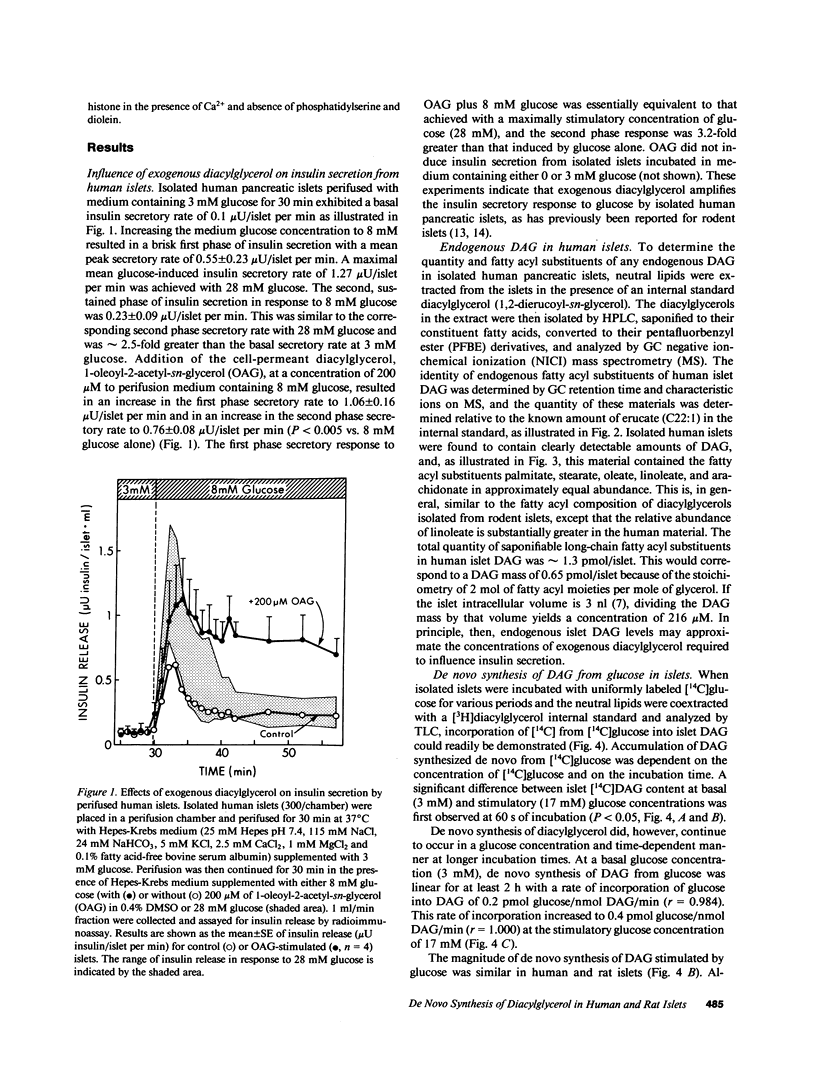
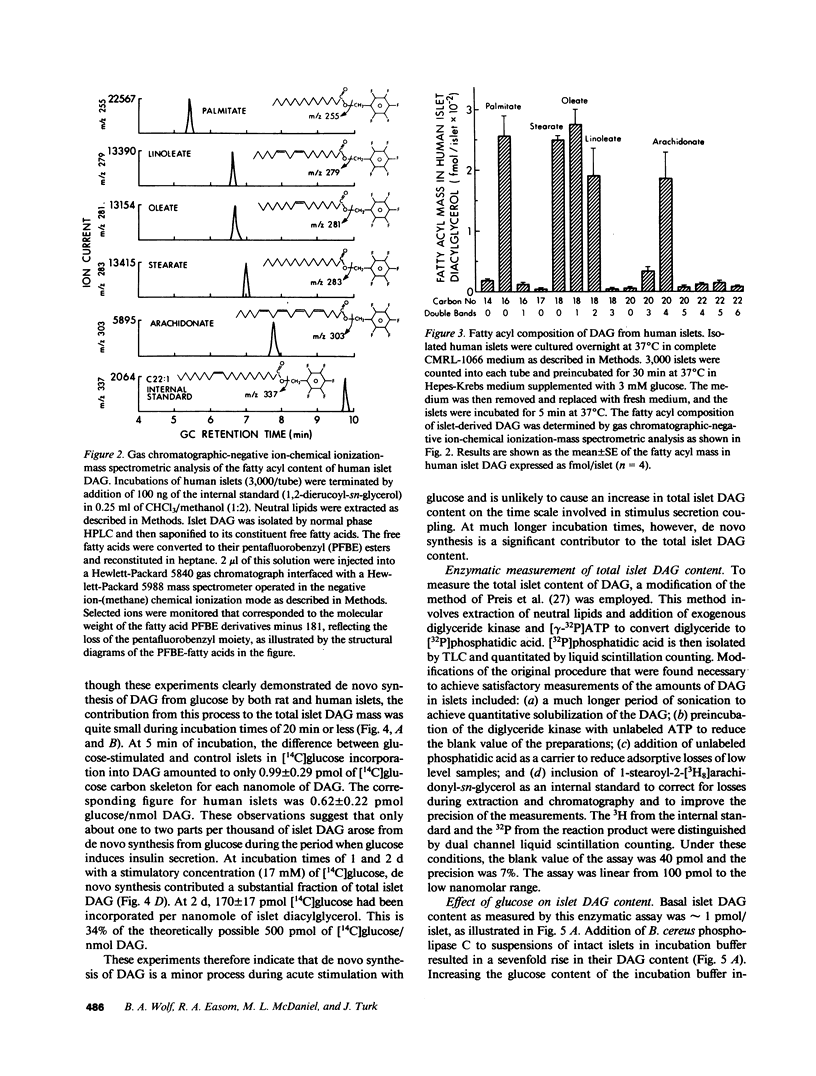
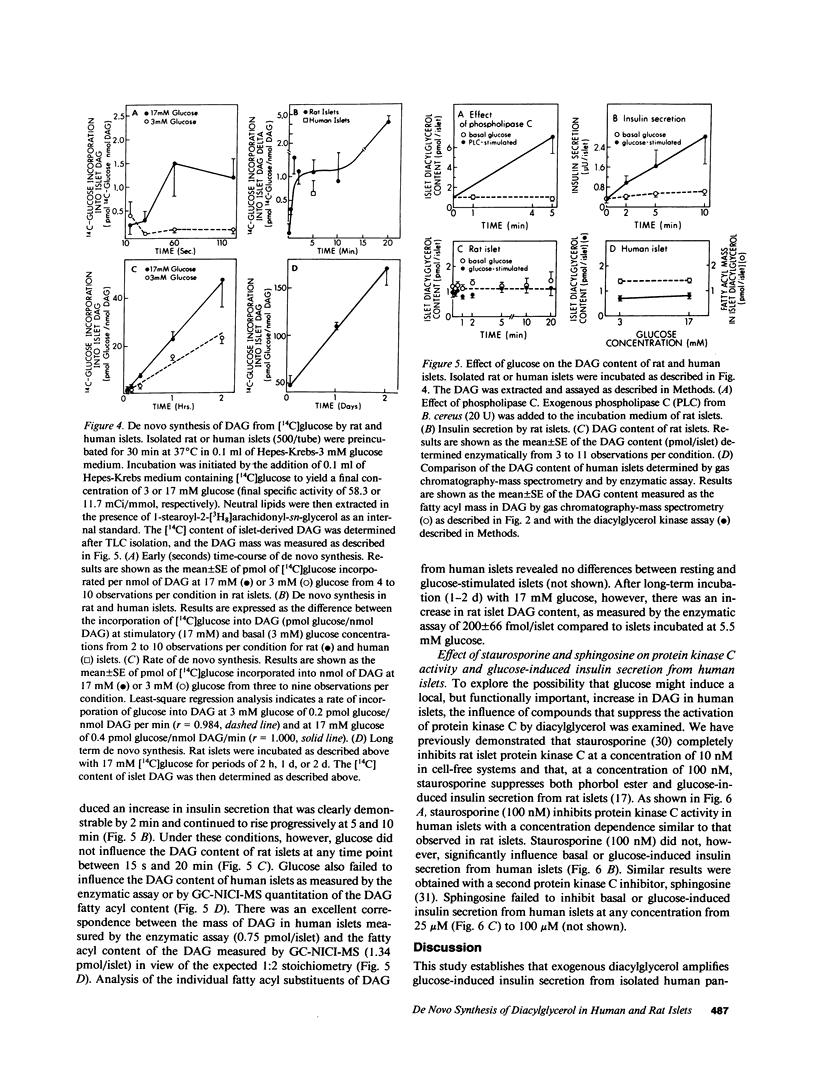
Abstract
Recent evidence has suggested that pancreatic islets isolated from rats synthesize 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol (DAG) de novo from glucose and that this process may constitute the long-sought link between the metabolism of glucose and the induction of insulin secretion. The cell-permeant diacylglycerol 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (200 microM) has been found here to amplify both the first and second phases of insulin secretion from perifused human islets. Measurements of the mass of endogenous DAG in human pancreatic islets by enzymatic and by mass spectrometric methods indicate that levels of 200 microM may be achieved under physiologic conditions. Conversion of [14C]glucose to [14C]DAG has been demonstrated here to occur within 60 s of exposure of rat and human islets to stimulatory concentrations of glucose. This process has been found to be a quantitatively minor contributor to the total islet DAG mass after acute stimulation with glucose, however, and glucose has been found not to induce a rise in total islet DAG content within 20 min of induction of insulin secretion. In contrast to the case with rodent islets, two pharmacologic inhibitors of DAG-induced activation of protein kinase C (staurosporine and sphingosine) have been found not to influence glucose-induced insulin secretion from isolated human islets. These findings indicate that de novo synthesis of DAG from glucose does not participate in acute signal-response coupling in islets.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft S. J. Glucoreceptor mechanisms and the control of insulin release and biosynthesis. Diabetologia. 1980 Jan;18(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01228295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M. Diacylglycerol stimulates phospholipase A2 from Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Small G. W., Schmitt J. D., Marasco C. J., Ishaq K., Piantadosi C. Alkyl-linked diglycerides inhibit protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerols. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. Pancreatic islets synthesize phospholipids de novo from glucose via acyl-dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M., Larkins R. G. Presence of membrane-associated phosphatidate phosphohydrolase activity in cultured islets and its stimulation by glucose. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. M. Diacylglycerols, lysolecithin, or hydrocarbons markedly alter the bilayer to hexagonal phase transition temperature of phosphatidylethanolamines. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7092–7095. