Abstract
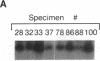
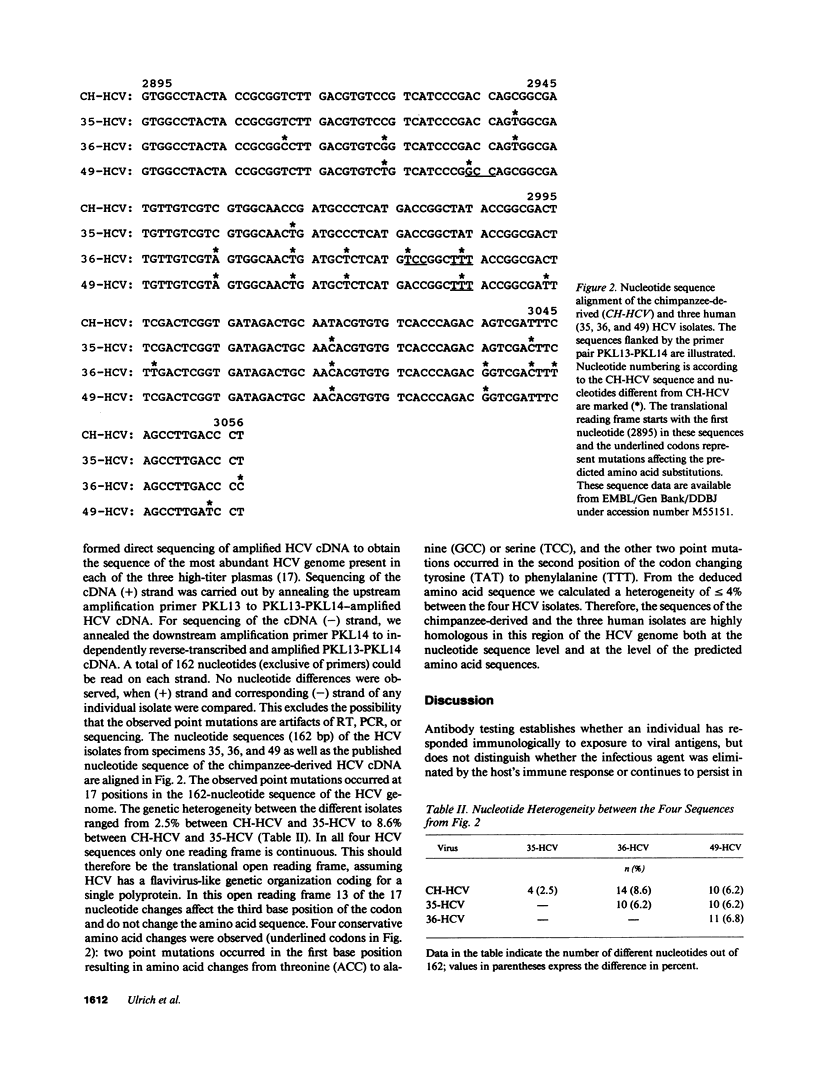
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is the predominant etiologic agent of posttransfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis, characterized by undulating elevation of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and chronic liver disease. A commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detected antibodies to HCV (anti-HCV) in 11 specimens among 101 nontransfusable plasma units obtained from asymptomatic, volunteer blood donors with elevated levels' of ALT. Using a combined reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay developed by us, HCV RNA was detected in 0.6 ml of plasma from 8 of 11 (73%) of the anti-HCV-positive but in none of the 90 anti-HCV-negative specimens. The relatively low concentration of HCV RNA could be detected in the remaining three anti-HCV-positive specimens when 2.4 ml of plasma was analyzed. The plasma concentration of virions was estimated to range from 10(2) to 5 x 10(7)/ml. Direct sequencing performed on the PCR-amplified HCV cDNAs (210 base pairs) from three specimens revealed heterogeneity between 2.5 and 8.6% at the nucleotide level and less than 4% at the amino acid level. Our findings demonstrate that RT-PCR can be performed with 2.4 ml of plasma, providing an assay for the direct detection of HCV RNA and confirming the existence of an asymptomatic carrier state for HCV infection in the apparently healthy anti-HCV-positive donors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aach R. D., Szmuness W., Mosley J. W., Hollinger F. B., Kahn R. A., Stevens C. E., Edwards V. M., Werch J. Serum alanine aminotransferase of donors in relation to the risk of non-A,non-B hepatitis in recipients: the transfusion-transmitted viruses study. N Engl J Med. 1981 Apr 23;304(17):989–994. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198104233041701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Shih J. W., Melpolder J. C., Houghton M., Choo Q. L., Kuo G. Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in prospectively followed transfusion recipients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1494–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Sampliner R. E. Hepatitis C: and miles to go before we sleep. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1538–1540. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Haase A. T., Harris J. D., Walker D., Vyas G. N. Asymmetric replication of hepatitis B virus DNA in human liver: demonstration of cytoplasmic minus-strand DNA by blot analyses and in situ hybridization. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W. The agents of non-A, non-B viral hepatitis. J Virol Methods. 1985 Apr;10(4):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90047-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Alter H. J. Non-A, non-B hepatitis: evolving epidemiologic and clinical perspective. Semin Liver Dis. 1986 Feb;6(1):67–81. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban J. I., Esteban R., Viladomiu L., López-Talavera J. C., González A., Hernández J. M., Roget M., Vargas V., Genescà J., Buti M. Hepatitis C virus antibodies among risk groups in Spain. Lancet. 1989 Aug 5;2(8658):294–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnl P., Seidl S., Stangel W., Beyer J., Sibrowski W., Flik J. Antibody to hepatitis C virus in German blood donors. Lancet. 1989 Aug 5;2(8658):324–324. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90500-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larzul D., Guigue F., Sninsky J. J., Mack D. H., Bréchot C., Guesdon J. L. Detection of hepatitis B virus sequences in serum by using in vitro enzymatic amplification. J Virol Methods. 1988 Jul;20(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis C virus shares amino acid sequence similarity with pestiviruses and flaviviruses as well as members of two plant virus supergroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2057–2061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Wang A., Mark D., Werb Z. Novel method for studying mRNA phenotypes in single or small numbers of cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jan;39(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Holland J. J. Rapid evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:409–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich P. P., Bhat R. A., Seto B., Mack D., Sninsky J., Vyas G. N. Enzymatic amplification of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum compared with infectivity testing in chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):37–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. J., Kuo G., Bradley D. W., Bonino F., Saracco G., Lee C., Rosenblatt J., Choo Q. L., Houghton M. Detection of hepatitis C viral sequences in non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1990 Jan 6;335(8680):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90134-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Dowling C. E., Saiki R. K., Higuchi R. G., Erlich H. A., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of beta-thalassaemia mutations using direct genomic sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):384–386. doi: 10.1038/330384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poel C. L., Reesink H. W., Lelie P. N., Leentvaar-Kuypers A., Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Houghton M. Anti-hepatitis C antibodies and non-A, non-B post-transfusion hepatitis in The Netherlands. Lancet. 1989 Aug 5;2(8658):297–298. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90486-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]