Abstract
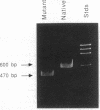
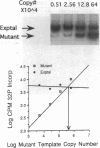
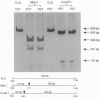
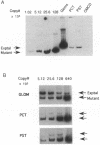
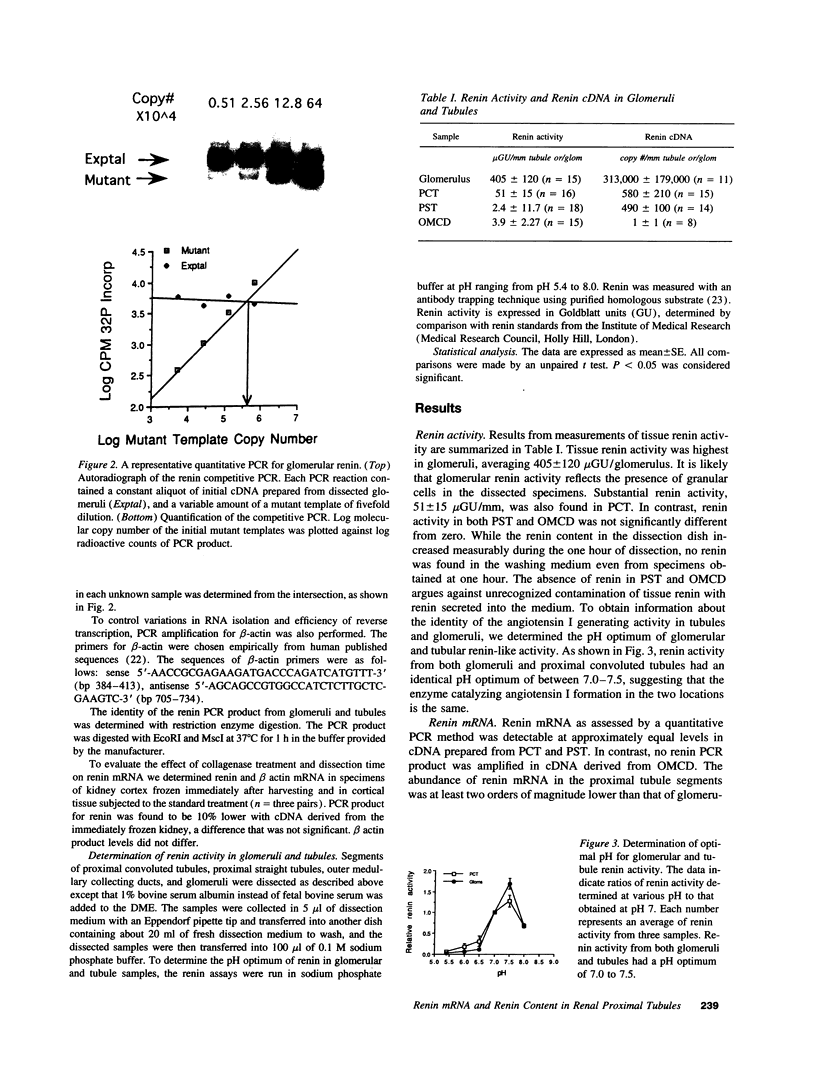
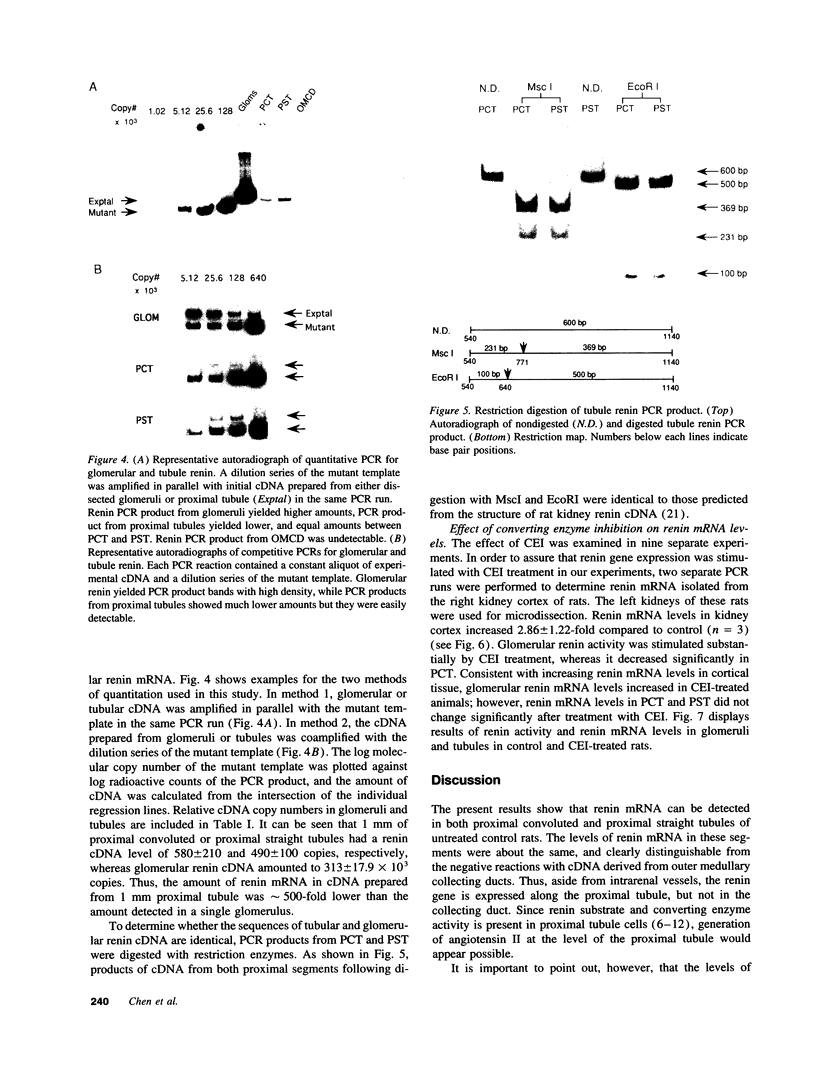
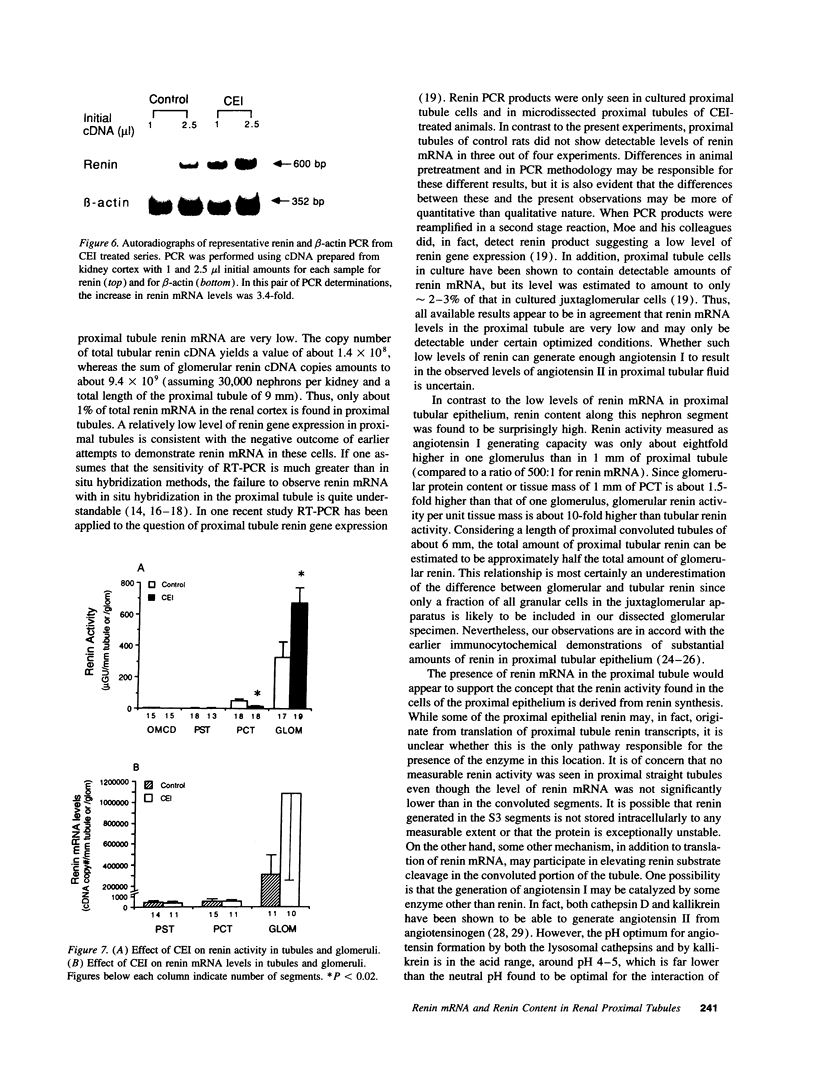
The present study was undertaken to assess the presence of renin enzymatic activity and renin mRNA in proximal tubules of rat kidneys, and to determine the effect of converting enzyme inhibition (CEI) on proximal tubule renin gene expression. Proximal convoluted tubules (PCT), proximal straight tubules (PST), outer medullary collecting ducts (OMCD), and glomeruli (Gloms) were isolated by microdissection. Renin activity was measured in sonicated segments by radioimmunoassay. Renin mRNA levels were assessed using a quantitative PCR. Renin activity in PCT averaged 51 +/- 15 microGU/mm compared to 405 +/- 120 microGU/glomerulus. No measurable renin activity was found in PST and OMCD. Renin activity in both glomeruli and tubules had the same pH optimum, between 7.0 and 7.5. Renin mRNA was consistently detectable in cDNA prepared from PCT and PST, although its abundance per mm tubule was about 1/500th that found in one glomerulus. Renin mRNA was not detectable in OMCD. Tubular renin PCR product identity was confirmed by restriction digestion. CEI administration increased glomerular renin activity and renin mRNA, but not proximal tubular renin. The absence of a stimulatory effect of CEI on proximal tubule renin gene expression suggests the operation of different intracellular signals in control of renin synthesis in the proximal tubule than in the vascular compartment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braam B., Mitchell K. D., Fox J., Navar L. G. Proximal tubular secretion of angiotensin II in rats. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 2):F891–F898. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.5.F891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneval P., Hinglais N., Alhenc-Gelas F., Tricottet V., Corvol P., Menard J., Camilleri J. P., Bariety J. Angiotensin I converting enzyme in human intestine and kidney. Ultrastructural immunohistochemical localization. Histochemistry. 1986;85(1):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00508656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham C. E., Hawelu-Johnson C. L., Frank B. M., Lynch K. R. Molecular cloning of rat renin cDNA and its gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5605–5609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. P., Reid I. A. Renin activity in dog brain: enzymological similarity to cathepsin D. Endocrinology. 1976 Jul;99(1):93–100. