Abstract
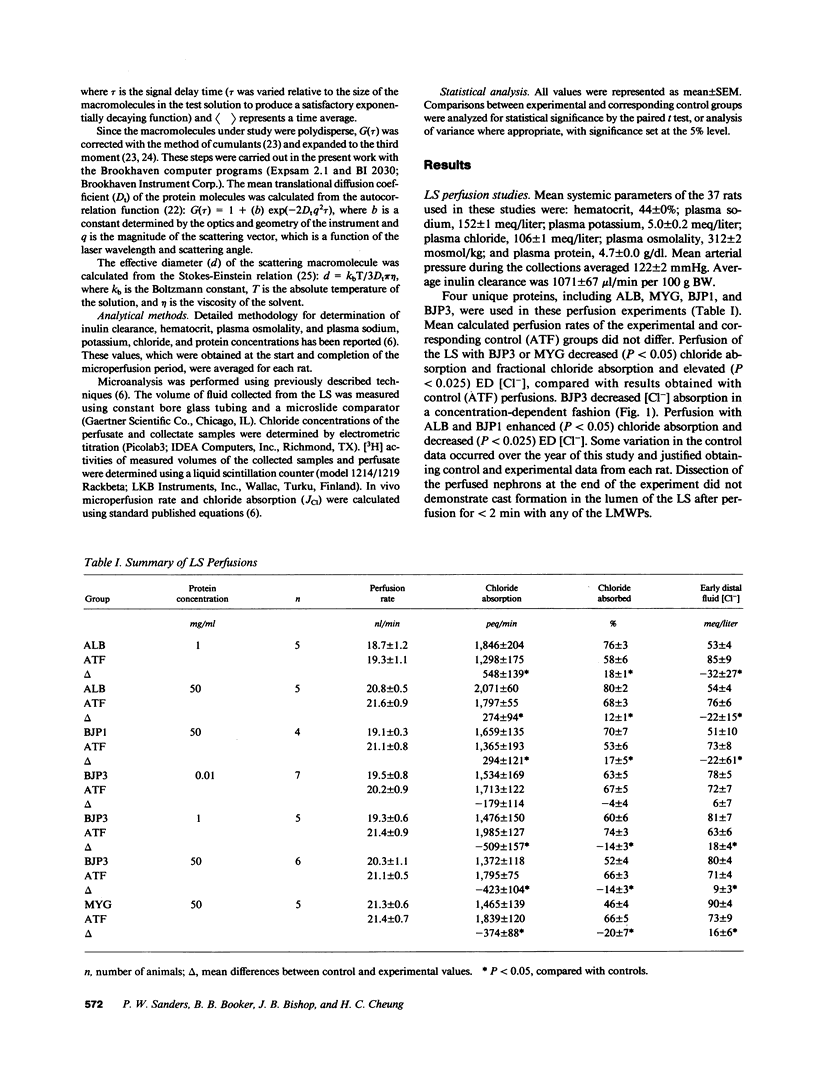
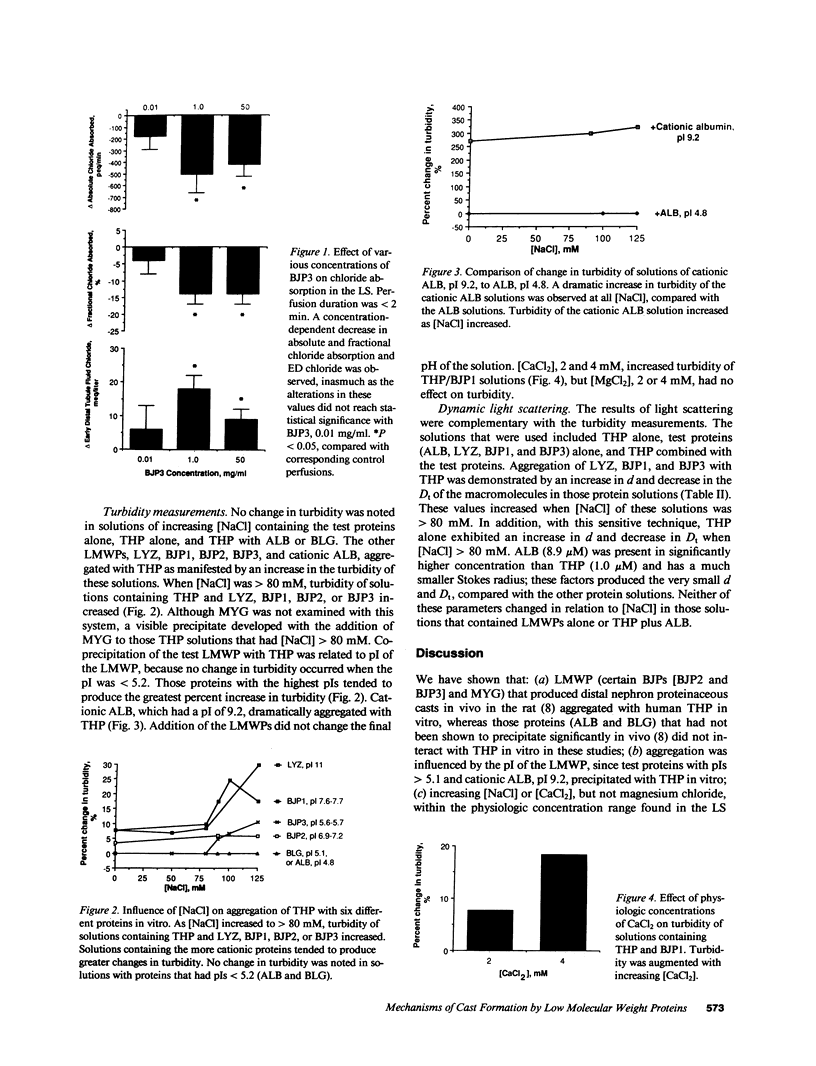
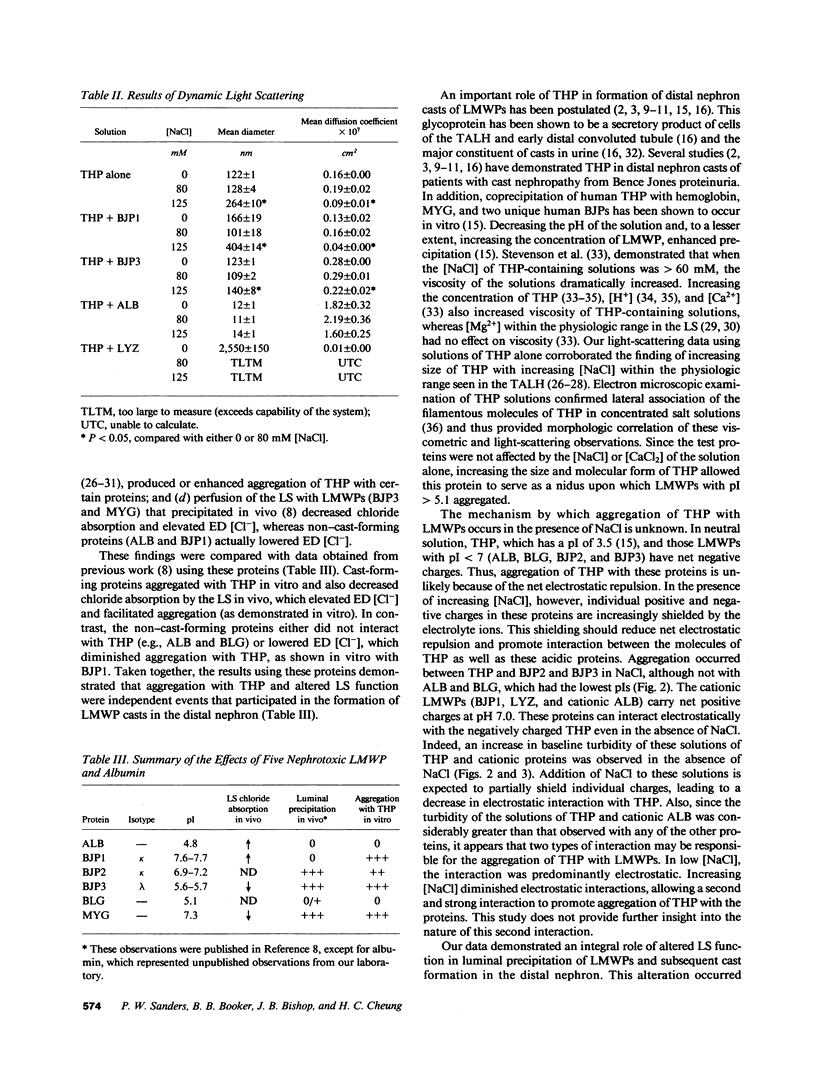
Proteinaceous cast formation in the distal nephron of the kidney from low molecular weight proteinuria is a significant, but poorly characterized, cause of renal failure. To study this phenomenon, we: (a) microperfused the loop segment (LS) of rats in vivo with artificial tubule fluid (ATF) containing four different low molecular weight proteins, 0.01-50 mg/ml, to detect alterations in LS function, and (b) examined the interaction between several proteins and Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein (THP) in vitro with turbidity and dynamic light-scattering measurements. Perfusion of the LS for less than 2 min with cast-forming proteins (Bence Jones protein [BJP3] and myoglobin) decreased chloride absorption and elevated early distal tubule fluid (ED) [Cl-], compared with results obtained with control perfusions that used ATF alone. BJP3 decreased chloride absorption in a concentration-dependent fashion. Perfusion with non-cast-forming proteins (albumin and BJP1) enhanced chloride absorption and decreased ED [Cl-]. In vitro, proteins that had isoelectric points (pI) greater than 5.1 aggregated with THP. Aggregation was enhanced with increasing [NaCl] or [CaCl2]. Albumin (pI 4.8) and beta-lactoglobulin (pI 5.1) did not coprecipitate. The molecular size of THP alone increased when [NaCl] greater than 80 mM. Thus, cast-forming proteins aggregated with THP in vitro and caused in vivo LS dysfunction, which elevated ED [Cl-], facilitating aggregation. In contrast, non-cast-forming proteins either did not interact with THP or lowered ED [Cl-], which did not provide an environment for aggregation. Altered LS function and interaction of some proteins with THP were related to different physicochemical properties of the proteins and independently contributed to the formation of proteinaceous casts in the kidney.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booker B. B., Williams R. H., Luke R. G. Effect of volume expansion and plasma chloride on function of the loop segment. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):F41–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.1.F41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTAIN C. C. The viscometric behaviour of a mucoprotein isolated from human urine. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Jun;31(3):255–265. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson F. D. The application of intensity fluctuation spectroscopy to molecular biology. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):243–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. H., Border W. A. Myeloma kidney. An immunomorphogenetic study of renal biopsies. Lab Invest. 1980 Feb;42(2):248–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Cooke C. R., Wright J. R., Humphrey R. L. Renal function in patients with multiple myeloma. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Mar;57(2):151–166. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197803000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defronzo R. A., Humphrey R. L., Wright J. R., Cooke C. R. Acute renal failure in multiple myeloma. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 May;54(3):209–223. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197505000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla J. H., Booker B. B., Luke R. G. Role of the loop segment in the urinary concentrating defect of hypercalcemia. Kidney Int. 1986 May;29(5):977–982. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbart D. R., Battilana C. A., Bhattacharya J., Lacy F. B., Jamison R. L. Transepithelial gradient and fractional delivery of chloride in thin loop of Henle. Am J Physiol. 1978 Sep;235(3):F192–F198. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.3.F192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. S., Morel-Maroger L., Méry J. P., Brouet J. C., Mignon F. Renal lesions in multiple myeloma: their relationship to associated protein abnormalities. Am J Kidney Dis. 1983 Jan;2(4):423–438. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(83)80075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg R. J., Kokko J. P. Comparison between the electrical potential profile and the chloride gradients in the thin limbs of Henle's loop in rats. Kidney Int. 1978 Nov;14(5):428–436. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Seiler M. W. Pathophysiology of Tamm-Horsfall protein. Kidney Int. 1979 Sep;16(3):279–289. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L. The renal concentrating mechanism: micropuncture studies of the renal medulla. Fed Proc. 1983 May 15;42(8):2392–2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koss M. N., Pirani C. L., Osserman E. F. Experimental Bence Jones cast nephropathy. Lab Invest. 1976 Jun;34(6):579–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTIRE K. R., POTTER M. STUDIES OF THIRTY DIFFERENT BENCE JONES PROTEIN-PRODUCING PLASMA CELL NEOPLASMS IN AN INBRED STRAIN OF MOUSE. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Oct;33:631–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J., Olbricht C., Takabatake T., Thurau K. The early phase of experimental acute renal failure. I. Intratubular pressure and obstruction. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Aug 29;370(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00581689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen E. G., Engel G. B. Factors determining the aggregation of urinary mucoprotein. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;19(4):392–396. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.4.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen E. G. The nature of urinary casts. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15(4):367–373. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., TAMM I. Direct visualization of a mucoprotein component of urine. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):135–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce A. J., Clyne D. H., Pollak V. E., Kant S. K., Foulkes E. C., Selenke W. M. Renal tubular interactions of proteins. Clin Biochem. 