Abstract
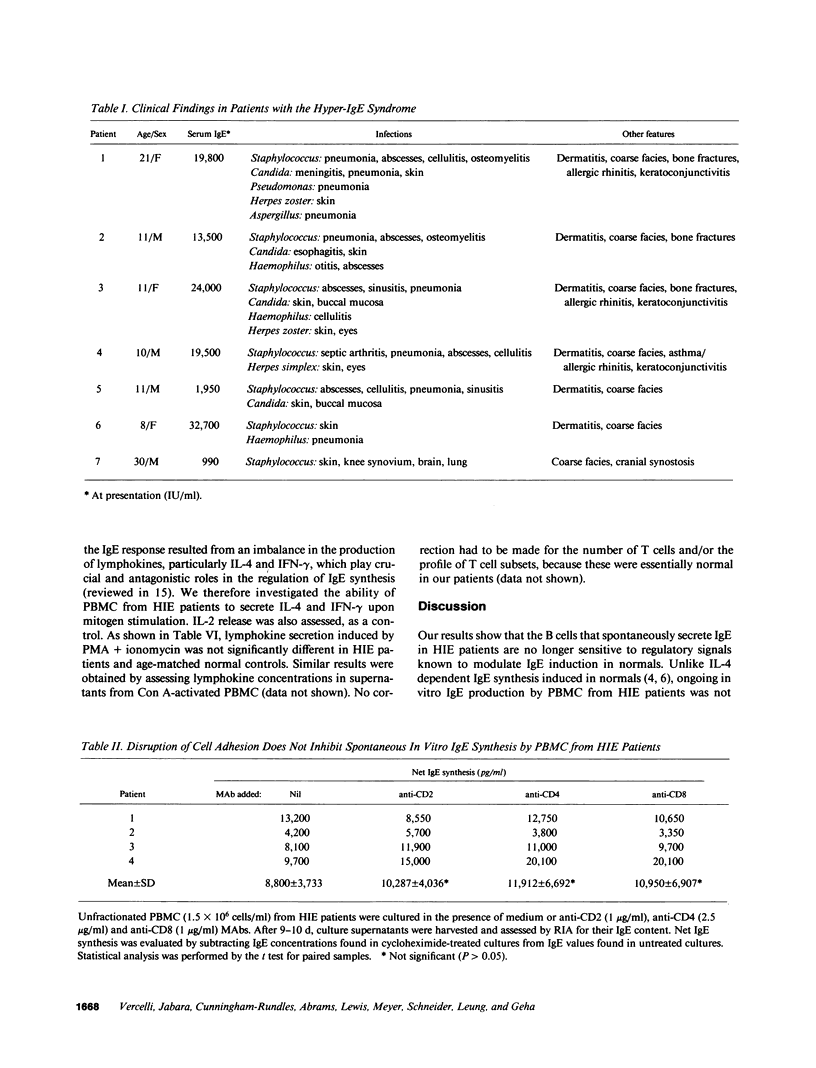
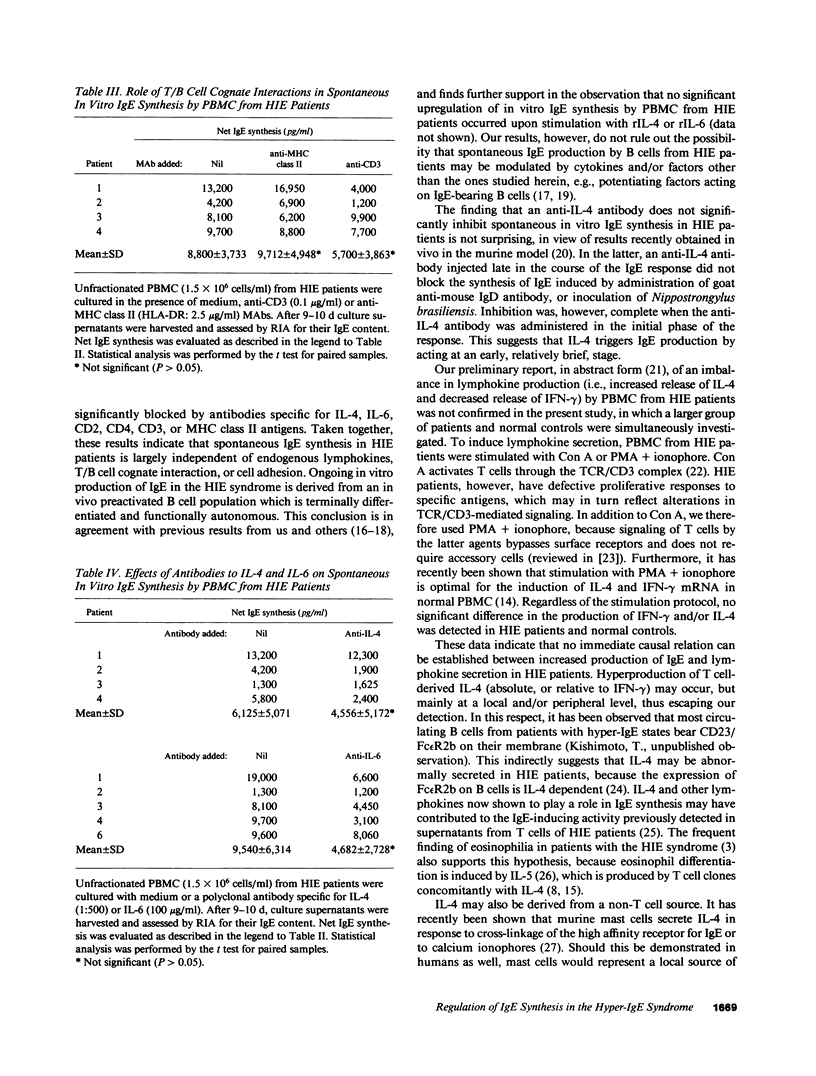
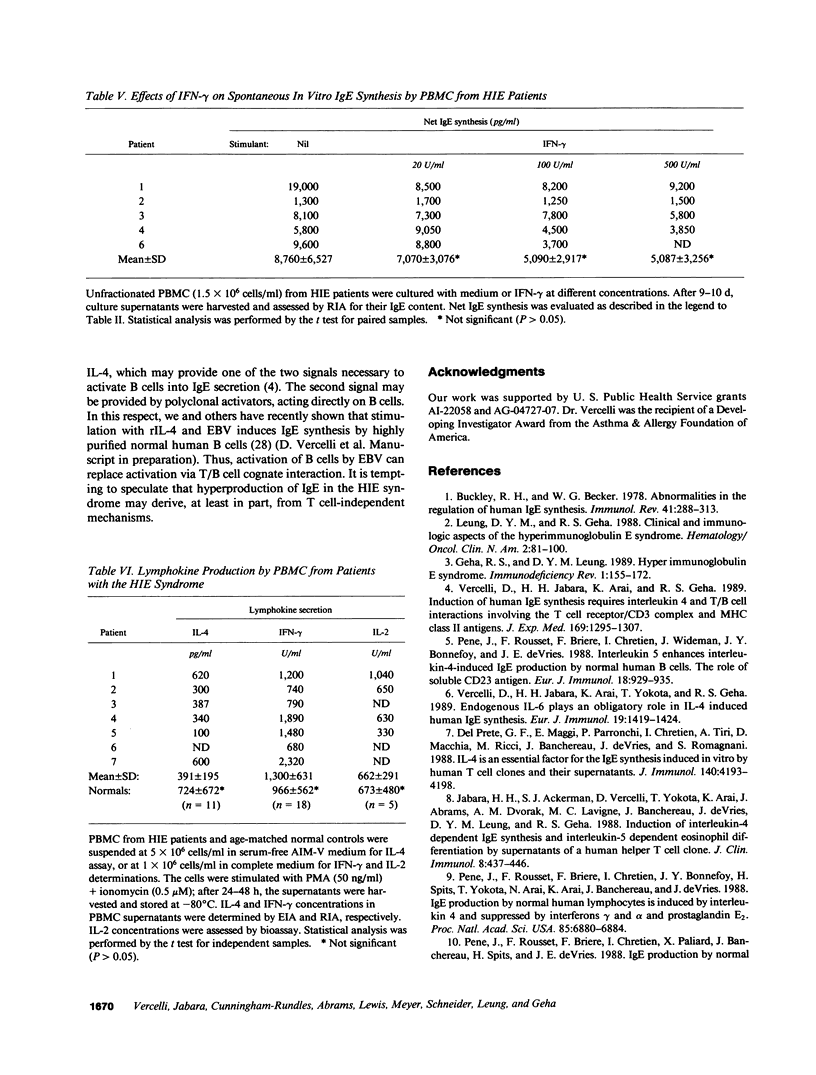
The hyper-IgE (HIE) syndrome is characterized by high IgE serum levels, chronic dermatitis, and recurrent infections. The mechanisms responsible for hyperproduction of IgE in HIE patients are presently unknown. We investigated whether spontaneous in vitro IgE synthesis by PBMC from seven HIE patients was sensitive to signals (cell adhesion, T/B cell cognate interaction and lymphokines: IL-4, IL-6, and IFN-gamma) known to regulate IgE induction in normals. Our results show that, unlike IL-4 dependent IgE synthesis induced in normals, spontaneous IgE production by PBMC from HIE patients was not blocked by monoclonal antibodies to CD2, CD4, CD3, and MHC class II antigens. Furthermore, antibodies to IL-4 and IL-6 did not significantly suppress IgE production. IFN-gamma had no significant effects on spontaneous in vitro IgE synthesis. To test whether an imbalance in lymphokine production might underlie hyperproduction of IgE in HIE patients, mitogen-induced secretion of IL-4 and IFN-gamma by PBMC was assessed. No significant difference was detected between HIE patients and normal controls. Thus, ongoing IgE synthesis in the HIE syndrome is largely independent of cell-cell interactions and endogenous lymphokines, and is due to a terminally differentiated B cell population, no longer sensitive to regulatory signals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckley R. H., Becker W. G. Abnormalities in the regulation of human IgE synthesis. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:288–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilson O. P., Kelly-Chilson A. E. Mitogenic lectins bind to the antigen receptor on human lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Feb;19(2):389–396. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., Maggi E., Parronchi P., Chrétien I., Tiri A., Macchia D., Ricci M., Banchereau J., De Vries J., Romagnani S. IL-4 is an essential factor for the IgE synthesis induced in vitro by human T cell clones and their supernatants. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4193–4198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Holmes J., Urban J. F., Jr, Paul W. E., Katona I. M. T help requirements for the generation of an in vivo IgE response: a late acting form of T cell help other than IL-4 is required for IgE but not for IgG1 production. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Leung D. Y. Hyper immunoglobulin E syndrome. Immunodefic Rev. 1989;1(2):155–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm R. M., Buckley R. H., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Squillace D. L., Gleich G. J., Yunginger J. W. Variability of IgE protein measurement in cell-culture supernatants: results from a multicenter collaborative study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Jun;77(6):880–890. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabara H. H., Ackerman S. J., Vercelli D., Yokota T., Arai K., Abrams J., Dvorak A. M., Lavigne M. C., Banchereau J., De Vries J. Induction of interleukin-4-dependent IgE synthesis and interleukin-5-dependent eosinophil differentiation by supernatants of a human helper T-cell clone. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Nov;8(6):437–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00916948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Clinical and immunologic aspects of the hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;2(1):81–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Control of IgE synthesis in man. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Jul;6(4):273–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00917327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Young M. C., Wood N., Geha R. S. Induction of IgE synthesis in normal human B cells. Sequential requirements for activation by an alloreactive T cell clone and IgE-potentiating factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):713–723. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Bonnefoy J. Y., Spits H., Yokota T., Arai N., Arai K., Banchereau J. IgE production by normal human lymphocytes is induced by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferons gamma and alpha and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6880–6884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Paliard X., Banchereau J., Spits H., De Vries J. E. IgE production by normal human B cells induced by alloreactive T cell clones is mediated by IL-4 and suppressed by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1218–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Wideman J., Bonnefoy J. Y., De Vries J. E. Interleukin 5 enhances interleukin 4-induced IgE production by normal human B cells. The role of soluble CD23 antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):929–935. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci M., Del Prete G. F., Maggi E., Lanzavecchia A., Sala P. G., Romagnani S. In vitro synthesis of human IgE: reappraisal of a 5-year study. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77(1-2):32–37. doi: 10.1159/000233749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hatake K., Dvorak A. M., Leiferman K. M., Donnenberg A. D., Arai N., Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Selective differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic cells induced by recombinant human interleukins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2288–2292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saryan J. A., Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Induction of human IgE synthesis by a factor derived from T cells of patients with hyper-IgE states. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyphronitis G., Tsokos G. C., June C. H., Levine A. D., Finkelman F. D. IgE secretion by Epstein-Barr virus-infected purified human B lymphocytes is stimulated by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5580–5584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umetsu D. T., Leung D. Y., Siraganian R., Jabara H. H., Geha R. S. Differential requirements of B cells from normal and allergic subjects for the induction of IgE synthesis by an alloreactive T cell clone. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):202–214. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Geha R. S. Regulation of IgE synthesis in humans. J Clin Immunol. 1989 Mar;9(2):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00916934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Arai K., Geha R. S. Induction of human IgE synthesis requires interleukin 4 and T/B cell interactions involving the T cell receptor/CD3 complex and MHC class II antigens. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1295–1307. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Arai K., Yokota T., Geha R. S. Endogenous interleukin 6 plays an obligatory role in interleukin 4-dependent human IgE synthesis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1419–1424. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota A., Kikutani H., Tanaka T., Sato R., Barsumian E. L., Suemura M., Kishimoto T. Two species of human Fc epsilon receptor II (Fc epsilon RII/CD23): tissue-specific and IL-4-specific regulation of gene expression. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. C., Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Production of IgE-potentiating factor in man by T cell lines bearing Fc receptors for IgE. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):871–878. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


