Abstract
Fogo selvagem (FS) is an autoimmune disease caused by IgG autoantibodies to desmoglein I (DG-I), a desmosomal glycoprotein. We have previously shown that the autoantibodies in these patients are pathogenic and restricted mainly to the IgG4 subclass. The purpose of this study was to determine if the Fc domain or the valence of FS autoantibodies were relevant in the induction of epidermal disease in neonatal mice. IgG4 was prepared from sera of FS patients by anion exchange chromatography, and digested with pepsin to yield F(ab')2 fragments. Monovalent FS Fab' were made by reduction and alkylation of FS F(ab')2. Intact FS IgG4, FS F(ab')2, and FS Fab' fragments were injected into neonatal mice. Intact FS IgG4 and both FS IgG fragments were pathogenic. The disease in the animals was dose dependent, and on the molar basis, FS Fab' fragments were more potent and efficient in producing disease than whole FS IgG. These results suggest: (a) simple binding of FS autoantibodies to DG-I may trigger keratinocyte detachment and epidermal disease; (b) DG-I may represent a keratinocyte cell adhesion molecule; and (c) complement activation and surface cross-linking may not be relevant in keratinocyte detachment.
Full text
PDF

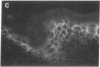
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diaz L. A., Marcelo C. L. Pemphigoid and pemphigus antigens in cultured epidermal cells. Br J Dermatol. 1978 Jun;98(6):631–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1978.tb03581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Patel H., Calvanico N. J. Bullous pemphigoid antigen. II. Isolation from the urine of a patient. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):605–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Sampaio S. A., Rivitti E. A., Martins C. R., Cunha P. R., Lombardi C., Almeida F. A., Castro R. M., Macca M. L., Lavrado C. Endemic pemphigus foliaceus (Fogo Selvagem): II. Current and historic epidemiologic studies. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Jan;92(1):4–12. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep13070394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Sampaio S. A., Rivitti E. A., Martins C. R., Cunha P. R., Lombardi C., Almeida F. A., Castro R. M., Macca M. L., Lavrado C. Endemic pemphigus foliaceus (fogo selvagem). I. Clinical features and immunopathology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Apr;20(4):657–669. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz L. A. Molecular structure of the epidermal extracellular spaces. Int J Dermatol. 1979 Jul-Aug;18(6):434–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1979.tb01946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana S., Diaz L. A., Rivitti E. A., Geoghegan W. D., Jordon R. E. Complement fixation by Brazilian Pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Mar;71(3):464–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis W. L., Anhalt G. J., Diaz L. A., Rivitti E. A., Martins C. R., Berger R. S. Calcium enhances the sensitivity of immunofluorescence for pemphigus antibodies. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Sep;89(3):302–304. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12471587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo T., Sano S. Functional aspects of dermo-epidermal junction. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1973;73:121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel H. P., Diaz L. A., Anhalt G. J., Labib R. S., Takahashi Y. Demonstration of pemphigus antibodies on the cell surface of murine epidermal cell monolayers and their internalization. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Dec;83(6):409–415. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12273480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock B., Martins C. R., Theofilopoulos A. N., Balderas R. S., Anhalt G. J., Labib R. S., Futamura S., Rivitti E. A., Diaz L. A. The pathogenic effect of IgG4 autoantibodies in endemic pemphigus foliaceus (fogo selvagem). N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 1;320(22):1463–1469. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906013202206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe J. T., Diaz L., Sampaio S. A., Castro R. M., Labib R. S., Takahashi Y., Patel H., Anhalt G. J. Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies are pathogenic to BALB/c mice by passive transfer. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Dec;85(6):538–541. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELBERG H. L., WEIGLE W. O. THE CATABOLISM OF HOMOLOGOUS AND HETEROLOGOUS 7S GAMMA GLOBULIN FRAGMENTS. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelz M., Duden R., Cowin P., Franke W. W. A constitutive transmembrane glycoprotein of Mr 165,000 (desmoglein) in epidermal and non-epidermal desmosomes. II. Immunolocalization and microinjection studies. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;42(2):184–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H. IgG subclasses--a review. Ann Allergy. 1987 Feb;58(2):89-96, 99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squiquera H. L., Diaz L. A., Sampaio S. A., Rivitti E. A., Martins C. R., Cunha P. R., Lombardi C., Lavrado C., Borges P., Friedman H. Serologic abnormalities in patients with endemic pemphigus foliaceus (Fogo selvagem), their relatives, and normal donors from endemic and non-endemic areas of Brazil. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Aug;91(2):189–191. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12464490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Koulu L., Klaus-Kovtun V., Steinberg M. S. A monoclonal antibody to the desmosomal glycoprotein desmoglein I binds the same polypeptide as human autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1227–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Bennich H. H., Natvig J. B. Simple method of subtyping human G-myeloma proteins based on sensitivity to pepsin digestion. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):853–855. doi: 10.1038/225853b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]