Abstract
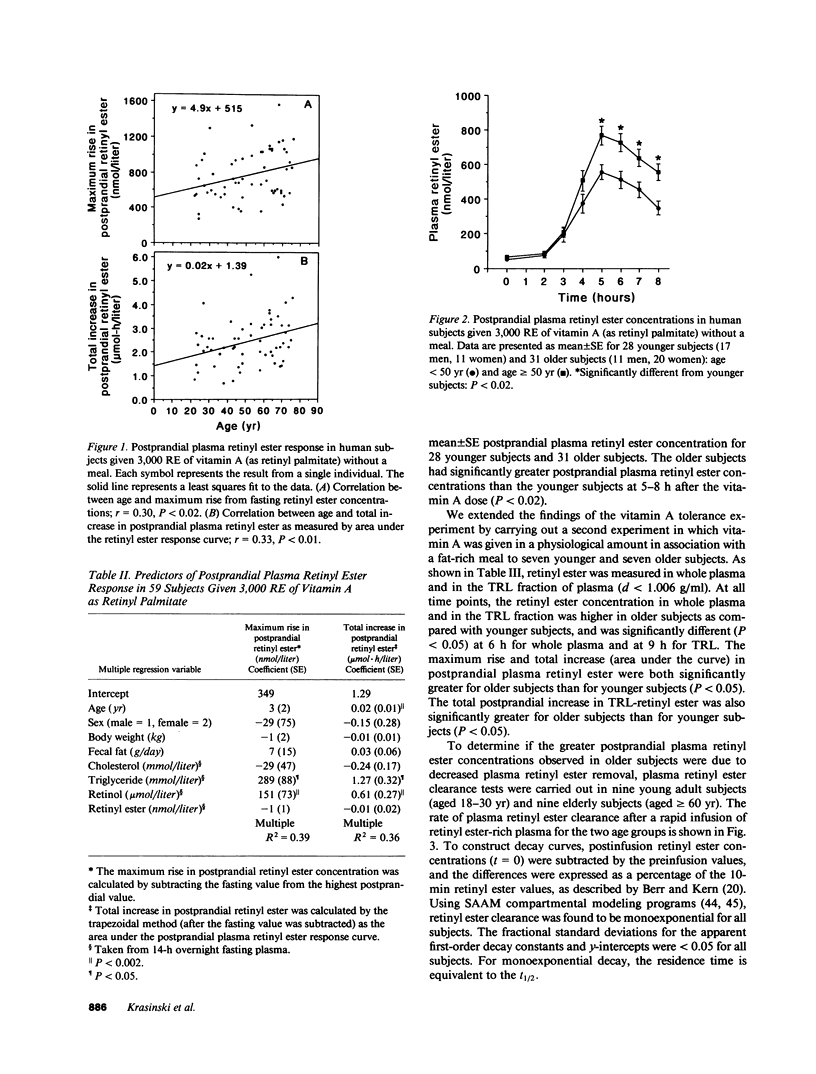
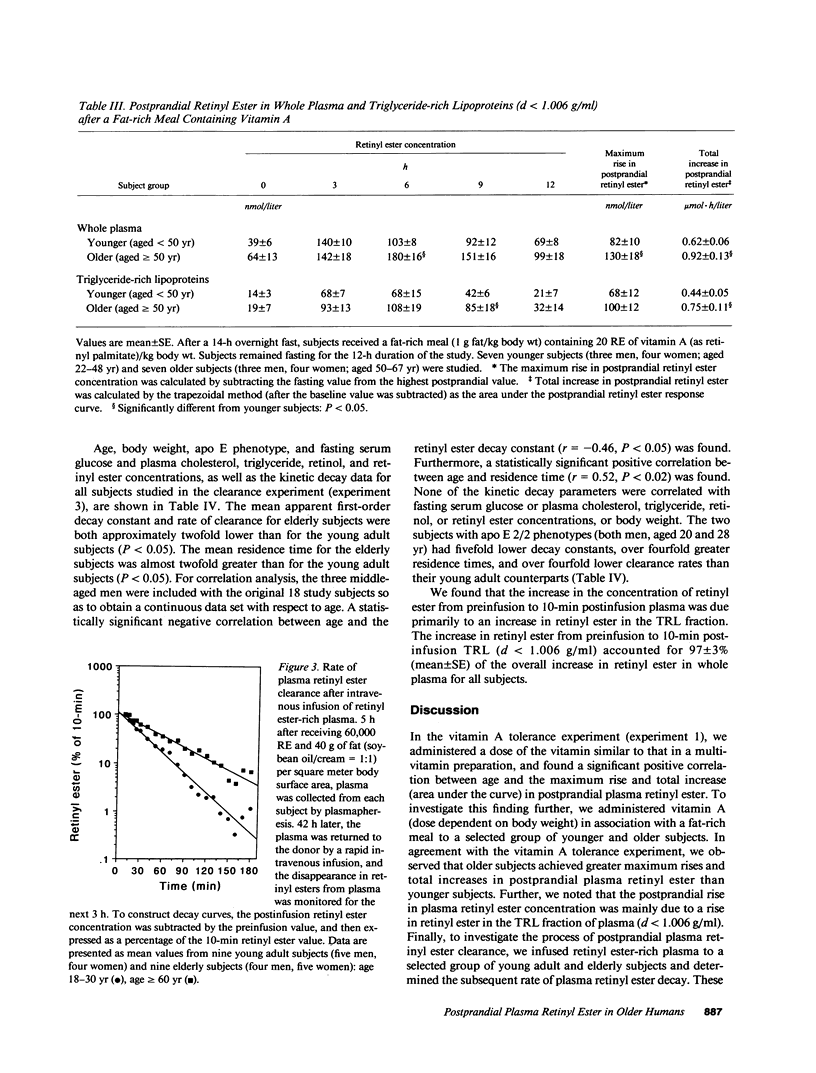
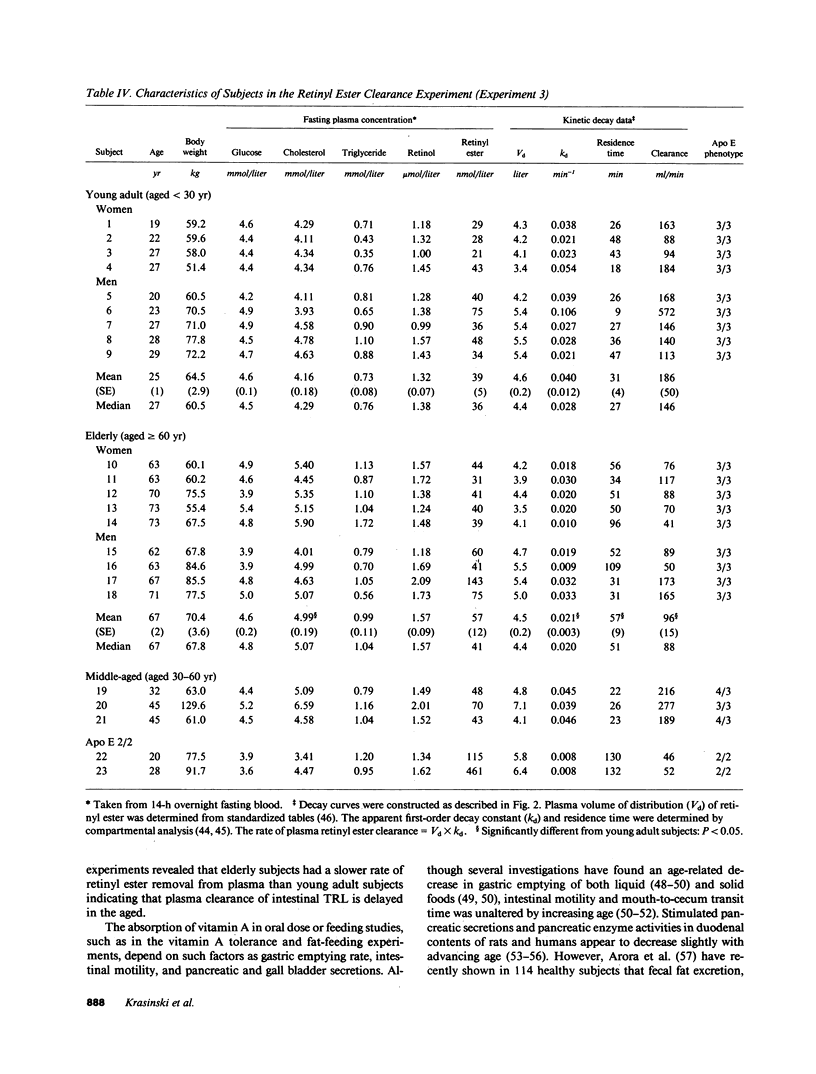
Postprandial vitamin A and intestinal lipoprotein metabolism was studied in 86 healthy men and women, aged 19-76 yr. Three independent experiments were carried out. In the first experiment, a supplement dose of vitamin A (3,000 retinol equivalents [RE]) was given without a meal to 59 subjects, aged 22-76 yr. In the second experiment, 20 RE/kg body wt was given with a fat-rich meal (1 g fat/kg body wt) to seven younger subjects (aged less than 50 yr) and seven older subjects (aged greater than or equal to 50 yr). In both experiments, postprandial plasma retinyl ester response increased significantly with advancing age (P less than 0.05). In the third experiment, retinyl ester-rich plasma was infused intravenously into nine young adult subjects (aged 18-30 yr) and nine elderly subjects (aged greater than or equal to 60 yr), and the rate of retinyl ester disappearance from plasma during the subsequent 3 h was determined. Mean (+/- SE) plasma retinyl ester residence time was 31 +/- 4 min in the young adult subjects vs. 57 +/- 8 min in the elderly subjects (P less than 0.05). These data are consistent with the concept that increased postprandial plasma retinyl ester concentrations in older subjects are due to delayed plasma clearance of retinyl esters in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of intestinal origin.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arora S., Kassarjian Z., Krasinski S. D., Croffey B., Kaplan M. M., Russell R. M. Effect of age on tests of intestinal and hepatic function in healthy humans. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jun;96(6):1560–1565. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90527-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTHELMAI W., CZOK R. [Enzymatic determinations of glucose in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid and urine]. Klin Wochenschr. 1962 Jun 1;40:585–589. doi: 10.1007/BF01478633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN M., SHAHN E., WEISS M. F. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models: a mathematical formalism for digital computers. Biophys J. 1962 May;2:275–287. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86855-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham A. D., Dingle J. T., Lucy J. A. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 9. Penetration of lipid monolayers by compounds in the vitamin A series. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj0900133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankson D. D., Russell R. M., Sadowski J. A. Determination of retinyl esters and retinol in serum or plasma by normal-phase liquid chromatography: method and applications. Clin Chem. 1986 Jan;32(1 Pt 1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartos V., Groh J. The effect of repeated stimulation of the pancreas on the pancreatic secretion in young and aged men. Gerontol Clin (Basel) 1969;11(1):56–62. doi: 10.1159/000245215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berr F., Kern F., Jr Plasma clearance of chylomicrons labeled with retinyl palmitate in healthy human subjects. J Lipid Res. 1984 Aug;25(8):805–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenninkmeijer B. J., Stuyt P. M., Demacker P. N., Stalenhoef A. F., van 't Laar A. Catabolism of chylomicron remnants in normolipidemic subjects in relation to the apoprotein E phenotype. J Lipid Res. 1987 Apr;28(4):361–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodows R. G., Campbell R. G. Effect of age on post-heparin lipase. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 9;287(19):969–970. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211092871907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrella M., Cooper A. D. High affinity binding of chylomicron remnants to rat liver plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):338–342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. S., McNamara J. R., Cohn S. D., Ordovas J. M., Schaefer E. J. Plasma apolipoprotein changes in the triglyceride-rich lipoprotein fraction of human subjects fed a fat-rich meal. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jul;29(7):925–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. S., McNamara J. R., Cohn S. D., Ordovas J. M., Schaefer E. J. Postprandial plasma lipoprotein changes in human subjects of different ages. J Lipid Res. 1988 Apr;29(4):469–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. S., McNamara J. R., Krasinski S. D., Russell R. M., Schaefer E. J. Role of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins from the liver and intestine in the etiology of postprandial peaks in plasma triglyceride concentration. Metabolism. 1989 May;38(5):484–490. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagher F. J., Lyons J. H., Finlayson D. C., Shamsai J., Moore F. D. Blood volume measurement: a critical study prediction of normal values: controlled measurement of sequential changes: choice of a bedside method. Adv Surg. 1965;1:69–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle J. T., Fell H. B., Goodman D. S. The effect of retinol and of retinol-binding protein on embryonic skeletal tissue in organ culture. J Cell Sci. 1972 Sep;11(2):393–402. doi: 10.1242/jcs.11.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. A., Triggs E. J., Cheung M., Broe G. A., Creasey H. Gastric emptying rate in the elderly: implications for drug therapy. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1981 May;29(5):201–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1981.tb01766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikry M. E. Exocrine pancreatic functions in the aged. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1968 Apr;16(4):463–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1968.tb02827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming B. B., Barrows C. H., Jr The influence of aging on intestinal absorption of vitamins A and D by the rat. Exp Gerontol. 1982;17(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(82)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Albers J. J., Bierman E. L. Uptake of chylomicron remnants causes cholesterol accumulation in cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 26;663(1):336–349. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame B., Jackson C. E., Reynolds W. A., Umphrey J. E. Hypercalcemia and skeletal effects in chronic hypervitaminosis A. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):44–48. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. W., HUANG H. S., SHIRATORI T. TISSUE DISTRIBUTION AND METABOLISM OF NEWLY ABSORBED VITAMIN A IN THE RAT. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:390–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry P. J., Hunt W. C., Bandrofchak J. L., VanderJagt D., Goodwin J. S. Vitamin A intake and plasma retinol levels in healthy elderly men and women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987 Dec;46(6):989–994. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/46.6.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Blomstrand R., Werner B., Huang H. S., Shiratori T. The intestinal absorption and metabolism of vitamin A and beta-carotene in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1615–1623. doi: 10.1172/JCI105468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: defective metabolism of an abnormal apolipoprotein E. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.7455696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Chao Y., Windler E. E., Kotite L., Guo L. S. Isoprotein specificity in the hepatic uptake of apolipoprotein E and the pathogenesis of familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Bierman E. L. Delayed clearance of chylomicron remnants following vitamin-A-containing oral fat loads in broad-beta disease (type III hyperlipoproteinemia). Metabolism. 1976 Jul;25(7):777–801. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks H. F., Blaner W. S., Wennekers H. M., Piantedosi R., Brouwer A., de Leeuw A. M., Goodman D. S., Knook D. L. Distributions of retinoids, retinoid-binding proteins and related parameters in different types of liver cells isolated from young and old rats. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander D., Dadufalza V. D. Aging-associated pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in the unanesthetized rat. Gerontology. 1984;30(4):218–222. doi: 10.1159/000212635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander D., Morgan D. Aging: its influence on vitamin A intestinal absorption in vivo by the rat. Exp Gerontol. 1979;14(6):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(79)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppner K., Phillips W. E., Murray T. K., Campbell J. S. Survey of liver vitamin A stores of Canadians. Can Med Assoc J. 1968 Nov 23;99(20):983–986. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Maddern G. J., Chatterton B. E., Collins P. J., Harding P. E., Shearman D. J. Changes in gastric emptying rates with age. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Aug;67(2):213–218. doi: 10.1042/cs0670213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Defective hepatic lipoprotein receptor binding of beta-very low density lipoproteins from type III hyperlipoproteinemic patients. Importance of apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):860–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen J. K., Ehnholm C., Kekki M., Nikkilä E. A. Post-heparin plasma lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase in normal subjects and in patients with hypertriglyceridaemia: correlations to sex, age and various parameters of triglyceride metabolism. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Apr;50(4):249–260. doi: 10.1042/cs0500249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Chen G. C., Hamilton R. L., Hardman D. A., Malloy M. J., Havel R. J. Remnants of lipoproteins of intestinal and hepatic origin in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):47–56. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap M. L., Barnhart R. L., Srivastava L. S., Perisutti G., Allen C., Hogg E., Glueck C. J., Jackson R. L. Alimentary lipemia: plasma high-density lipoproteins and apolipoproteins CII and CIII in healthy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983 Feb;37(2):233–243. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/37.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent G., Gay S., Inouye T., Bahu R., Minick O. T., Popper H. Vitamin A-containing lipocytes and formation of type III collagen in liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3719–3722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasinski S. D., Russell R. M., Otradovec C. L., Sadowski J. A., Hartz S. C., Jacob R. A., McGandy R. B. Relationship of vitamin A and vitamin E intake to fasting plasma retinol, retinol-binding protein, retinyl esters, carotene, alpha-tocopherol, and cholesterol among elderly people and young adults: increased plasma retinyl esters among vitamin A-supplement users. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989 Jan;49(1):112–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/49.