Abstract
The propensity of Staphylococcus aureus to cause acute endovascular infections during transient bacteremia is poorly understood. To examine the events leading to the attachment of staphylococci to endothelium, adherence assays were developed to study the role of blood factors in the mediation of staphylococcal adherence to cultured human umbilical vein endothelium in vitro. Results indicate that the preferential attachment of S. aureus to endothelial cells is mediated by fibrinogen adsorbed from plasma onto the endothelial surface. The binding is apparently specific because it could be blocked by goat anti-human fibrinogen antibody in a dose-dependent fashion while nonimmune goat IgG, mouse MAb against AG-1 (a platelet antigen found on the endothelial cell surface), nonspecific mouse MAb and rabbit antibodies to human vitronectin and fibronectin were not inhibitory. Our data also indicate that fibrinogen is a necessary but not the only blood constituent in the mediation of binding of S. aureus to endothelium. This was supported by the finding that fibrinogen alone, at a concentration equivalent to that in plasma, did not potentiate staphylococcal adherence as much as plasma while afibrinogenemic plasma reconstituted with fibrinogen did. Because fibrinogen is known to bind to endothelial cells, our data is consistent with the hypothesis that fibrinogen and additional plasma factor(s), possibly activated during inflammation, promote staphylococcal adherence to endothelium. In addition, the role of the fibrinogen binding receptor of S. aureus as an adherence factor to native endothelium is also suggested.
Full text
PDF


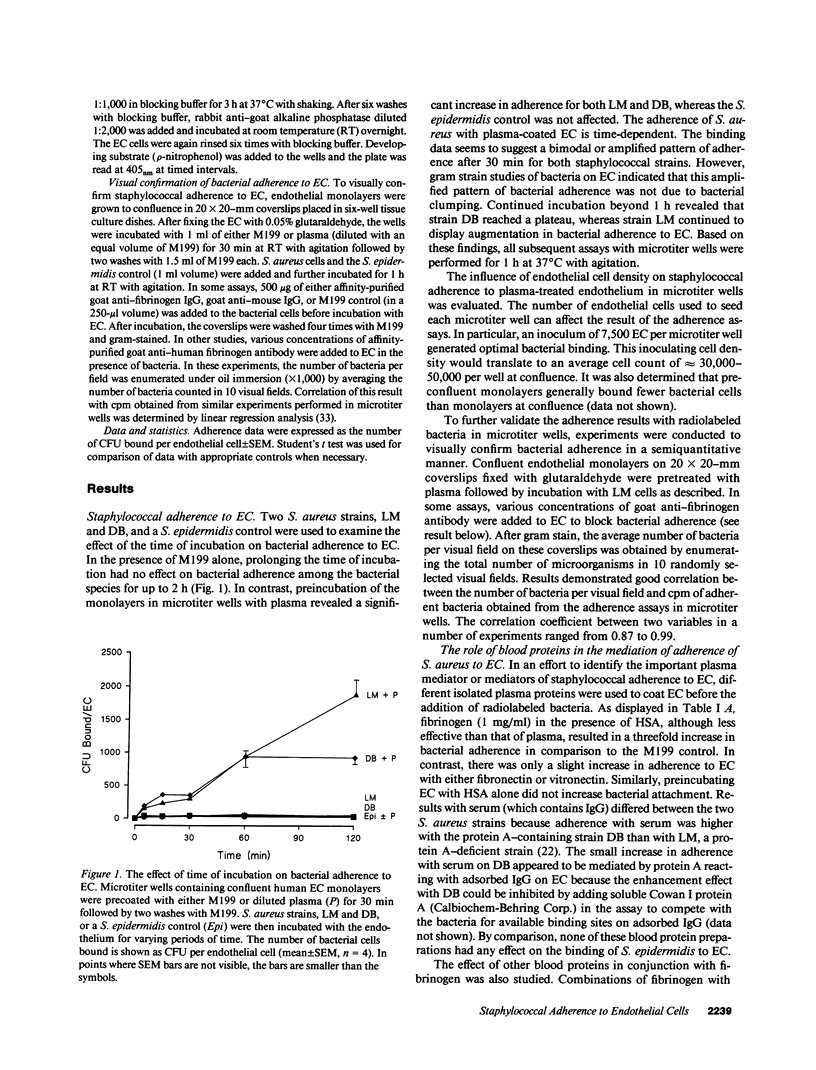
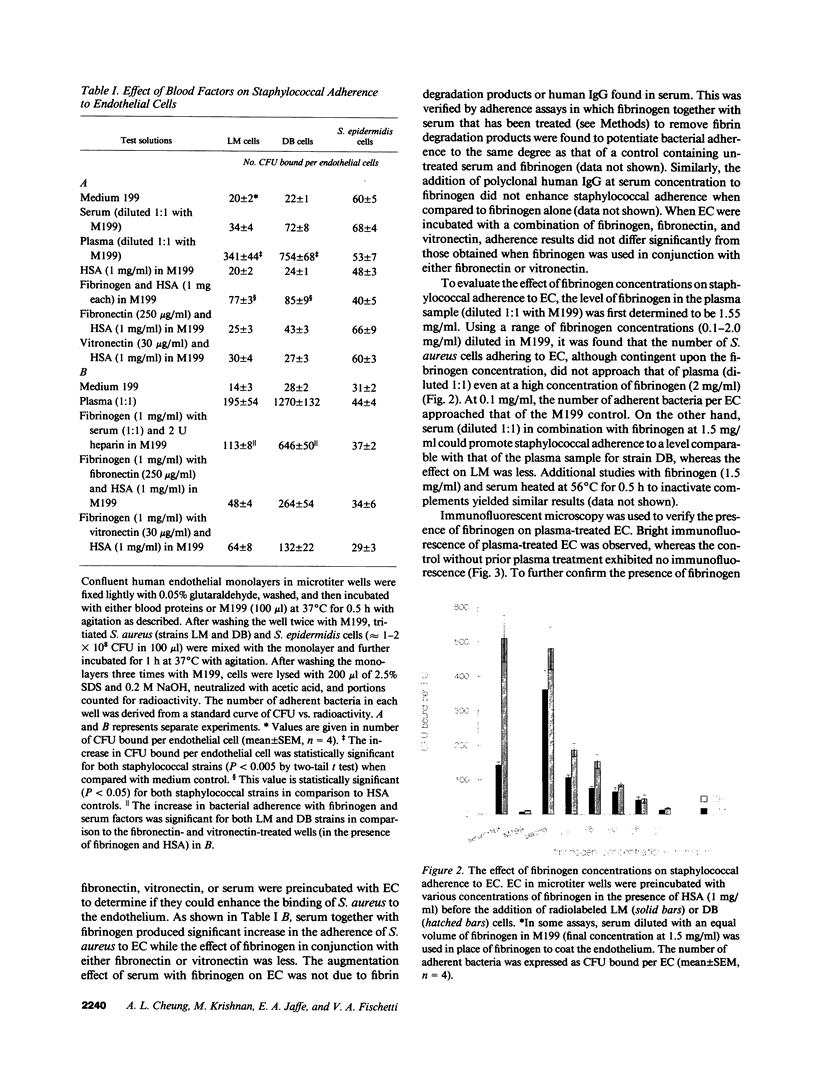




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A. Human endothelial cells synthesize and express an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed adhesion receptor involved in attachment to fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6471–6475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Fischetti V. A. The role of fibrinogen in staphylococcal adherence to catheters in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1177–1186. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Fischetti V. A. Variation in the expression of cell wall proteins of Staphylococcus aureus grown on solid and liquid media. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1061–1065. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1061-1065.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Blobel H. Specific binding of the human S protein (vitronectin) to streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1878–1883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1878-1883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Colella S., Languino L. R., Balconi G., Corbascio G. C., Marchisio P. C. Fibrinogen induces adhesion, spreading, and microfilament organization of human endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1403–1411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Languino L. R., Polentarutti N., Balconi G., Ryckewaert J. J., Larrieu M. J., Donati M. B., Mantovani A., Marguerie G. Interaction between fibrinogen and cultured endothelial cells. Induction of migration and specific binding. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):11–18. doi: 10.1172/JCI111661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Zanetti A., Conforti G. Biochemical and functional characteristics of fibrinogen interaction with endothelial cells. Haemostasis. 1988;18(4-6):262–270. doi: 10.1159/000215812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I., Barkholt V. Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):700–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.700-708.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Isolation of a fibronectin-binding protein from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.526-531.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Scott J. R. Streptococcal M6 protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Localization, purification, and comparison with streptococcal-derived M protein. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1083–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K., Ramirez-Ronda C. H., Holmes R. K., Sanford J. P. Adherence of bacteria to heart valves in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1364–1370. doi: 10.1172/JCI108216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grannis G. F. Plasma fibrinogen: determination, normal values, physiopathologic shifts, and fluctuations. Clin Chem. 1970 Jun;16(6):486–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Fischetti V. A. The importance of the location of antibody binding on the M6 protein for opsonization and phagocytosis of group A M6 streptococci. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1114–1123. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Attachment of staphylococci and streptococci on fibronectin, fibronectin fragments, and fibrinogen bound to a solid phase. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.77-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowder J. N., Lazarus H. M., Herzig R. H. Bacteremias and fungemias in oncologic patients with central venous catheters: changing spectrum of infection. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Aug;142(8):1456–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr, Parrott P. L., Duty V. P. Nosocomial bacteremia. Potential for prevention of procedure-related cases. JAMA. 1977 Jun 20;237(25):2727–2729. doi: 10.1001/jama.237.25.2727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Kupinski J. M., Hustad K. O. Characterization of a platelet membrane protein of low molecular weight associated with platelet activation following binding by monoclonal antibody AG-1. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S. K., Yurberg E. R., Hatcher V. B., Levitt M. A., Lowy F. D. Bacterial adherence to human endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):218–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.218-224.