Abstract
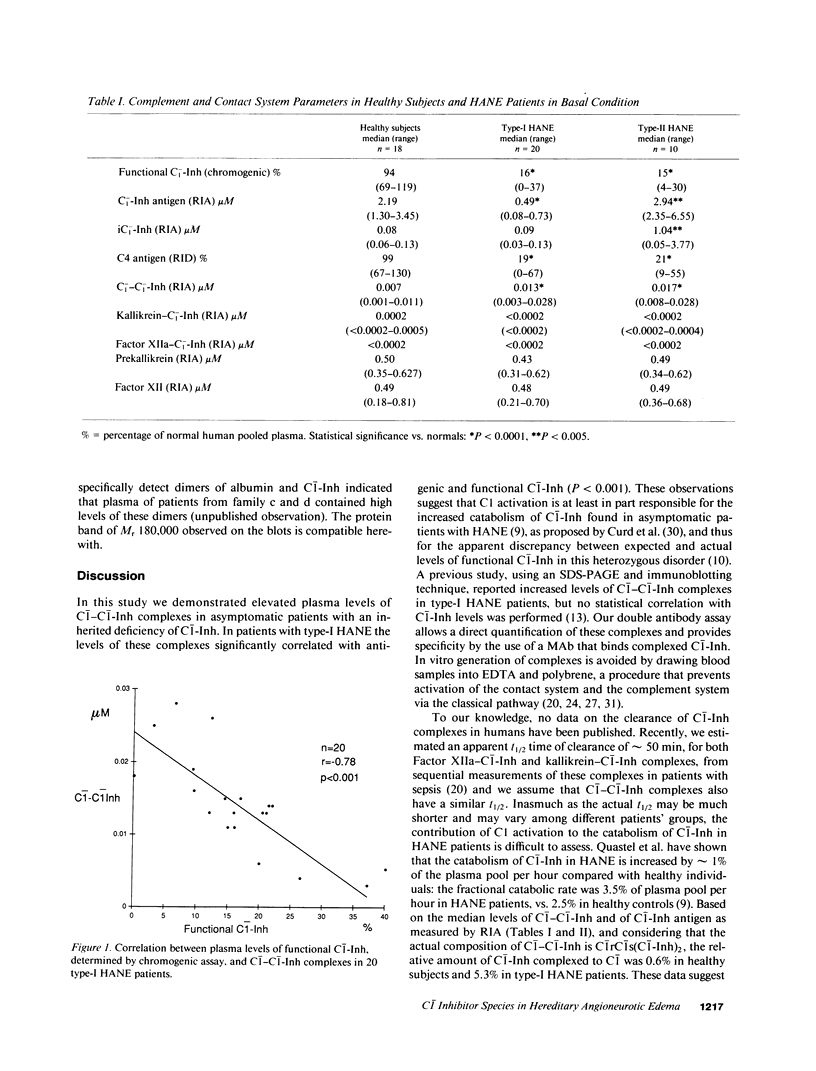
C1- inhibitor (C1(-)-Inh) catabolism in plasma of patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema (HANE) was assessed by measuring the complexes formed by C1(-)-Inh with its target proteases (C1-s, Factor XIIa, and kallikrein) and a modified (cleaved) inactive form of C1(-)-Inh (iC1(-)-Inh). This study was performed in plasma from 18 healthy subjects and 30 patients with HANE in remission: 20 with low antigen concentration (type I) and 10 (from 5 different kindreds) with dysfunctional protein (type II). Both type-I and type-II patients had increased C1(-)-C1(-)-Inh complexes (P less than 0.0001), which in type I inversely correlated with the levels of C1(-)-Inh (P less than 0.001). iC1(-)-Inh was normal in all type-I patients and in type-II patients from three families with increased C1(-)-Inh antigen, whereas iC1(-)-Inh was higher than 20 times the normal values in patients from the remaining two families with C1(-)-Inh antigen in the normal range. None of the subjects had an increase of either Factor XIIa-C1(-)-Inh or kallikrein-C1(-)-Inh complexes. This study shows that the hypercatabolism of C1(-)-Inh in HANE patients at least in part occurs via the formation of complexes with C1- and that genetically determined differences in catabolism of dysfunctional C1(-)-Inh proteins are present in type-II patients.