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Selective measurement of two lipase activities in postheparin plasma from normal subjects and patients with hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1107–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI107855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer R. M., Heppell M., Haggith J. W., Bateman D. N. Gastric emptying and small-bowel transit rate in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1985 May;33(5):340–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1985.tb07134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. R., Schaefer E. J. Automated enzymatic standardized lipid analyses for plasma and lipoprotein fractions. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Jun 30;166(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior G. W., Mahley R. W., Buckhold D. K. Chylomicron metabolism during dietary-induced hypercholesterolemia in dogs. J Lipid Res. 1981 May;22(4):598–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. V., Young M., Seward C. R. Vitamin A and carotene levels of a selected population in metropolitan Washington, D. C. Am J Clin Nutr. 1973 Sep;26(9):992–997. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/26.9.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganroth J., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. The biochemical, clinical, and genetic features of type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Feb;82(2):158–174. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-2-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenter M. D., Perry H. O., Ludwig J. Chronic vitamin A intoxication in adults. Hepatic, neurologic and dermatologic complications. Am J Med. 1971 Jan;50(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90212-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTEL P. J. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PLASMA TRIGLYCERIDES AND REMOVAL OF CHYLOMICRONS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:943–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI104980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEMI T., NIKKILA E. A. Effect of age on the lipemia clearing activity of serum after administration of heparin to human subjects. J Gerontol. 1957 Jan;12(1):44–47. doi: 10.1093/geronj/12.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordovas J. M., Litwack-Klein L., Wilson P. W., Schaefer M. M., Schaefer E. J. Apolipoprotein E isoform phenotyping methodology and population frequency with identification of apoE1 and apoE5 isoforms. J Lipid Res. 1987 Apr;28(4):371–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch J. R., Karlin J. B., Scott L. W., Smith L. C., Gotto A. M., Jr Inverse relationship between blood levels of high density lipoprotein subfraction 2 and magnitude of postprandial lipemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1449–1453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon M. F., Nestel P. J., Craig I. H., Harper R. W. Lipoprotein predictors of the severity of coronary artery disease in men and women. Circulation. 1985 May;71(5):881–888. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.71.5.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Florman A. L., Degnan T., Diaz J. Hepatic injury in chronic hypervitaminosis A. Am J Dis Child. 1970 Feb;119(2):132–138. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1970.02100050134008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. M., Boyer J. L., Bagheri S. A., Hruban Z. Hepatic injury from chronic hypervitaminosis a resulting in portal hypertension and ascites. N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 29;291(9):435–440. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408292910903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Gregg R. E., Ghiselli G., Forte T. M., Ordovas J. M., Zech L. A., Brewer H. B., Jr Familial apolipoprotein E deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1206–1219. doi: 10.1172/JCI112704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Utermann G., Weber W., Havel R. J., Kotite L., Kane J. P., Innerarity T. L. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Abnormal binding of mutant apoprotein E to low density lipoprotein receptors of human fibroblasts and membranes from liver and adrenal of rats, rabbits, and cows. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI110330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Smith L. C. Role of capillary endothelium in the clearance of chylomicrons. A model for lipid transport from blood by lateral diffusion in cell membranes. Circ Res. 1976 Aug;39(2):149–162. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Rapid hepatic clearance of the canine lipoproteins containing only the E apoprotein by a high affinity receptor. Identity with the chylomicron remnant transport process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1804–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons L. A., Dwyer T., Simons J., Bernstein L., Mock P., Poonia N. S., Balasubramaniam S., Baron D., Branson J., Morgan J. Chylomicrons and chylomicron remnants in coronary artery disease: a case-control study. Atherosclerosis. 1987 May;65(1-2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. R., Goodman D. S. Vitamin A transport in human vitamin A toxicity. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 8;294(15):805–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604082941503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatami R., Mabuchi H., Ueda K., Ueda R., Haba T., Kametani T., Ito S., Koizumi J., Ohta M., Miyamoto S. Intermediate-density lipoprotein and cholesterol-rich very low density lipoprotein in angiographically determined coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1981 Dec;64(6):1174–1184. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.64.6.1174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. H., Hughes L. B., Zilversmit D. B. Lack of secretion of retinyl ester by livers of normal and cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Nutr. 1983 Oct;113(10):1995–2001. doi: 10.1093/jn/113.10.1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood B. A., Siegel H., Weisell R. C., Dolinski M. Liver stores of vitamin A in a normal population dying suddenly or rapidly from unnatural causes in New York City. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Aug;23(8):1037–1042. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.8.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener M., Börsch G., Schaffstein J., Lüth I., Rickels R., Ricken D. Effect of ageing on the gastro-intestinal transit of a lactulose-supplemented mixed solid-liquid meal in humans. Digestion. 1988;39(1):40–46. doi: 10.1159/000199606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub M. S., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L. Dietary fat clearance in normal subjects is regulated by genetic variation in apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1571–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI113243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2518–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. E., Chan I. F., Ball M. Plasma lipoprotein retinoids after vitamin A feeding in normal man: minimal appearance of retinyl esters among low-density lipoproteins. Metabolism. 1983 May;32(5):514–517. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Determinants of hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. Atherogenesis: a postprandial phenomenon. Circulation. 1979 Sep;60(3):473–485. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.60.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


