Abstract
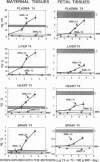
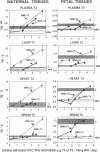
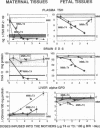
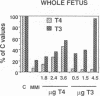
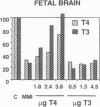
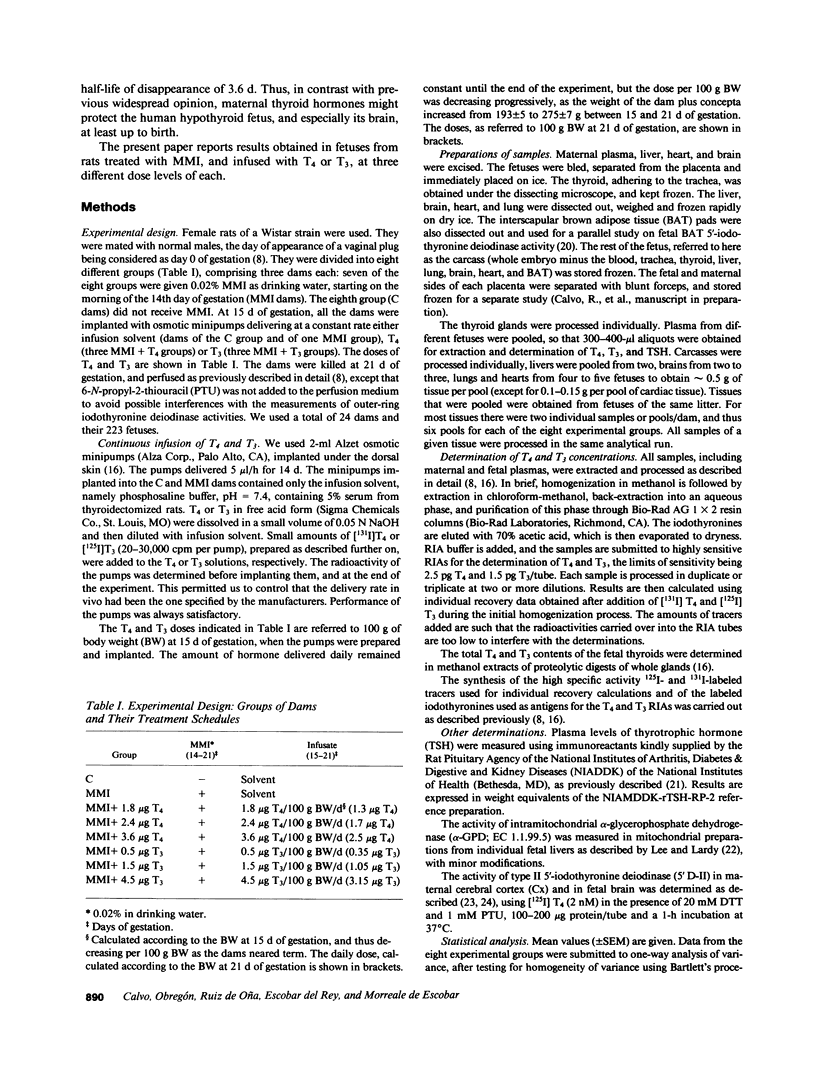
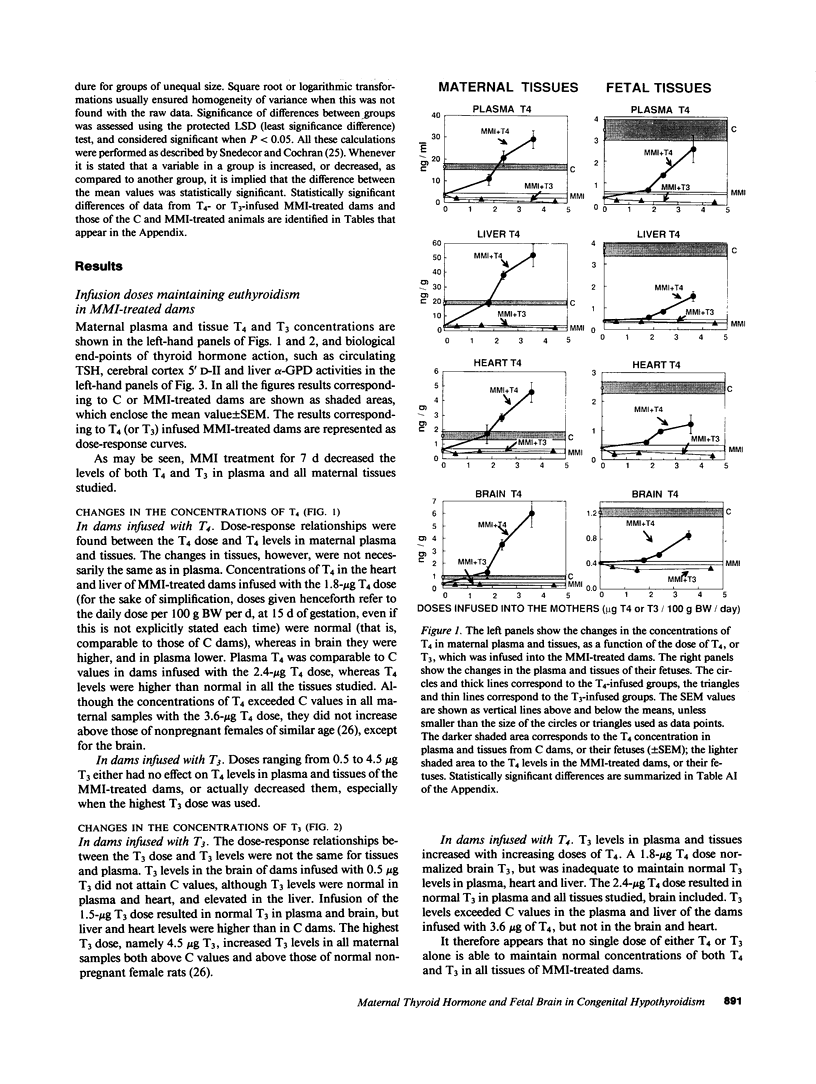
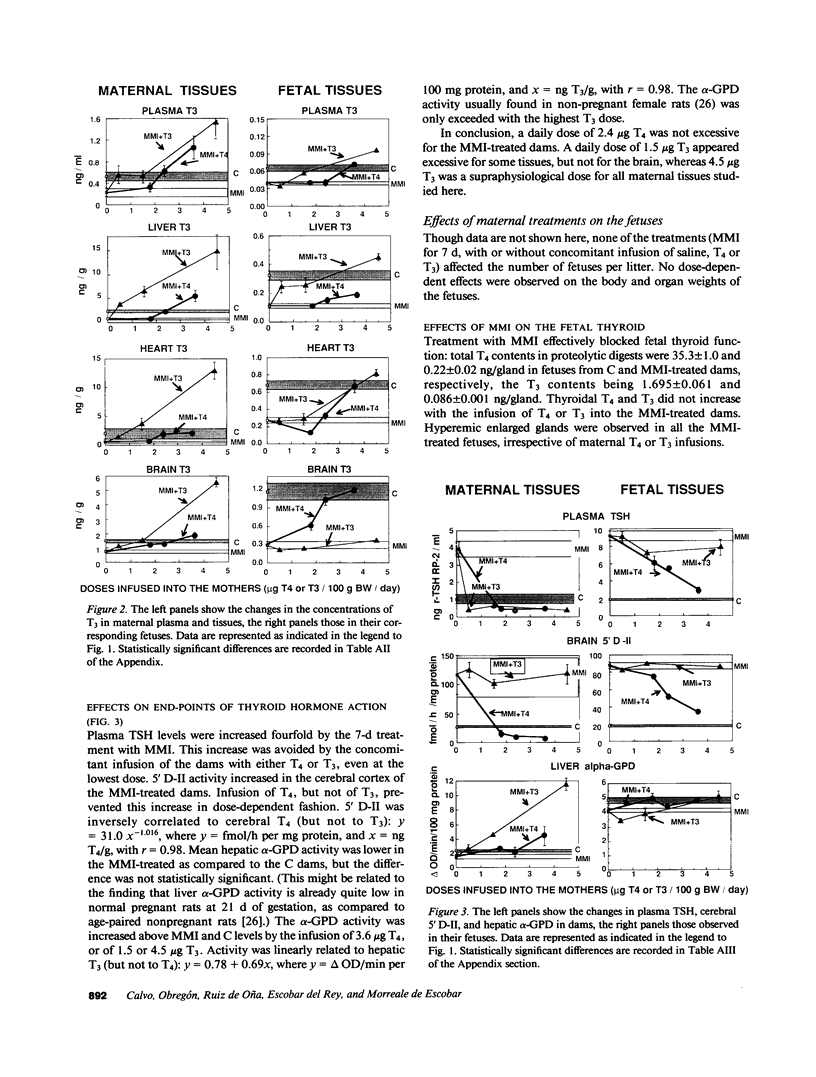
To study the protective effects of maternal thyroxine (T4) and 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3) in congenital hypothyroidism, we gave pregnant rats methimazole (MMI), an antithyroid drug that crosses the placenta, and infused them with three different doses of T4 or T3. The concentrations of both T4 and T3 were determined in maternal and fetal plasma and tissues (obtained near term) by specific RIAs. Several thyroid hormone-dependent biological end-points were also measured. MMI treatment resulted in marked fetal T4 and T3 deficiency. Infusion of T4 into the mothers increased both these pools in a dose-dependent fashion. There was a preferential increase of T3 in the fetal brain. Thus, with a T4 dose maintaining maternal euthyroidism, fetal brain T3 reached normal values, although fetal plasma T4 was 40% of normal and plasma TSH was high. The infusion of T3 pool into the mothers increased the total fetal extrathyroidal T3 pool in a dose-dependent fashion. The fetal T4 pools were not increased, however, and this deprived the fetal brain (and possibly the pituitary) of local generation of T3 from T4. As a consequence, fetal brain T3 deficiency was not mitigated even when dams were infused with a toxic dose of T3. The results show that (a) there is a preferential protection of the brain of the hypothyroid fetus from T3 deficiency; (b) maternal T4, but not T3, plays a crucial role in this protection, and (c) any condition which lowers maternal T4 (including treatment with T3) is potentially harmful for the brain of a hypothyroid fetus. Recent confirmation of transplacental passage of T4 in women at term suggests that present results are relevant for human fetuses with impairment of thyroid function. Finding signs of hypothyroidism at birth does not necessarily mean that the brain was unprotected in utero, provided maternal T4 is normal. It is crucial to realize that maintainance of maternal "euthyroidism" is not sufficient, as despite hypothyroxinemia, the mothers may be clinically euthyroid if their T3 levels are normal.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J. N. Fetal and neonatal cerebral blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1966 Apr;210(4):897–902. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.4.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernal J., Pekonen F. Ontogenesis of the nuclear 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptor in the human fetal brain. Endocrinology. 1984 Feb;114(2):677–679. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-2-677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARR E. A., Jr, BEIERWALTES W. H., RAMAN G., DODSON V. N., TANTON J., BETTS J. S., STAMBAUGH R. A. The effect of maternal thyroid function of fetal thyroid function and development. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Jan;19(1):1–18. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crantz F. R., Silva J. E., Larsen P. R. An analysis of the sources and quantity of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine specifically bound to nuclear receptors in rat cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):367–375. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delange F., Costa A., Ermans A. M., Ibbertson H. K., Querido A., Stanbury J. B. A survey of the clinical and metabolic patterns of endemic cretinism. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;30:175–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson P. W., Aldred A. R., Menting J. G., Marley P. D., Sawyer W. H., Schreiber G. Thyroxine transport in choroid plexus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13907–13915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dussault J., Row V. V., Lickrish G., Volpé R. Studies of serum triiodothyronine concentration in maternal and cord blood: transfer of triiodothyronine across the human placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Apr;29(4):595–603. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-4-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar del Rey F., Ruiz de Oña C., Bernal J., Obregón M. J., Morreale de Escobar G. Generalized deficiency of 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3) in tissues from rats on a low iodine intake, despite normal circulating T3 levels. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Apr;120(4):490–498. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1200490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER D. A., LEHMAN H., LACKEY C. PLACENTAL TRANSPORT OF THYROXINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 May;24:393–400. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-5-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Klein A. H. Thyroid development and disorders of thyroid function in the newborn. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 19;304(12):702–712. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103193041205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A. The unique endocrine milieu of the fetus. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):603–611. doi: 10.1172/JCI112616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUMBACH M. M., WERNER S. C. Transfer of thyroid hormone across the human placenta at term. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Oct;16(10):1392–1395. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-10-1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B., Galton V. A. The transplacental passage of thyroxine and foetal thyroid function in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Apr;75(4):725–733. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0750725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamburgh M. The role of thyroid and growth hormones in neurogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1969;4:109–148. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerfield F., Hollander C. S. Thyroidal complications of pregnancy. Med Clin North Am. 1977 Jan;61(1):67–87. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEARNS J. E., HUTSON W. TAGGED ISOMERS AND ANALOGUES OF THYROXINE (THEIR TRANSMISSION ACROSS THE HUMAN PLACENTA AND OTHER STUDIES). J Nucl Med. 1963 Nov;4:453–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOBIL E., JOSIMOVICH J. B. Placental transfer of thyrotropic hormone, thyroxine, triiodothyronine, and insulin in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Jan 9;75:895–904. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE Y. P., LARDY H. A. INFLUENCE OF THYROID HORMONES ON L-ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASES AND OTHER DEHYDROGENASES IN VARIOUS ORGANS OF THE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1427–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R. Maternal thyroxine and congenital hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):44–46. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Kaplan M. M., Visser T. J., Silva J. E., Larsen P. R. Cerebral cortex responds rapidly to thyroid hormones. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.7291997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morreale de Escobar G., Obregon M. J., Escobar del Rey F. Fetal and maternal thyroid hormones. Horm Res. 1987;26(1-4):12–27. doi: 10.1159/000180681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morreale de Escobar G., Obregon M. J., Ruiz de Oña C., Escobar del Rey F. Transfer of thyroxine from the mother to the rat fetus near term: effects on brain 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine deficiency. Endocrinology. 1988 Apr;122(4):1521–1531. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-4-1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morreale de Escobar G., Pastor R., Obregon M. J., Escobar del Rey F. Effects of maternal hypothyroidism on the weight and thyroid hormone content of rat embryonic tissues, before and after onset of fetal thyroid function. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):1890–1900. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-1890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obregon M. J., Mallol J., Pastor R., Morreale de Escobar G., Escobar del Rey F. L-thyroxine and 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in rat embryos before onset of fetal thyroid function. Endocrinology. 1984 Jan;114(1):305–307. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-1-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obregón M. J., Ruiz de Oña C., Hernandez A., Calvo R., Escobar del Rey F., Morreale de Escobar G. Thyroid hormones and 5'-deiodinase in rat brown adipose tissue during fetal life. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):E625–E631. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.5.E625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Koerner D., Dillmann W. H. Nuclear receptors and the initiation of thyroid hormone action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:529–565. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Castillo A., Bernal J., Ferreiro B., Pans T. The early ontogenesis of thyroid hormone receptor in the rat fetus. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2457–2461. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. A., Ehrlich R. M., Walfish P. G. Congenital hypothyroidism. Clinical and laboratory characteristics in infants detected by neonatal screening. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Nov;56(11):845–851. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.11.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiti S., Holzman G. B., Scott R. L., Blizzard R. M. Evidence for the placental transfer of tri-iodothyronine in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1967 Aug 31;277(9):456–459. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196708312770903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roti E., Gnudi A., Braverman L. E. The placental transport, synthesis and metabolism of hormones and drugs which affect thyroid function. Endocr Rev. 1983 Spring;4(2):131–149. doi: 10.1210/edrv-4-2-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz de Oña C., Obregón M. J., Escobar del Rey F., Morreale de Escobar G. Developmental changes in rat brain 5'-deiodinase and thyroid hormones during the fetal period: the effects of fetal hypothyroidism and maternal thyroid hormones. Pediatr Res. 1988 Nov;24(5):588–594. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198811000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santisteban P., Obregon M. J., Rodriguez-Peña A., Lamas L., Del Rey F. E., De Escobar G. M. Are iodine-deficient rats euthyroid? Endocrinology. 1982 May;110(5):1780–1789. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-5-1780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selenkow H. A., Birnbaum M. D., Hollander C. S. Thyroid function and dysfunction during pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Sep;16(3):66–108. doi: 10.1097/00003081-197309000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. E., Leonard J. L. Regulation of rat cerebrocortical and adenohypophyseal type II 5'-deiodinase by thyroxine, triiodothyronine, and reverse triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1627–1635. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. E., Matthews P. S. Production rates and turnover of triiodothyronine in rat-developing cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Responses to hypothyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):1035–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI111471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulsma T., Gons M. H., de Vijlder J. J. Maternal-fetal transfer of thyroxine in congenital hypothyroidism due to a total organification defect or thyroid agenesis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):13–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Coulombe P., Dussault J. H. Effects of triiodothyronine on thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced thyrotropin release in the neonatal rat. Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):1731–1737. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolter R., Noël P., De Cock P., Craen M., Ernould C., Malvaux P., Verstaeten F., Simons J., Mertens S., Van Broeck N. Neuropsychological study in treated thyroid dysgenesis. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1979;277:41–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb06190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods R. J., Sinha A. K., Ekins R. P. Uptake and metabolism of thyroid hormones by the rat foetus in early pregnancy. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Sep;67(3):359–363. doi: 10.1042/cs0670359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Doorn J., van der Heide D., Roelfsema F. Sources and quantity of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine in several tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1778–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI111138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]