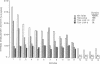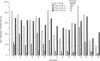Abstract
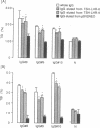
We examined the relative effects of thyrotropin (TSH) and TSH receptor autoantibodies in the sera of patients with autoimmune thyroid disease on three TSH-lutropin/chorionic gonadotropin (LH/CG) receptor extracellular domain chimeras. Each chimera binds TSH with high affinity. Only the chimera with TSH receptor extracellular domains ABC (amino acids 1-260) had a functional (cAMP) response to thyroid stimulatory IgG. The chimeras with TSH receptor domains CD (amino acids 171-360) and DE (amino acids 261-418) were unresponsive. The lack of response of the chimera with TSH receptor domains DE was anticipated because it fails to transduce a signal with TSH stimulation, unlike the other two chimeras. A different spectrum of responses occurred when the TSH-LH/CG chimeras were examined in terms of autoantibody competition for TSH binding. IgG with TSH binding-inhibitory activity when tested with the wild-type TSH receptor also inhibited TSH binding to the chimera with TSH receptor domains DE. Dramatically, however, these IgG did not inhibit TSH binding to the chimera with TSH receptor domains CD, and had weak or absent activity with the chimera with TSH receptor domains ABC. Chimeras with TSH receptor domains ABC and DE were equally effective in affinity-purifying IgG with thyroid-stimulatory and TSH binding-inhibitory activities. Nonstimulatory IgG with TSH binding-inhibitory activity inhibited the action of stimulatory IgG on the wild-type TSH receptor, but not with the chimera containing TSH receptor domains ABC. In summary, TSH receptor autoantibodies and TSH bind to regions in both domains ABC and DE of the TSH receptor extracellular region. Stimulatory and inhibitory TSH receptor autoantibodies, as well as TSH, appear to bind to different sites in domains ABC, but similar sites in domains DE, of the receptor. Alternatively, TSH and the different TSH receptor antibodies bind with differing affinities to the same site in the ABC region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amino N., Watanabe Y., Tamaki H., Iwatani Y., Miyai K. In-vitro conversion of blocking type anti-TSH receptor antibody to the stimulating type by anti-human IgG antibodies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1987 Nov;27(5):615–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1987.tb01192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Padlan E. A., Sheriff S. Antibody-antigen complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:439–473. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruin T. W., Braverman L. E., Brown R. S. Heterogeneity of TSH receptor-binding antibodies in Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease. Am J Med Sci. 1990 May;299(5):291–297. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199005000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealey P. A., Kohn L. D., Ekins R. P., Marshall N. J. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies derived from lymphocytes from Graves' disease patients in a cytochemical bioassay for thyroid stimulators. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 May;58(5):909–914. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-5-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filetti S., Foti D., Costante G., Rapoport B. Recombinant human thyrotropin (TSH) receptor in a radioreceptor assay for the measurement of TSH receptor autoantibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 May;72(5):1096–1101. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-5-1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier A. L., Robbins L. S., Stork P. J., Sprengel R., Segaloff D. L., Cone R. D. Isolation of TSH and LH/CG receptor cDNAs from human thyroid: regulation by tissue specific splicing. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1264–1276. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyma P., Harrison L. C. Precipitation of the thyrotropin receptor and identification of thyroid autoantigens using Graves' disease immunoglobulins. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):1090–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI111476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds W. E., Takai N., Rapoport B., Filetti S., Clark O. H. Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin bioassay using cultured human thyroid cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jun;52(6):1204–1210. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-6-1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasagi K., Konishi J., Arai K., Misaki T., Iida Y., Endo K., Torizuka K. A sensitive and practical assay for thyroid-stimulating antibodies using crude immunoglobulin fractions precipitated with polyethylene glycol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 May;62(5):855–862. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-5-855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Smith-Gill S. J. Epitopes on protein antigens: misconceptions and realities. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90464-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Lefort A., Gerard C., Parmentier M., Perret J., Ludgate M., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Cloning, sequencing and expression of the human thyrotropin (TSH) receptor: evidence for binding of autoantibodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1250–1255. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92736-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosfelt H., Misrahi M., Atger M., Salesse R., Vu Hai-Luu Thi M. T., Jolivet A., Guiochon-Mantel A., Sar S., Jallal B., Garnier J. Cloning and sequencing of porcine LH-hCG receptor cDNA: variants lacking transmembrane domain. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.2502844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland K. C., Sprengel R., Phillips H. S., Köhler M., Rosemblit N., Nikolics K., Segaloff D. L., Seeburg P. H. Lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor: an unusual member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):494–499. doi: 10.1126/science.2502842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misrahi M., Loosfelt H., Atger M., Sar S., Guiochon-Mantel A., Milgrom E. Cloning, sequencing and expression of human TSH receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):394–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91958-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita S., Izumi M., Nagataki S. Interactions between TSH binding inhibiting--and adenylate cyclase stimulating--antibodies in Graves' disease. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1986 Aug;112(4):517–522. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1120517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Mori M. Identification of immunogenic regions in human thyrotropin receptor for immunoglobulin G of patients with Graves' disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):512–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91423-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama Y., Kaufman K. D., Seto P., Rapoport B. Molecular cloning, sequence and functional expression of the cDNA for the human thyrotropin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1184–1190. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92727-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama Y., Russo D., Chazenbalk G. D., Wadsworth H. L., Rapoport B. Extracellular domain chimeras of the TSH and LH/CG receptors reveal the mid-region (amino acids 171-260) to play a vital role in high affinity TSH binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1150–1156. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80906-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama Y., Wadsworth H. L., Chazenbalk G. D., Russo D., Seto P., Rapoport B. Thyrotropin-luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor extracellular domain chimeras as probes for thyrotropin receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):902–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piraphatdist T., Sugawa H., Inoue D., Enomoto T., Mori T., Imura H. Possible binding site of thyrotropin binding inhibitor immunoglobulin (TBII) on the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor, which is different from TSH binding site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 30;172(2):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90705-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport B., Filetti S., Takai N., Seto P., Halverson G. Studies on the cyclic AMP response to thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) and thyrotropin (TSH) in human thyroid cell monolayers. Metabolism. 1982 Nov;31(11):1159–1167. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees Smith B., McLachlan S. M., Furmaniak J. Autoantibodies to the thyrotropin receptor. Endocr Rev. 1988 Feb;9(1):106–121. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-1-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewring G., Smith B. R. An improved radioreceptor assay for TSH receptor antibodies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1982 Oct;17(4):409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1982.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Hall R. Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins in Graves' disease. Lancet. 1974 Aug 24;2(7878):427–431. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91815-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Braun T., Nikolics K., Segaloff D. L., Seeburg P. H. The testicular receptor for follicle stimulating hormone: structure and functional expression of cloned cDNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):525–530. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valente W. A., Vitti P., Yavin Z., Yavin E., Rotella C. M., Grollman E. F., Toccafondi R. S., Kohn L. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the thyrotropin receptor: stimulating and blocking antibodies derived from the lymphocytes of patients with Graves disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6680–6684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth H. L., Chazenbalk G. D., Nagayama Y., Russo D., Rapoport B. An insertion in the human thyrotropin receptor critical for high affinity hormone binding. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1423–1425. doi: 10.1126/science.2169649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama N., Izumi M., Katamine S., Nagataki S. Heterogeneity of Graves' immunoglobulin G: comparison of thyrotropin receptor antibodies in serum and in culture supernatants of lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Feb;64(2):215–218. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarija M., Garcia A., McKenzie J. M. Studies on multiple thyroid cell membrane-directed antibodies in Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1885–1891. doi: 10.1172/JCI112183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarija M., McKenzie J. M., Eidson M. S. Transient neonatal hypothyroidism: characterization of maternal antibodies to the thyrotropin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 May;70(5):1239–1246. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-5-1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarija M., McKenzie J. M., Munro D. S. Immunoglobulin G inhibitor of thyroid-stimulating antibody is a cause of delay in the onset of neonatal Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1352–1356. doi: 10.1172/JCI111091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin T. W., van der Heide D. Anti-thyrotrophin receptor antibodies in Graves' disease as demonstrated directly by immunoprecipitation assay. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Jan;102(1):49–56. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin T. W., van der Heide D., Querido A., Krol M. C. Direct and quantitative measurement by immunoprecipitation assay of anti-thyrotrophin receptor antibodies in sera of patients with Graves' disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1984 Feb;20(2):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1984.tb00069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]