Full text
PDF
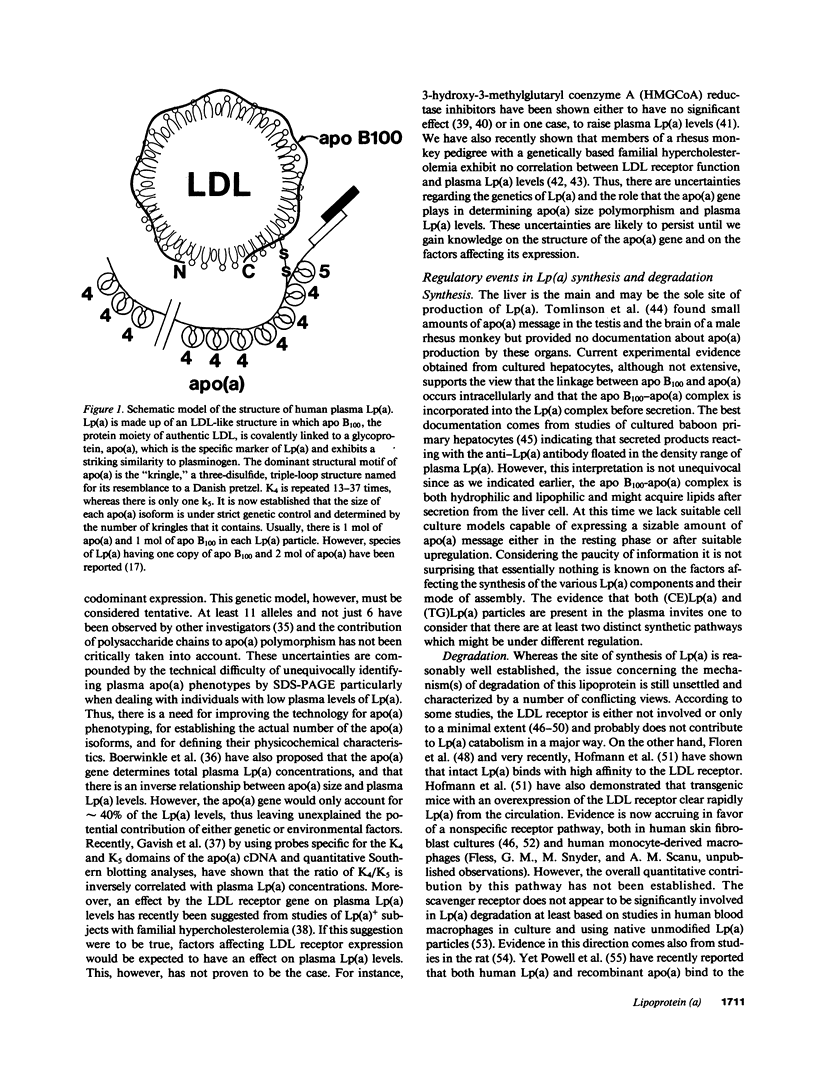




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Adolphson J. L., Hazzard W. R. Radioimmunoassay of human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong V. W., Cremer P., Eberle E., Manke A., Schulze F., Wieland H., Kreuzer H., Seidel D. The association between serum Lp(a) concentrations and angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Dependence on serum LDL levels. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Dec;62(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong V. W., Schleef J., Thiery J., Muche R., Schuff-Werner P., Eisenhauer T., Seidel D. Effect of HELP-LDL-apheresis on serum concentrations of human lipoprotein(a): kinetic analysis of the post-treatment return to baseline levels. Eur J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;19(3):235–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1989.tb00223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong V. W., Walli A. K., Seidel D. Isolation, characterization, and uptake in human fibroblasts of an apo(a)-free lipoprotein obtained on reduction of lipoprotein(a). J Lipid Res. 1985 Nov;26(11):1314–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG K. A NEW SERUM TYPE SYSTEM IN MAN--THE LP SYSTEM. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bersot T. P., Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Fat feeding in humans induces lipoproteins of density less than 1.006 that are enriched in apolipoprotein [a] and that cause lipid accumulation in macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):622–630. doi: 10.1172/JCI112345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Utermann G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00288277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Hamsten A., Asplund A. Pronounced lowering of serum levels of lipoprotein Lp(a) in hyperlipidaemic subjects treated with nicotinic acid. J Intern Med. 1989 Oct;226(4):271–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1989.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing G. L., Gaubatz J. W., Nava M. L., Burdick B. J., Bocan T. M., Guyton J. R., Weilbaecher D., DeBakey M. E., Lawrie G. M., Morrisett J. D. Quantitation and localization of apolipoproteins [a] and B in coronary artery bypass vein grafts resected at re-operation. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):593–603. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlen G. H., Guyton J. R., Attar M., Farmer J. A., Kautz J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Association of levels of lipoprotein Lp(a), plasma lipids, and other lipoproteins with coronary artery disease documented by angiography. Circulation. 1986 Oct;74(4):758–765. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.4.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén G., Berg K., Gillnäs T., Ericson C. Lp(a) lipoprotein/pre-beta1-lipoprotein in Swedish middle-aged males and in patients with coronary heart disease. Clin Genet. 1975 Apr;7(4):334–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D. T., Hegele R. A., Hass P. E., Emi M., Wu L. L., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M., Williams R. R., White R. L., Lalouel J. M. Genetic linkage between lipoprotein(a) phenotype and a DNA polymorphism in the plasminogen gene. Genomics. 1988 Oct;3(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrington P. N., Ishola M., Hunt L., Arrol S., Bhatnagar D. Apolipoproteins (a), AI, and B and parental history in men with early onset ischaemic heart disease. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1070–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91895-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Fless G. M., Kohr W. J., McLean J. W., Xu Q. T., Miller C. G., Lawn R. M., Scanu A. M. Partial amino acid sequence of apolipoprotein(a) shows that it is homologous to plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3224–3228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelberg J. M., Gonzalez-Gronow M., Pizzo S. V. Lipoprotein a inhibits streptokinase-mediated activation of human plasminogen. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., Fischer-Dzoga K., Juhn D. J., Bates S., Scanu A. M. Structural and functional changes of rhesus serum low density lipoproteins during cycles of diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):475–486. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.6.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., Rolih C. A., Scanu A. M. Heterogeneity of human plasma lipoprotein (a). Isolation and characterization of the lipoprotein subspecies and their apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11470–11478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., Snyder M. L., Scanu A. M. Enzyme-linked immunoassay for Lp[a]. J Lipid Res. 1989 May;30(5):651–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., Scanu A. M. Physicochemical properties of apolipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein(a-) derived from the dissociation of human plasma lipoprotein (a). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8712–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floren C. H., Albers J. J., Bierman E. L. Uptake of Lp (a) lipoprotein by cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 30;102(2):636–639. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. L., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Tomlinson J. E., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M., Lusis A. J. The apolipoprotein(a) gene resides on human chromosome 6q26-27, in close proximity to the homologous gene for plasminogen. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):352–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00282175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick M. H., Dahlén G., Berg K., Valle M., Hekali P. Serum lipids in angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Chest. 1978 Jan;73(1):62–65. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish D., Azrolan N., Breslow J. L. Plasma Ip(a) concentration is inversely correlated with the ratio of Kringle IV/Kringle V encoding domains in the apo(a) gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2021–2027. doi: 10.1172/JCI114395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gronow M., Edelberg J. M., Pizzo S. V. Further characterization of the cellular plasminogen binding site: evidence that plasminogen 2 and lipoprotein a compete for the same site. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurakar A., Hoeg J. M., Kostner G., Papadopoulos N. M., Brewer H. B., Jr Levels of lipoprotein Lp(a) decline with neomycin and niacin treatment. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Nov;57(2-3):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton J. R., Dahlen G. H., Patsch W., Kautz J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Relationship of plasma lipoprotein Lp(a) levels to race and to apolipoprotein B. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):265–272. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Gavish D., Breslow J. L., Nachman R. L. Lipoprotein(a) modulation of endothelial cell surface fibrinolysis and its potential role in atherosclerosis. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):303–305. doi: 10.1038/339303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkes L., Jürgens G., Holasek A., van Berkel T. J. In vivo studies on the binding sites for lipoprotein (a) on parenchymal and non-parenchymal rat liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 18;227(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Gordon B. R., Parker T. S. Plasmin catalyzes binding of lipoprotein (a) to immobilized fibrinogen and fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3847–3851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvie N. R., Schultz J. S. Studies on the heterogeneity of human serum Lp lipoproteins and on the occurrence of double Lp lipoprotein variants. Biochem Genet. 1973 Jul;9(3):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00485737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havekes L., Vermeer B. J., Brugman T., Emeis J. Binding of LP(a) to the low density lipoprotein receptor of human fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Britten M. L., Manis G. S., Rainwater D. L. Apolipoprotein(a) (Apo(a)) glycoprotein isoforms result from size differences in Apo(a) mRNA in baboons. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6013–6016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karàdi I., Kostner G. M., Gries A., Nimpf J., Romics L., Malle E. Lipoprotein (a) and plasminogen are immunochemically related. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 2;960(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Avogaro P., Cazzolato G., Marth E., Bittolo-Bon G., Qunici G. B. Lipoprotein Lp(a) and the risk for myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jan-Feb;38(1-2):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Gavish D., Leopold B., Bolzano K., Weintraub M. S., Breslow J. L. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors lower LDL cholesterol without reducing Lp(a) levels. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1313–1319. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Armstrong V. W., Niehaus M., Hilschmann N., Seidel D. Structural relationship of an apolipoprotein (a) phenotype (570 kDa) to plasminogen: homologous kringle domains are linked by carbohydrate-rich regions. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Dec;368(12):1533–1544. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krempler F., Kostner G. M., Roscher A., Haslauer F., Bolzano K., Sandhofer F. Studies on the role of specific cell surface receptors in the removal of lipoprotein (a) in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1431–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI110896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Költringer P., Jürgens G. A dominant role of lipoprotein(a) in the investigation and evaluation of parameters indicating the development of cervical atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Dec;58(1-3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplaud P. M., Beaubatie L., Rall S. C., Jr, Luc G., Saboureau M. Lipoprotein[a] is the major apoB-containing lipoprotein in the plasma of a hibernator, the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). J Lipid Res. 1988 Sep;29(9):1157–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leren T. P., Hjermann I., Berg K., Leren P., Foss O. P., Viksmoen L. Effects of lovastatin alone and in combination with cholestyramine on serum lipids and apolipoproteins in heterozygotes for familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Oct;73(2-3):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Gersdorf E., Menzel H. J., Duba C., Cleve H., Humphries S., Utermann G. The gene for the Lp(a)-specific glycoprotein is closely linked to the gene for plasminogen on chromosome 6. Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;81(2):149–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00293891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J., Weinfeld M., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M. Lipoprotein(a), fibrin binding, and plasminogen activation. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):240–245. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.2.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maartmann-Moe K., Berg K. Lp(a) lipoprotein enters cultured fibroblasts independently of the plasma membrane low density lipoprotein receptor. Clin Genet. 1981 Nov;20(5):352–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb01047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Abe A., Seishima M., Makino K., Noma A., Kawade M. Transient changes of serum lipoprotein(a) as an acute phase protein. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Aug;78(2-3):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Abe A., Maeda S., Noma A., Kawade M., Takenaka O. Lipoprotein(a) in nonhuman primates. Presence and characteristics of Lp(a) immunoreactive materials using anti-human Lp(a) serum. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Jul;78(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Fless G. M., Levin E. G., Scanu A. M., Plow E. F. A potential basis for the thrombotic risks associated with lipoprotein(a). Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):301–303. doi: 10.1038/339301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai A., Miyahara T., Fujimoto N., Matsuda M., Kameyama M. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Feb;59(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainwater D. L., Lanford R. E. Production of lipoprotein(a) by primary baboon hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 15;1003(1):30–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath M., Niendorf A., Reblin T., Dietel M., Krebber H. J., Beisiegel U. Detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall of 107 coronary bypass patients. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):579–592. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Dahlen G., Berg K., Morton N. E., Dannenberg A. L. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1986 Nov 14;256(18):2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M. Lipoprotein(a). A potential bridge between the fields of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Oct;112(10):1045–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J., Armstrong V. W., Schleef J., Creutzfeldt C., Creutzfeldt W., Seidel D. Serum lipoprotein Lp(a) concentrations are not influenced by an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor. Klin Wochenschr. 1988 May 16;66(10):462–463. doi: 10.1007/BF01745519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson J. E., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M. Rhesus monkey apolipoprotein(a). Sequence, evolution, and sites of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5957–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hoppichler F., Dieplinger H., Seed M., Thompson G., Boerwinkle E. Defects in the low density lipoprotein receptor gene affect lipoprotein (a) levels: multiplicative interaction of two gene loci associated with premature atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4171–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a). Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):904–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2530631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W., Hitchens J., Magnani H. N., Khan M. A study of methods of identification and estimation of Lp(a) lipoprotein and of its significance in health, hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1974 Sep-Oct;20(2):323–346. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(74)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzki Z., Tercé F., Seman L. J., Theolis R. T., Breckenridge W. C., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L. The linkage with apolipoprotein (a) in lipoprotein (a) modifies the immunochemical and functional properties of apolipoprotein B. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8474–8481. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