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., DiMarco P. E., Barnes D. E., Sabir M. A., Larson R. E., Davis J. S., Morrison A. D. Rapid glucose-dependent increases in phosphatidic acid and phosphoinositides in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1498–1503. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goppelt-Strübe M., Pfannkuche H. J., Gemsa D., Resch K. The diacylglycerols dioctanoylglycerol and oleoylacetylglycerol enhance prostaglandin synthesis by inhibition of the lysophosphatide acyltransferase. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):773–777. doi: 10.1042/bj2470773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Greenberg C. S., Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of agonist-dependent secretion and activation of human platelets implies that protein kinase C is a necessary and common event of the signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13620–13626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeskov C. J. Mechanism of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):442–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hii C. S., Jones P. M., Persaud S. J., Howell S. L. A re-assessment of the role of protein kinase C in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):489–493. doi: 10.1042/bj2460489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. M., Stutchfield J., Howell S. L. Effects of Ca2+ and a phorbol ester on insulin secretion from islets of Langerhans permeabilised by high-voltage discharge. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 21;191(1):102–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnick R. N. 1,2-Diacylglycerols but not phorbol esters stimulate sphingomyelin hydrolysis in GH3 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16759–16762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Walker M. M., Fink C. J. Perifusion of isolated rat islets in vitro. Participation of the microtubular system in the biphasic release of insulin. Diabetes. 1972 Oct;21(10):987–998. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.10.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. S., MacGregor L. C., Fluharty S. J., King G. L. Differential regulation of protein kinase C and (Na,K)-adenosine triphosphatase activities by elevated glucose levels in retinal capillary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):90–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI113889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Malaisse W. J., Dunlop M. E., Mathias P. C., Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A. Stimulation of protein kinase C and insulin release by 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-glycerol. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 15;149(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Hutton J. C. Insulin release: the fuel hypothesis. Metabolism. 