Full text
PDF

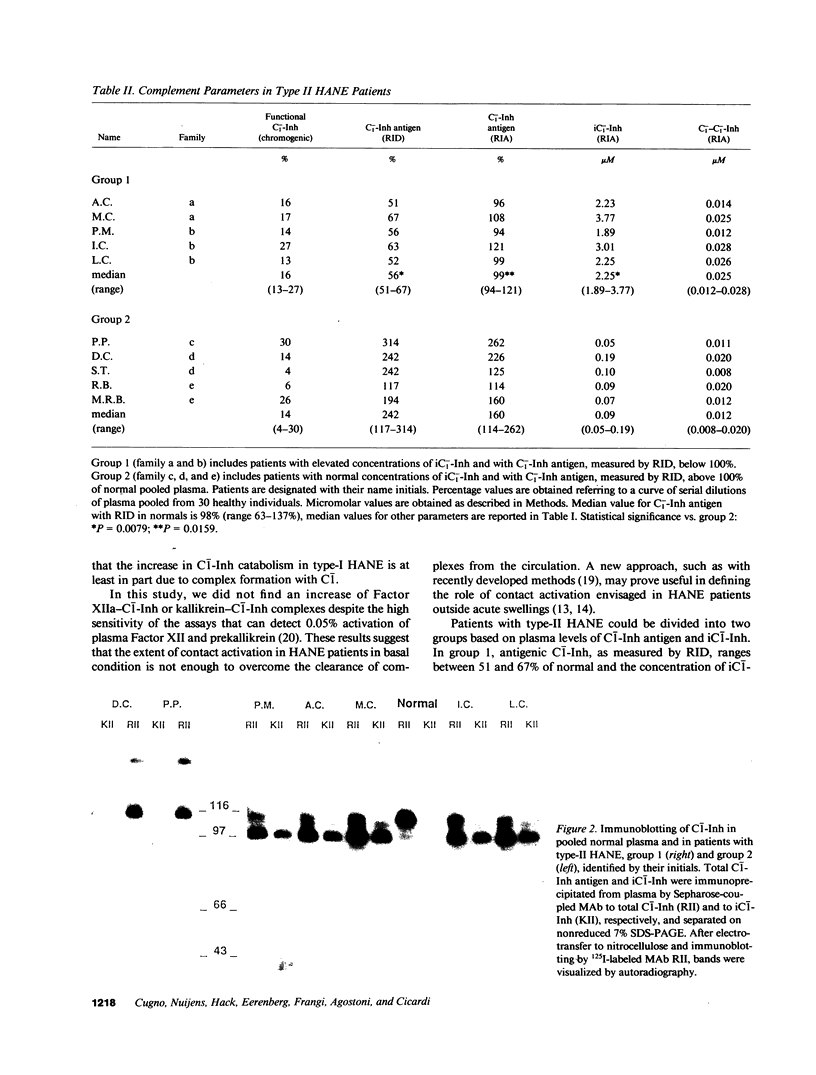


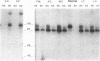
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTEN K. F., SHEFFER A. L. DETECTION OF HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA BY DEMONSTRATION OF A REDUCTION IN THE SECOND COMPONENT OF HUMAN COMPLEMENT. N Engl J Med. 1965 Apr 1;272:649–656. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196504012721301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aulak K. S., Pemberton P. A., Rosen F. S., Carrell R. W., Lachmann P. J., Harrison R. A. Dysfunctional C1-inhibitor(At), isolated from a type II hereditary-angio-oedema plasma, contains a P1 'reactive centre' (Arg444----His) mutation. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 15;253(2):615–618. doi: 10.1042/bj2530615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicardi M., Igarashi T., Rosen F. S., Davis A. E., 3rd Molecular basis for the deficiency of complement 1 inhibitor in type I hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):698–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI112873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cugno M., Bergamaschini L., Uziel L., Cicardi M., Agostoni A., Jie A. F., Kluft C. Haemostasis contact system and fibrinolysis in hereditary angioedema (C1-inhibitor deficiency). J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1988 Jul;26(7):423–427. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1988.26.7.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullmann W., Kövary P. M., Müller N., Dick W. Complement, coagulation and fibrinolytic parameters in hereditary angioedema (HAE). Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Sep;49(3):618–622. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curd J. G., Prograis L. J., Jr, Cochrane C. G. Detection of active kallikrein in induced blister fluids of hereditary angioedema patients. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):742–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curd J. G., Yelvington M., Ziccardi R. J., Mathison D. A., Griffin J. H. Purification and characterization of two functionally distinct forms of C1 inhibitor from a patient with angioedema. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Aug;45(2):261–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., ROSEN F. S. ACTION OF COMPLEMENT IN HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: THE ROLE OF C'1-ESTERASE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2204–2213. doi: 10.1172/JCI105094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd C1 inhibitor and hereditary angioneurotic edema. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:595–628. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Harrison R. A., Rosen F. S., Bing D. H., Kindness G., Canar J., Wagner C. J., Awad S. Variability in purified dysfunctional C1(-)-inhibitor proteins from patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. Functional and analytical gel studies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):124–132. doi: 10.1172/JCI111664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Wagner C. J., Tsuei B., Kindness G., Bing D. H., Harrison R. A., Rosen F. S. Interactions of plasma kallikrein and C1-s with normal and dysfunctional C1(-)-inhibitor proteins from patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema: analytic gel studies. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1096–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldering E., Nuijens J. H., Hack C. E. Expression of functional human C1 inhibitor in COS cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11776–11779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Gelfand J. A., Atkinson J. P. Hereditary angioedema: the clinical syndrome and its management. Ann Intern Med. 1976 May;84(5):580–593. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Hosea S. W., Gelfand J. A., Frank M. M. Response of variant hereditary angioedema phenotypes to danazol therapy. Genetic implications. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):280–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Hannema A. J., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Out T. A., Aalberse R. C. A C1-inhibitor-complex assay (INCA): a method to detect C1 activation in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1450–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekzema R., Hannema A. J., Swaak T. J., Paardekooper J., Hack C. E. Low molecular weight C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Gruber B., Harpel P. C. Assessment of Hageman factor activation in human plasma: quantification of activated Hageman factor-C1 inactivator complexes by an enzyme-linked differential antibody immunosorbent assay. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDERMAN N. S., WEBSTER M. E., BECKER E. L., RATCLIFFE H. E. Hereditary angioneurotic edema. II. Deficiency of inhibitor for serum globulin permeability factor and/or plasma kallikrein. J Allergy. 1962 Jul-Aug;33:330–341. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(62)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Rosen F. S. The catabolism of C1(-)-inhibitor and the pathogenesis of hereditary angio-edema. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl. 1984;284:35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Mårtensson U., Sjöholm A. G. Quantitation of Clr-Cls-Cl inactivator complexes by electroimmunoassay. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Feb;87C(1):79–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin M. F., Kaplan A. P., Harpel P. C. Studies of C1 inactivator-plasma kallikrein complexes in purified systems and in plasma. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6415–6421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmle B., Zuraw B. L., Heeb M. J., Schwarz H. P., Berrettini M., Curd J. G., Griffin J. H. Detection and quantitation of cleaved and uncleaved high molecular weight kininogen in plasma by ligand blotting with radiolabeled plasma prekallikrein or factor XI. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Apr 8;59(2):151–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Huijbregts C. C., Schreuder W. O., Felt-Bersma R. J., Abbink J. J., Thijs L. G., Hack C. E. Proteolytic inactivation of plasma C1- inhibitor in sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):443–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI114185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Huijbregts C. C., Cohen M., Navis G. O., de Vries A., Eerenberg A. J., Bakker J. C., Hack C. E. Detection of activation of the contact system of coagulation in vitro and in vivo: quantitation of activated Hageman factor-C-1-inhibitor and kallikrein-C-1-inhibitor complexes by specific radioimmunoassays. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Aug 4;58(2):778–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Huijbregts C. C., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Abbink J. J., Strack van Schijndel R. J., Felt-Bersma R. J., Thijs L. G., Hack C. E. Quantification of plasma factor XIIa-Cl(-)-inhibitor and kallikrein-Cl(-)-inhibitor complexes in sepsis. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Huijbregts C. C., van Mierlo G. M., Hack C. E. Inactivation of C-1 inhibitor by proteases: demonstration by a monoclonal antibody of a neodeterminant on inactivated, non-complexed C-1 inhibitor. Immunology. 1987 Jul;61(3):387–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel M., Harrison R., Cicardi M., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Behavior in vivo of normal and dysfunctional C1 inhibitor in normal subjects and patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):1041–1046. doi: 10.1172/JCI110831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Alper C. A., Pensky J., Klemperer M. R., Donaldson V. H. Genetically determined heterogeneity of the C1 esterase inhibitor in patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2143–2149. doi: 10.1172/JCI106708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Silver L. D., Scott C. F., Schmaier A. H., Prograis L. J., Jr, Curd J. G., Colman R. W. Prekallikrein activation and high-molecular-weight kininogen consumption in hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 5;308(18):1050–1053. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305053081802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver K., Radziejewska E., Silbermann J. A., Donaldson V. H., Bock S. C. CpG mutations in the reactive site of human C1 inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3066–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuraw B. L., Curd J. G. Demonstration of modified inactive first component of complement (C1) inhibitor in the plasmas of C1 inhibitor-deficient patients. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):567–575. doi: 10.1172/JCI112610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]