecular cloning of cDNA and chromosomal assignment of the gene for human phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, the enzyme for epinephrine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7672–7677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B., Elayan H., Ziegler M. G. Glucocorticoid elevation of mRNA encoding epinephrine-forming enzyme in lung. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):L117–L120. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.265.2.L117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B., Elayan H., Ziegler M. G. Glucocorticoid hypertension and nonadrenal phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. Hypertension. 1993 Apr;21(4):415–419. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.21.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B., Elayan H., Ziegler M. G. Glucocorticoid induction of epinephrine synthesizing enzyme in rat skeletal muscle and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):303–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI116567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B., Elayan H., Ziegler M. G. Lung epinephrine synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):L227–L231. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.4.L227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B., Ziegler M. G. A more sensitive and specific radioenzymatic assay for catecholamines. Life Sci. 1990;47(23):2143–2153. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90314-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B., Ziegler M. G. Cardiac epinephrine synthesis. Regulation by a glucocorticoid. Circulation. 1991 Aug;84(2):891–895. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.2.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeill R. S., Ingram C. G. Effect of propranolol on ventilatory function. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Sep;18(3):473–475. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F., Teale C., Pearson S. B., Marshall P., Dwyer N. M., Jones S., Dean H. G. Adrenaline and nocturnal asthma. BMJ. 1990 Sep 8;301(6750):473–476. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6750.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S. S., Burton D. W., Deftos L. J. The coregulation of secretion and cytoplasmic ribonucleic acid of chromogranin-A and calcitonin by phorbol ester in cells that produce both substances. Endocrinology. 1988 Feb;122(2):495–499. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-2-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu T. Genes for human catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes. Neurosci Res. 1991 Oct;12(2):315–345. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(91)90001-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne N. N., Nesselhut T. Adrenaline: occurrence in the bovine retina. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Aug 19;39(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendleton R. G., Gessner G., Sawyer J. Studies on lung N-methyltransferases, a pharmacological approach. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;313(3):263–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00505743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendleton R. G., Gessner G., Weiner G., Jenkins B., Sawyer J., Bondinell W., Intoccia A. Studies on SK&F 29661, an organ-specific inhibitor of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jan;208(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J., Béland J. Nonadrenergic inhibitory nervous system in human airways. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Nov;41(5 Pt 1):764–771. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.5.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb O. J., Webster J., Petrie J. C., Harry J. D., Young J. Effects of the beta 2-adrenoceptor antagonist ICI 118,551 on blood pressure in hypertensive patients known to respond to beta 1-adrenoceptor antagonists. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;25(4):433–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüller H. M., Orloff M., Reznik G. K. Antiproliferative effects of the Ca2+/calmodulin antagonist B859-35 and the Ca(2+)-channel blocker verapamil on human lung cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Dec;12(12):2301–2303. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.12.2301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. D., Tse T. F., Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E. The human sympathochromaffin system. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):E380–E384. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.3.E380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhees L., Aubert A., Fagard R., Hespel P., Amery A. Influence of beta 1- versus beta 2-adrenoceptor blockade on left ventricular function in humans. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):1086–1091. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198609000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W. H., Lewis L. E., Boehme D. H. Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase activity in various areas of human brain, tissues and fluids. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 15;115(2):357–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler M. G., Kennedy B., Elayan H. A sensitive radioenzymatic assay for epinephrine forming enzymes. Life Sci. 1988;43(25):2117–2122. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90361-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler M. G., Kennedy B., Elayan H. Extraadrenal adrenaline formation by two separate enzymes. Experientia. 1989 Aug 15;45(8):718–720. doi: 10.1007/BF01974566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler M. G., Kennedy B., Elayan H. Rat renal epinephrine synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1130–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI114276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von EULER U., IKKOS D., LUFT R. Adrenaline excretion during resting conditions and after insulin in adrenalectomized human subjects. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1961 Nov;38:441–448. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0380441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]