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper C. F., Mellon S. H., Cumin F., Baxter J. D., Ganong W. F. Analysis by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization of renin and its mRNA in kidney, testis, adrenal, and pituitary of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7552–7556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. G. Angiotensin receptor subtypes of the kidney cortex. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):F1–F7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Ellison K. E., Brody T., Ingelfinger J., Pratt R. E. A comparative study of the distributions of renin and angiotensinogen messenger ribonucleic acids in rat and mouse tissues. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2334–2338. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geibel J., Giebisch G., Boron W. F. Angiotensin II stimulates both Na(+)-H+ exchange and Na+/HCO3- cotransport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7917–7920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Lynch K. R., Sturgill B. C., Elwood J. P., Chevalier R. L., Carey R. M., Peach M. J. Distribution of renin mRNA and its protein in the developing kidney. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F850–F858. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackenthal E., Koch C., Bergemann T., Gross F. Partial purification and characterization of a renin-like enzyme from rat submandibular gland. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Oct 15;21(20):2779–2792. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingelfinger J. R., Zuo W. M., Fon E. A., Ellison K. E., Dzau V. J. In situ hybridization evidence for angiotensinogen messenger RNA in the rat proximal tubule. An hypothesis for the intrarenal renin angiotensin system. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):417–423. doi: 10.1172/JCI114454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwao H., Nakamura N., Ikemoto F., Yamamoto K., Mizuhira V., Ono M., Sugiura Y. Distribution of exogenously administered renin in mouse kidney. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1982;4(11-12):2449–2456. doi: 10.3109/10641968209062402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykkegård S., Poulsen K. Ultramicroassay for plasma renin concentration in the rat using the antibody-trapping technique. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):250–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Arakawa K. Confirmation of direct angiotensin formation by kallikrein. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 1;213(1):193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj2130193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. W., Ujiie K., Star R. A., Miller R. T., Widell J., Alpern R. J., Henrich W. L. Renin expression in renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):774–779. doi: 10.1172/JCI116296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richoux J. P., Cordonnier J. L., Bouhnik J., Clauser E., Corvol P., Menard J., Grignon G. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensinogen in rat liver and kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;233(2):439–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00238309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rix E., Ganten D., Schüll B., Unger T., Taugner R. Converting-enzyme in the choroid plexus, brain, and kidney: immunocytochemical and biochemical studies in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Mar 10;22(2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schunkert H., Ingelfinger J. R., Dzau V. J. Evolving concepts of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in health and disease: contributions of molecular biology. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1991 Jul-Oct;14(4-5):146–154. doi: 10.1159/000173400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seikaly M. G., Arant B. S., Jr, Seney F. D., Jr Endogenous angiotensin concentrations in specific intrarenal fluid compartments of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1352–1357. doi: 10.1172/JCI114846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner C., Poulsen K., Hackenthal E., Taugner R. Immunocytochemical localization of renin in mouse kidney. Histochemistry. 1979 Jul;62(1):19–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00537003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Hackenthal E., Inagami T., Nobiling R., Poulsen K. Vascular and tubular renin in the kidneys of mice. Histochemistry. 1982;75(4):473–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00640599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Hackenthal E., Nobiling R., Harlacher M., Reb G. The distribution of renin in the different segments of the renal arterial tree: immunocytochemical investigation in the mouse kidney. Histochemistry. 1981;73(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00493135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Kim S. J., Murakami K., Waldherr R. The fate of prorenin during granulopoiesis in epithelioid cells. Immunocytochemical experiments with antisera against renin and different portions of the renin prosegment. Histochemistry. 1987;86(3):249–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00490255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Erdös E. G. Isolation of membrane-bound renal kallikrein and kininase. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):755–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1510755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa N., Capparelli A. W., Jo O. D., Friedal A., Barrett J. D., Eggena P. Production of angiotensinogen and renin-like activity by rabbit proximal tubular cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1991 May;39(5):938–941. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]