Abstract
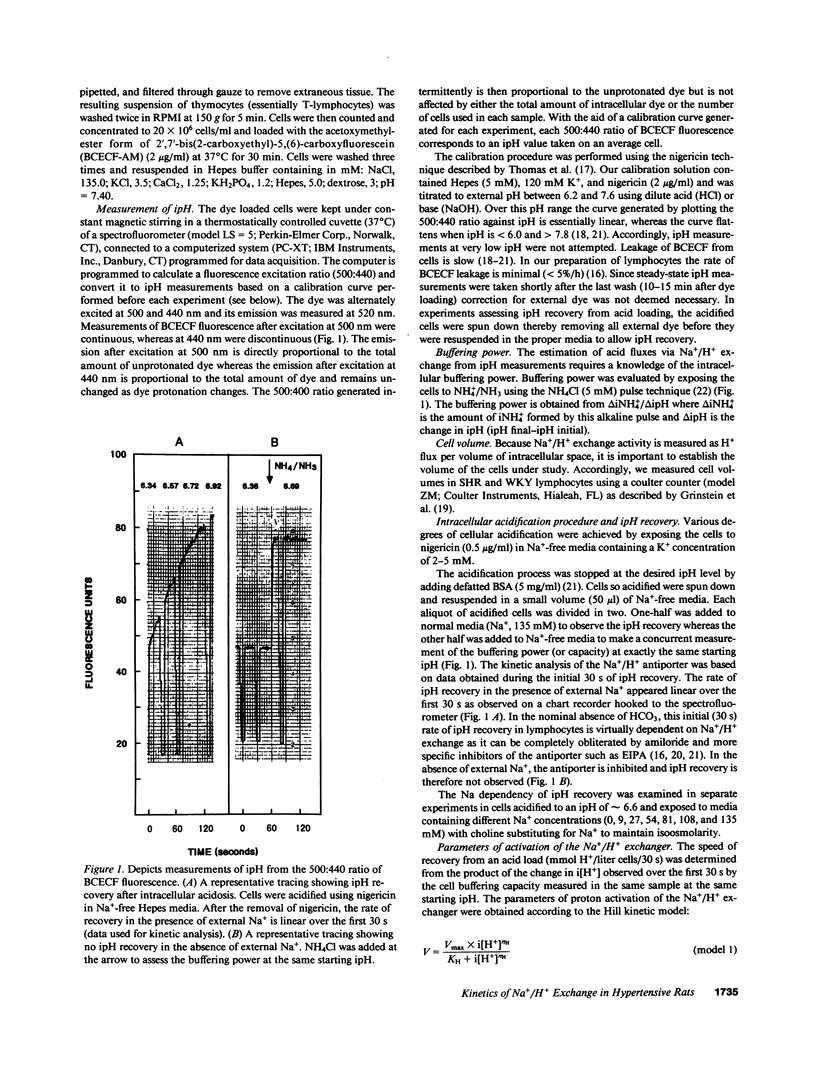
Enhanced activity of the Na+/H+ antiporter is increasingly reported as a feature of cells from hypertensive subjects but the intracellular pH (ipH) dependency of its activity has not been examined. This study was designed to characterize the kinetic properties of the Na+/H+ antiporter in lymphocytes from adult spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and in those from age-matched normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) controls. Steady-state ipH, estimated from the measurement of BCECF fluorescence, was significantly lower in lymphocytes from the SHR than in those from WKY rats (7.09 +/- 0.02, n = 17 and 7.17 +/- 0.03, n = 19, respectively, P less than 0.025). The velocity of the antiporter determined from the product of the change in intracellular hydrogen ion concentration (i[H+]) by the buffering power measured concurrently at each starting ipH exhibited similar kinetic parameters in SHR and WKY cells: Vmax, 72 +/- 18 vs. 79 +/- 24 mM H+/30 s; pKH, 10.04 +/- 0.87 vs. 8.49 +/- 0.80; and Hill coefficient, 1.67 +/- 0.12 vs. 1.44 +/- 0.10, respectively. Likewise, no significant differences were observed between SHR and WKY cells in either the Km (29 +/- 5 and 32 +/- 8 mM, respectively) or the Vmax (6.0 +/- 1.0 and 5.53 +/- 1.0 mM H+/30 s, respectively) of the sodium activation curve. We conclude that while the ipH of SHR lymphocytes is reduced, the kinetic properties of the Na+/H+ antiporter are virtually identical in SHR and WKY lymphocytes. Consequently, a primary abnormality in the activity of this antiporter is not an inherent feature of lymphocytes from the SHR model of genetic hypertension. We propose that the activity of the Na+/H+ antiporter in SHR cells is apt to be increased as a result of reduction in ipH which dictates a higher set point in its steady-state activity.
