Abstract
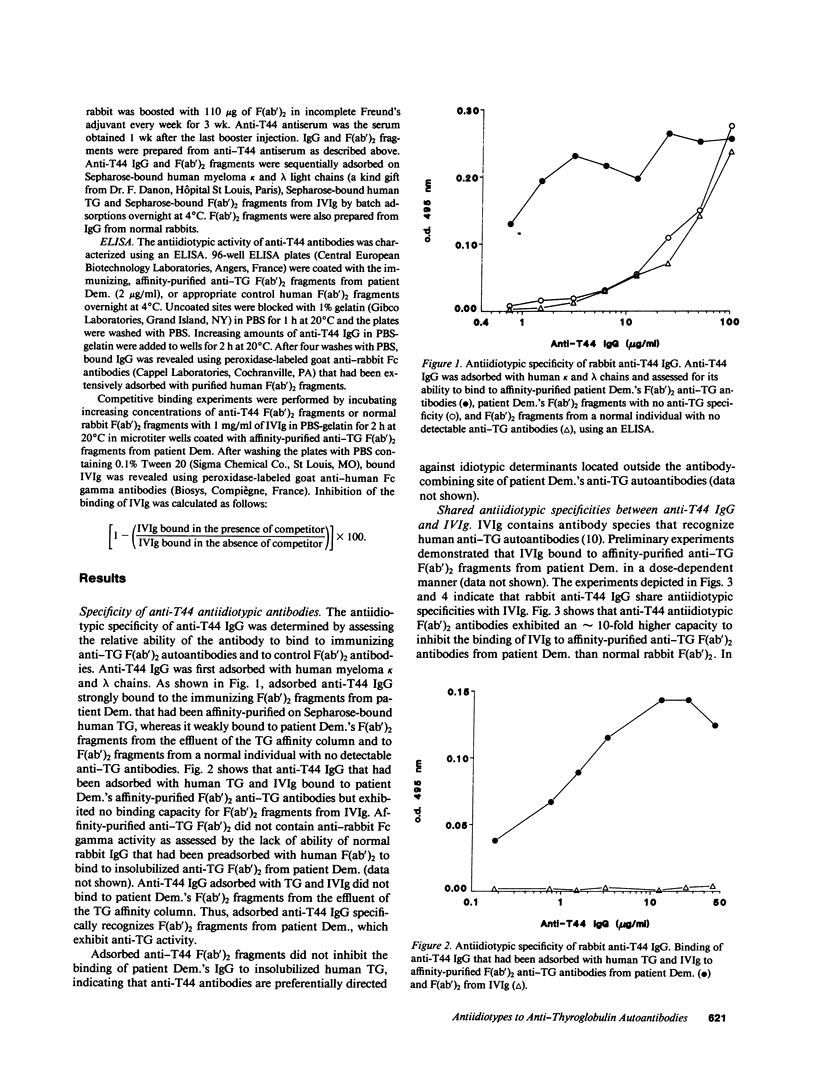
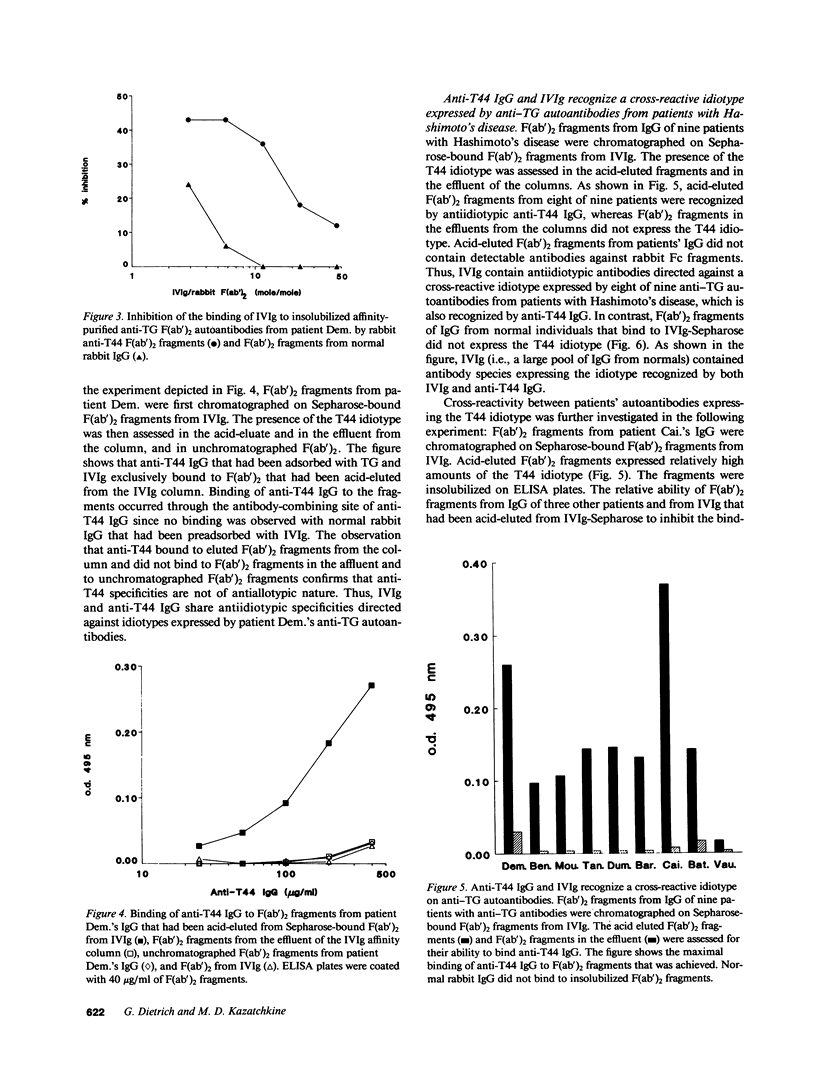
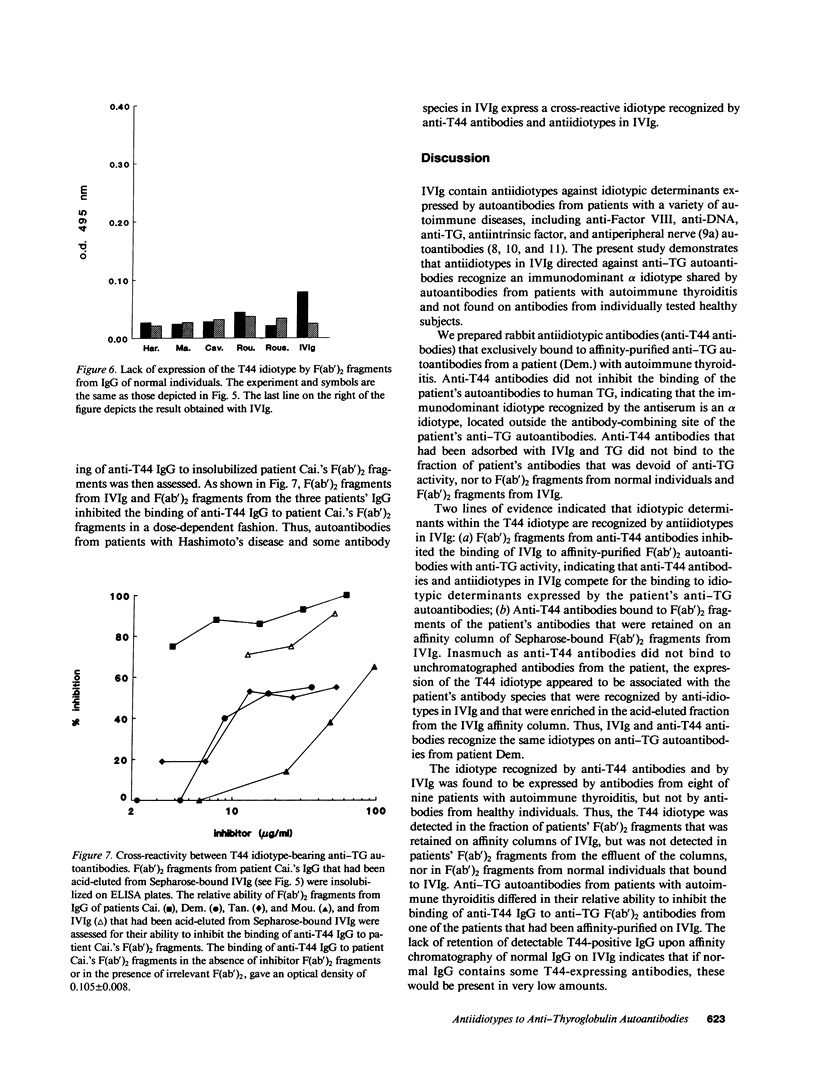
Pooled normal polyspecific IgG for therapeutic use (IVIg) contain anti-idiotypes against idiotypic determinants expressed by autoantibodies from patients with a variety of autoimmune diseases. In the present study, antiidiotypes in IVIg are shown to recognize a cross-reactive idiotype on human anti-thyroglobulin (TG) autoantibodies, that was defined by heterologous antiidiotypic antibodies, termed anti-T44 antibodies. The T44 idiotype is located outside the antibody-combining site of anti-TG autoantibodies. F(ab')2 fragments from anti-T44 antibodies inhibited the binding of IVIg to affinity-purified F(ab')2 anti-TG autoantibodies. Anti-T44 antibodies bound to F(ab')2 fragments of patients' antibodies, which were retained on an affinity column of Sepharose-bound F(ab')2 fragments from IVIg, but not to F(ab')2 fragments from the effluent of the column. The T44 idiotype was expressed on antibodies that bound to IVIg from eight of nine patients with autoimmune thyroiditis, but not on IVIg-binding Igs from healthy individuals. A small amount of the T44 idiotype was also expressed on the fraction of IVIg that bound to itself upon affinity chromatography. The T44 idiotype was cross-reactive between antibodies from patients with autoimmune thyroiditis. Thus, IVIg contain antiidiotypic antibodies directed against an immunodominant disease-associated cross-reactive alpha-idiotype of human anti-TG autoantibodies. These results support the concept that IVIg may be beneficial in selected autoimmune diseases by modulating the function of the idiotypic network.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clauvel J. P., Vainchenker W., Herrera A., Dellagi K., Vinci G., Tabilio A., Lacombe C. Treatment of pure red cell aplasia by high dose intravenous immunoglobulins. Br J Haematol. 