Abstract
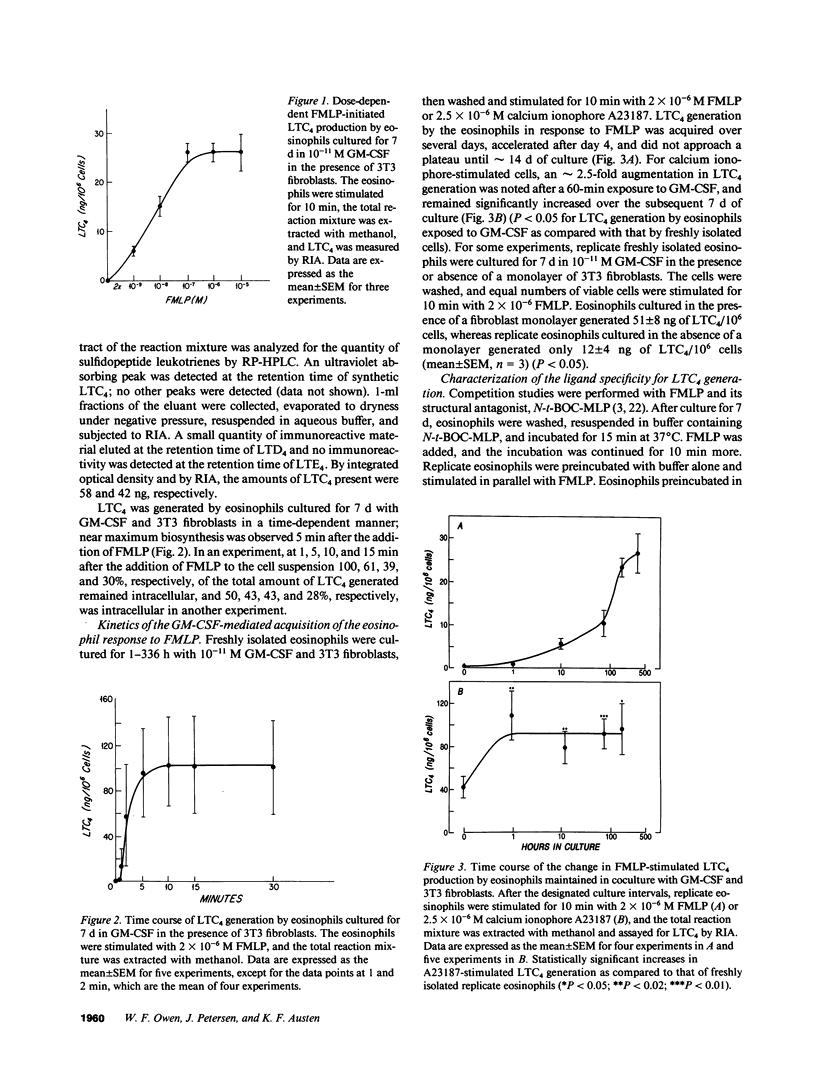
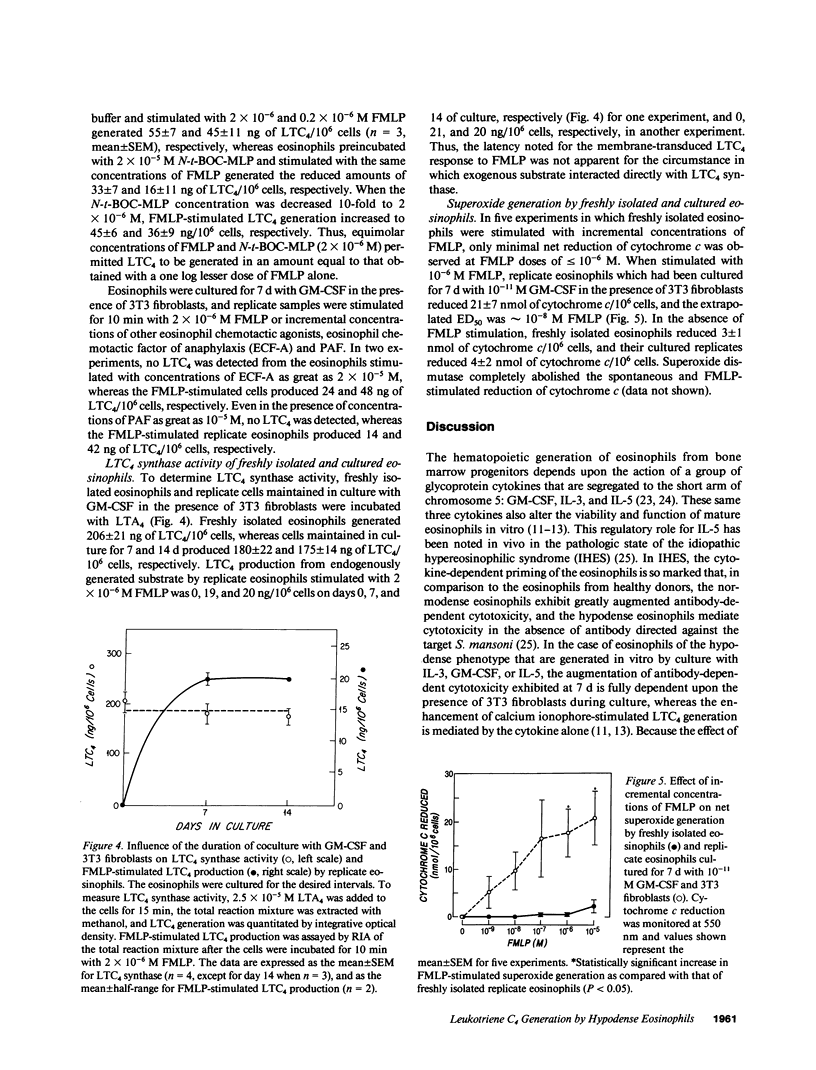
Normodense eosinophils failed to generate leukotriene C4 (LTC4) in response to incremental concentrations of FMLP but did produce LTC4 when stimulated with calcium ionophore A23187. Normodense eosinophils, maintained in culture with 10(-11) M granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in the presence of 3T3 fibroblasts, became responsive to transmembrane stimulation with FMLP by day 4 with a maximal effect by day 7. After 7 d of culture, hypodense eosinophils stimulated with 2 x 10(-7) M FMLP generated 26 ng LTC4/10(6) cells, and LTC4 biosynthesis was blocked by N-tertbutoxy-carbonyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine (N-t-BOC-MLP). Neither calcium ionophore stimulation of LTC4 from endogenous arachidonic acid nor substrate-initiated production of LTC4 from incorporated LTA4 changed when eosinophils were cocultured with GM-CSF and 3T3 fibroblasts. Furthermore, when incubated with 10(-6) M FMLP, normodense eosinophils generated no net superoxide measured by the reduction of cytochrome c, whereas replicate eosinophils cultured for 7 d with 10(-11) M GM-CSF and 3T3 fibroblasts reduced a net of 17 nmol of cytochrome c/10(6) cells. These studies suggest that primed and phenotypically altered eosinophils present at an extravascular site may exert pathobiologic effects by responding to soluble ligands in the tissues.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruynzeel P. L., Kok P. T., Hamelink M. L., Kijne A. M., Verhagen J. Exclusive leukotriene C4 synthesis by purified human eosinophils induced by opsonized zymosan. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck E. J., Hirst E. M., Sanderson C. J. Human interleukin-5 (IL-5) regulates the production of eosinophils in human bone marrow cultures: comparison and interaction with IL-1, IL-3, IL-6, and GMCSF. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1504–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone C., Donneli G., Meli D., Rosati F., Sorice F. Human eosinophils and parasitic diseases. II. Characterization of two cell fractions isolated at different densities. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):249–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J. F., Billing P., Williams R., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines prime human neutrophils for enhanced arachidonic acid release and leukotriene B4 synthesis. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4315–4322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda T., Dunnette S. L., Reed C. E., Ackerman S. J., Peters M. S., Gleich G. J. Increased numbers of hypodense eosinophils in the blood of patients with bronchial asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Nov;132(5):981–985. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.5.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruart V., Balloul J. M., Prin L., Tomassini M., Loiseau S., Capron A., Capron M. Variations in protein expression related to human eosinophil heterogeneity. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4416–4421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges M. K., Weller P. F., Gerard N. P., Ackerman S. J., Drazen J. M. Heterogeneity of leukotriene C4 production by eosinophils from asthmatic and from normal subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):799–804. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajita T., Yui Y., Mita H., Taniguchi N., Saito H., Mishima T., Shida T. Release of leukotriene C4 from human eosinophils and its relation to the cell density. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;78(4):406–410. doi: 10.1159/000233922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam B. K., Owen W. F., Jr, Austen K. F., Soberman R. J. The identification of a distinct export step following the biosynthesis of leukotriene C4 by human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12885–12889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Lemons R. S., Espinosa R., 3rd, Larson R. A., Arai N., Rowley J. D. