Abstract
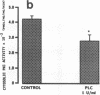
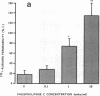
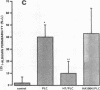
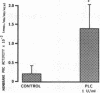
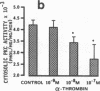
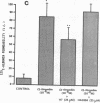
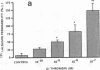
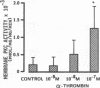
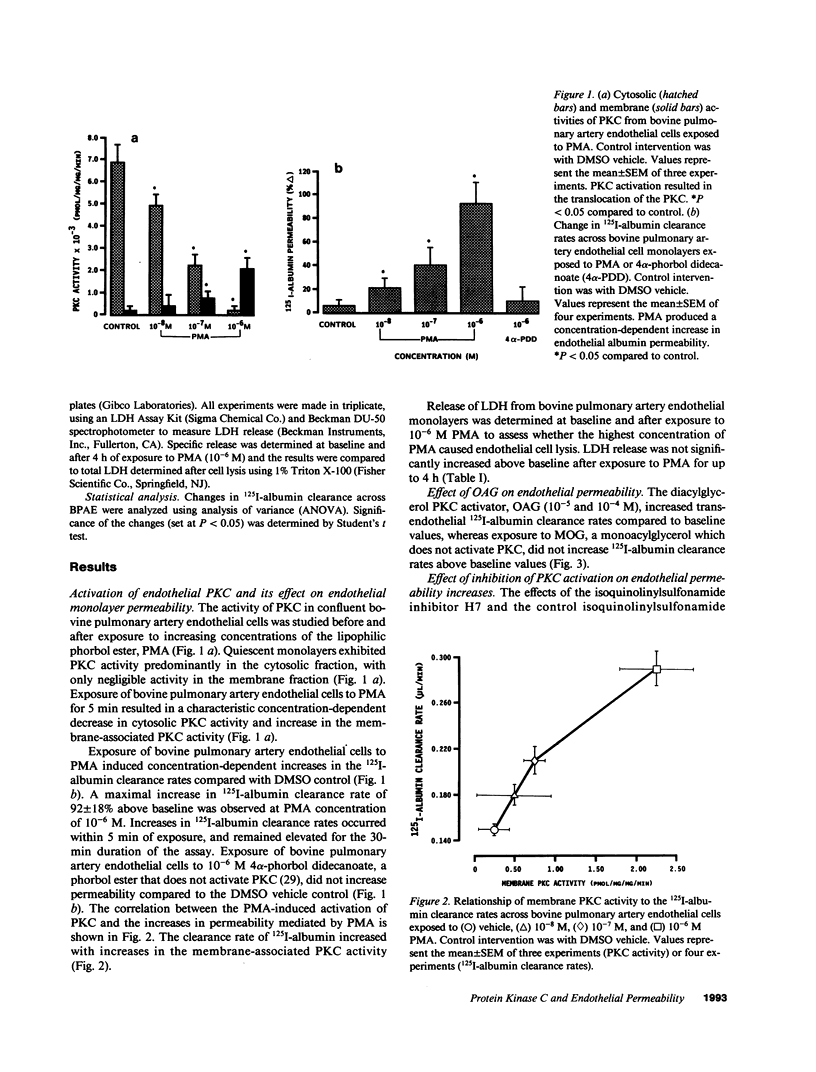
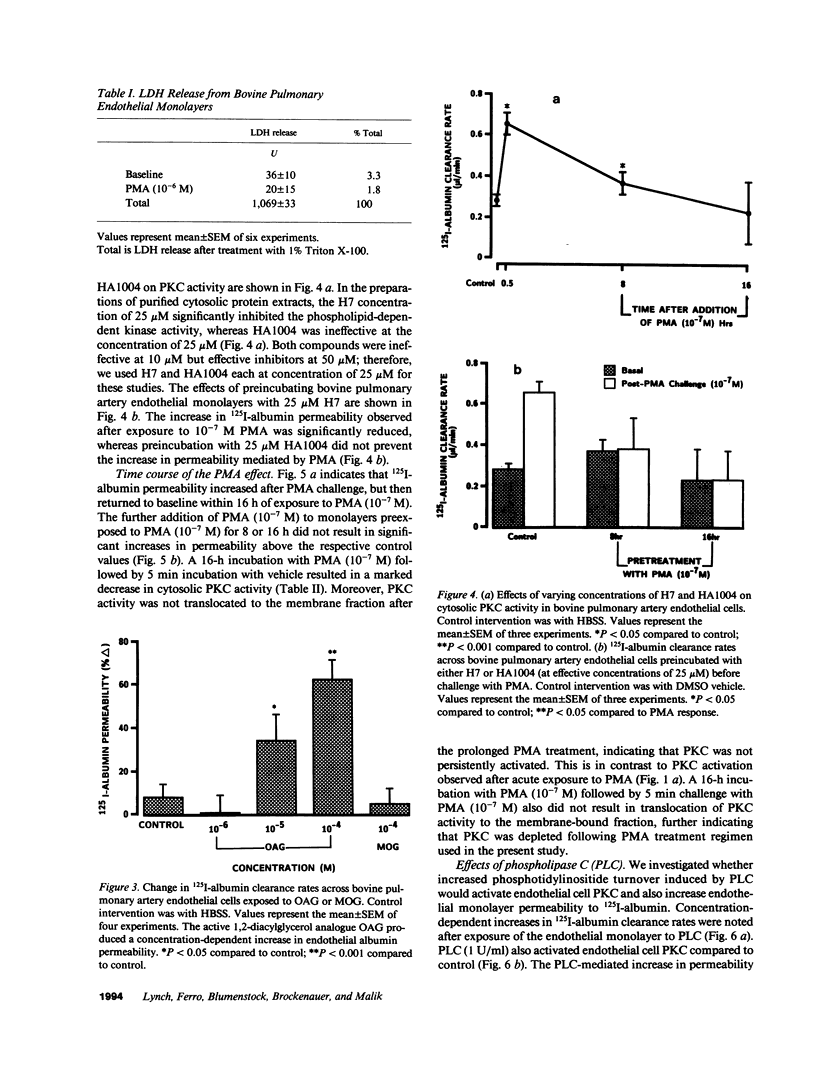
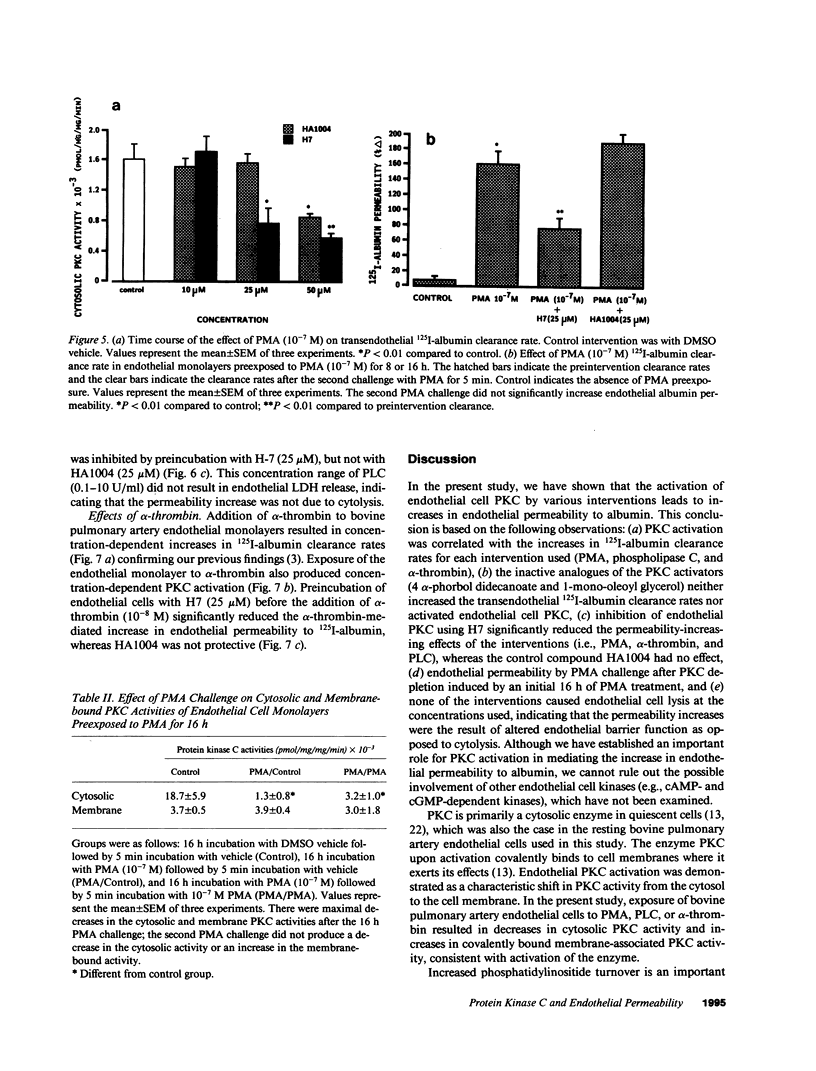
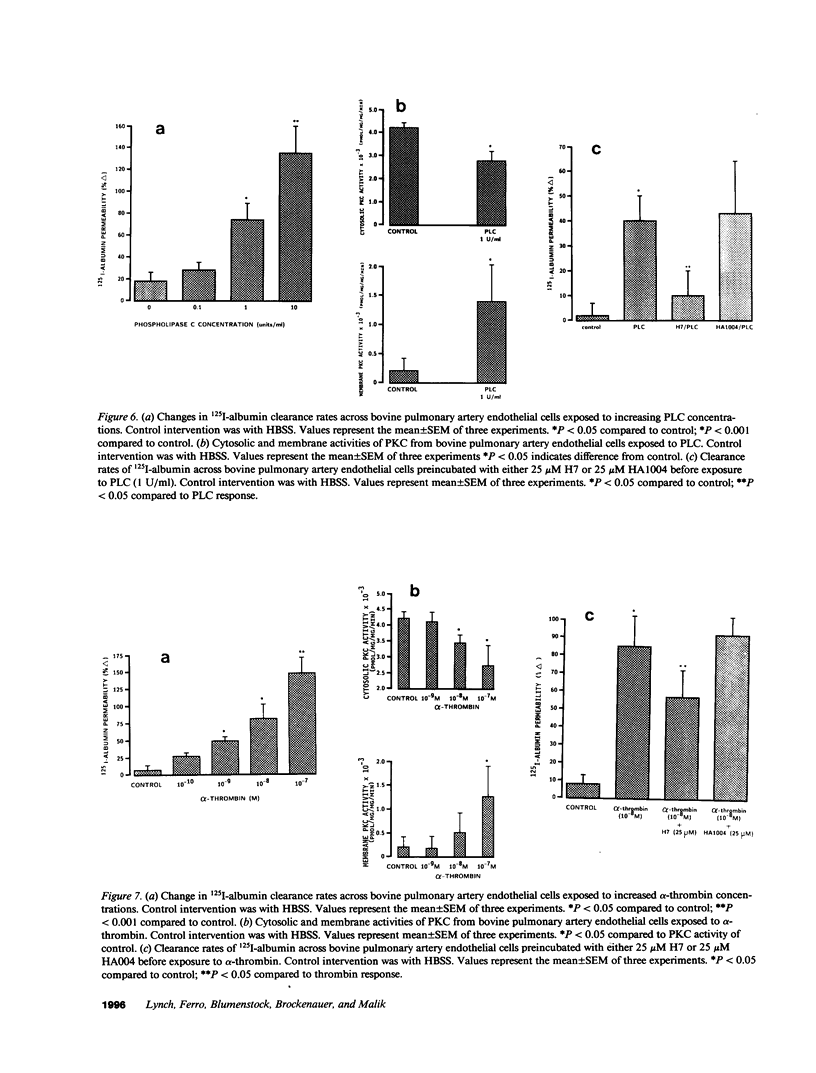
We examined the effects of activation of endothelial protein kinase C (PKC) of the endothelial barrier function. Exposure of confluent bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cell monolayers to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) resulted in concentration-dependent (10(-8)-10(-6) M) increases in PKC activity and in the transendothelial flux of 125I-albumin. Exposure of the endothelium to 1-oleoyl 2-acetyl glycerol (OAG) also increased the transendothelial flux of 125I-albumin in a concentration-dependent manner. Neither 4 alpha-phorbol didecanoate nor 1-mono-oleoyl glycerol, which do not activate PKC, altered permeability. The increase in 125I-albumin permeability induced by PMA was inhibited by 25 microM H7 (a PKC inhibitor), but not by the control compound HA1004 (25 microM). After 16 h of exposure to PMA, 125I-albumin permeability returned to baseline and a significant reduction in cytosolic PKC activity was noted. Further challenge with PMA at this time resulted in no significant increase in PKC activity indicating downregulation of the enzyme; moreover, this PMA challenge did not increase endothelial permeability. Exposure of endothelial monolayers to phospholipase C (PLC), which increases membrane phosphatidylinositide turnover, or to alpha-thrombin also induced concentration-dependent activation of PKC and increases in 125I-albumin endothelial permeability. The thrombin- and PLC-induced permeability increases were inhibited by H7, but not by HA1004. The activation of endothelial PKC directly by PMA or OAG and by PLC and alpha-thrombin increases the transendothelial albumin permeability, indicating that PKC activation is an important signal transduction pathway by which extracellular mediators increase endothelial macromolecular transport.