1979 Apr;28(4):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M., Ghosh A. K., Meglasson M. D., Prentki M., June V., von Allman D. Metabolic concomitants in pure, pancreatic beta cells during glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14057–14061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel M. L., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., Lacy P. E. A subcellular fractionation approach for studying insulin release mechanisms and calcium metabolism in islets of Langerhans. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:182–200. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Matschinsky F. M. Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(3-4):163–214. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Exogenous arachidonic acid promotes insulin release from intact or permeabilized rat islets by dual mechanisms. Putative activation of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C. Diabetes. 1988 Nov;37(11):1453–1469. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.11.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Perspectives in diabetes. Is protein kinase C required for physiologic insulin release? Diabetes. 1988 Jan;37(1):3–7. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Akiyama N., Hashimoto H., Ogawa K., Satake T. Alteration of 1,2-diacylglycerol content in myocardium from diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Sep;37(9):1168–1172. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.9.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persaud S. J., Jones P. M., Sugden D., Howell S. L. Translocation of protein kinase C in rat islets of Langerhans. Effects of a phorbol ester, carbachol and glucose. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):80–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter-Riesch B., Fathi M., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Glucose and carbachol generate 1,2-diacylglycerols by different mechanisms in pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI113430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer M. A., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr Insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90579-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J. E., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:294–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo D., Kozody D. J., Knauf P. A. Synthetic diacylglycerols trigger an increase of intracellular free calcium in promyelocytic HL60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):776–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricordi C., Lacy P. E., Finke E. H., Olack B. J., Scharp D. W. Automated method for isolation of human pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1988 Apr;37(4):413–420. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.4.