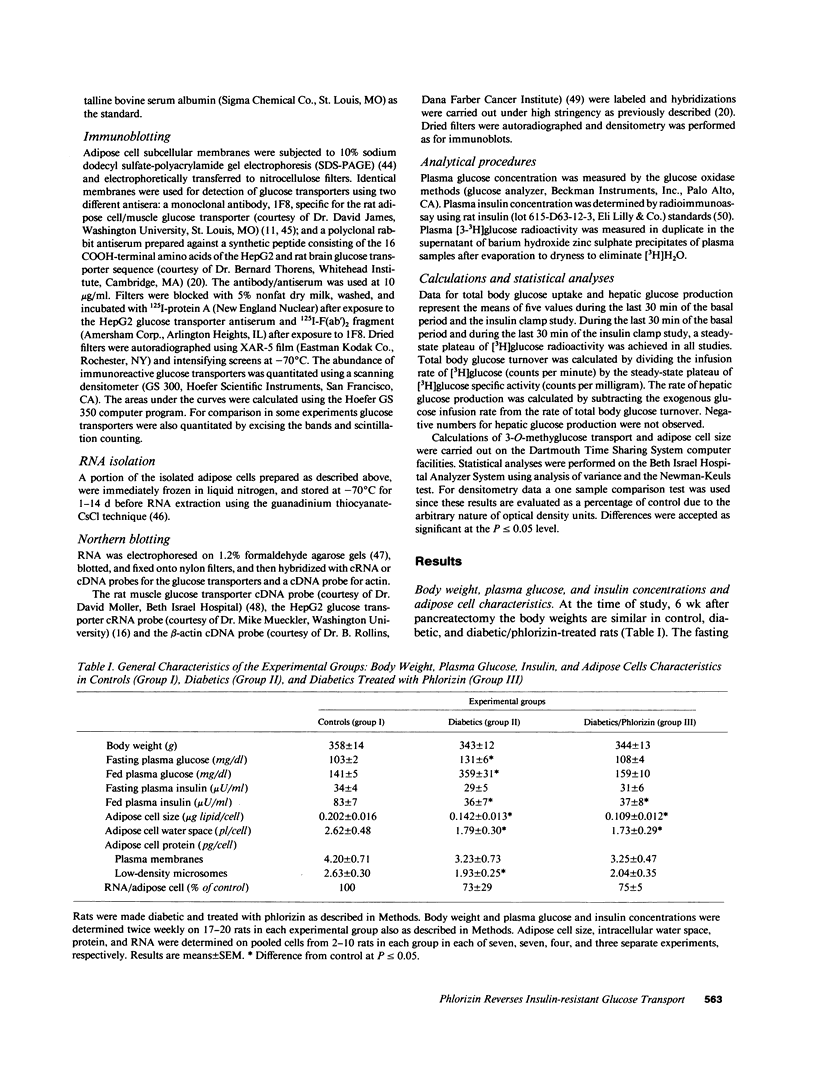
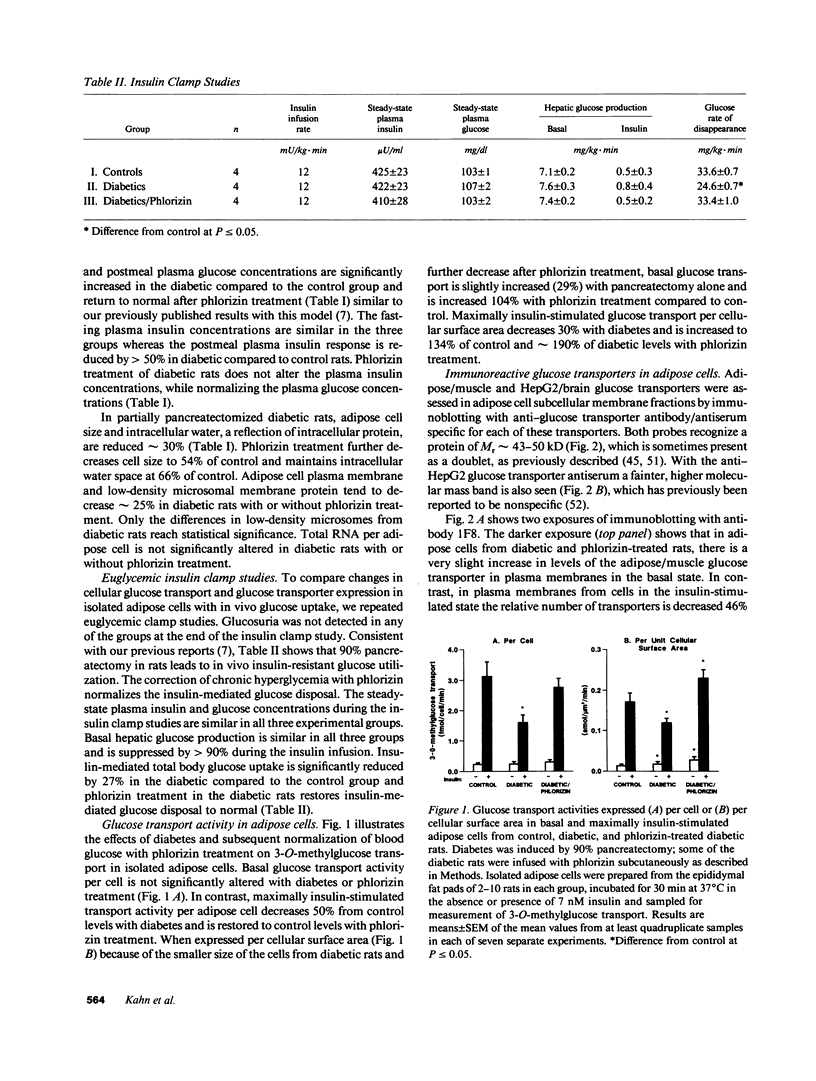
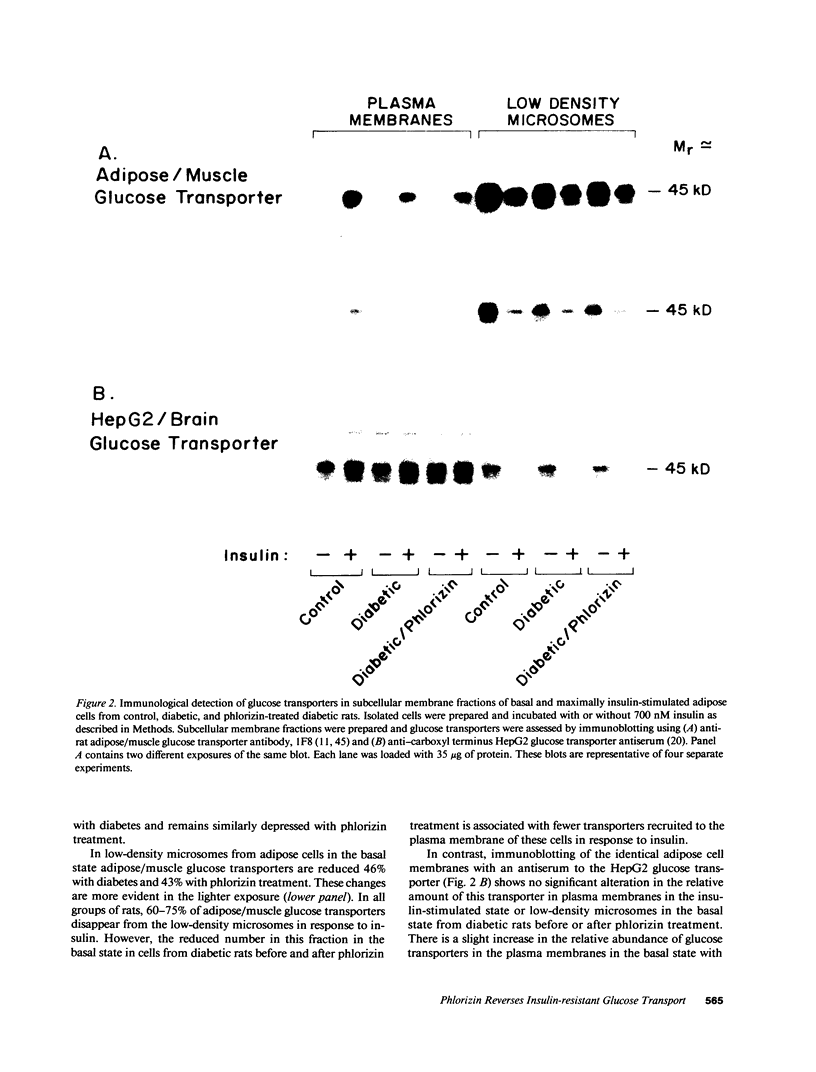
Abstract
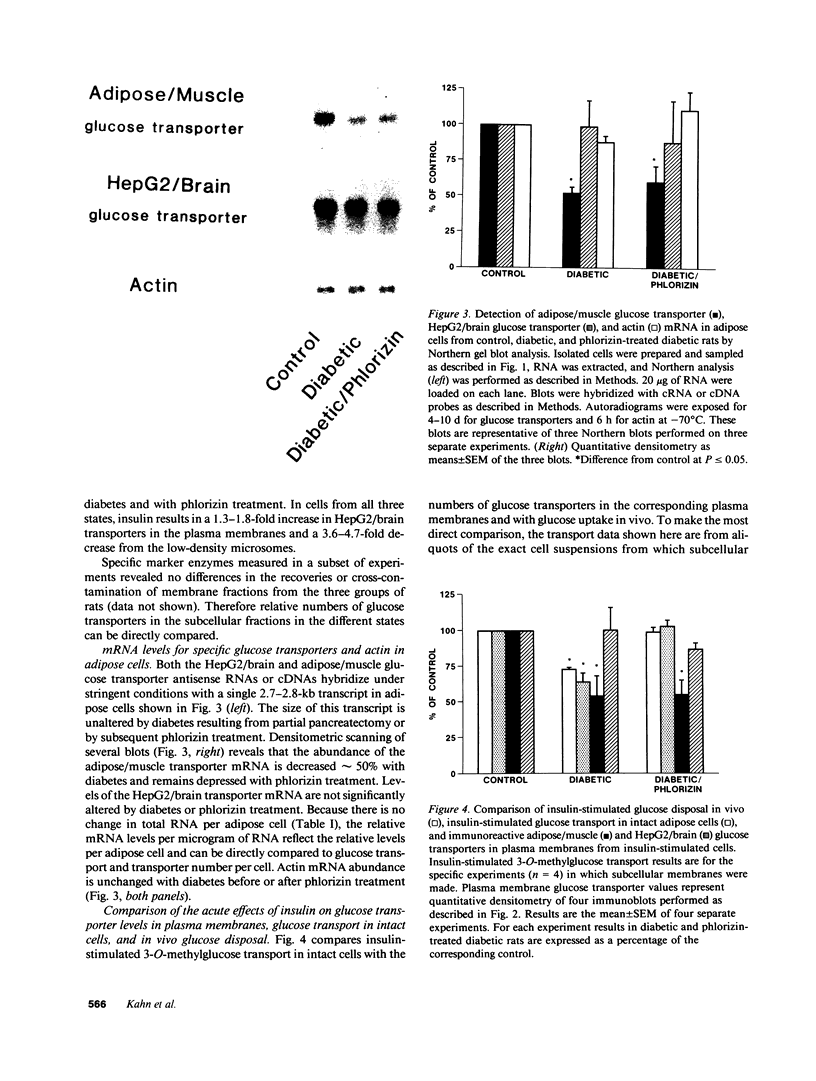
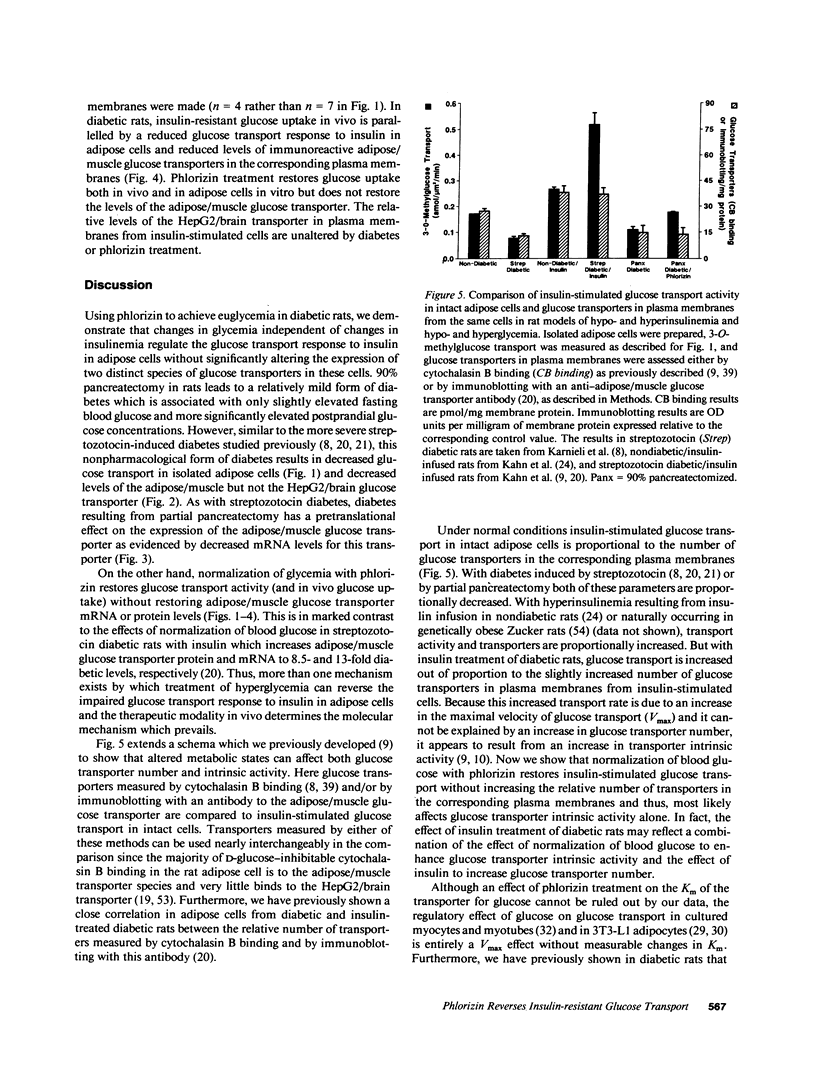
Evidence is emerging for a direct role of glucose, independent of changes in insulin, in the regulation of cellular glucose transport and glucose utilization in vivo. In this study we investigate potential cellular and molecular mechanisms for this regulatory effect of glucose by determining how normalization of glycemia without insulin therapy in diabetic rats influences 3-O-methylglucose transport and the expression and translocation of two genetically distinct species of glucose transporters (GTs) in adipose cells. These results are compared with alterations in glucose disposal in vivo measured by euglycemic clamp. In rats rendered diabetic by 90% pancreatectomy, insulin-stimulated glucose transport in adipose cells is decreased 50% in parallel with reduced insulin-mediated glucose disposal in vivo. Levels of adipose/muscle GTs measured by immunoblotting are decreased in adipose cell subcellular membrane fractions, as are the corresponding mRNA levels assessed by Northern blotting of total adipose cell RNA. Normalization of blood glucose in diabetic rats with phlorizin, which impairs renal tubular glucose reabsorption and thus enhances glucose excretion, restores insulin-stimulated glucose transport in adipose cells and insulin-mediated glucose disposal in vivo. Importantly, levels of the adipose/muscle GT protein remain 43% reduced in the low-density microsomes in the basal state and 46% reduced in the plasma membranes in the insulin-stimulated state. Adipose/muscle GT mRNA levels remain approximately 50% depressed. Levels of the HepG2/brain GT protein and mRNA are unaltered by diabetes or phlorizin treatment. Thus, changes in ambient glucose independent of changes in ambient insulin can regulate the glucose transport response to insulin in isolated adipose cells and changes in responsiveness parallel alterations in glucose uptake in vivo. Since this effect can occur without alteration in the expression of the two species of glucose transporters present in adipose cells or in their translocation to the plasma membrane in response to insulin, it may result from changes in GT functional activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Biswas C., Vicario P. P., Strout H. V., Saperstein R., Pilch P. F. Decreased expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in diabetes and fasting. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):70–72. doi: 10.1038/340070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Mott D., Reaven G. R., Kashiwagi A., Foley J. E. Relationship between obesity and maximal insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in vivo and in vitro in Pima Indians. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):800–805. doi: 10.1172/JCI111274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Brosius F. C., 3rd, Alper S. L., Lodish H. F. A glucose transport protein expressed predominately in insulin-responsive tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2535–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Hendler R., Simonson D. Insulin resistance is a prominent feature of insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):795–801. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Edwards Y., Pilch P. F., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and characterization of the major insulin-responsive glucose transporter expressed in human skeletal muscle and other insulin-responsive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7776–7779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Bell G. I. Characterization and expression of human HepG2/erythrocyte glucose-transporter gene. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):657–661. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Birnbaum M. J. Pretranslational suppression of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter in rats with diabetes mellitus. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2662408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Matthaei S., Olefsky J. M. Role of glucose transporters in the cellular insulin resistance of type II non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1528–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI113485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Olefsky J. M., Matthaei S., Marshall S. Glucose and insulin co-regulate the glucose transport system in primary cultured adipocytes. A new mechanism of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):189–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjedde A., Crone C. Blood-brain glucose transfer: repression in chronic hyperglycemia. Science. 1981 Oct 23;214(4519):456–457. doi: 10.1126/science.7027439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerre-Millo M., Lavau M., Horne J. S., Wardzala L. J. Proposed mechanism for increased insulin-mediated glucose transport in adipose cells from young, obese Zucker rats. Large intracellular pool of glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2197–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Rosenfeld M. G., Rosen O. M. Characterization of antisera to a synthetic carboxyl-terminal peptide of the glucose transporter protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Wilk E. W., Birnbaum M. J., Cushman S. W., Rosen O. M. Glucose deprivation and hexose transporter polypeptides of murine fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6778–6789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Matthaei S., Olefsky J. M., Baly D. L., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Biochemical and functional heterogeneity of rat adipocyte glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., McLenithan J. C., Braiterman L. T., Cornelius P., Pekala P. H., Lane M. D. Sequence, tissue distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for a putative insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3150–3154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in adipose cells from diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):404–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI114180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W. Mechanism for markedly hyperresponsive insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity in adipose cells from insulin-treated streptozotocin diabetic rats. Evidence for increased glucose transporter intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5118–5124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Horton E. S., Cushman S. W. Mechanism for enhanced glucose transport response to insulin in adipose cells from chronically hyperinsulinemic rats. Increased translocation of glucose transporters from an enlarged intracellular pool. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):853–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI112894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Armoni M., Cohen P., Kanter Y., Rafaeloff R. Reversal of insulin resistance in diabetic rat adipocytes by insulin therapy. Restoration of pool of glucose transporters and enhancement of glucose-transport activity. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):925–931. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. A possible mechanism of insulin resistance in the rat adipose cell in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Depletion of intracellular glucose transport systems. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):811–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI110318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Perdue J. F. Induction of sugar transport in chick embryo fibroblasts by hexose starvation. Evidence for transcriptional regulation of transport. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):593–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaki A., Kuzuya H., Yoshimasa Y., Yamada K., Okamoto M., Nishimura H., Kakehi T., Takeda J., Seino Y., Imura H. Regulation of glucose-transporter gene expression by insulin in cultured human fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1988 Nov;37(11):1583–1586. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.11.1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lager I., Lönnroth P., von Schenck H., Smith U. Reversal of insulin resistance in type I diabetes after treatment with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Dec 3;287(6406):1661–1664. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6406.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall A. L., Fixman L. B., Fleming N., Tornheim K., Chick W., Ruderman N. B. Chronic hypoglycemia increases brain glucose transport. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):E442–E447. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.4.E442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Takaku F. Studies with antipeptide antibody suggest the presence of at least two types of glucose transporter in rat brain and adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13432–13439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G., Scarlett J. A. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and noninsulin-dependent type II diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):E15–E30. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.1.E15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Bak J. F., Andersen P. H., Lund S., Moller D. E., Flier J. S., Kahn B. B. Evidence against altered expression of GLUT1 or GLUT4 in skeletal muscle of patients with obesity or NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Jul;39(7):865–870. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.7.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter E. A., Hansen B. F., Hansen S. A. Glucose-induced insulin resistance of skeletal-muscle glucose transport and uptake. