Abstract
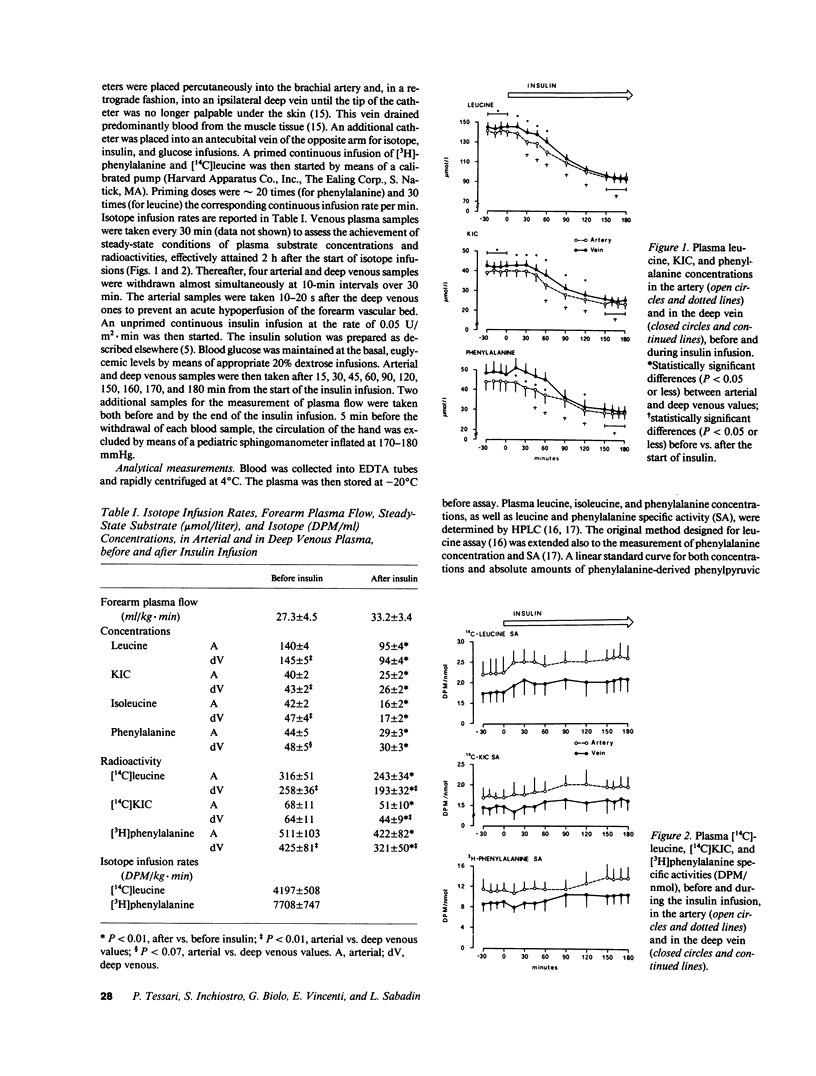
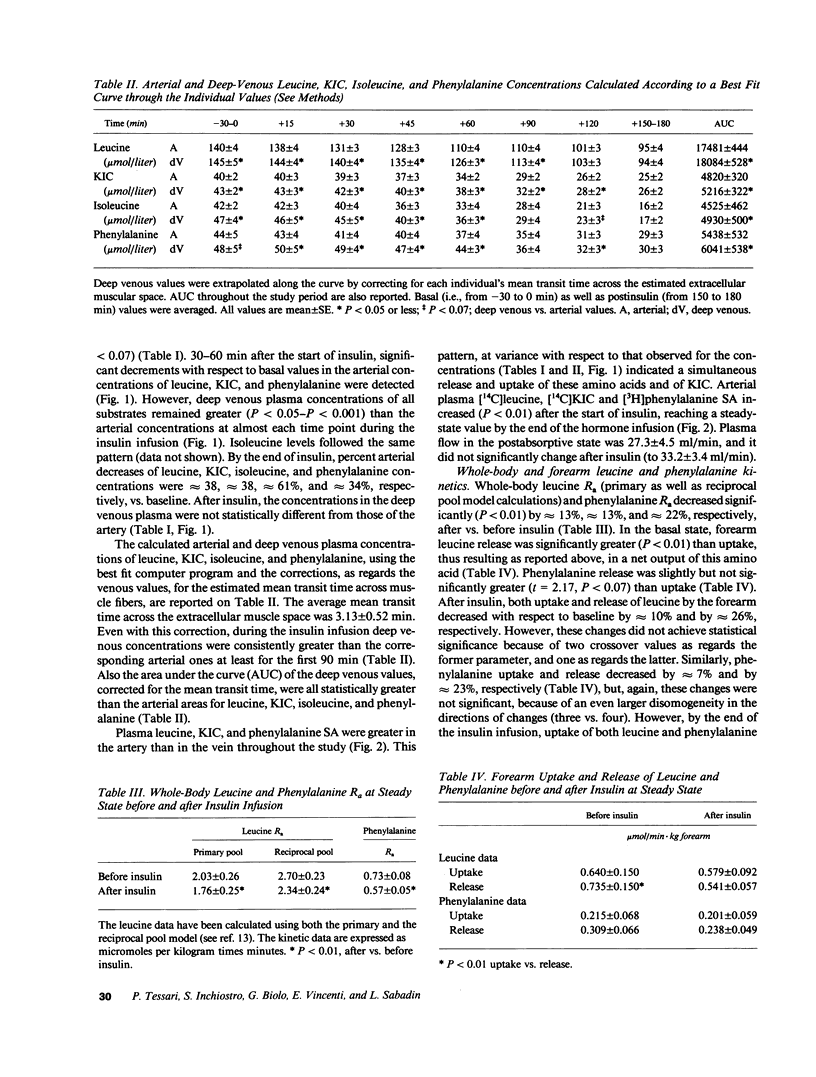
To investigate the mechanism(s) of insulin-induced suppression of plasma amino acid concentration and release, we studied forearm as well as whole-body leucine and phenylalanine uptake and release during a peripheral insulin infusion in postabsorptive normal subjects using isotope-dilution methods. Before insulin, leucine and phenylalanine release exceeded uptake (P less than 0.01 and P less than 0.07, respectively). A net output of alpha-ketoisocaproate (KIC) was also observed. During insulin, arterial plasma leucine, KIC and phenylalanine concentrations decreased (P less than 0.05 or less vs. basal), despite ongoing net output of these substrates by the forearm, that persisted after correction for the mean transit time spent through the extracellular muscular space. By the end of insulin, whole-body leucine and phenylalanine concentrations and rate of appearance were decreased (P less than 0.01 vs. basal). However, release and uptake of both amino acids by the forearm were not significantly decreased vs. the preinsulin values. These data indicate that systemic hyperinsulinemia acutely decreases plasma amino acid concentrations by acting primarily at sites other than skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRES R., ZIERLER K. L., ANDERSON H. M., STAINSBY W. N., CADER G., GHRAYYIB A. S., LILIENTHAL J. L., Jr Measurement of blood flow and volume in the forearm of man; with notes on the theory of indicator-dilution and on production of turbulence, hemolysis, and vasodilatation by intra-vascular injection. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):482–504. doi: 10.1172/JCI102919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abumrad N. N., Jefferson L. S., Rannels S. R., Williams P. E., Cherrington A. D., Lacy W. W. Role of insulin in the regulation of leucine kinetics in the conscious dog. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1031–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI110690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. J., Revkin J. H., Young L. H., Zaret B. L., Jacob R., Gelfand R. A. An isotopic method for measurement of muscle protein synthesis and degradation in vivo. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):223–228. doi: 10.1042/bj2450223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier D. M. Intrinsically difficult problems: the kinetics of body proteins and amino acids in man. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1989 Mar;5(2):111–132. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER K. E., EDHOLM O. G., MOTTRAM R. F. The blood flow in skin and muscle of the human forearm. J Physiol. 1955 May 27;128(2):258–267. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldo B., Santoro D., Riccardi G., Perrotti N., Saccà L. Direct evidence for a stimulatory effect of hyperglycemia per se on peripheral glucose disposal in type II diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1285–1290. doi: 10.1172/JCI112432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino P., Luzi L., Simonson D. C., Haymond M., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of insulin and plasma amino acid concentrations on leucine metabolism in man. Role of substrate availability on estimates of whole body protein synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1784–1793. doi: 10.1172/JCI113272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Interorgan amino acid nutrition. Physiol Rev. 1982 Oct;62(4 Pt 1):1193–1233. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.4.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobelli C., Saccomani M. P., Ferrannini E., Defronzo R. A., Gelfand R., Bonadonna R. A compartmental model to quantitate in vivo glucose transport in the human forearm. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):E943–E958. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.6.E943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa N. K., Minaker K. L., Rowe J. W., Goodman M. N., Matthews D. E., Bier D. M., Young V. R. Insulin-mediated reduction of whole body protein breakdown. Dose-response effects on leucine metabolism in postabsorptive men. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2306–2311. doi: 10.1172/JCI112240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand R. A., Barrett E. J. Effect of physiologic hyperinsulinemia on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI113033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand R. A., Glickman M. G., Castellino P., Louard R. J., DeFronzo R. A. Measurement of L-[1-14C]leucine kinetics in splanchnic and leg tissues in humans. Effect of amino acid infusion. Diabetes. 1988 Oct;37(10):1365–1372. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.10.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Borghetti A. F., Gazzola G. C. The regulation of amino acid transport in animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 15;515(4):329–366. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani H., Williams P., Morris J. A., May M. E., Abumrad N. N. Effect of insulin-induced hypoglycemia on protein metabolism in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):E342–E350. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.3.E342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. E., Schwarz H. P., Yang R. D., Motil K. J., Young V. R., Bier D. M. Relationship of plasma leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproate during a L-[1-13C]leucine infusion in man: a method for measuring human intracellular leucine tracer enrichment. Metabolism. 1982 Nov;31(11):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90160-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair K. S., Welle S. L., Halliday D., Campbell R. G. Effect of beta-hydroxybutyrate on whole-body leucine kinetics and fractional mixed skeletal muscle protein synthesis in humans. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):198–205. doi: 10.1172/JCI113570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen S. L., Van Huysen C., Haymond M. W. Measurement of branched chain amino acids and branched chain alpha-ketoacids in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 Oct 8;232(1):170–175. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)86021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacy P. J., Nair K. S., Ford C., Halliday D. Failure of insulin infusion to stimulate fractional muscle protein synthesis in type I diabetic patients. Anabolic effect of insulin and decreased proteolysis. Diabetes. 1989 May;38(5):618–624. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.5.