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Jones P. M., Howell S. L. The effects of polymyxin B, a protein kinase C inhibitor, on insulin secretion from intact and permeabilized islets of Langerhans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):1001–1006. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söling H. D., Machado-DeDomenech E., Kleineke J., Fest W. Early effects of beta-adrenergic and muscarinic secretagogues on lipid and phospholipid metabolism in guinea pig parotid acinar cells. Stimulation of 2,3-sn-diacylglycerol formation by isoproterenol. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16786–16792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., McDaniel M. L. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. II. The effects of glucose and of inhibitors of arachidonate metabolism on insulin secretion and metabolite synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., McDaniel M. L. The role of phospholipid-derived mediators including arachidonic acid, its metabolites, and inositoltrisphosphate and of intracellular Ca2+ in glucose-induced insulin secretion by pancreatic islets. Prog Lipid Res. 1987;26(2):125–181. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(87)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara E., Tamarit-Rodriguez J. Glucose stimulation of insulin secretion in islets of fed and starved rats and its dependence on lipid metabolism. Metabolism. 1986 Mar;35(3):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Easom R. A., Hughes J. H., McDaniel M. L., Turk J. Secretagogue-induced diacylglycerol accumulation in isolated pancreatic islets. Mass spectrometric characterization of the fatty acyl content indicates multiple mechanisms of generation. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4291–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Turk J., Sherman W. R., McDaniel M. L. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization by arachidonic acid. Comparison with myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in isolated pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3501–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Dunne M. J., Peter-Riesch B., Bruzzone R., Pozzan T., Petersen O. H. Activators of protein kinase C depolarize insulin-secreting cells by closing K+ channels. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2443–2449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamatani T., Chiba T., Kadowaki S., Hishikawa R., Yamaguchi A., Inui T., Fujita T., Kawazu S. Dual action of protein kinase C activation in the regulation of insulin release by muscarinic agonist from rat insulinoma cell line (RINr). Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2826–2832. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W., Brown C., Rasmussen H. Insulin secretion: combined effects of phorbol ester and A23187. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