1980 Oct;13(5):209–215. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(80)80025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirani C. L., Silva F., D'Agati V., Chander P., Striker L. M. Renal lesions in plasma cell dyscrasias: ultrastructural observations. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987 Sep;10(3):208–221. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(87)80176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quamme G. A. Control of magnesium transport in the thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):F197–F210. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.2.F197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quamme G. A. Effect of furosemide on calcium and magnesium transport in the rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F340–F347. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Herrera G. A., Chen A., Booker B. B., Galla J. H. Differential nephrotoxicity of low molecular weight proteins including Bence Jones proteins in the perfused rat nephron in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2086–2096. doi: 10.1172/JCI113830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Herrera G. A., Galla J. H. Human Bence Jones protein toxicity in rat proximal tubule epithelium in vivo. Kidney Int. 1987 Dec;32(6):851–861. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Herrera G. A., Lott R. L., Galla J. H. Morphologic alterations of the proximal tubules in light chain-related renal disease. Kidney Int. 1988 Apr;33(4):881–889. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Volanakis J. E., Rostand S. G., Galla J. H. Human complement protein D catabolism by the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1299–1304. doi: 10.1172/JCI112434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Cleave A. J., Kent P. W. The effect of ions on the viscometric and ultracentrifugal behaviour of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Characterization and separation of an inhibitor of viral hemagglutination present in urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 May;74(1):106–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. H., Williams R. H., Galla J. H., Gottschall J. L., Rees E. D., Bhathena D., Luke R. G. Pathophysiology of acute Bence-Jones protein nephrotoxicity in the rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Aug;20(2):198–210. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirdnam P. K., Milner R. D. Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein release from rat kidney cortex slices in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Nov;67(5):529–534. doi: 10.1042/cs0670529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zager R. A., Gamelin L. M. Pathogenetic mechanisms in experimental hemoglobinuric acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):F446–F455. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.3.F446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


