Abstract
Group B streptococcal infection is a major cause of neonatal mortality. Antibody to the capsular polysaccharide protects against invasive neonatal disease, but immunization with capsular polysaccharides fails to elicit protective antibody in many recipients. Conjugation of the polysaccharide to tetanus toxoid has been shown to increase immune response to the polysaccharide. In animal models, C proteins of group B streptococci are also protective determinants. We examined the ability of the beta C protein to serve in the dual role of carrier for the polysaccharide and protective immunogen. Type III polysaccharide was covalently coupled to beta C protein by reductive amination. Immunization of rabbits with the polysaccharide-protein conjugate elicited high titers of antibody to both components, and the serum induced opsonophagocytic killing of type III, Ia/C, and Ib/C strains of group B streptococci. Female mice were immunized with the conjugate vaccine and then bred; 93% of neonatal pups born to these dams vaccinated with conjugate survived type III group B streptococcal challenge and 76% survived type Ia/C challenge, compared with 3% and 8% survival, respectively, in controls (P < 0.001). The beta C protein acted as an effective carrier for the type III polysaccharide while simultaneously induced protective immunity against beta C protein--containing strains of group B streptococci.
Full text
PDF



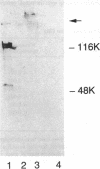
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F., Concepcion N. F., Puentes S. M., Payne N. R. Nonimmune binding of human immunoglobulin A to type II group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1789–1795. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1789-1795.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Edwards M. S., Schiffman G. Influence of preimmunization antibody levels on the specificity of the immune response to related polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):173–178. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Vaccination as a measure for prevention of neonatal GBS infection. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;35:281–290. doi: 10.1159/000410381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Rench M. A., Edwards M. S., Carpenter R. J., Hays B. M., Kasper D. L. Immunization of pregnant women with a polysaccharide vaccine of group B streptococcus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 3;319(18):1180–1185. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811033191802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Rench M. A., Kasper D. L. Response to type III polysaccharide in women whose infants have had invasive group B streptococcal infection. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 28;322(26):1857–1860. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006283222606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Goroff D. K. Antigenic specificity of opsonophagocytic antibodies in rabbit anti-sera to group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barington T., Skettrup M., Juul L., Heilmann C. Non-epitope-specific suppression of the antibody response to Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccines by preimmunization with vaccine components. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.432-438.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevanger L., Naess A. I. Mouse-protective antibodies against the Ibc proteins of group B streptococci. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Apr;93(2):121–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L. J., Boyle M. D. Identification of non-immunoglobulin A-Fc-binding forms and low-molecular-weight secreted forms of the group B streptococcal beta antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1573–1581. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1573-1581.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker M. D., Edwards K. M., Bradley R., Palmer P. Responses of children to booster immunization with their primary conjugate Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine or with polyribosylribitol phosphate conjugated with diphtheria toxoid. J Pediatr. 1993 Mar;122(3):410–413. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley M. M., Harvey R. C., Stull T., Smith J. D., Schuchat A., Wenger J. D., Stephens D. S. A population-based assessment of invasive disease due to group B Streptococcus in nonpregnant adults. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jun 24;328(25):1807–1811. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199306243282503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores A. E., Ferrieri P. Molecular species of R-protein antigens produced by clinical isolates of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1050–1054. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1050-1054.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores A. E., Nelson J. A., Wu X. Y., Ferrieri P. Antibody profiles to the group B streptococcal beta antigen in maternal and infant paired sera. APMIS. 1993 Jan;101(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1993.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedén L. O., Frithz E., Lindahl G. Molecular characterization of an IgA receptor from group B streptococci: sequence of the gene, identification of a proline-rich region with unique structure and isolation of N-terminal fragments with IgA-binding capacity. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1481–1490. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Tokuhisa T. Epitope-specific regulation. I. Carrier-specific induction of suppression for IgG anti-hapten antibody responses. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1730–1740. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C. Immunochemistry of groups A, B, and C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Ferrieri P. Group B streptococcal Ibc protein antigen: distribution of two determinants in wild-type strains of common serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):506–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.506-510.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Goroff D. K., Baker C. J. Immunochemical characterization of native polysaccharides from group B streptococcus: the relationship of the type III and group B determinants. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1096–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagergard T., Shiloach J., Robbins J. B., Schneerson R. Synthesis and immunological properties of conjugates composed of group B streptococcus type III capsular polysaccharide covalently bound to tetanus toxoid. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.687-694.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Akerström B., Vaerman J. P., Stenberg L. Characterization of an IgA receptor from group B streptococci: specificity for serum IgA. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2241–2247. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindén V., Christensen K. K., Christensen P. Correlation between low levels of maternal IgG antibodies to R protein and neonatal septicemia with group B streptococci carrying R protein. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;71(2):168–172. doi: 10.1159/000233382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Hori S., Michel J. L., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Phenotypic diversity in the alpha C protein of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2638–2644. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2638-2644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Michel J. L., Gong E. W., Rodewald A. K., Kasper D. L. Protection of neonatal mice from group B streptococcal infection by maternal immunization with beta C protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):4989–4994. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.4989-4994.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Michel J. L., Kasper D. L. A monoclonal antibody identifies a protective C-protein alpha-antigen epitope in group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.204-210.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. L., Madoff L. C., Kling D. E., Kasper D. L., Ausubel F. M. Cloned alpha and beta C-protein antigens of group B streptococci elicit protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2023–2028. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2023-2028.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti L. C., Kasper D. L., Michon F., DiFabio J., Holme K., Jennings H. J., Wessels M. R. An oligosaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine against type III group B Streptococcus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18278–18283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti L. C., Wessels M. R., Michon F., DiFabio J., Jennings H. J., Kasper D. L. Group B Streptococcus type II polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4009–4014. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4009-4014.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald A. K., Onderdonk A. B., Warren H. B., Kasper D. L. Neonatal mouse model of group B streptococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):635–639. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C., Blake M. S. A surface receptor specific for human IgA on group B streptococci possessing the Ibc protein antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1467–1475. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutze M. P., Leclerc C., Jolivet M., Audibert F., Chedid L. Carrier-induced epitopic suppression, a major issue for future synthetic vaccines. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2319–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutze M. P., Leclerc C., Vogel F. R., Chedid L. Epitopic suppression in synthetic vaccine models: analysis of the effector mechanisms. Cell Immunol. 1987 Jan;104(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. A., Gray G. R. Proteins containing reductively aminated disaccharides. Synthesis and chemical characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålhammar-Carlemalm M., Stenberg L., Lindahl G. Protein rib: a novel group B streptococcal cell surface protein that confers protective immunity and is expressed by most strains causing invasive infections. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1593–1603. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Paoletti L. C., Kasper D. L., DiFabio J. L., Michon F., Holme K., Jennings H. J. Immunogenicity in animals of a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine against type III group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1428–1433. doi: 10.1172/JCI114858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Paoletti L. C., Rodewald A. K., Michon F., DiFabio J., Jennings H. J., Kasper D. L. Stimulation of protective antibodies against type Ia and Ib group B streptococci by a type Ia polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4760–4766. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4760-4766.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Eagon R. G. Type-specific antigens of group B type Ic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):596–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.596-604.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]