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-5 map to human chromosome 5 in a region encoding growth factors and receptors and are deleted in myeloid leukemias with a del(5q). Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):647–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling C. J., Owen W. F., Jr, Austen K. F. Human fibroblasts maintain the viability and augment the functional response of human neutrophils in culture. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):601–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI114480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey D. R., Dorsky D. I., Nicholson-Weller A., Weller P. F. Human eosinophils express CD4 protein and bind human immunodeficiency virus 1 gp120. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):327–332. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey D. R., Nicholson-Weller A., Weller P. F. Mature human eosinophils have the capacity to express HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1348–1351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Faucher N., Borgeat P., Gasson J. C., DiPersio J. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor modulates the excitation-response coupling sequence in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3541–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. F., Jr, Rothenberg M. E., Silberstein D. S., Gasson J. C., Stevens R. L., Austen K. F., Soberman R. J. Regulation of human eosinophil viability, density, and function by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the presence of 3T3 fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):129–141. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. F., Jr, Soberman R. J., Yoshimoto T., Sheffer A. L., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Synthesis and release of leukotriene C4 by human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. F., Rothenberg M. E., Petersen J., Weller P. F., Silberstein D., Sheffer A. L., Stevens R. L., Soberman R. J., Austen K. F. Interleukin 5 and phenotypically altered eosinophils in the blood of patients with the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):343–348. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Lu A. Y. Glutathione S-transferases: gene structure, regulation, and biological function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:743–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prin L., Capron M., Tonnel A. B., Bletry O., Capron A. Heterogeneity of human peripheral blood eosinophils: variability in cell density and cytotoxic ability in relation to the level and the origin of hypereosinophilia. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;72(4):336–346. doi: 10.1159/000234893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Lewis R. A., Corey E. J., Austen K. F. Generation of leukotriene C4 from a subclass of mast cells differentiated in vitro from mouse bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4665–4667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Stevens R. L., Lewis R. A., Liu F. T., Corey E., Austen K. F. IgE-mediated release of leukotriene C4, chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan, beta-hexosaminidase, and histamine from cultured bone marrow-derived mouse mast cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):189–201. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg M. E., Owen W. F., Jr, Silberstein D. S., Soberman R. J., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Eosinophils cocultured with endothelial cells have increased survival and functional properties. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):645–647. doi: 10.1126/science.3110954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg M. E., Owen W. F., Jr, Silberstein D. S., Woods J., Soberman R. J., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Human eosinophils have prolonged survival, enhanced functional properties, and become hypodense when exposed to human interleukin 3. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1986–1992. doi: 10.1172/JCI113547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg M. E., Petersen J., Stevens R. L., Silberstein D. S., McKenzie D. T., Austen K. F., Owen W. F., Jr IL-5-dependent conversion of normodense human eosinophils to the hypodense phenotype uses 3T3 fibroblasts for enhanced viability, accelerated hypodensity, and sustained antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2311–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B., Chused T. M., Gallin J. I. Differential binding of chemoattractant peptide to subpopulations of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2641–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. J., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Preferential generation of leukotriene C4 by human eosinophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jun;56(3):716–722. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. J., Walsh G. M., Cromwell O., Moqbel R., Spry C. J., Kay A. B. Activated human eosinophils generate SRS-A leukotrienes following IgG-dependent stimulation. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):150–152. doi: 10.1038/316150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Griffin J. D., Simons E. R., Schafer A. I., Meshulam T., Fredette J. P., Maas A. K., Gadenne A. S., Leavitt J. L., Melnick D. A. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors on signal transduction pathways in human granulocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3422–3430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura N., Agrawal D. K., Townley R. G. Leukotriene C4 production from human eosinophils in vitro. Role of eosinophil chemotactic factors on eosinophil activation. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4291–4297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Moqbel R., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Platelet-activating factor. A potent chemotactic and chemokinetic factor for human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1701–1706. doi: 10.1172/JCI112765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Lee C. W., Foster D. W., Corey E. J., Austen K. F., Lewis R. A. Generation and metabolism of 5-lipoxygenase pathway leukotrienes by human eosinophils: predominant production of leukotriene C4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7626–7630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Czop J. K., Austen K. F. Release of leukotrienes by human monocytes on stimulation of their phagocytic receptor for particulate activators. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3034–3040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Lee T. H., Lewis R. A., Austen F. Intracellular retention of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway product, leukotriene B4, by human neutrophils activated with unopsonized zymosan. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2624–2630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winqvist I., Olofsson T., Olsson I., Persson A. M., Hallberg T. Altered density, metabolism and surface receptors of eosinophils in eosinophilia. Immunology. 1982 Nov;47(3):531–539. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Soberman R. J., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Isolation and characterization of leukotriene C4 synthetase of rat basophilic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8399–8403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


