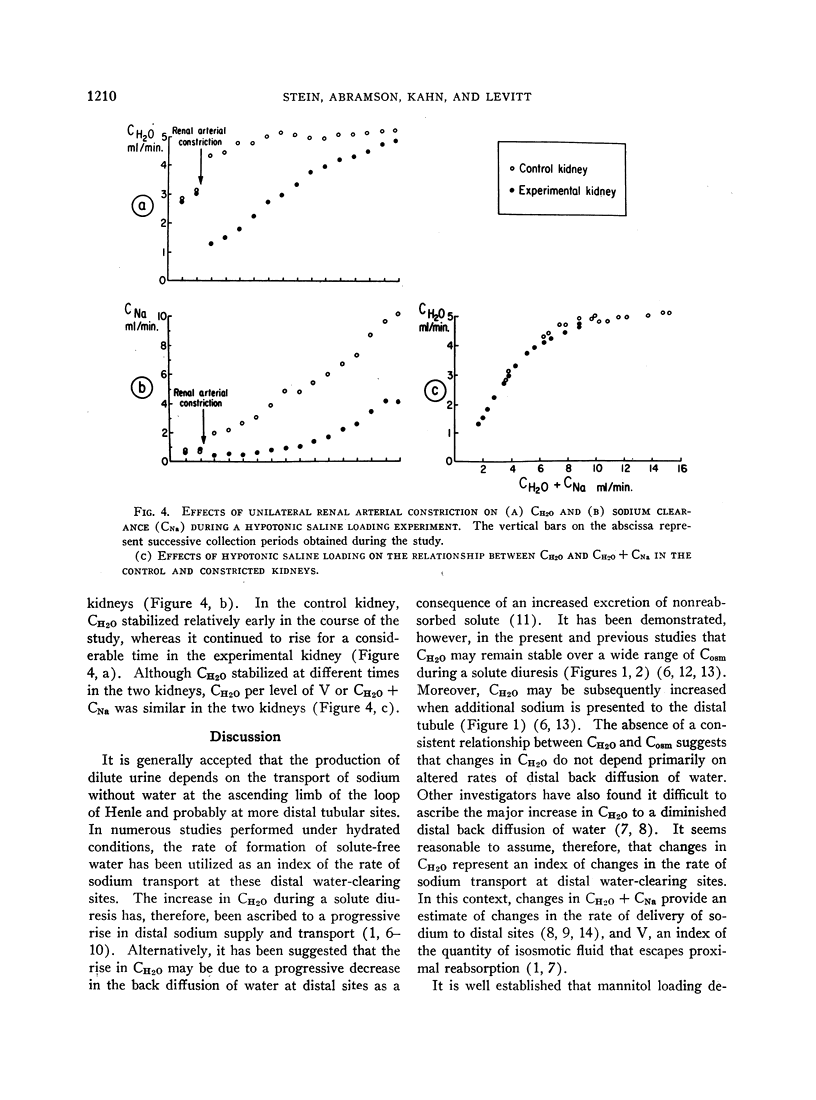
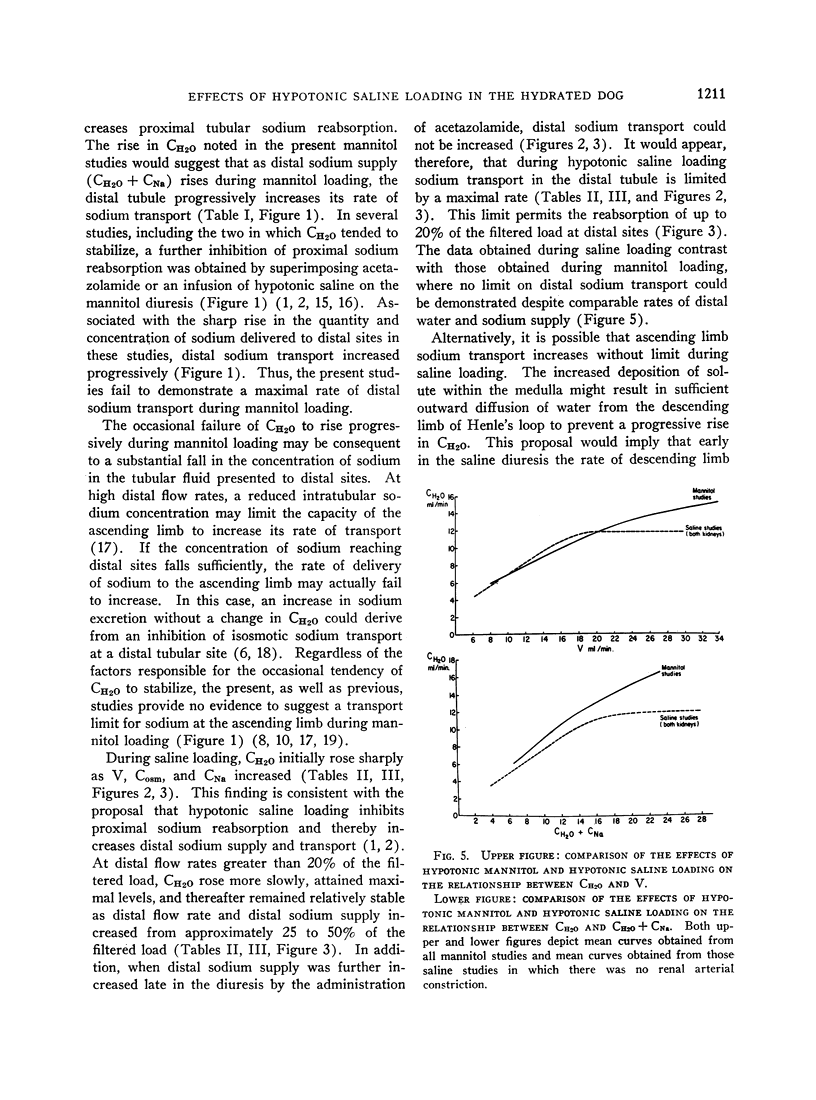
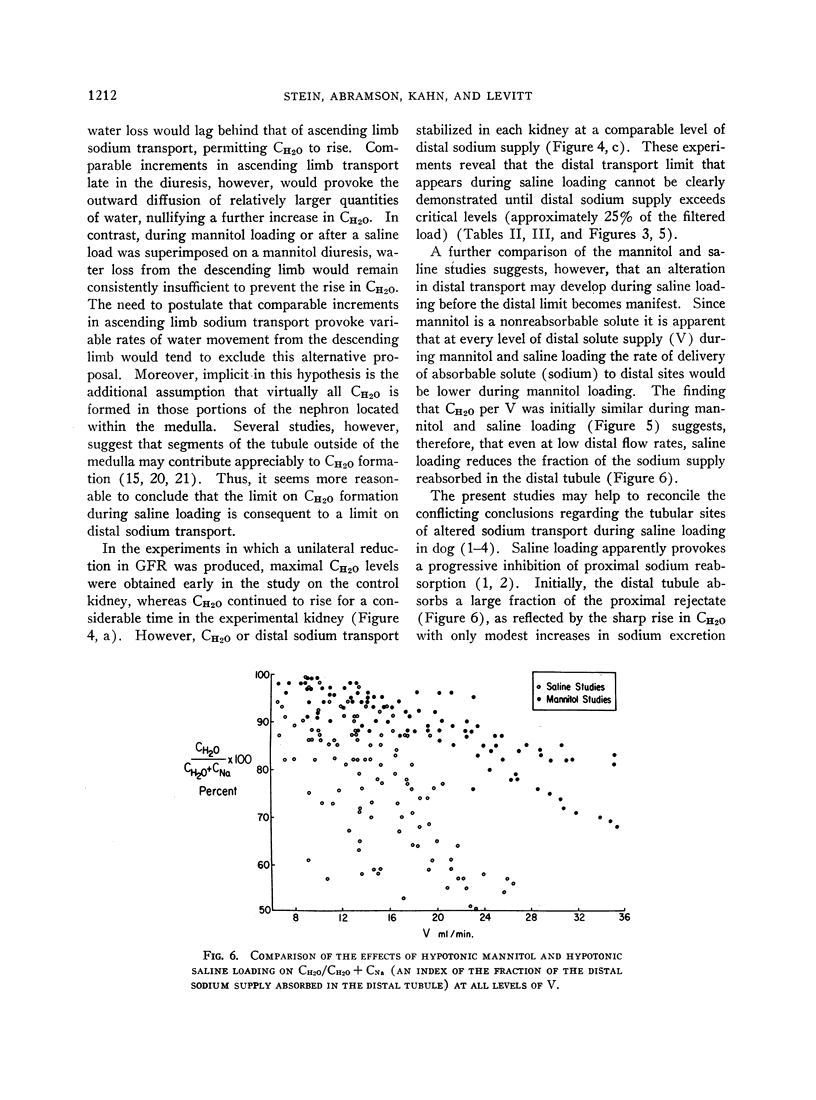
Abstract
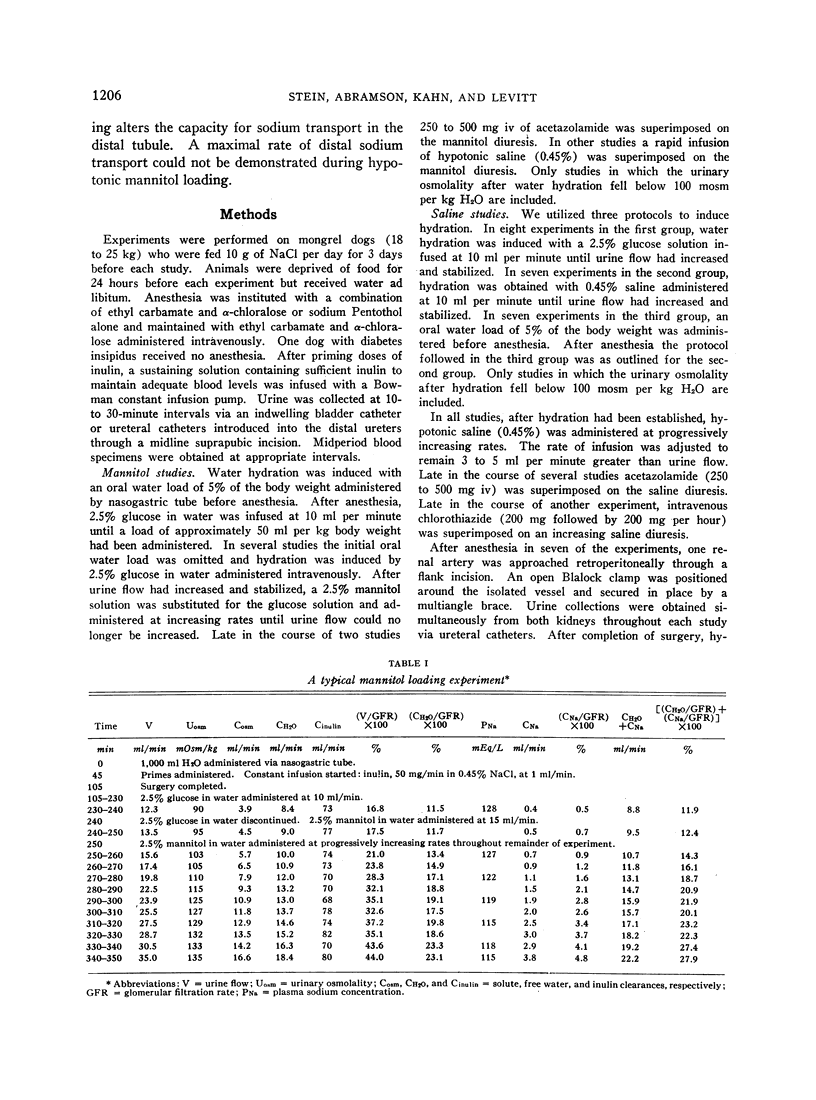