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Mosher D. F., Olbrantz P. J. Fibronectin binding to Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14788–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack S. M., Bohnert J. L., Horbett T. A. The effects of surface chemistry and coagulation factors on fibrinogen adsorption from plasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;516:223–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb33044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman R. M., Soliman F., Garcia L., Sawyer P. N. Etiology of catheter-associated sepsis. Correlation with thrombogenicity. Arch Surg. 1977 Dec;112(12):1497–1499. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1977.01370120087011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins D. C., Hatcher V. B., Patel D., Orr G. A., Higgins L. L., Lowy F. D. A human endothelial cell membrane protein that binds Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI114560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usui Y. Biochemical properties of fibrinogen binding protein (clumping factor) of the staphylococcal cell surface. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Sep;262(3):287–297. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Weigand P., Grulich-Henn J., Chhatwal G. S., Müller-Berghaus G., Blobel H., Preissner K. T. Mediation of adherence of streptococci to human endothelial cells by complement S protein (vitronectin). Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2851–2855. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2851-2855.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann J. M., Hamill R. J., Albrecht R. M., Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of fibronectin in adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):538–542. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., Lussenhop D., Peterson P. K., Furcht L. T., McCarthy J. B., Jacob H. S., Moldow C. F. Bacterial adherence to fibronectin and endothelial cells: a possible mechanism for bacterial tissue tropism. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Jan;103(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Reyn C. F., Levy B. S., Arbeit R. D., Friedland G., Crumpacker C. S. Infective endocarditis: an analysis based on strict case definitions. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Apr;94(4 Pt 1):505–518. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-4-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Baird I. M. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis associated with a removable infected intravenous device. Am J Med. 1977 Aug;63(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Schlesinger J. J. Pathoanatomic, pathophysiologic and clinical correlations in endocarditis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 17;291(16):832–837. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410172911609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]