Abstract
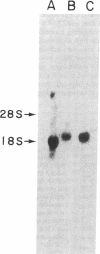
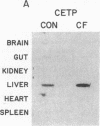
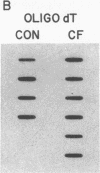
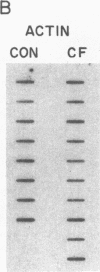
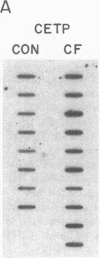
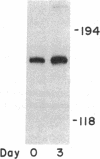
Cholesteryl ester transfer activity is increased in plasma of cholesterol-fed rabbits. To investigate the mechanisms leading to changes in activity, we measured cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) mass by RIA and CETP mRNA abundance by Northern and slot blot analysis using a human CETP cDNA probe in control (n = 8) and cholesterol-fed rabbits (n = 10). Cholesterol feeding (chow plus 0.5% cholesterol, 10% corn oil) for 30 d increased CETP mass in plasma 3.2-fold in the cholesterol-fed rabbits (12.45 +/- 0.82 micrograms/ml) compared with controls (3.86 +/- 0.38 micrograms/ml). In the hypercholesterolemic rabbit, liver CETP mRNA levels were increased 2.8 times control mRNA levels. Actin, apo E, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase, and albumin mRNA abundances were unchanged. In contrast to the widespread tissue distribution in humans, CETP mRNA was not detected in extrahepatic tissues of either control or cholesterol-fed animals. Using a sensitive RNase protection assay, the increase in liver CETP mRNA was detectable within 3 d of beginning the high cholesterol diet. Thus, in response to the atherogenic diet there is an early increase in liver CETP mRNA, probably causing increased CETP synthesis and secretion, and increased plasma CETP. The results indicate that the CETP gene may be regulated by diet-induced changes in lipid metabolism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azoulay M., Henry I., Tata F., Weil D., Grzeschik K. H., Chaves M. E., McIntyre N., Williamson R., Humphries S. E., Junien C. The structural gene for lecithin:cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT) maps to 16q22. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 May;51(Pt 2):129–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., Dani C., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Pouyssegur J., Jeanteur P. c-myc gene is transcribed at high rate in G0-arrested fibroblasts and is post-transcriptionally regulated in response to growth factors. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):443–445. doi: 10.1038/317443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y. S., Yamin T. T., Thompson G. M., Kroon P. A. Tissue-specific expression of genes encoding apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein A-I in rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5306–5309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Jarnagin A. S., McLean J., Henzel W., Kohr W., Fielding C., Lawn R. Cloning and sequencing of human cholesteryl ester transfer protein cDNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):632–634. doi: 10.1038/327632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust R. A., Albers J. J. Synthesis and secretion of plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein by human hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. Arteriosclerosis. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):267–275. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.7.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha Y. C., Barter P. J. Differences in plasma cholesteryl ester transfer activity in sixteen vertebrate species. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1982;71(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(82)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Hybridization of oligo(dT) to RNA on nitrocellulose. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 Mar-Apr;4(2):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesler C. B., Swenson T. L., Tall A. R. Purification and characterization of a human plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2275–2282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesler C. B., Tall A. R., Swenson T. L., Weech P. K., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W. Monoclonal antibodies to the Mr 74,000 cholesteryl ester transfer protein neutralize all of the cholesteryl ester and triglyceride transfer activities in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5020–5023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon P. A., DeMartino J. A., Thompson G. M., Chao Y. S. Molecular cloning of partial cDNAs for rabbit liver apolipoprotein B and the regulation of its mRNA levels by dietary cholesterol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Tanimura M., Luo C. C., Datta S., Chan L. The apolipoprotein multigene family: biosynthesis, structure, structure-function relationships, and evolution. J Lipid Res. 1988 Mar;29(3):245–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Lee Y. C., Kao F. T., Cheung P., Chan L. Apolipoprotein E gene mapping and expression: localization of the structural gene to human chromosome 19 and expression of ApoE mRNA in lipoprotein- and non-lipoprotein-producing tissues. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3751–3756. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Zollman S., Sparkes R. S., Klisak I., Mohandas T., Drayna D., Lawn R. M. Assignment of the human gene for cholesteryl ester transfer protein to chromosome 16q12-16q21. Genomics. 1987 Nov;1(3):232–235. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. E. Free cholesterol is a potent regulator of lipid transfer protein function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12235–12241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. E., Zilversmit D. B. A plasma inhibitor of triglyceride and cholesteryl ester transfer activities. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11992–11995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima M., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M. Cloning and mRNA tissue distribution of rabbit cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Lipid Res. 1988 Dec;29(12):1643–1649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quig D. W., Zilversmit D. B. Dissociation between cholesterol secretion and plasma lipid transfer activity in rabbits. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2712–2716. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.3396808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quig D. W., Zilversmit D. B. Parallel changes in plasma cholesterol and lipid transfer activity in pregnant rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Jul;182(3):386–392. doi: 10.3181/00379727-182-42356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quig D. W., Zilversmit D. B. Plasma lipid transfer activity in rabbits: effects of dietary hyperlipidemias. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Apr;70(3):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson T. L., Simmons J. S., Hesler C. B., Bisgaier C., Tall A. R. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein is secreted by Hep G2 cells and contains asparagine-linked carbohydrate and sialic acid. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16271–16274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Green P. H., Glickman R. M., Riley J. W. Metabolic fate of chylomicron phospholipids and apoproteins in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):977–989. doi: 10.1172/JCI109564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A., Granot E., Brocia R., Tabas I., Hesler C., Williams K., Denke M. Accelerated transfer of cholesteryl esters in dyslipidemic plasma. Role of cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1217–1225. doi: 10.1172/JCI112940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefson J. H., Faust R., Albers J. J., Chait A. Secretion of a lipid transfer protein by human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5887–5890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]