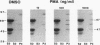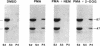Abstract
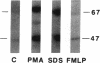
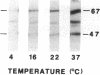
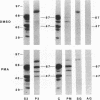
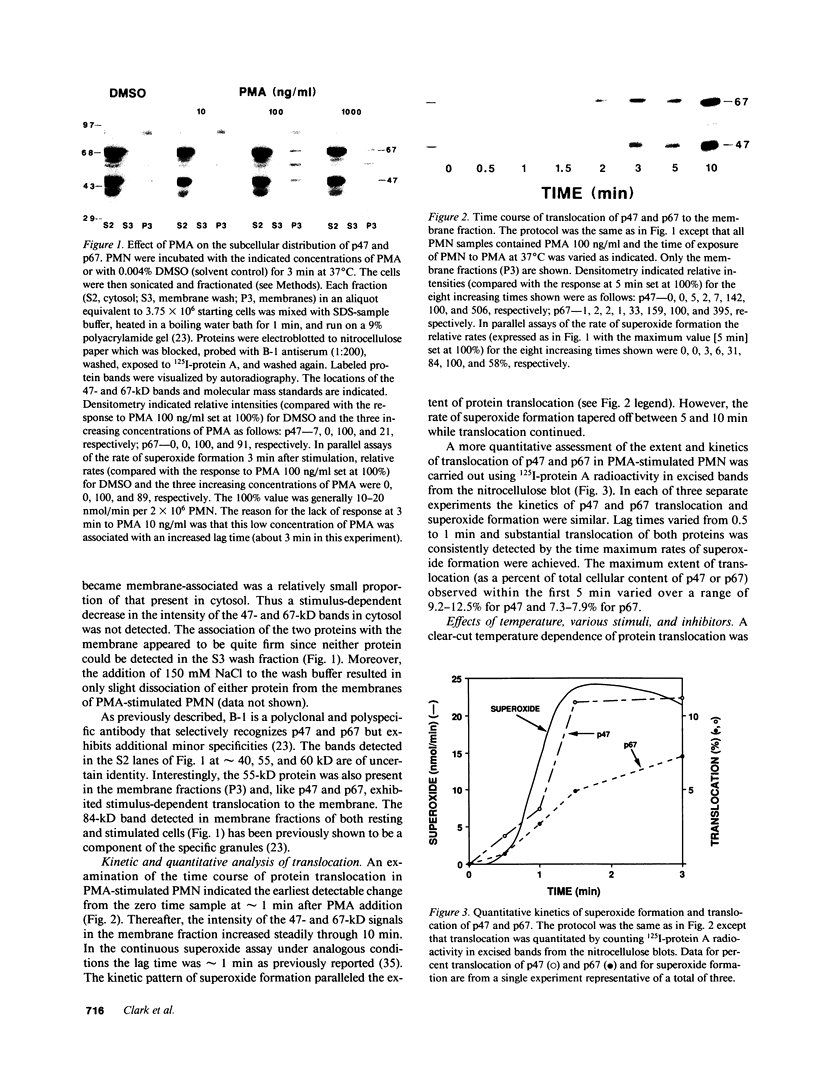
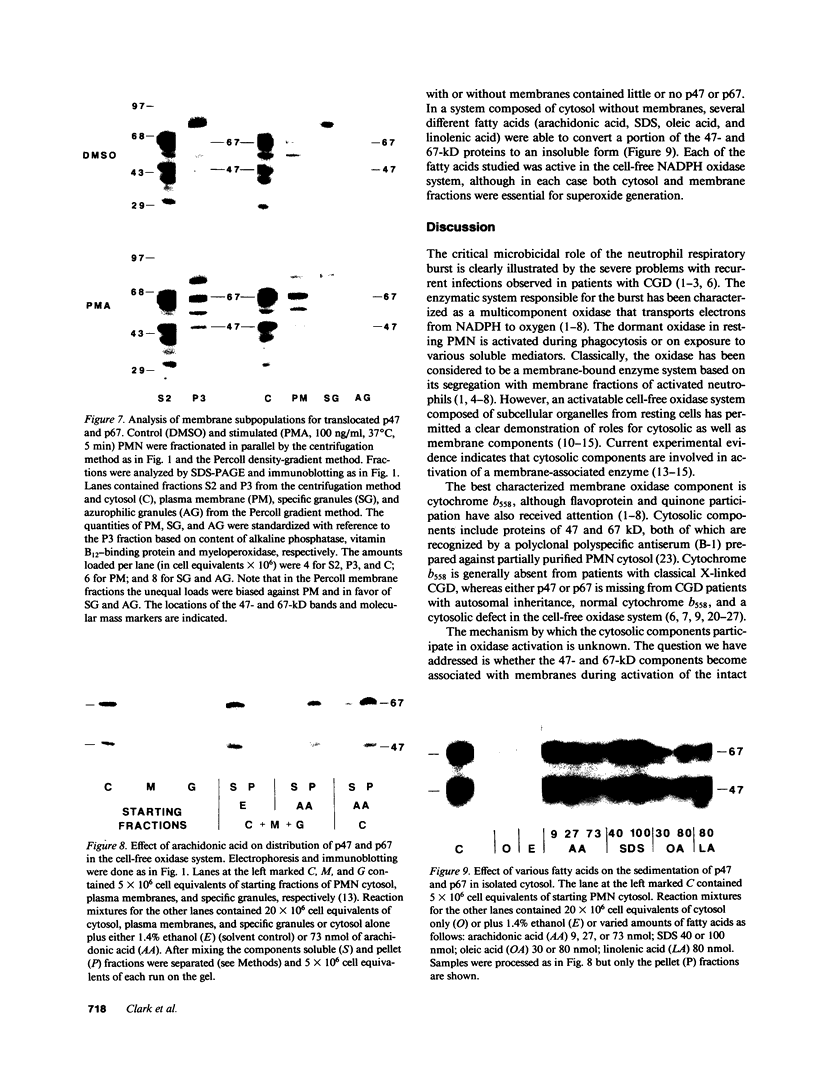
The superoxide-forming respiratory burst oxidase of human neutrophils is composed of membrane-associated catalytic components and cytosolic constituents required for oxidase activation. This study concerns the hypothesis that cytosolic oxidase components translocate to a membrane fraction when neutrophils are stimulated and the oxidase is activated. A polyclonal antiserum that recognizes two discrete cytosolic oxidase components of 47 and 67 kD was used to probe transfer blots of electrophoresed membrane and cytosol fractions of resting and stimulated neutrophils. In contrast to their strictly cytosolic localization in unstimulated cells, both proteins were detected in membrane fractions of neutrophils activated by phorbol esters and other stimuli. This translocation event was a function of stimulus concentration as well as time and temperature of exposure to the stimulus. It was inhibited by concentrations of N-ethylmaleimide that blocked superoxide formation but was unaffected by 2-deoxyglucose. There was a correlation between translocation of the cytosolic proteins and activation of the oxidase as determined by superoxide formation. Quantitative analyses suggested that approximately 10% of total cellular p47 and p67 became membrane-associated during phorbol ester activation of the oxidase. Analysis of Percoll density gradient fractions indicated that the target membrane for translocation of both proteins was the plasma membrane rather than membranes of either specific or azurophilic granules. In the cell-free oxidase system arachidonate-dependent but membrane-independent precipitation of the cytosolic oxidase proteins was demonstrated. The data show that activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in stimulated human neutrophils is closely associated with translocation of the 47- and 67-kD cytosolic oxidase components to the plasma membrane. We suggest that this translocation event is important in oxidase activation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. A., Albert K. A., Keum M. M., Wang J. K., Greengard P., Cohn Z. A. Stimulus-dependent myristoylation of a major substrate for protein kinase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):362–364. doi: 10.1038/332362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aderem A. A., Marratta D. E., Cohn Z. A. Interferon gamma induces the myristoylation of a 48-kDa protein in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6310–6313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akard L. P., English D., Gabig T. G. Rapid deactivation of NADPH oxidase in neutrophils: continuous replacement by newly activated enzyme sustains the respiratory burst. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):322–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kuver R., Curnutte J. T. Kinetics of activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in a fully soluble system from human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1713–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. The respiratory burst oxidase. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):201–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellavite P. The superoxide-forming enzymatic system of phagocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1988;4(4):225–261. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(88)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borregaard N., Heiple J. M., Simons E. R., Clark R. A. Subcellular localization of the b-cytochrome component of the human neutrophil microbicidal oxidase: translocation during activation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):52–61. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Pick E. Activation of NADPH-dependent superoxide production in a cell-free system by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13539–13545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell S. E., McCall C. E., Hendricks C. L., Leone P. A., Bass D. A., McPhail L. C. Coregulation of NADPH oxidase activation and phosphorylation of a 48-kD protein(s) by a cytosolic factor defective in autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1485–1496. doi: 10.1172/JCI113480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Leidal K. G., Pearson D. W., Nauseef W. M. NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils. Subcellular localization and characterization of an arachidonate-activatable superoxide-generating system. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4065–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Malech H. L., Gallin J. I., Nunoi H., Volpp B. D., Pearson D. W., Nauseef W. M., Curnutte J. T. Genetic variants of chronic granulomatous disease: prevalence of deficiencies of two cytosolic components of the NADPH oxidase system. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 7;321(10):647–652. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909073211005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide production by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. The effects of N-ethyl maleimide, divalent cations; and glycolytic and mitochondrial inhibitors on the activation of the superoxide generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1088–1096. doi: 10.1172/JCI109008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Activation of human neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced (triphosphopyridine nucleotide, reduced) oxidase by arachidonic acid in a cell-free system. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1740–1743. doi: 10.1172/JCI111885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Berkow R. L., Roberts R. L., Shurin S. B., Scott P. J. Chronic granulomatous disease due to a defect in the cytosolic factor required for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):606–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI113360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Classification of chronic granulomatous disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Kuver R., Scott P. J. Activation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase in a cell-free system. Partial purification of components and characterization of the activation process. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5563–5569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Brown R., Jesaitis A. J., Parkos C. A. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):717–720. doi: 10.1038/327717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doussiere J., Pilloud M. C., Vignais P. V. Activation of bovine neutrophil oxidase in a cell free system. GTP-dependent formation of a complex between a cytosolic factor and a membrane protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):993–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., English D., Akard L. P., Schell M. J. Regulation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase activation in a cell-free system by guanine nucleotides and fluoride. Evidence for participation of a pertussis and cholera toxin-insensitive G protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1685–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth P. G., Shrimpton C. F., Segal A. W. Localization of the 47 kDa phosphoprotein involved in the respiratory-burst NADPH oxidase of phagocytic cells. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):243–248. doi: 10.1042/bj2600243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakinuma K., Fukuhara Y., Kaneda M. The respiratory burst oxidase of neutrophils. Separation of an FAD enzyme and its characterization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12316–12322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., Verhoeven A. J., van der Bend R. L., Weening R. S., Roos D. Purified protein kinase C phosphorylates a 47-kDa protein in control neutrophil cytoplasts but not in neutrophil cytoplasts from patients with the autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2352–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T. Neutrophils and host defense. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):127–142. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax K. J., Leto T. L., Nunoi H., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Recombinant 47-kilodalton cytosol factor restores NADPH oxidase in chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):409–412. doi: 10.1126/science.2547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malech H. L., Gallin J. I. Current concepts: immunology. Neutrophils in human diseases. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):687–694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert M., Glass G. A., Babior B. M. Respiratory burst oxidase from human neutrophils: purification and some properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3144–3148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A. Depolarization blunts the oxidative burst of human neutrophils. Parallel effects of monoclonal antibodies, depolarizing buffers, and glycolytic inhibitors. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3928–3935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Shirley P. S., Clayton C. C., Snyderman R. Activation of the respiratory burst enzyme from human neutrophils in a cell-free system. Evidence for a soluble cofactor. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI111884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauseef W. M., Metcalf J. A., Root R. K. Role of myeloperoxidase in the respiratory burst of human neutrophils. Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):483–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoi H., Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Two forms of autosomal chronic granulomatous disease lack distinct neutrophil cytosol factors. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1298–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.2848319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Curnutte J. T., Roberts R. L., Babior B. M. Relationship of protein phosphorylation to the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Defects in the phosphorylation of a group of closely related 48-kDa proteins in two forms of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6777–6782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Allen R. A., Cochrane C. G., Jesaitis A. J. Purified cytochrome b from human granulocyte plasma membrane is comprised of two polypeptides with relative molecular weights of 91,000 and 22,000. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):732–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI113128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Allen R. A., Cochrane C. G., Jesaitis A. J. The quaternary structure of the plasma membrane b-type cytochrome of human granulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 20;932(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(88)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Dinauer M. C., Walker L. E., Allen R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Orkin S. H. Primary structure and unique expression of the 22-kilodalton light chain of human neutrophil cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petreccia D. C., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A. Respiratory burst of normal human eosinophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Apr;41(4):283–288. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.4.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W. Absence of both cytochrome b-245 subunits from neutrophils in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):88–91. doi: 10.1038/326088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Heyworth P. G., Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M. Stimulated neutrophils from patients with autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease fail to phosphorylate a Mr-44,000 protein. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):547–549. doi: 10.1038/316547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W. The molecular and cellular pathology of chronic granulomatous disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;18(5):433–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1988.tb01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Fatty-acid-induced activation of NADPH oxidase in plasma membranes of human neutrophils depends on neutrophil cytosol and is potentiated by stable guanine nucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):563–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'ag D., Pick E. Macrophage-derived superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase in an amphiphile-activated, cell-free system; partial purification of the cytosolic component and evidence that it may contain the NADPH binding site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 29;952(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Affinity labeling of the cytosolic and membrane components of the respiratory burst oxidase by the 2',3'-dialdehyde derivative of NADPH. Evidence for a cytosolic location of the nucleotide-binding site in the resting cell. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1958–1962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Borregaard N., Simons E., Wright J. Chronic granulomatous disease: a syndrome of phagocyte oxidase deficiencies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Sep;62(5):286–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teahan C., Rowe P., Parker P., Totty N., Segal A. W. The X-linked chronic granulomatous disease gene codes for the beta-chain of cytochrome b-245. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):720–721. doi: 10.1038/327720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umei T., Takeshige K., Minakami S. NADPH binding component of neutrophil superoxide-generating oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5229–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpp B. D., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A. Two cytosolic neutrophil oxidase components absent in autosomal chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1295–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.2848318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpp B. D., Nauseef W. M., Donelson J. E., Moser D. R., Clark R. A. Cloning of the cDNA and functional expression of the 47-kilodalton cytosolic component of human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitin J. C., Cohen H. J. Disorders of respiratory burst termination. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]