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOCCI V. EFFICIENT LABELLING OF SERUM PROTEINS WITH I-131 USING CHLORAMINE T. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1964 Aug;15:449–456. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(64)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Structural alterations of lung parenchyma in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Chest Med. 1982 Jan;3(1):35–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Francis P. B., Pierce A. K. Intravascular coagulation associated with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Med. 1976 Nov;61(5):585–589. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cintora I., Goodale R. L., Yamoor A. The effect of endotoxin on the alveolocapillary permeability coefficient in the dog. J Surg Res. 1972 Aug;13(2):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(72)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Del Vecchio P. J., Minnear F. L., Burhop K. E., Selig W. M., Garcia J. G., Malik A. B. Measurement of albumin permeability across endothelial monolayers in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Mar;62(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.3.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J., Stackrow A. B. Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3587–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainer H. S., Murray A. W. Diacylglycerol inhibits gap junctional communication in cultured epidermal cells: evidence for a role of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 15;126(3):1109–1113. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdal K. S., Evensen S. A., Nilsen E. Thrombin-induced shape changes of cultured endothelial cells: metabolic and functional observations. Thromb Res. 1983 Oct 1;32(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. G., Siflinger-Birnboim A., Bizios R., Del Vecchio P. J., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Malik A. B. Thrombin-induced increase in albumin permeability across the endothelium. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jul;128(1):96–104. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Tosco R., Wheelis R. F., Gould N. S., Kapanci Y. Oxygen pneumonitis in man. Ultrastructural observations on the development of alveolar lesions. Lab Invest. 1972 May;26(5):499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Devanney J. F., Kennedy S. P. Vimentin, a cytoskeletal substrate of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90728-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. Regulation of phosphoinositide breakdown by guanine nucleotides. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 21;39(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum H., Del Vecchio P. J., Schneider A. S., Goligorsky M. S., Malik A. B. Calcium dependence of the thrombin-induced increase in endothelial albumin permeability. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1471–1476. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. B. Pulmonary microembolism. Physiol Rev. 1983 Jul;63(3):1114–1207. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.3.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin J. M., O'Brien T. G. Effects of tumor promoters on LLC-PK1 renal epithelial tight junctions and transepithelial fluxes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C597–C602. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojakian G. K. Tumor promoter-induced changes in the permeability of epithelial cell tight junctions. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90274-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltier L. F. Fat embolism. An appraisal of the problem. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984 Jul-Aug;(187):3–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory-distress syndrome: changing concepts of lung injury and repair. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 15;306(15):900–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204153061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahal D., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Protein kinase assay by paper-trichloroacetic acid method: high performance using phosphocellulose paper and washing an ensemble of samples on flat sheets. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 15;167(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Yorek M., Shasby S. S. Exogenous oxidants initiate hydrolysis of endothelial cell inositol phospholipids. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):491–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Weber P. C., Lapetina E. G. Activation of phospholipase C is dissociated from arachidonate metabolism during platelet shape change induced by thrombin or platelet-activating factor. Epinephrine does not induce phospholipase C activation or platelet shape change. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8286–8292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siflinger-Birnboim A., Cooper J. A., del Vecchio P. J., Lum H., Malik A. B. Selectivity of the endothelial monolayer: effects of increased permeability. Microvasc Res. 1988 Nov;36(3):216–227. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L. Prostaglandin biosynthesis and its compartmentation in vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:251–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. P., Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Hormone- and tumor promoter-induced activation or membrane association of protein kinase C in intact cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:399–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werth D. K., Niedel J. E., Pastan I. Vinculin, a cytoskeletal substrate of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11423–11426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson M., McPhail L. C., Nasrallah V. N., Snyderman R. Phorbol myristate acetate mediates redistribution of protein kinase C in human neutrophils: potential role in the activation of the respiratory burst enzyme. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2057–2062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Enomoto T., Martel N., Shiba Y., Kanno Y. Tumour promoter-mediated reversible inhibition of cell-cell communication (electrical coupling). Relationship with phorbol ester binding and de novo macromolecule synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jul;146(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lanerolle P., Nishikawa M. Regulation of embryonic smooth muscle myosin by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9071–9074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]