Abstract
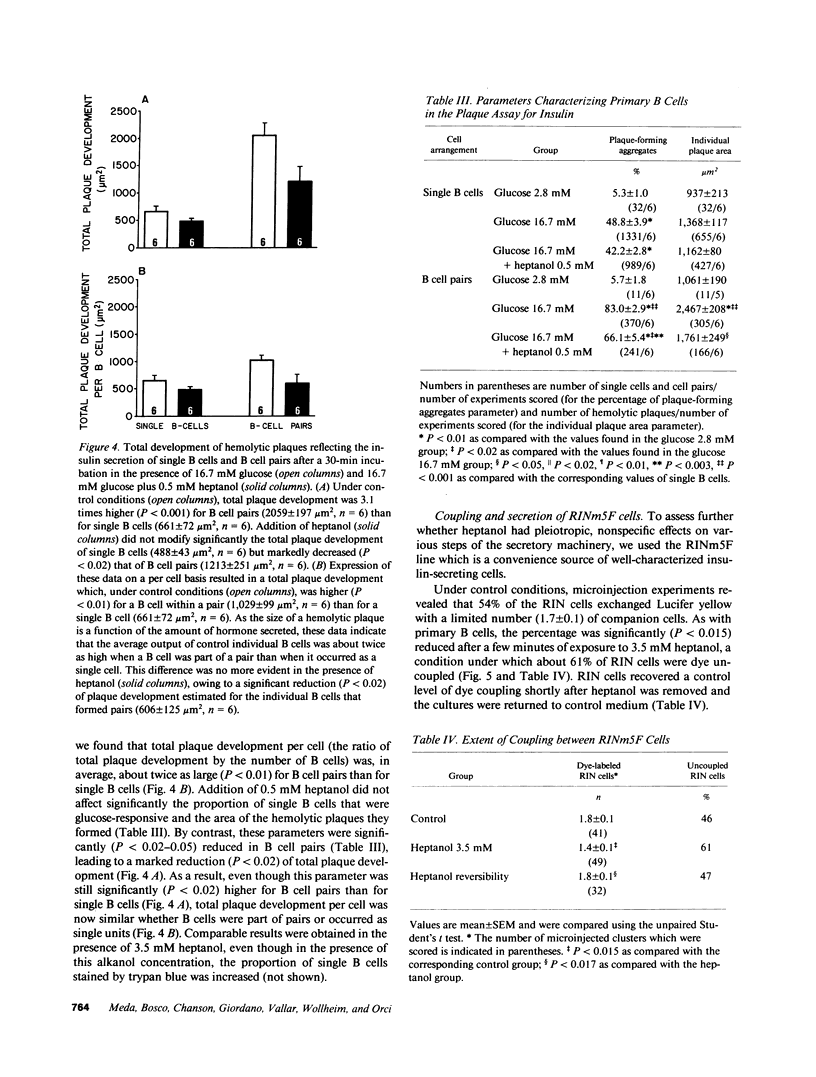
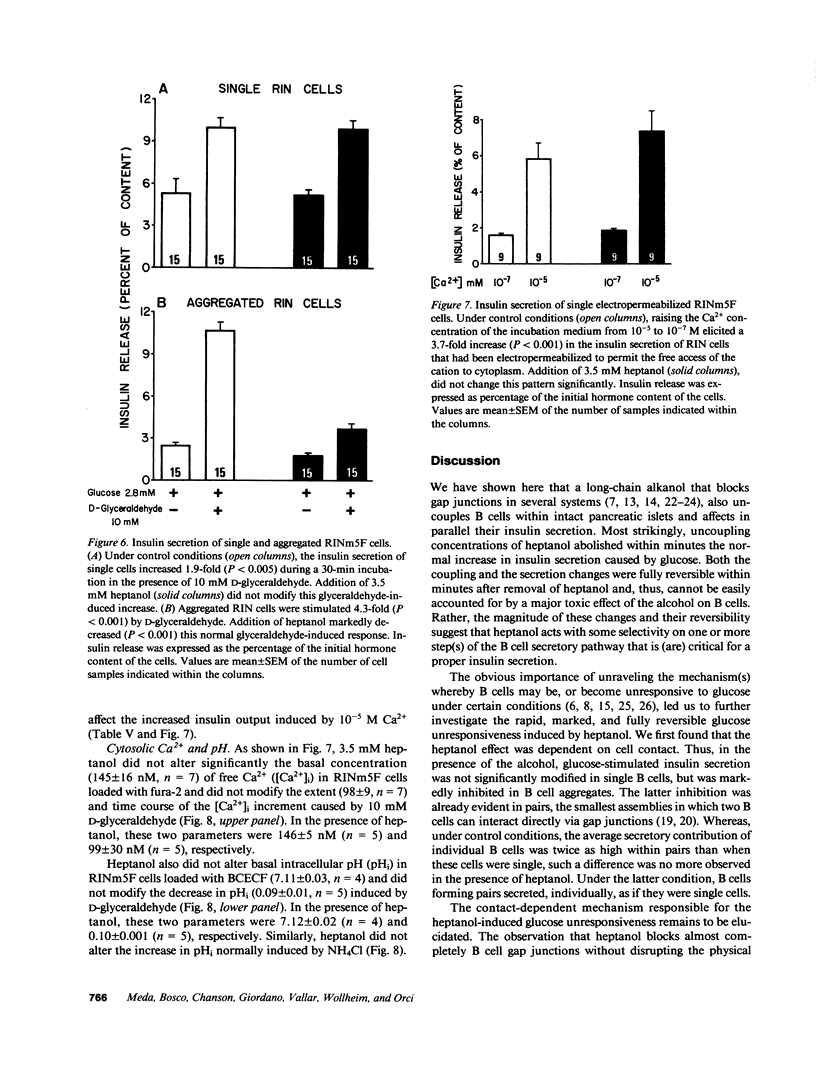
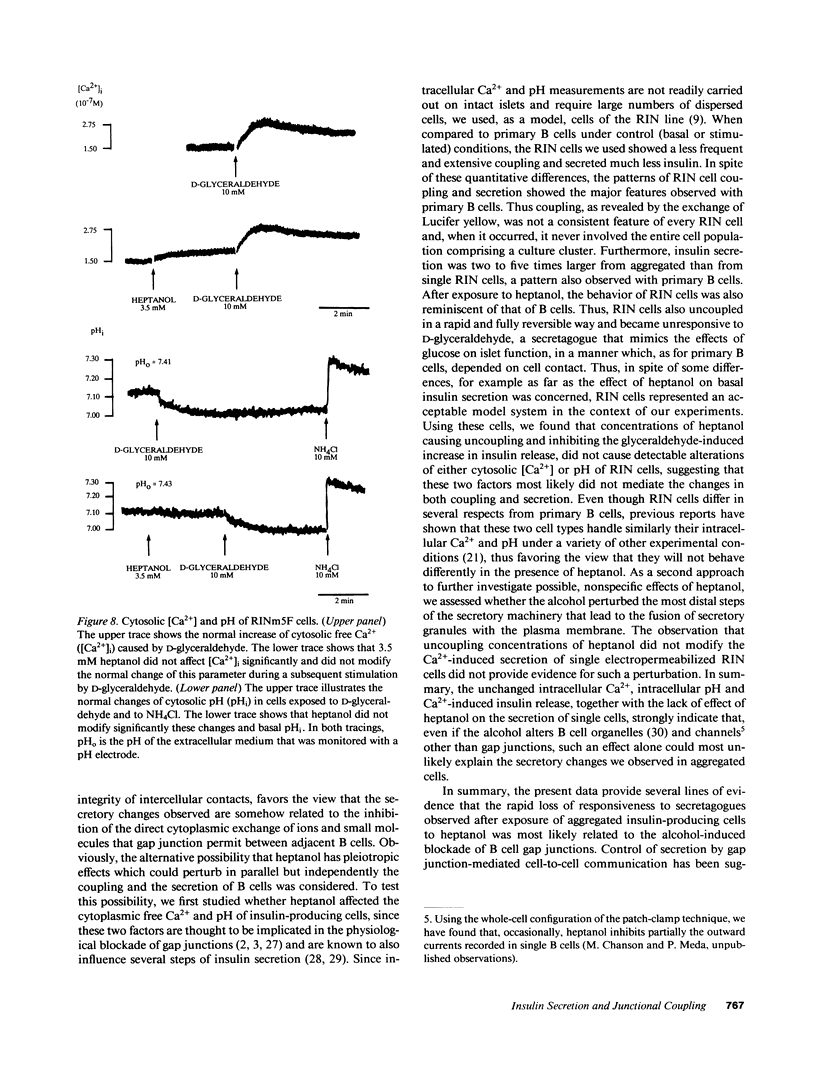
To determine whether insulin secretion is affected by a blockage of gap junctions between B cells, we have studied the secretion of rat pancreatic islets of Langerhans, primary dispersed islet cells, and cells of the RINm5F line, during short-term exposure to heptanol. Within minutes, this alkanol blocked gap junctions between the B cells of intact islets and abolished their normal secretory response to glucose. These two changes were rapidly and fully reversible after return of the islets to control medium. We further found that heptanol had no significant effect on the glucose-stimulated secretion of single B cells but inhibited that of B cell pairs. In the clone of RINm5F cells, whose junctional coupling and D-glyceraldehyde-induced stimulation of insulin release by aggregated cells were also inhibited by heptanol, this alkanol did not perturb intracellular pH and Ca2+ and the most distal steps of the secretion pathway. In summary, a gap junction blocker affected the secretion of insulin-producing cells by a mechanism which is dependent on cell contact and is not associated with detectable pleiotropic perturbations of the cell secretory machinery. The data provide evidence for the involvement of junctional coupling in the control of insulin secretion.
Full text
PDF
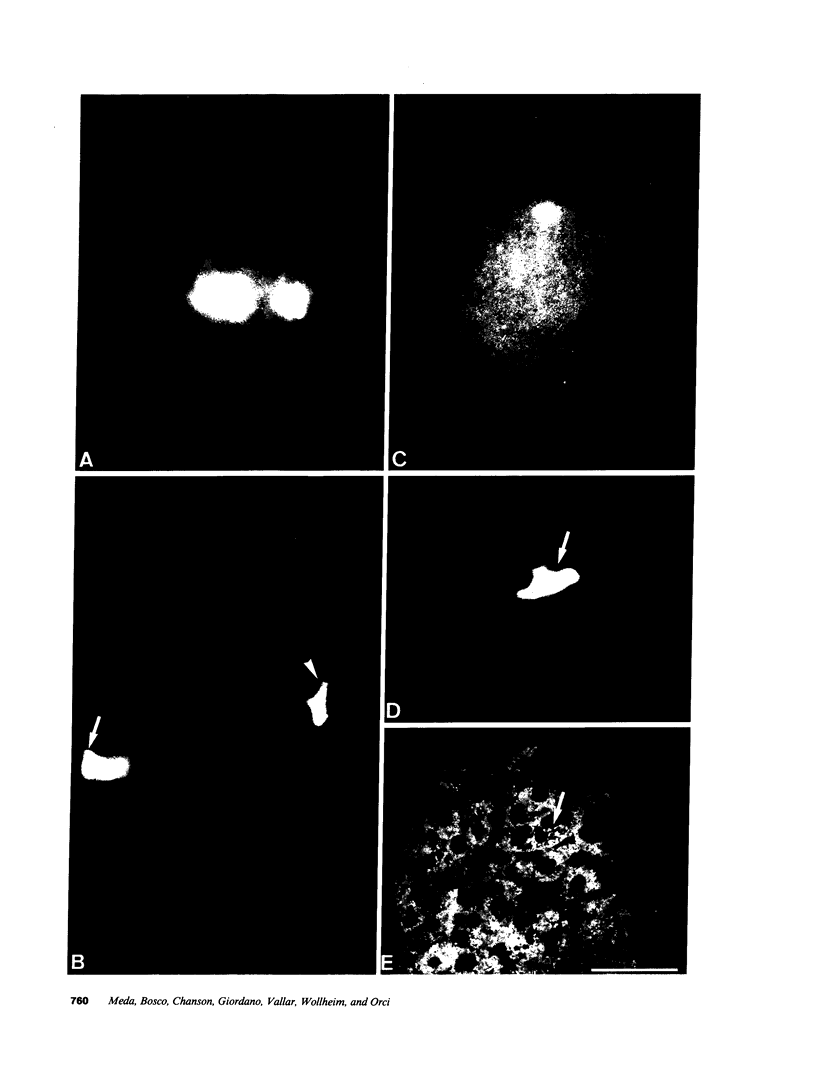