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J. J., Beaufrere B., Koziet J., Desjeux J. F., Bier D. M., Young V. R., Lestradet H. Whole body de novo amino acid synthesis in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes studied with stable isotope-labeled leucine, alanine, and glycine. Diabetes. 1985 Jan;34(1):67–73. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk W. F., Beaufrere B., Haymond M. W. Use of reciprocal pool specific activities to model leucine metabolism in humans. Am J Physiol. 1985 Dec;249(6 Pt 1):E646–E650. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.6.E646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu S., Inoue K., Tani Y., Yamada H. Enzymatic microdetermination of serum free fatty acids. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick F. L., Harper A. E. Branched-chain amino acid oxidation by isolated rat tissue preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Inchiostro S., Biolo G., Trevisan R., Fantin G., Marescotti M. C., Iori E., Tiengo A., Crepaldi G. Differential effects of hyperinsulinemia and hyperaminoacidemia on leucine-carbon metabolism in vivo. Evidence for distinct mechanisms in regulation of net amino acid deposition. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1062–1069. doi: 10.1172/JCI112919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Nissen S. L., Miles J. M., Haymond M. W. Inverse relationship of leucine flux and oxidation to free fatty acid availability in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):575–581. doi: 10.1172/JCI112339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Trevisan R., Inchiostro S., Biolo G., Nosadini R., De Kreutzenberg S. V., Duner E., Tiengo A., Crepaldi G. Dose-response curves of effects of insulin on leucine kinetics in humans. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):E334–E342. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.3.E334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevisan R., Nosadini R., Avogaro A., Lippe G., Duner E., Fioretto P., Deana R., Tessari P., Tiengo A., Velussi M. Type I diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance not only with regard to glucose, but also to lipid and amino acid metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jun;62(6):1155–1162. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-6-1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umpleby A. M., Boroujerdi M. A., Brown P. M., Carson E. R., Sönksen P. H. The effect of metabolic control on leucine metabolism in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1986 Mar;29(3):131–141. doi: 10.1007/BF02427082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umpleby A. M., Sönksen P. H. Measurement of the turnover of substrates of carbohydrate and protein metabolism using radioactive isotopes. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Nov;1(4):773–796. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(87)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicklmayr M., Rett K., Schwiegelshohn B., Wolfram G., Hailer S., Dietze G. Inhibition of muscular amino acid release by lipid infusion in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;17(4):301–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1987.tb02191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