1983 Oct;55(2):380–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfraissy J. F., Tchernia G., Laurian Y., Wallon C., Galanaud P., Dormont J. Suppressor cell function after intravenous gammaglobulin treatment in adult chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1985 Jun;60(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delves P. J., Roitt I. M. Idiotypic determinants on human thyroglobulin autoantibodies derived from the serum of Hashimoto patients and EB virus transformed cell lines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):33–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr J., Hofmann V., Kappeler U. Transient reversal of thrombocytopenia in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura by high-dose intravenous gamma globulin. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 27;306(21):1254–1258. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205273062102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdos P., Outin H., Elkharrat D., Brunel D., de Rohan-Chabot P., Raphael J. C., Goulon M., Goulon-Goeau C., Morel E. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1984 Feb 18;1(8373):406–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert B., Dighiero G., Avrameas S. Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in human sera. I. Detection, isolation and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbach P., Barandun S., d'Apuzzo V., Baumgartner C., Hirt A., Morell A., Rossi E., Schöni M., Vest M., Wagner H. P. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood. Lancet. 1981 Jun 6;1(8232):1228–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno Y., Nakajima H., Tarutani O. Interspecies cross-reactive determinants of thyroglobulin recognized by autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jul;61(1):44–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Fukumori J., Tanaka H. Evidence of unique idiotypic determinants and similar idiotypic determinants on human antithyroglobulin antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):381–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. A., Yang H. H., Bruno E., Brandt J., Briddell R., Coates T. D., Hoffman R. Treatment of antibody-mediated pure red-cell aplasia with high-dose intravenous gamma globulin. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):1004–1008. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Dietrich G., Kazatchkine M. D. Anti-idiotypes against autoantibodies in normal immunoglobulins: evidence for network regulation of human autoimmune responses. Immunol Rev. 1989 Aug;110:135–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Kazatchkine M. D. Antiidiotypes against autoantibodies in pooled normal human polyspecific Ig. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4104–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Sultan Y., Kazatchkine M. D. Anti-idiotypes against autoantibodies and alloantibodies to VIII:C (anti-haemophilic factor) are present in therapeutic polyspecific normal immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):311–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultan Y., Kazatchkine M. D., Maisonneuve P., Nydegger U. E. Anti-idiotypic suppression of autoantibodies to factor VIII (antihaemophilic factor) by high-dose intravenous gammaglobulin. Lancet. 1984 Oct 6;2(8406):765–768. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90701-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultan Y., Rossi F., Kazatchkine M. D. Recovery from anti-VIII:C (antihemophilic factor) autoimmune disease is dependent on generation of antiidiotypes against anti-VIII:C autoantibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):828–831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen M., van der Meché F. G., Speelman J. D., Weber A., Busch H. F. Plasma and gamma-globulin infusion in chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Oct;70(3):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Barton R. W., Bigazzi P. E. Anti-idiotypic immunity and autoimmunity. II. Idiotypic determinants of autoantibodies and lymphocytes in spontaneous and experimentally induced autoimmune thyroiditis. Cell Immunol. 1983 Feb 1;75(2):292–299. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Bigazzi P. E. Anti-idiotypic immunity and autoimmunity. I. In vitro and in vivo effects of anti-idiotypic antibodies to spontaneously occurring autoantibodies to rat thyroglobulin. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):187–195. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., De Baets M., Rogers J. High degree of idiotypic cross-reactivity among murine monoclonal antibodies to thyroglobulin. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2452–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