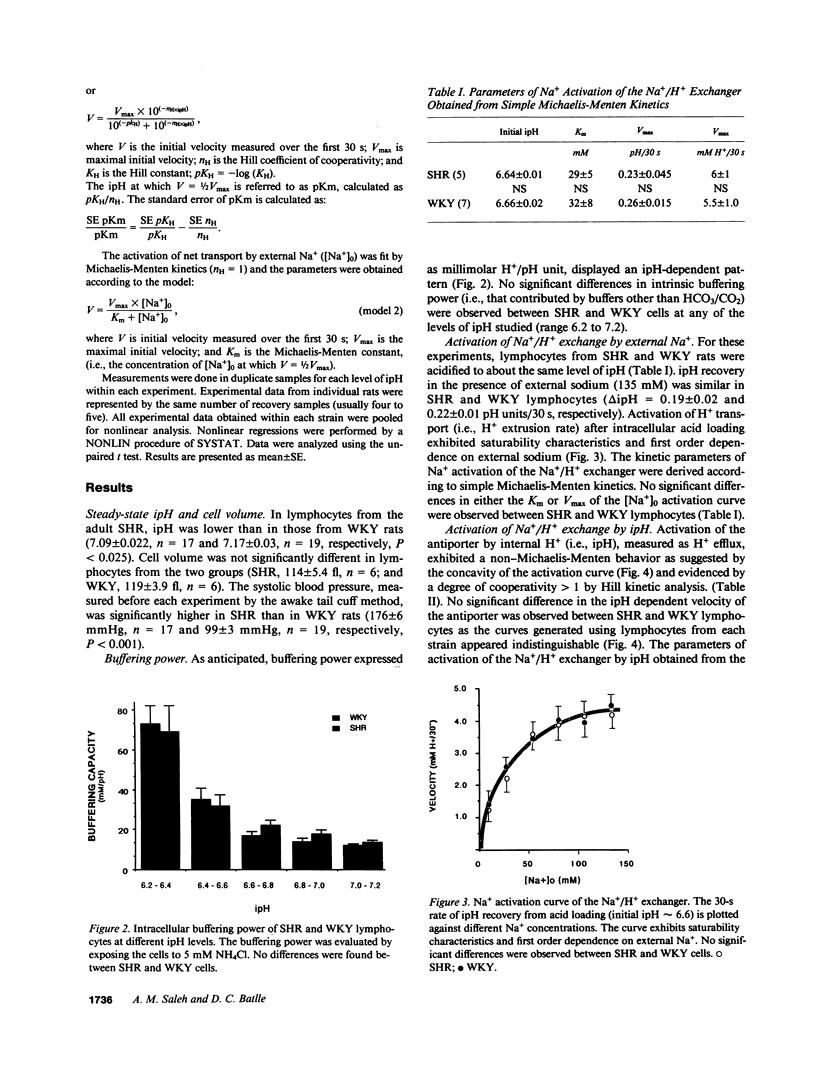
Full text
PDF
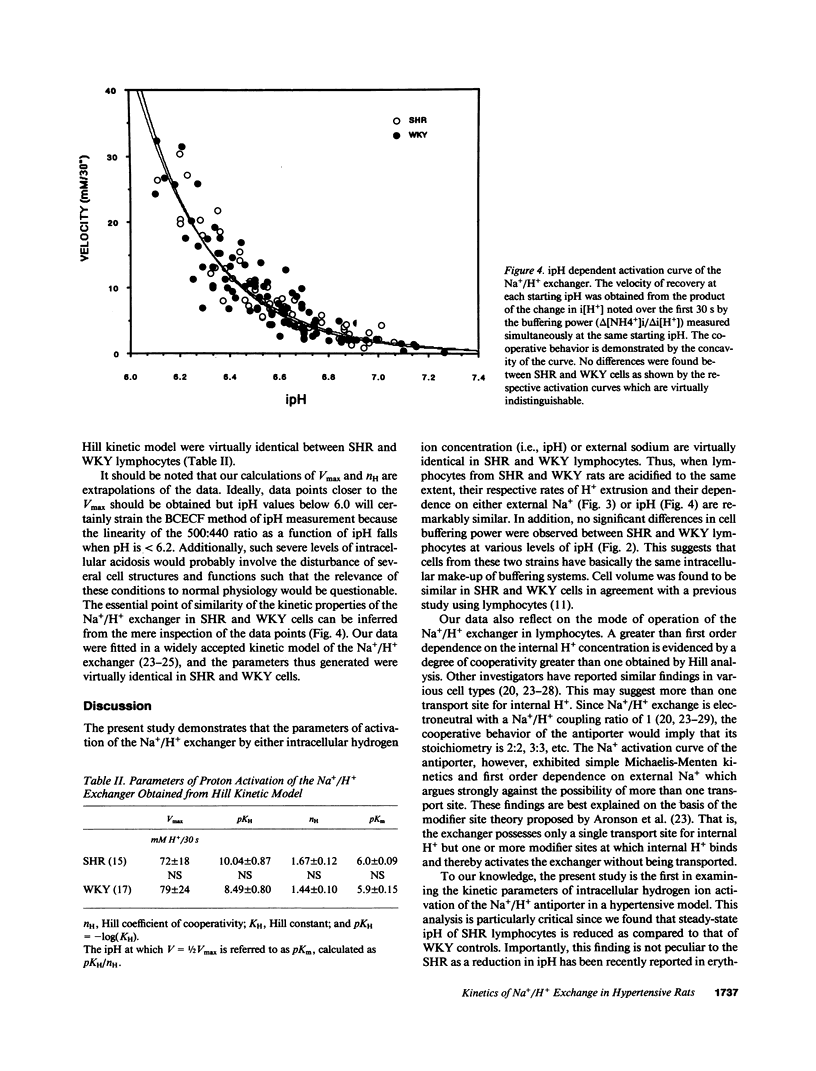


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson P. S. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:545–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S. Red-cell sodium-lithium countertransport and essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 29;307(5):317–317. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207293070517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv A., Livne A. The Na+/H+ antiport, cytosolic free Ca2+, and essential hypertension: a hypothesis. Am J Hypertens. 1988 Oct;1(4 Pt 1):410–413. doi: 10.1093/ajh/1.4.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batlle D. C., Saleh A., Rombola G. Reduced intracellular pH in lymphocytes from the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1990 Jan;15(1):97–103. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Vallega G., Muslin A. J., Gordon H. M., Canessa M., Alexander R. W. Spontaneously hypertensive rat vascular smooth muscle cells in culture exhibit increased growth and Na+/H+ exchange. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):822–829. doi: 10.1172/JCI113964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Na-H exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):29–52. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa M. L., Morgan K., Semplicini A. Genetic differences in lithium-sodium exchange and regulation of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger in essential hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 (Suppl 3):S92–S98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa M., Adragna N., Solomon H. S., Connolly T. M., Tosteson D. C. Increased sodium-lithium countertransport in red cells of patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 3;302(14):772–776. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004033021403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke K. R., Macknight A. D. Effects of medium acetate on cellular volume in rabbit renal cortical slices. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:135–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R., LeGrady D., Nanas S., Trevisan M., Mansour M., Histand P., Ostrow D., Stamler J. Increased sodium-lithium countertransport in college students with elevated blood pressure. JAMA. 1983 Feb 25;249(8):1030–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig P. U., D'Occhio M. A., Boylan J. W. Lymphocyte membrane sodium-proton exchange in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1987 Mar;9(3):282–288. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz M. B., Boyarsky G., Sterzel R. B., Boron W. F. Arginine vasopressin enhances pHi regulation in the presence of HCO3- by stimulating three acid-base transport systems. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):648–651. doi: 10.1038/337648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Cohen S., Rothstein A. Cytoplasmic pH regulation in thymic lymphocytes by an amiloride-sensitive Na+/H+ antiport. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):341–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Goetz J. D., Rothstein A. 22Na+ fluxes in thymic lymphocytes. II. Amiloride-sensitive Na+/H+ exchange pathway; reversibility of transport and asymmetry of the modifier site. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Oct;84(4):585–600. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatori N., Fine B. P., Nakamura A., Cragoe E., Jr, Aviv A. Angiotensin II effect on cytosolic pH in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5073–5078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L., Cogan M. G., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Ives H. E. Thrombin activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger in vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for a kinase C-independent pathway which is Ca2+-dependent and pertussis toxin-sensitive. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14134–14140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Determination of the coupling ratio for Na+ -H+ exchange in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 14;689(1):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama S., Denny T. N., Aviv A. 22Na+ and 86Rb+ transport in vascular smooth muscle of SHR, Wistar Kyoto, and Wistar rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;11(6):722–729. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198806000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Franchi A., Cragoe E., Jr, Pouysségur J. Blockade of the Na+/H+ antiport abolishes growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in fibroblasts. Structure-activity relationships in the amiloride series. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4313–4319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livne A., Balfe J. W., Veitch R., Marquez-Julio A., Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Increased platelet Na+-H+ exchange rates in essential hypertension: application of a novel test. Lancet. 1987 Mar 7;1(8532):533–536. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90176-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D., McLaughlin C. W., Scott R. J. Sodium-hydrogen ion exchange in rabbit renal cortical slices incubated in acetate media. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:523–541. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahnensmith R. L., Aronson P. S. The plasma membrane sodium-hydrogen exchanger and its role in physiological and pathophysiological processes. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):773–788. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meininger G. A., Harris P. D., Joshua I. G. Distributions of microvascular pressure in skeletal muscle of one-kidney, one clip, two-kidney, one clip, and deoxycorticosterone-salt hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):27–34. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.6.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. T., Pollock A. S. Modification of the internal pH sensitivity of the Na+/H+ antiporter by parathyroid hormone in a cultured renal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9115–9120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi T., Ives H. E. Intracellular Ca2+ requirement for activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8790–8795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tsien R. Y., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Na+/H+ exchange and cytoplasmic pH in the action of growth factors in human fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):645–648. doi: 10.1038/304645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Hopfer U., Kinne R. Sodium/proton antiport in brush-border-membrane vesicles isolated from rat small intestine and kidney. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):597–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso A. M., Tsien R. Y., Machen T. E. Na+-H+ exchange in gastric glands as measured with a cytoplasmic-trapped, fluorescent pH indicator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7436–7440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Gupta R. K., Sosa R. E., Corbett M. L., Laragh J. H. Intracellular pH in human and experimental hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7663–7667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Brock T. A. Analysis of angiotensin-stimulated sodium transport in cultured smooth muscle cells from rat aorta. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Mar;114(3):284–290. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. The Na+-dependent regulation of the internal pH in chick skeletal muscle cells. The role of the Na+/H+ exchange system and its dependence on internal pH. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1865–1870. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


