Abstract
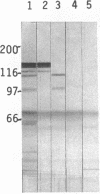
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD) is a rare blistering skin disease characterized by basement membrane zone deposition of IgA. This study identifies a tissue antigen detected by patient serum and then isolates the autoantibody using epidermis and protein bands blotted on nitrocellulose as immunoabsorbents. Sera from 10 patients (9 with cutaneous disease and 1 with cicatrizing conjunctivitis) were evaluated. Indirect immunofluorescence revealed an IgA anti-basement membrane antibody in 6 of 10 sera with monkey esophagus substrate and 9 of 10 sera with human epidermal substrate. Immunoblotting was performed on epidermal and dermal extracts prepared from skin separated at the basement membrane zone with either sodium chloride or EDTA. Saline-separated skin expressed a 97-kD band in dermal extract alone that was recognized by 4 of 10 sera. EDTA-separated skin expressed the 97-kD band in both epidermal (4 of 10 sera) and dermal (6 of 10 sera) extract. Immunoabsorption of positive sera with epidermis purified an IgA antibody that reacted uniquely with the 97-kD band. In addition, IgA antibody bound to nitrocellulose was eluted from the 97-kD band and found to uniquely bind basement membrane zone. It is likely that the 97-kD protein identified by these techniques is responsible for basement membrane binding of IgA in LABD.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker K. W., Habowsky J. E. EDTA separation and ATPase Langerhans cell staining in the mouse epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Feb;80(2):104–107. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12531712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhogal B., Wojnarowska F., Marsden R. A., Das A., Black M. M., McKee P. H. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis of adults and children: an immunoelectron microscopic study. Br J Dermatol. 1987 Sep;117(3):289–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1987.tb04134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon W. R., Briggaman R. A., Inman A. O., 3rd, Queen L. L., Wheeler C. E. Differentiating anti-lamina lucida and anti-sublamina densa anti-BMZ antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence on 1.0 M sodium chloride-separated skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Feb;82(2):139–144. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. P. The pathogenesis of dermatitis herpetiformis: recent advances. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987 Jun;16(6):1129–1144. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70148-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadunce D. P., Meyer L. J., Zone J. J. IgA class antibodies in dermatitis herpetiformis: reaction with tissue antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Aug;93(2):253–258. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Strober W. The pathogenesis of dermatitis herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Feb;70(2):63–75. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labib R. S., Anhalt G. J., Patel H. P., Mutasim D. F., Diaz L. A. Molecular heterogeneity of the bullous pemphigoid antigens as detected by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1231–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley T. J., Strober W., Yaoita H., Katz S. I. Small intestinal biopsies and HLA types in dermatitis herpetiformis patients with granular and linear IgA skin deposits. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jan;74(1):9–12. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. N., Haffenden G. P., Ring N. P., McMinn R. M., Sidgwick A., Mowbray J. F., Unsworth D. J., Holborow E. J., Blenkinsopp W. K., Swain A. F. Linear IgA disease in adults. Br J Dermatol. 1982 Sep;107(3):301–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer L. J., Carioto L., Zone J. J. Dermatitis herpetiformis: extraction of intact IgA from granular deposits in dermal papillae. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 May;88(5):559–563. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost T. T., Maize J. C., Ahmed A. R., Strauss J. S., Dobson R. L. Unusual subepidermal bullous diseases with immunologic features of bullous pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol. 1979 Feb;115(2):156–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Yuspa S. H., Shevach E. M., Katz S. I. Characterization of bullous pemphigoid antigen: a unique basement membrane protein of stratified squamous epithelia. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Woodley D. T., Katz S. I. Identification and partial characterization of pemphigoid antigen extracted from normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jan;82(1):108–111. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Hönigsmann H., Holubar K., Wolff K. Ultrastructural localization of immunoglobulins in skin of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Oct;67(4):507–512. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12664537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Briggaman R. A., O'Keefe E. J., Inman A. O., Queen L. L., Gammon W. R. Identification of the skin basement-membrane autoantigen in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 19;310(16):1007–1013. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404193101602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Burgeson R. E., Lunstrum G., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Reese M. J., Briggaman R. A. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen is the globular carboxyl terminus of type VII procollagen. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):683–687. doi: 10.1172/JCI113373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D., Sauder D., Talley M. J., Silver M., Grotendorst G., Qwarnstrom E. Localization of basement membrane components after dermal-epidermal junction separation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Aug;81(2):149–153. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita H., Katz S. I. Immunoelectronmicroscopic localization of IgA in skin of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Oct;67(4):502–506. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12664534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]