Abstract
Induction of HLA class I antigens on cultured melanoma cells FO-1 after transfection with a human or a mouse B2m gene was associated with a statistically significant reduction in their susceptibility to natural killer (NK) cell-mediated lysis. These results indicate that the structural differences between human and mouse beta 2-mu do not abolish the ability of the HLA class I molecular complex to modulate NK cell-mediated lysis of melanoma cells FO-1. The role of HLA class I antigens in the phenomenon is corroborated by the ability of anti-HLA class I MAb to enhance, although to a different extent, the susceptibility of transfected FO-1 cells to NK cell-mediated lysis. Gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) significantly reduced the susceptibility to NK cell-mediated lysis of transfected FO-1 cells. Surprisingly, TNF-alpha reduced the extent of lysis more than IFN-gamma, although the latter cytokine enhanced HLA class I antigen expression more than the former one. This finding, in conjunction with a reduction in the susceptibility to NK cell-mediated lysis of untransfected FO-1 cells incubated with IFN-gamma or TNF-alpha, suggests that the two cytokines reduce NK cell-mediated lysis of transfected cells by modulating not only the expression of HLA class I antigens, but also that of other structures. Induction of HLA class I antigens and their modulation with IFN-gamma did not affect the susceptibility to lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell-mediated lysis of transfected FO-1 cells. Characterization of the molecular mechanism(s) underlying abnormalities in HLA class I antigen expression by melanoma cells and of the role of these molecules in the interactions of melanoma cells with various types of effector cells may suggest novel immunotherapeutic approaches to melanoma.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Algarra I., Ohlén C., Perez M., Ljunggren H. G., Klein G., Garrido F., Kärre K. NK sensitivity and lung clearance of MHC-class-I-deficient cells within a heterogeneous fibrosarcoma. Int J Cancer. 1989 Oct 15;44(4):675–680. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlow D. A., Payne U., Hozumi N., Roder J. C., Czitrom A. A. Class I (H-2Kb) gene transfection reduces susceptibility of YAC-1 lymphoma targets to natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):841–846. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
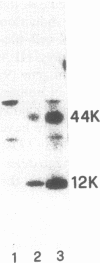
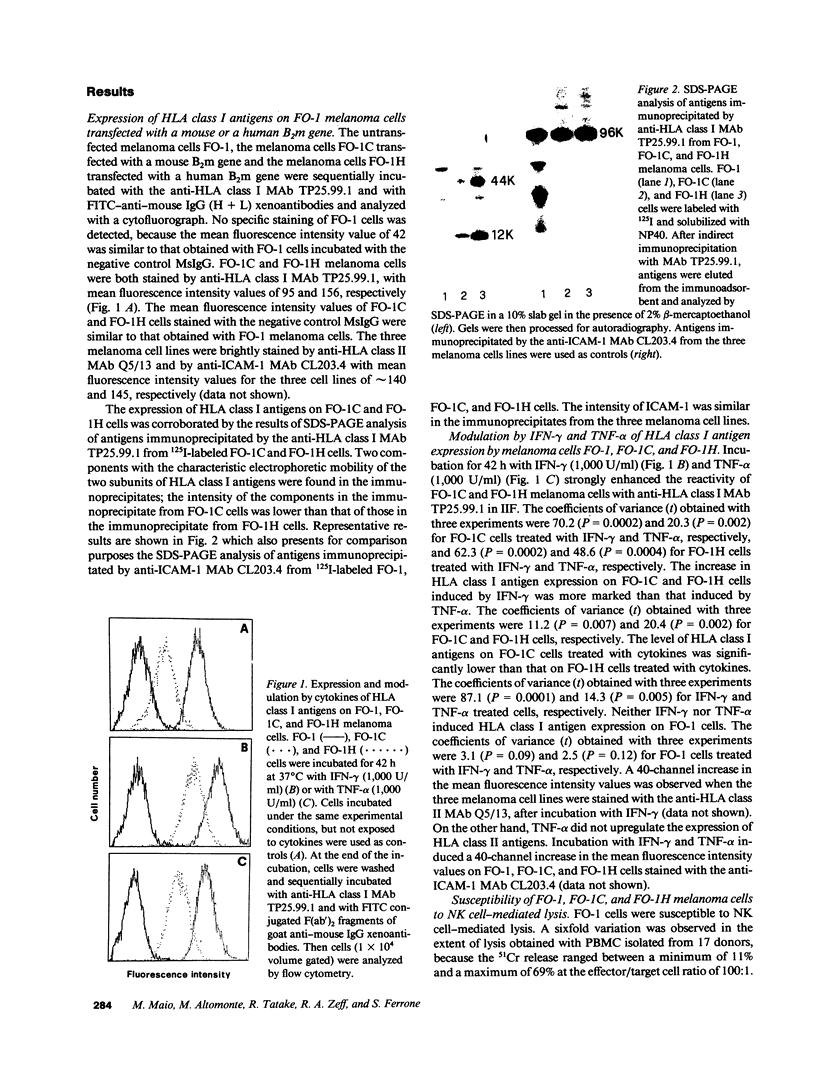
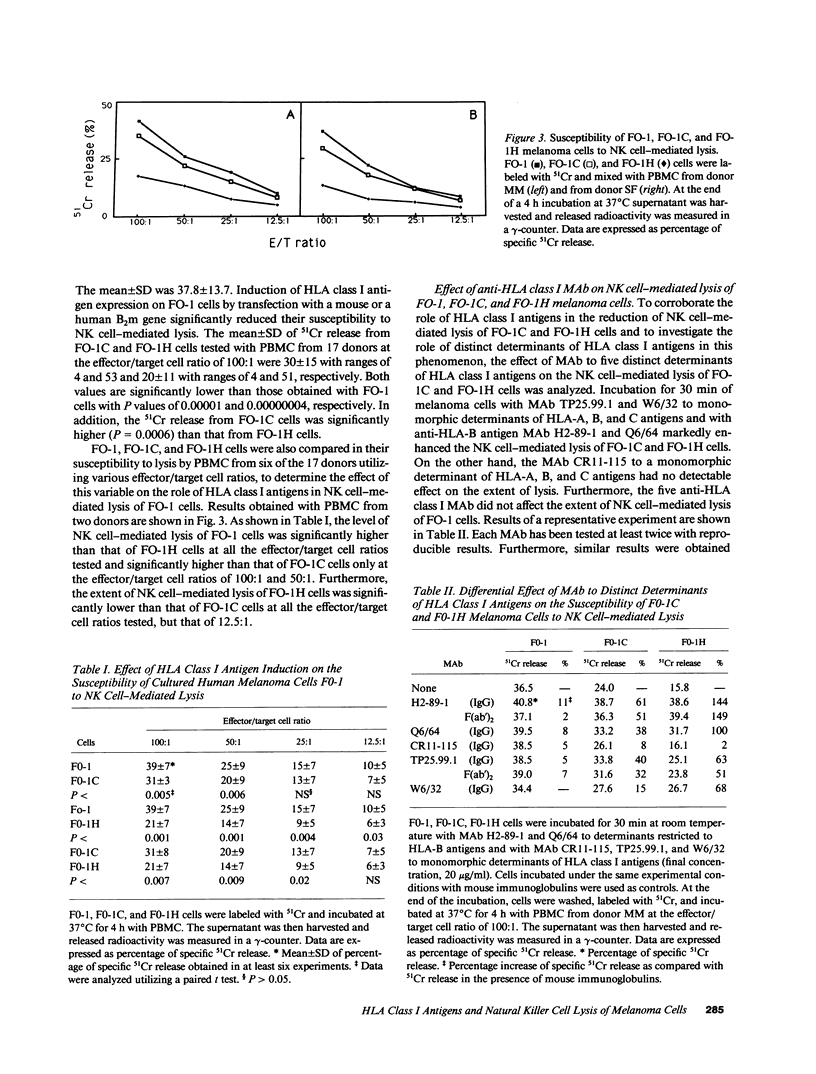
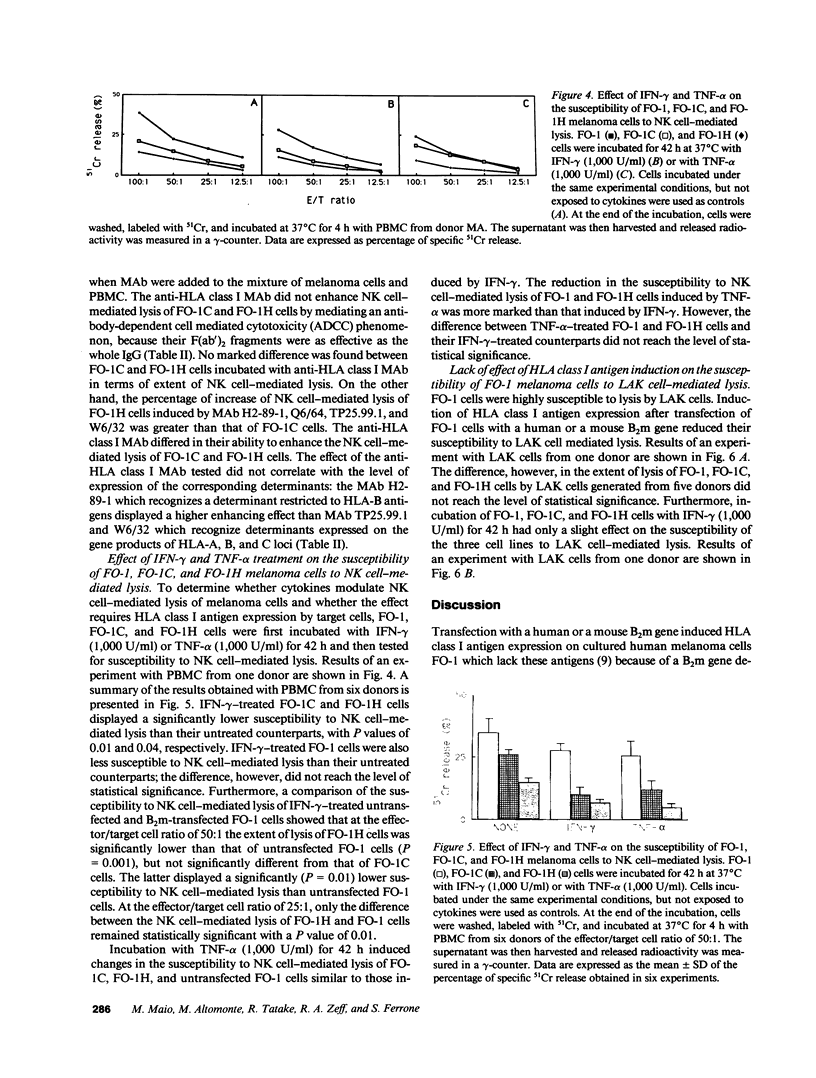
- D'Urso C. M., Wang Z. G., Cao Y., Tatake R., Zeff R. A., Ferrone S. Lack of HLA class I antigen expression by cultured melanoma cells FO-1 due to a defect in B2m gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):284–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI114984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Layet C., Caillol D. H., Jordan B. R., Lemonnier F. A. The association between murine beta 2-microglobulin and HLA class I heavy chains results in serologically detectable conformational changes of both chains. