Abstract
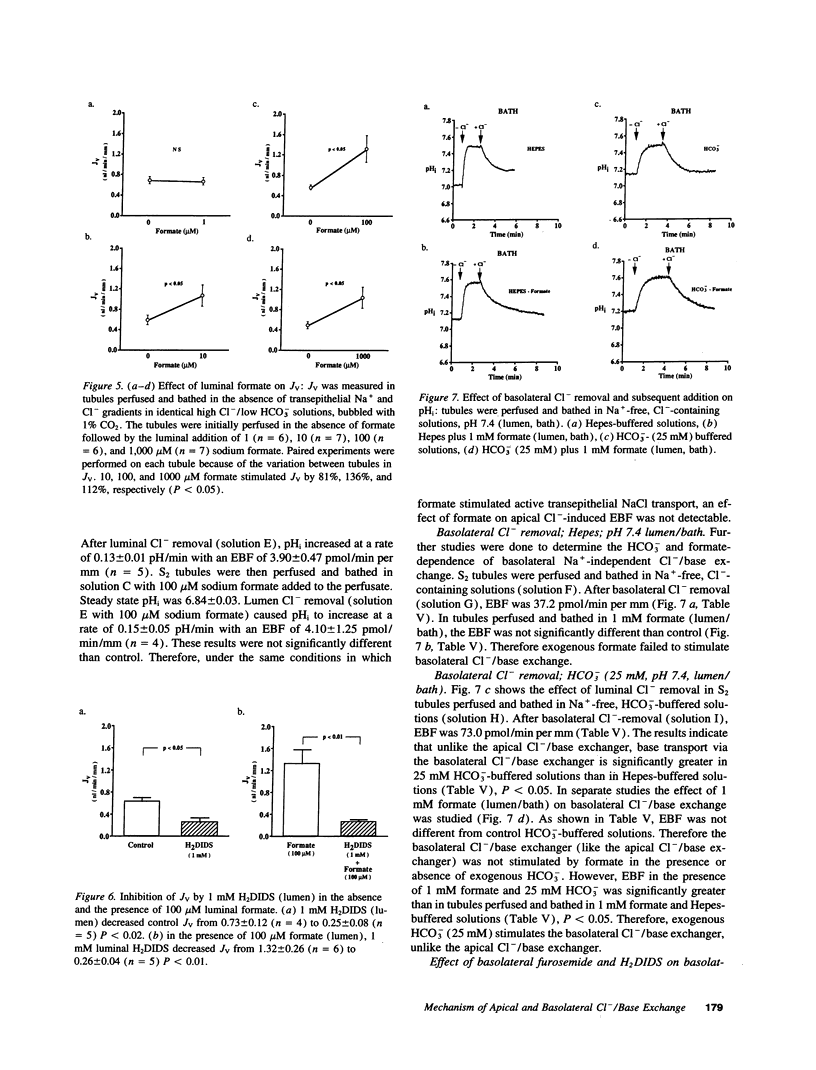
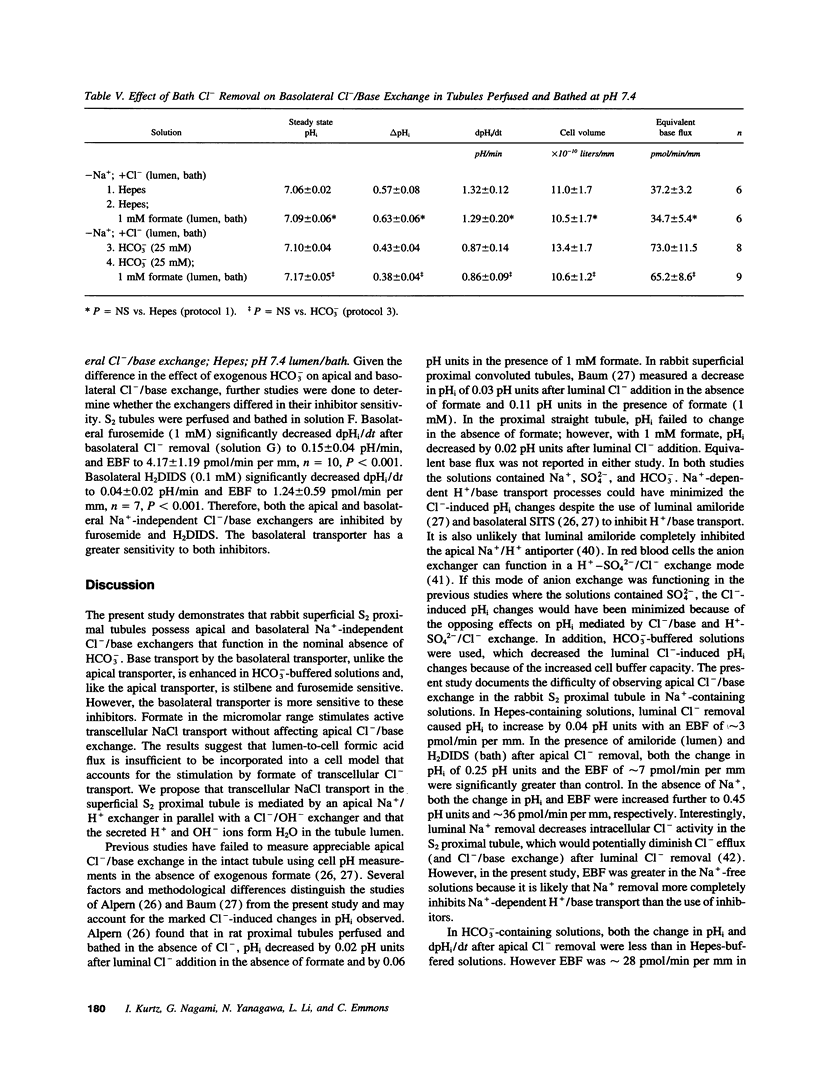
The present study was undertaken to determine the magnitude and mechanism of base transport via the apical and basolateral Na(+)-independent Cl-/base exchangers in rabbit isolated perfused superficial S2 proximal tubules. The results demonstrate that there is an apical Na(+)-independent Cl-/base exchanger on both membranes. HCO3- fails to stimulate apical Cl-/base exchange in contrast to the basolateral exchanger. Inhibition of endogenous HCO3- production does not alter the rate of apical Cl-/base exchange in Hepes-buffered solutions. Both exchangers are inhibited by H2DIDS and furosemide; however, the basolateral anion exchanger is more sensitive to these inhibitors. The results indicate that the apical and basolateral Cl-/base exchangers differ in their transport properties and are able to transport base equivalents in the absence of formate. The formate concentration in rabbit arterial serum is approximately 6 microM and in vitro tubule formate production is < 0.6 pmol/min per mm. Formate in the micromolar range stimulates Jv in a dose-dependent manner in the absence of a transepithelial Na+ and Cl- gradient and without a measurable effect on Cl(-)-induced equivalent base flux. Apical formic acid recycling cannot be an important component of any cell model, which accounts for formic acid stimulation of transcellular NaCl transport in the rabbit superficial S2 proximal tubule. We propose that transcellular NaCl transport in this nephron segment is mediated by an apical Na+/H+ exchanger in parallel with a Cl-/OH- exchanger and that the secreted H+ and OH- ions form H2O in the tubule lumen.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNISON E. F. Studies on the volatile fatty acids of sheep blood with special reference to formic acid. Biochem J. 1954 Dec;58(4):670–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0580670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Apical membrane chloride/base exchange in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1026–1030. doi: 10.1172/JCI112914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Chambers M. Basolateral membrane Cl/HCO3 exchange in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Na-dependent and -independent modes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Apr;89(4):581–598. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M. Developmental changes in rabbit juxtamedullary proximal convoluted tubule acidification. Pediatr Res. 1992 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):411–414. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199204000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M. Effect of luminal chloride on cell pH in rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 2):F677–F683. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.5.F677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M. Evidence that parallel Na+-H+ and Cl(-)-HCO3-(OH-) antiporters transport NaCl in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 2):F338–F345. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.2.F338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. A., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of proximal NaCl reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the mammalian kidney. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Mar;11(2):86–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham C., Munzesheimer C., Rabon E., Sachs G. Ion pathways in renal brush border membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 8;685(3):260–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassano G., Stieger B., Murer H. Na/H- and Cl/OH-exchange in rat jejunal and rat proximal tubular brush border membrane vesicles. Studies with acridine orange. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Mar;400(3):309–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00581565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. Y., Illsley N. P., Verkman A. S. Renal brush-border chloride transport mechanisms characterized using a fluorescent indicator. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 2):F114–F120. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.1.F114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. Y., Verkman A. S. Sodium-dependent chloride transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit proximal tubule. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):655–660. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corman B., Thomas R., McLeod R., de Rouffignac C. Water and total CO2 reabsorption along the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Dec;389(1):45–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00587927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickman K. G., Mandel L. J. Relationship between HCO3- transport and oxidative metabolism in rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):F342–F351. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.2.F342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Aronson P. S. Na+/HCO3-co-transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8778–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Holohan P. D., Ross C. R. HCO3- transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rat renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Yamaguchi D. T., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Cytosolic pH regulation in osteoblasts. Regulation of anion exchange by intracellular pH and Ca2+ ions. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jan;95(1):121–145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggino S. E., Martin G. J., Aronson P. S. Specificity and modes of the anion exchanger in dog renal microvillus membranes. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):F612–F621. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.6.F612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi K., Sasaki S., Yoshiyama N. Intracellular chloride activity of rabbit proximal straight tubule perfused in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):F49–F56. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.1.F49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ives H. E., Chen P. Y., Verkman A. S. Mechanism of coupling between Cl- and OH- transport in renal brush-border membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 1;863(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Characteristics of the binding site for extracellular substrate anions in human red blood cell band 3. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;574:84–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb25138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollie D. R., Lipscomb J. D. Formate dehydrogenase from Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Purification and spectroscopic characterization of the cofactors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21853–21863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniski L. P., Aronson P. S. Chloride/formate exchange with formic acid recycling: a mechanism of active chloride transport across epithelial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6362–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr, Berry C. A. Basolateral membrane Na/base cotransport is dependent on CO2/HCO3 in the proximal convoluted tubule. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Dec;90(6):833–853. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.6.