Abstract
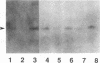
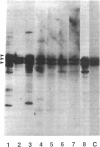
Gene rearrangement studies were performed on blood lymphocytes from eight patients with acute Epstein-Barr virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. The diagnosis in each case was based on characteristic clinical, hematologic, and serologic findings. The blood lymphocytes in each patient consisted predominantly of CD8+ T cells. EBV DNA was detected in seven patients by Southern blot analysis (EBV Bam HI W probe, Bam HI). A germline configuration was found for the immunoglobulin heavy and light chain genes (JH probe, Bam HI and Eco RI; C kappa probe, Bam HI; and C lambda probe, Eco RI). T cell receptor gene rearrangements were detected with J gamma and J beta 1 + 2 probes. Using a J gamma probe with two different restriction enzymes (Bgl II and Eco RI), the blood from each patient showed several bands corresponding to the polyclonal pattern previously described in the blood of normal individuals. Using J beta 1 + 2 probes with two different restriction enzymes (Bgl II and Bam HI), each case showed from 3 to about 12 extragermline bands of varying intensity and in different locations from case to case. In addition, each case showed relative deletion of the J beta 1 germline band. This oligoclonal pattern of T cell receptor gene rearrangements has not been previously reported in benign or malignant T cell populations.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertness V., Kirsch I., Hollis G., Johnson B., Bunn P. A., Jr T-cell receptor gene rearrangements as clinical markers of human T-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 29;313(9):534–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508293130902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., Kieff E. Long internal direct repeat in Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):286–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.286-294.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Chao J., Warnke R., Sklar J. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement as a diagnostic criterion of B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):593–597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waele M., Thielemans C., Van Camp B. K. Characterization of immunoregulatory T cells in EBV-induced infectious mononucleosis by monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 19;304(8):460–462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102193040804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flug F., Pelicci P. G., Bonetti F., Knowles D. M., 2nd, Dalla-Favera R. T-cell receptor gene rearrangements as markers of lineage and clonality in T-cell neoplasms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. E., Horwitz C. A. Epstein-Barr virus specific diagnostic tests in infectious mononucleosis. Hum Pathol. 1974 Sep;5(5):551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Polesky H., Balfour H. H., Jr, Siem R. A., Borken S., Ward P. C. Heterophil-negative infectious mononucleosis and mononucleosis-like illnesses. Laboratory confirmation of 43 cases. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):947–957. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90550-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Vonderheid E. C., Sako D., Clayton L. K., Olbricht S. Clonal composition of T cells in lymphomatoid papulosis. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):13–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Zandrew F., Davidsohn I. Horse agglutinins in infectious mononueleosis. 3. riterion for differential diagnosis. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Sep;21(5):631–634. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.5.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Hutt L. M., Shaw J. E., Li J. L., Pagano J. S. Replication of EBV in epithelial cells during infectious mononucleosis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):268–270. doi: 10.1038/268268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden M. D., Toyonaga B., Ha K., Yanagi Y., Chin B., Gelfand E., Mak T. Somatic rearrangement of T-cell antigen receptor gene in human T-cell malignancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1224–1227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Hamilton-Dutoit S., Herbst H., Finn T., Vetner M., Pallesen G., Stein H. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in tonsils of acute infectious mononucleosis by in situ hybridization. Hum Pathol. 1989 Aug;20(8):796–799. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor N. T., Wainscoat J. S., Weatherall D. J., Gatter K. C., Feller A. C., Isaacson P., Jones D., Lennert K., Pallesen G., Ramsey A. Rearrangement of the T-cell-receptor beta-chain gene in the diagnosis of lymphoproliferative disorders. Lancet. 1985 Jun 8;1(8441):1295–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92791-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci P. G., Knowles D. M., 2nd, Arlin Z. A., Wieczorek R., Luciw P., Dina D., Basilico C., Dalla-Favera R. Multiple monoclonal B cell expansions and c-myc oncogene rearrangements in acquired immune deficiency syndrome-related lymphoproliferative disorders. Implications for lymphomagenesis. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2049–2060. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Flynn K. The structure of the termini of the Epstein-Barr virus as a marker of clonal cellular proliferation. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):883–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90803-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Crawford D., Epstein M. A. Inhibition of the in vitro outgrowth of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphocytes by thymus-dependent lymphocytes from infectious mononucleosis patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Apr;28(1):72–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi G., Felici A., Ragona G., Heinz A. Quantitative evaluation of Epstein-Barr-virus-infected mononuclear peripheral blood leukocytes in infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jan 20;296(3):132–134. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197701202960302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley R. T., Arbit D. I., Henle W., Hirsch M. S. T-lymphocyte subset interactions in the cell-mediated immune response to Epstein-Barr virus. Cell Immunol. 1984 Jul;86(2):402–412. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar J., Weiss L. M. Applications of antigen receptor gene rearrangements to the diagnosis and characterization of lymphoid neoplasms. Annu Rev Med. 1988;39:315–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.39.020188.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Chess L., Strominger J. L. Suppression of in vitro Epstein-Barr virus infection. A new role for adult human T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):495–508. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Kersey J. H., Houston L. L., Vallera D. A. Use of a novel colony assay to evaluate the cytotoxicity of an immunotoxin containing pokeweed antiviral protein against blast progenitor cells freshly obtained from patients with common B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):347–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uppenkamp M., Pittaluga S., Lipford E. H., Cossman J. Limited diversity and selection of rearranged gamma genes in polyclonal T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1618–1620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Davis M. M., Bongiovanni K. F., Korsmeyer S. J. Rearrangements of genes for the antigen receptor on T cells as markers of lineage and clonality in human lymphoid neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 1985 Sep 26;313(13):776–783. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198509263131303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Hu E., Wood G. S., Moulds C., Cleary M. L., Warnke R., Sklar J. Clonal rearrangements of T-cell receptor genes in mycosis fungoides and dermatopathic lymphadenopathy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 29;313(9):539–544. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508293130903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A. In situ demonstration of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in viral-associated B cell lymphoproliferations. Am J Pathol. 1989 Mar;134(3):651–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Picker L. J., Copenhaver C. M., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Large-cell hematolymphoid neoplasms of uncertain lineage. Hum Pathol. 1988 Aug;19(8):967–973. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Picker L. J., Grogan T. M., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Absence of clonal beta and gamma T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in a subset of peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):436–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Wood G. S., Ellisen L. W., Reynolds T. C., Sklar J. Clonal T-cell populations in pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (Mucha-Habermann disease). Am J Pathol. 1987 Mar;126(3):417–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Wood G. S., Hu E., Abel E. A., Hoppe R. T., Sklar J. Detection of clonal T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in the peripheral blood of patients with mycosis fungoides/Sezary syndrome. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Apr;92(4):601–604. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12712131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Wood G. S., Hu E., Abel E. A., Hoppe R. T., Sklar J. Detection of clonal T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in the peripheral blood of patients with mycosis fungoides/Sezary syndrome. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Apr;92(4):601–604. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12712131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Wood G. S., Trela M., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Clonal T-cell populations in lymphomatoid papulosis. Evidence of a lymphoproliferative origin for a clinically benign disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 21;315(8):475–479. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608213150802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen T., Mellstedt H., Jondal M. Presence of clonal T cell populations in chronic B lymphocytic leukemia and smoldering myeloma. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):659–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Weiss L. M., Hu C. H., Abel E. A., Hoppe R. T., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. T-cell antigen deficiencies and clonal rearrangements of T-cell receptor genes in pagetoid reticulosis (Woringer-Kolopp disease). N Engl J Med. 1988 Jan 21;318(3):164–167. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198801213180307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]