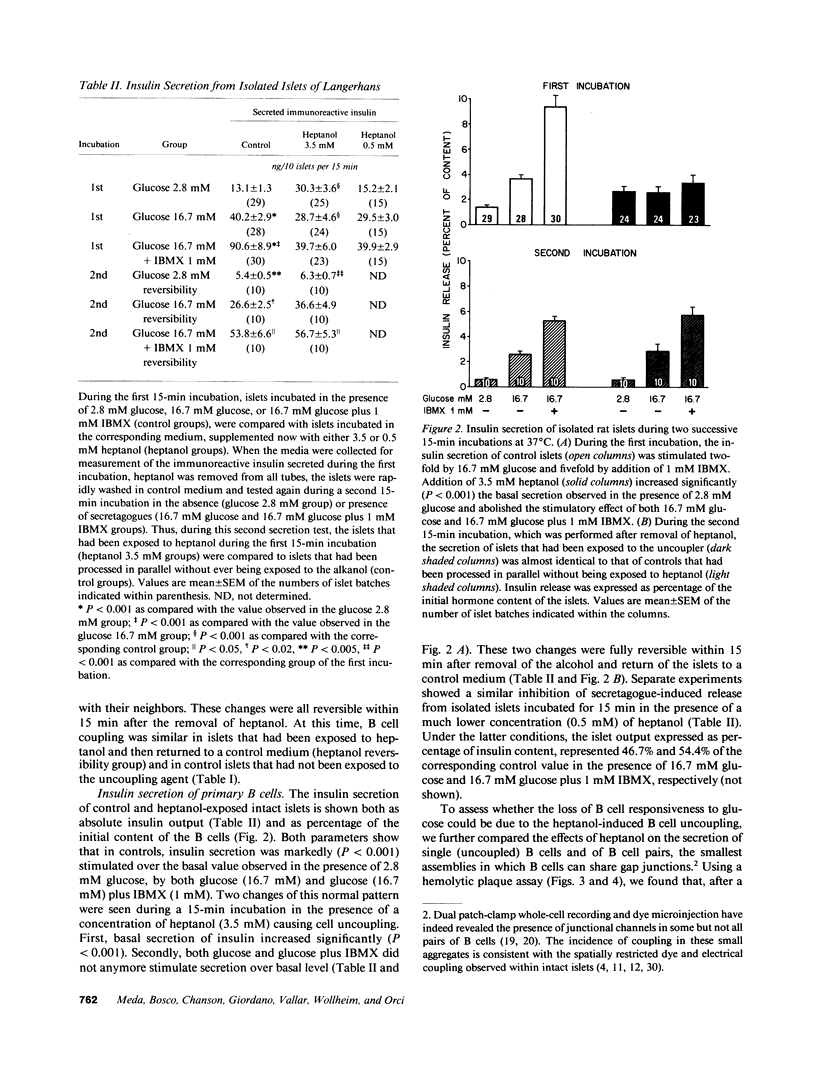



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaerts W., Wouters A., Van der Massen D., Persoons A., Denef C. A diffusion-adsorption model for the computation of the amount of hormone around a secreting cell, detected by the reverse hemolytic plaque assay. J Theor Biol. 1988 Apr 21;131(4):441–459. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini G., Peracchia C., Peracchia L. L. Reversible effects of heptanol on gap junction structure and cell-to-cell electrical coupling. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;34(2):307–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Trent D. F., Honey R. N., Weir G. C. Responses of neonatal rat islets to streptozotocin: limited B-cell regeneration and hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):64–69. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosco D., Orci L., Meda P. Homologous but not heterologous contact increases the insulin secretion of individual pancreatic B-cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Sep;184(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90365-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., Meda P. The gap junction: a channel for multiple functions? Eur J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;18(5):444–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1988.tb01038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendic S. Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. A glucose dose-response study. Diabetes. 1972 Apr;21(4):224–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanson M., Bruzzone R., Bosco D., Meda P. Effects of n-alcohols on junctional coupling and amylase secretion of pancreatic acinar cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):147–156. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Délèze J., Hervé J. C. Effect of several uncouplers of cell-to-cell communication on gap junction morphology in mammalian heart. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(3):203–215. doi: 10.1007/BF02332124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Meda P., Niesor E. N., Mintz D. H. The possible importance of contact between pancreatic islet cells for the control of insulin release. Endocrinology. 1982 Jul;111(1):86–94. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-1-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Henry C., Nordin A. A., Fuji H., Koros A. M., Lefkovits I. Plaque forming cells: methodology and theory. Transplant Rev. 1974;18:130–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. F., Simon S. A., Ramón F. Interaction of anaesthetics with electrical synapses. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):498–500. doi: 10.1038/286498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knodel S., Meda P., Orci L. Rapid in vitro formation of smooth endoplasmic reticulum aggregates within peptide-producing islet cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Oct;133(1):111–118. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Bruzzone R., Chanson M., Bosco D., Orci L. Gap junctional coupling modulates secretion of exocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4901–4904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Bruzzone R., Knodel S., Orci L. Blockage of cell-to-cell communication within pancreatic acini is associated with increased basal release of amylase. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):475–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Michaels R. L., Halban P. A., Orci L., Sheridan J. D. In vivo modulation of gap junctions and dye coupling between B-cells of the intact pancreatic islet. Diabetes. 1983 Sep;32(9):858–868. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.9.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Perrelet A., Orci L. Increase of gap junctions between pancreatic B-cells during stimulation of insulin secretion. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):441–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Santos R. M., Atwater I. Direct identification of electrophysiologically monitored cells within intact mouse islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):232–236. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H., Renold A. E. Structural coupling between pancreatic islet cells. Experientia. 1973 Aug 15;29(8):1015–1018. doi: 10.1007/BF01930436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Tarvin J. T., Smith J. S. Stimulus-secretion coupling in beta-cells: modulation by pH. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):E3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.1.E3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D., Meda P. Heterogeneity and contact-dependent regulation of hormone secretion by individual B cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Feb;162(2):507–520. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Physiology and pharmacology of gap junctions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:281–303. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Guanine nucleotides induce Ca2+-independent insulin secretion from permeabilized RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Biden T. J. Second messenger function of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Early changes in inositol phosphates, cytosolic Ca2+, and insulin release in carbamylcholine-stimulated RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8314–8319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Biden T. J. Signal transduction in insulin secretion: comparison between fuel stimuli and receptor agonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:317–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]