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I. Apical Na+/H+ antiporter and glycolysis-dependent H+-ATPase regulate intracellular pH in the rabbit S3 proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):928–935. doi: 10.1172/JCI113184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I. Basolateral membrane Na+/H+ antiport, Na+/base cotransport, and Na+-independent Cl-/base exchange in the rabbit S3 proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):616–622. doi: 10.1172/JCI113925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I., Golchini K. Na+-independent Cl(-)-HCO-3- exchange in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Role in intracellular pH regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4516–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I., Star R., Balaban R. S., Garvin J. L., Knepper M. A. Spontaneous luminal disequilibrium pH in S3 proximal tubules. Role in ammonia and bicarbonate transport. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):989–996. doi: 10.1172/JCI112690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Axial heterogeneity of bicarbonate, chloride, and water transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Effects of change in luminal flow rate and of alkalemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1547–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI112747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucci M. S., Warnock D. G. Effects of anion-transport inhibitors on NaCl reabsorption in the rat superficial proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):570–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makar A. B., McMartin K. E., Palese M., Tephly T. R. Formate assay in body fluids: application in methanol poisoning. Biochem Med. 1975 Jun;13(2):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(75)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makar A. B., Tephly T. R. Improved estimation of formate in body fluids and tissues. Clin Chem. 1982 Feb;28(2):385–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., De Mello Aires M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of renal tubular hydrogen ion transport in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):147–158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel L. J., Balaban R. S. Stoichiometry and coupling of active transport to oxidative metabolism in epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol. 1981 May;240(5):F357–F371. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.5.F357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMartin K. E., Makar A. B., Martin G., Palese M., Tephly T. R. Methanol poisoning. I. The role of formic acid in the development of metabolic acidosis in the monkey and the reversal by 4-methylpyrazole. Biochem Med. 1975 Aug;13(4):319–333. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(75)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugharbil A., Knickelbein R. G., Aronson P. S., Dobbins J. W. Rabbit ileal brush-border membrane Cl-HCO3 exchanger is activated by an internal pH-sensitive modifier site. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):G666–G670. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.4.G666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhoul N. L., Chen L. K., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH regulation in rabbit S3 proximal tubule: basolateral Cl-HCO3 exchange and Na-HCO3 cotransport. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F371–F381. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls P. The effect of formate on cytochrome aa3 and on electron transport in the intact respiratory chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 9;430(1):13–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso A. M., Tsien R. Y., Demarest J. R., Machen T. E. Na-H and Cl-HCO3 exchange in rabbit oxyntic cells using fluorescence microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C30–C36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Contributions of cellular leak pathways to net NaHCO3 and NaCl absorption. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1859–1867. doi: 10.1172/JCI114092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Rector F. C., Jr Role of Na+-H+ antiport in rat proximal tubule NaCl absorption. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F461–F465. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Burckhardt G. Proton pathways in rat renal brush-border and basolateral membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 12;734(2):210–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Yoshiyama N. Interaction of chloride and bicarbonate transport across the basolateral membrane of rabbit proximal straight tubule. Evidence for sodium coupled chloride/bicarbonate exchange. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1004–1011. doi: 10.1172/JCI113410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild L., Giebisch G., Karniski L. P., Aronson P. S. Effect of formate on volume reabsorption in the rabbit proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI112803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J. Absence of Cl- -OH- or Cl- -HCO3- exchange in the rabbit renal proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):F462–F469. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.4.F462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki G., Frömter E. The chloride/base exchanger in the basolateral cell membrane of rabbit renal proximal tubule S3 segment requires bicarbonate to operate. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Sep;417(1):37–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00370766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahangian S., Ash K. O., Rollins D. E. An enzymatic method for the analysis of formate in human plasma. J Anal Toxicol. 1984 Nov-Dec;8(6):273–276. doi: 10.1093/jat/8.6.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Naruse M., Takeda M., Nakamura M., Yoshitomi K., Imai M. Mechanism of PGE2-induced cell swelling in distal nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):F824–F832. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.5.F824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiuan D., Weinstein S. W. Evidence for electroneutral chloride transport in rabbit renal cortical brush border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):F837–F847. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.5.F837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønnessen T. I., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Role of Na(+)-H+ and Cl(-)-HCO3- antiports in the regulation of cytosolic pH near neutrality. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1117–C1126. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Giebisch G., Aronson P. S. Effects of formate and oxalate on volume absorption in rat proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 2):F37–F42. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.1.F37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Yee V. J. Chloride uptake by brush border membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. Coupling to proton gradients and K+ diffusion potentials. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):103–115. doi: 10.1172/JCI110002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling L. W., Welling D. J. Surface areas of brush border and lateral cell walls in the rabbit proximal nephron. Kidney Int. 1975 Dec;8(6):343–348. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdas W. F., Baker G. F. The physiological properties of the band 3 anion exchanger as derived from pH and other studies with human red cells. Cytobios. 1993;74(297):111–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi K., Hoshi T. Intracellular Cl- activity of the proximal tubule of Triturus kidney: dependence on extracellular ionic composition and transmembrane potential. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):F359–F366. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.3.F359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