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1281–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorelik E., Gunji Y., Herberman R. B. H-2 antigen expression and sensitivity of BL6 melanoma cells to natural killer cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2096–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönberg A., Ferm M. T., Ng J., Reynolds C. W., Ortaldo J. R. IFN-gamma treatment of K562 cells inhibits natural killer cell triggering and decreases the susceptibility to lysis by cytoplasmic granules from large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4397–4402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönberg A., Kiessling R., Fiers W. Interferon-gamma is a strong modulator of NK susceptibility and expression of beta 2-microglobulin but not of transferrin receptors of K562 cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Oct 1;95(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarini L., Temponi M., Edwalds G. M., Vita J. R., Fisher P. B., Ferrone S. In vitro differentiation and antigenic changes in human melanoma cell lines. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1989;30(5):262–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01744892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güssow D., Rein R., Ginjaar I., Hochstenbach F., Seemann G., Kottman A., Ploegh H. L. The human beta 2-microglobulin gene. Primary structure and definition of the transcriptional unit. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3132–3138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Quillet A., Marchiol C., DeMars R., Tursz T., Fradelizi D. Natural killer susceptibility of human cells may be regulated by genes in the HLA region on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabrane-Ferrat N., Calvo F., Faille A., Lagabrielle J. F., Boisson N., Quillet A., Fradelizi D. Recombinant gamma interferon provokes resistance of human breast cancer cells to spontaneous and IL-2 activated non-MHC restricted cytotoxicity. Br J Cancer. 1990 Apr;61(4):558–562. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar D., Hämmerling G. J. Induction of assembly of MHC class I heavy chains with beta 2microglobulin by interferon-gamma. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):475–481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03400.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Karpinski B. A., Gottschalk L., Kornbluth J. Susceptibility to natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis is independent of the level of target cell class I HLA expression. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2140–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K. In search of the 'missing self': MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90097-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Sturmhöfel K., Wolpert E., Hämmerling G. J., Kärre K. Transfection of beta 2-microglobulin restores IFN-mediated protection from natural killer cell lysis in YAC-1 lymphoma variants. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Spencer C. E. Use of anti-HLA antibodies to mask major histocompatibility complex gene products on tumor cells can enhance susceptibility of these cells to lysis by natural killer cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):278–287. doi: 10.1172/JCI113870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main E. K., Monos D. S., Lampson L. A. IFN-treated neuroblastoma cell lines remain resistant to T cell-mediated allo-killing, and susceptible to non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):2943–2950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio M., Gulwani B., Langer J. A., Kerbel R. S., Duigou G. J., Fisher P. B., Ferrone S. Modulation by interferons of HLA antigen, high-molecular-weight melanoma associated antigen, and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression by cultured melanoma cells with different metastatic potential. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2980–2987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Temponi M., Ferrone S. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody-defined human melanoma-associated antigen susceptible to induction by immune interferon. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2088–2095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maziarz R. T., Mentzer S. J., Burakoff S. J., Faller D. V. Distinct effects of interferon-gamma and MHC class I surface antigen levels on resistance of the K562 tumor cell line to natural killer-mediated lysis. Cell Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;130(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90276-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J. HLA restriction of human cytotoxic T cells. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 May;3(1):3–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00199923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlén C., Bejarano M. T., Grönberg A., Torsteinsdottir S., Franksson L., Ljunggren H. G., Klein E., Klein G., Kärre K. Studies of sublines selected for loss of HLA expression from an EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell line. Changes in sensitivity to cytotoxic T cells activated by allostimulation and natural killer cells activated by IFN or IL-2. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3336–3341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ng A. K., Russo C., Ferrone S. Heterogeneous distribution of the determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies on HLA-A and B antigens bearing molecules. Transplantation. 1982 Jul;34(1):18–23. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198207000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perarnau B. M., Gillet A. C., Hakem R., Barad M., Lemonnier F. A. Human beta 2-microglobulin specifically enhances cell-surface expression of HLA class I molecules in transfected murine cells. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1383–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña J., Alonso C., Solana R., Serrano R., Carracedo J., Ramirez R. Natural killer susceptibility is independent of HLA class I antigen expression on cell lines obtained from human solid tumors. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Nov;20(11):2445–2448. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta V., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. The monoclonal xenoantibody Q6/64 recognizes a determinant expressed by certain gene products of the A and B loci of the HLA region. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(5):403–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00373320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta V., Walker L. E., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Purification of immunologically functional subsets of human Ia-like antigens on a monoclonal antibody (Q5/13) immunoadsorbent. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1421–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quillet A., Presse F., Marchiol-Fournigault C., Harel-Bellan A., Benbunan M., Ploegh H., Fradelizi D. Increased resistance to non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity related to HLA A, B expression. Direct demonstration using beta 2-microglobulin-transfected Daudi cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein R. S., Seemann G. H., Neefjes J. J., Hochstenbach F. M., Stam N. J., Ploegh H. L. Association with beta 2-microglobulin controls the expression of transfected human class I genes. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1178–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., DeMars R. Demonstration by class I gene transfer that reduced susceptibility of human cells to natural killer cell-mediated lysis is inversely correlated with HLA class I antigen expression. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Mar;19(3):447–451. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam N. J., Kast W. M., Voordouw A. C., Pastoors L. B., van der Hoeven F. A., Melief C. J., Ploegh H. L. Lack of correlation between levels of MHC class I antigen and susceptibility to lysis of small cellular lung carcinoma (SCLC) by natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4113–4117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Alexander J., Payne J. A., Cresswell P., Dawson J. R. The alpha 1/alpha 2 domains of class I HLA molecules confer resistance to natural killing. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3853–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Alexander J., Payne J. A., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. Reversal of natural killing susceptibility in target cells expressing transfected class I HLA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2361–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Howell D. N., Salter R. D., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. NK susceptibility varies inversely with target cell class I HLA antigen expression. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1657–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturmhöfel K., Hämmerling G. J. Reconstitution of H-2 class I expression by gene transfection decreases susceptibility to natural killer cells of an EL4 class I loss variant. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):171–177. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temponi M., Kageshita T., Perosa F., Ono R., Okada H., Ferrone S. Purification of murine IgG monoclonal antibodies by precipitation with caprylic acid: comparison with other methods of purification. Hybridoma. 1989 Feb;8(1):85–95. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temponi M., Romano G., D'Urso C. M., Wang Z., Kekish U., Ferrone S. Profile of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) synthesized by human melanoma cell lines. Semin Oncol. 1988 Dec;15(6):595–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L., Ohlén C., Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K., Hansson M., Kiessling R. Effect of IFN-gamma treatment and in vivo passage of murine tumor cell lines on their sensitivity to lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell lysis in vitro; association with H-2 expression on the target cells. Int J Cancer. 1989 Oct 15;44(4):669–674. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco M. C., De Felice M., Corbo L., Morrone G., Mertelsmann R., Ferrone S., Venuta S. Regulatory role of a monomorphic determinant of HLA Class I antigens in T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2268–2273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versteeg R., Peltenburg L. T., Plomp A. C., Schrier P. I. High expression of the c-myc oncogene renders melanoma cells prone to lysis by natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4331–4337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Indiveri F., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. DR (Ia-like) antigens on human melanoma cells. Serological detection and immunochemical characterization. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):658–668. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duinen S. G., Ruiter D. J., Broecker E. B., van der Velde E. A., Sorg C., Welvaart K., Ferrone S. Level of HLA antigens in locoregional metastases and clinical course of the disease in patients with melanoma. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):1019–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]