Abstract
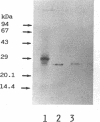
That structural abnormalities may be responsible for nonamyloid immunoglobulin (Ig) light chain deposition disease (LCDD) is suggested by previous results of Ig biosynthesis studies, but this hypothesis was not documented at the molecular level. We report on the first complete primary sequence deduced from cDNA analysis of a kappa light chain responsible for LCDD associated with an apparently nonsecretory myeloma. Bone marrow myeloma cells contained intracellular kappa chains and no heavy chains by immunofluorescence. Kidney biopsy showed typical nonamyloid PAS-positive kappa chain deposits. SDS-PAGE analysis of material extracted from a kidney biopsy specimen and of Ig produced by the myeloma cells revealed kappa chains of abnormally high apparent molecular mass (30,000). Comparison of the NH2-terminal aminoacid sequence of the kappa chain deposited in the kidney and of the complete sequence of several identical kappa cDNA clones from bone marrow cells showed the identity of the tissue deposited and plasma cell kappa chain. The kappa mRNA had an overall normal structure and corresponded to the V kappa IV gene rearranged to J kappa 1 and followed by a normal constant exon of the Km(3) allotype. The variable sequence differed from the V kappa IV germline gene by nine point mutations, including an Asp----Asn substitution at position +70 resulting in a potential N-glycosylation site. In vitro biosynthesis experiments and treatment with N-glycosidase provided evidence for the intracellular glycosylation of the monoclonal kappa chain. The peculiar sequence and the glycosylation of a kappa chain of the rare V kappa IV subgroup might be responsible for structural abnormalities leading to tissue deposition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellotti V., Merlini G., Bucciarelli E., Perfetti V., Quaglini S., Ascari E. Relevance of class, molecular weight and isoelectric point in predicting human light chain amyloidogenicity. Br J Haematol. 1990 Jan;74(1):65–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Dwulet F. E., Madura D., Wheeler G. Amyloidosis related to a lambda IV immunoglobulin light chain protein. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):175–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briault S., Courtois-Capella M., Duarte F., Aucouturier P., Preud'Homme J. L. Isotypy of serum monoclonal immunoglobulins in human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):182–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Pongor S., Cerami A. Covalent attachment of soluble proteins by nonenzymatically glycosylated collagen. Role in the in situ formation of immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1739–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J. N., Chuba J. V., Hellman G. C., Solomon A., Gallo G. R. Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease: light chain and light and heavy chain deposition diseases and their relation to light chain amyloidosis. Clinical features, immunopathology, and molecular analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Mar 15;112(6):455–464. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-3-112-6-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J. Aberrant immunoglobulin synthesis in light chain amyloidosis. Free light chain and light chain fragment production by human bone marrow cells in short-term tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):798–806. doi: 10.1172/JCI112643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Canonical structures for the hypervariable regions of immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):901–917. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M., Tramontano A., Levitt M., Smith-Gill S. J., Air G., Sheriff S., Padlan E. A., Davies D., Tulip W. R. Conformations of immunoglobulin hypervariable regions. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):877–883. doi: 10.1038/342877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogné M., Mounir S., Preud'homme J. L., Nau F., Guglielmi P. Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines producing truncated mu immunoglobulin heavy chains lacking part of the variable region. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1485–1489. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S. Polypeptide microsequence analysis with the commercially available gas-phase sequencer. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eulitz M., Breuer M., Linke R. P. Is the formation of AL-type amyloid promoted by structural peculiarities of immunoglobulin L-chains? Primary structure of an amyloidogenic lambda-L-chain (BJP-ZIM). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Jul;368(7):863–870. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eulitz M., Linke R. Amyloid fibrils derived from V-region together with C-region fragments from a lambda II-immunoglobulin light chain (HAR). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Sep;366(9):907–915. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G., Picken M., Buxbaum J., Frangione B. The spectrum of monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease associated with immunocytic dyscrasias. Semin Hematol. 1989 Jul;26(3):234–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlag P. G., Koene R. A., Berden J. H. Renal transplantation in light chain nephropathy: case report and review of the literature. Clin Nephrol. 1986 Feb;25(2):101–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. Cloned human and mouse kappa immunoglobulin constant and J region genes conserve homology in functional segments. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm E., Sletten K., Husby G. Structural studies of a carbohydrate-containing immunoglobulin-lambda-light-chain amyloid-fibril protein (AL) of variable subgroup III. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):545–551. doi: 10.1042/bj2390545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquot C., Saint-Andre J. P., Touchard G., Nochy D., D'Auzac de Lamartinie C., Oriol R., Druet P., Bariety J. Association of systemic light-chain deposition disease and amyloidosis: a report of three patients with renal involvement. Clin Nephrol. 1985 Aug;24(2):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Bornkamm G. W., Combriato G., Mocikat R., Pohlenz H. D., Zachau H. G. Subgroup IV of human immunoglobulin K light chains is encoded by a single germline gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6515–6529. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liepnieks J. J., Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Amino acid sequence of a kappa I primary (AL) amyloid protein (AND). Mol Immunol. 1990 Jun;27(6):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J. Diabetic retinopathy. A synthesis of perspectives. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 5;322(14):978–983. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004053221406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihaesco E., Ayadi H., Congy N., Gendron M. C., Roy J. P., Heyermann H., Frangione B., Brouet J. C. Multiple mutations in the variable region of the kappa light chains of three monoclonal human IgM with anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21481–21485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken M. M., Frangione B., Barlogie B., Luna M., Gallo G. Light chain deposition disease derived from the kappa I light chain subgroup. Biochemical characterization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):749–754. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken M. M., Gallo G. R., Pruzanski W., Frangione B. Biochemical characterization of amyloid derived from the variable region of the kappa light chain subgroup III. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):880–884. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken M. M., Gallo G., Buxbaum J., Frangione B. Characterization of renal amyloid derived from the variable region of the lambda light chain subgroup II. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jul;124(1):82–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'Homme J. L., Morel-Maroger L., Brouet J. C., Mihaesco E., Mery J. P., Seligmann M. Synthesis of abnormal heavy and light chains in multiple myeloma with visceral deposition of monoclonal immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):545–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Ganeval D., Grünfeld J. P., Striker L., Brouet J. C. Immunoglobulin synthesis in primary and myeloma amyloidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):389–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Labaume S., Praloran V. Synthesis of abnormal heavy chains in Bence-Jones plasma cell leukemia with intracellular IgG. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1136–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Morel-Maroger L., Brouet J. C., Cerf M., Mignon F., Guglielmi P., Seligmann M. Synthesis of abnormal immunoglobulins in lymphoplasmacytic disorders with visceral light chain deposition. Am J Med. 1980 Nov;69(5):703–710. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall R. E., Williamson W. C., Jr, Mullinax F., Tung M. Y., Still W. J. Manifestations of systemic light chain deposition. Am J Med. 1976 Feb;60(2):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Natvig J. B., Husby G., Juul J. The complete amino acid sequence of a prototype immunoglobulin-lambda light-chain-type amyloid-fibril protein AR. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1950561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. M., Malcolm A. J. Simultaneous AL-type amyloid and light chain deposit disease in a liver biopsy: a case report. Histopathology. 1986 Oct;10(10):1057–1064. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1986.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Bence Jones proteins and light chains of immunoglobulins. Preferential association of the V lambda VI subgroup of human light chains with amyloidosis AL (lambda). J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):453–460. doi: 10.1172/JCI110635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A., Weiss D. T. Serologically defined V region subgroups of human lambda light chains. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):824–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox H. C., Jr, Hood L. Attachment of carbohydrate to the variable region of myeloma immunoglobulin light chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):975–982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft K. G., Sletten K., Husby G. The amino-acid sequence of the variable region of a carbohydrate-containing amyloid fibril protein EPS (immunoglobulin light chain, type lambda). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Jul;366(7):617–625. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonoike H., Kametani F., Hoshi A., Shinoda T., Isobe T. Primary structure of the variable region of an amyloidogenic Bence Jones protein NIG-77. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 15;126(3):1228–1234. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90317-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troussard X., Hurault de Ligny B., Gallet B., Ganeval D., Mandard J. C., Ryckelynck J. P., Leporrier M. Massive systemic amyloidosis associated with light-chain deposition disease. Nephron. 1989;52(2):139–143. doi: 10.1159/000185616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tveteraas T., Sletten K., Westermark P. The amino acid sequence of a carbohydrate-containing immunoglobulin-light-chain-type amyloid-fibril protein. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):183–190. doi: 10.1042/bj2320183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verroust P., Morel-Maroger L., Preud'Homme J. L. Renal lesions in dysproteinemias. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1982;5(3):333–356. doi: 10.1007/BF01892092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]