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):733–737. doi: 10.1042/bj2520733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Smith C. J., Fung C., Rubin C. S. Development of hormone receptors and hormone responsiveness in vitro. Effect of prolonged insulin treatment on hexose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7579–7583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Giaccari A. Relative contribution of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis to insulin-mediated glucose uptake. A dose-response euglycemic clamp study in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Lauglin M. R. Correction of chronic hyperglycemia with vanadate, but not with phlorizin, normalizes in vivo glycogen repletion and in vitro glycogen synthase activity in diabetic skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):892–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI114250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Smith D., Shulman G. I., Papachristou D., DeFronzo R. A. Correction of hyperglycemia with phlorizin normalizes tissue sensitivity to insulin in diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1510–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI112981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasson S., Cerasi E. Substrate regulation of the glucose transport system in rat skeletal muscle. Characterization and kinetic analysis in isolated soleus muscle and skeletal muscle cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16827–16833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlett J. A., Kolterman O. G., Ciaraldi T. P., Kao M., Olefsky J. M. Insulin treatment reverses the postreceptor defect in adipocyte 3-O-methylglucose transport in type II diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jun;56(6):1195–1201. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-6-1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Sonne O. A simple, rapid, and sensitive method for measuring protein concentration in subcellular membrane fractions prepared by sucrose density ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):424–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90608-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivitz W. I., DeSautel S. L., Kayano T., Bell G. I., Pessin J. E. Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA in insulin-deficient states. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):72–74. doi: 10.1038/340072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivitz W. I., DeSautel S. L., Kayano T., Bell G. I., Pessin J. E. Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA levels in rat adipose tissue by insulin. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):583–588. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Farmer S. R. Decreases in tubulin and actin gene expression prior to morphological differentiation of 3T3 adipocytes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordjman K. M., Leingang K. A., James D. E., Mueckler M. M. Differential regulation of two distinct glucose transporter species expressed in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: effect of chronic insulin and tolbutamide treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7761–7765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxinger R. R., Marshall S. Recovery of maximal insulin responsiveness and insulin sensitivity after induction of insulin resistance in primary cultured adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8156–8163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrey D. B., Kalckar H. M. The nature of regulation of hexose transport in cultured mammalian fibroblasts: aerobic "repressive" control by D-glucosamine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrey D., Gammon M. T., Kalckar H. M. Uptake patterns and transport enhancements in cultures of hamster cells deprived of carbohydrates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Apr;167(2):410–416. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Donovan J. A., Van Ness B. G., Fellows R. E., Pessin J. E. Glucose-dependent regulation of glucose transport activity, protein, and mRNA in primary cultures of rat brain glial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15594–15601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Ramlal T., Donovan J. A., Doering T. P., Sandra A., Klip A., Pessin J. E. Insulin and glucose-dependent regulation of the glucose transport system in the rat L6 skeletal muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6587–6595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Koivisto V. A. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy decreases insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Apr;58(4):659–666. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-4-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Putten J. P., Krans H. M. Glucose as a regulator of insulin-sensitive hexose uptake in 3T3 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7996–8001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]