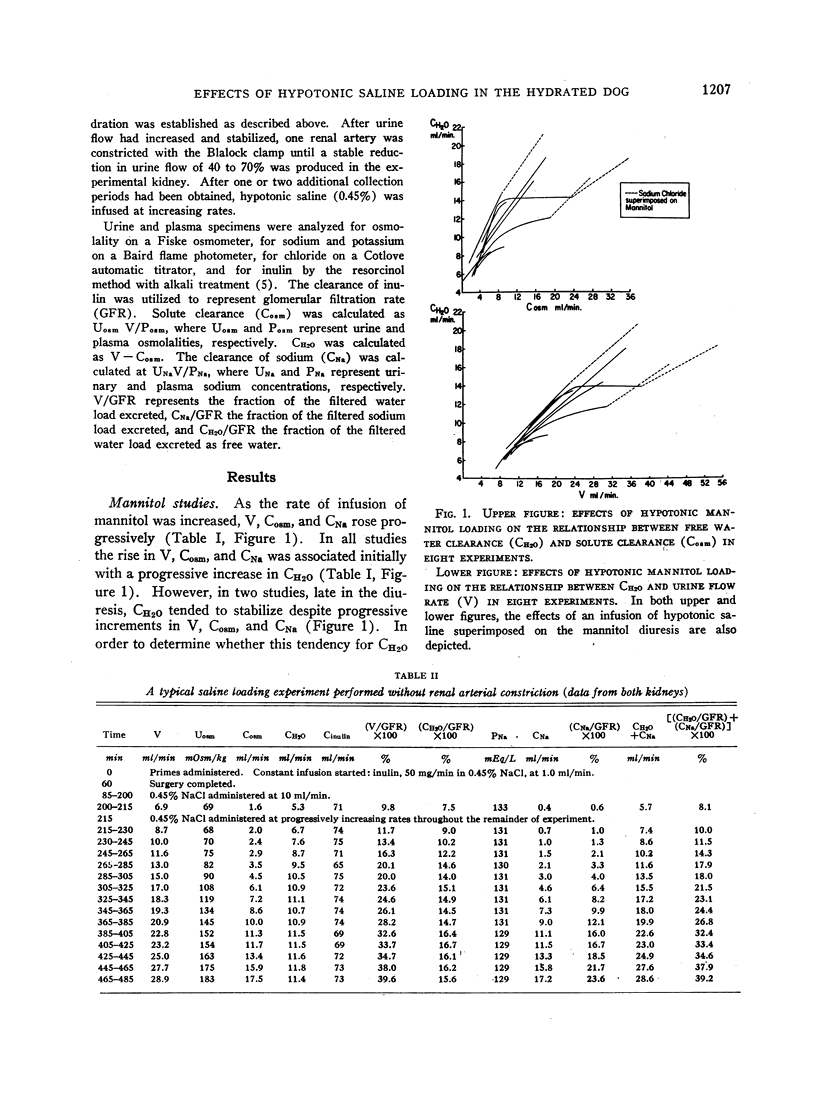
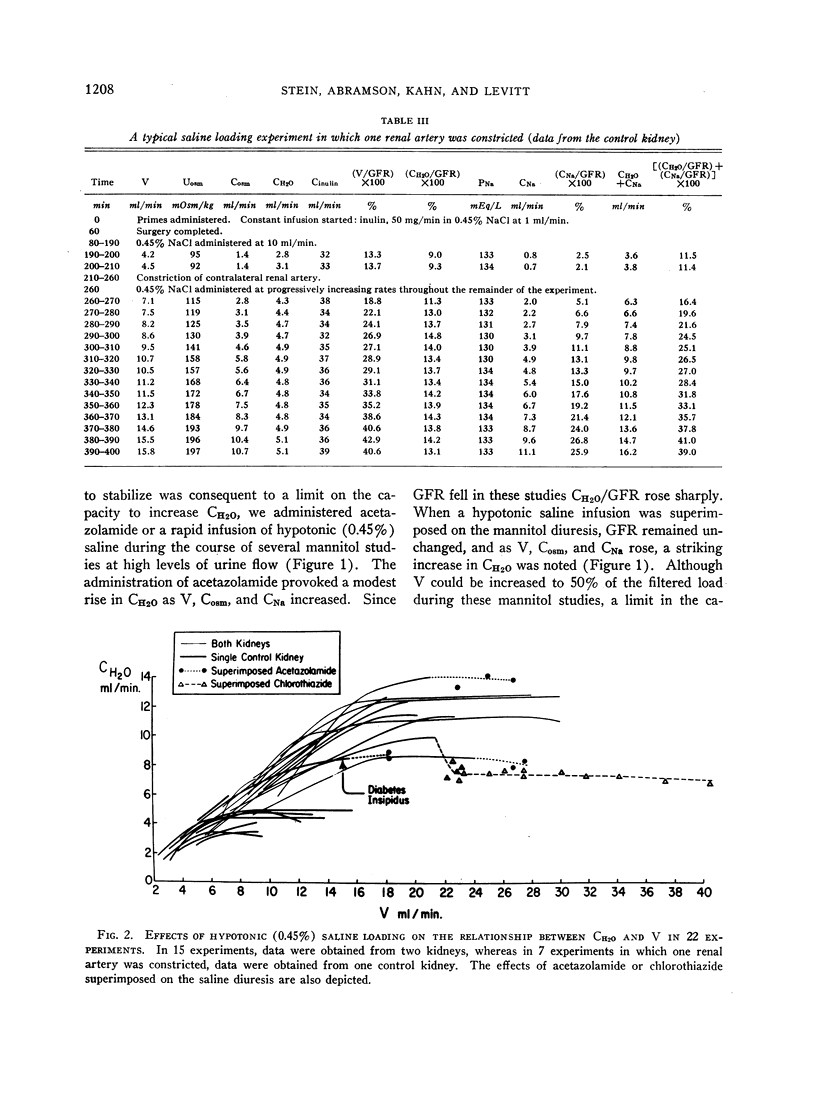
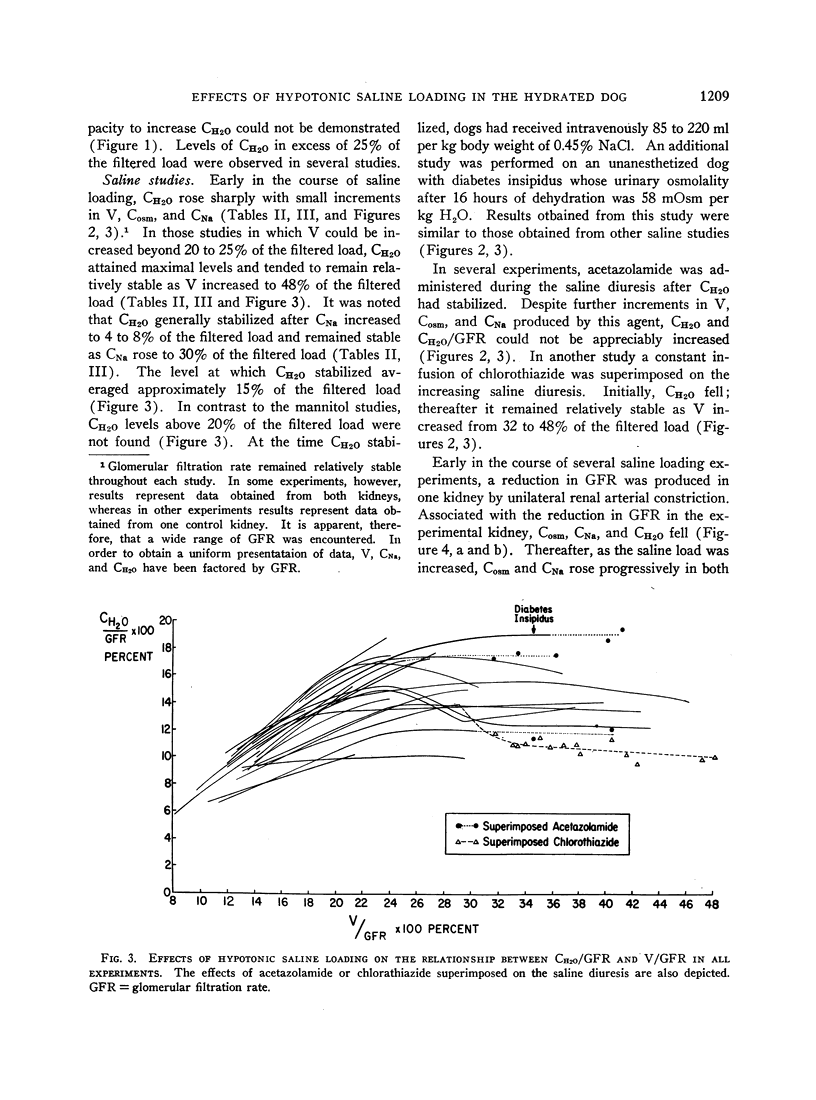
We performed studies on dogs under hydrated conditions, utilizing the rate of free water formation (CH2O) as an index of the rate of distal tubular sodium transport. Since CH2O could be progressively increased with no evidence of a maximal rate during loading with hypotonic (2.5%) mannitol, it was concluded that there is no limit on distal tubular sodium transport during mannitol loading. In contrast, during hypotonic (0.45%) saline loading CH2O rose initially, but as urine flow (V) exceeded 25% of the filtered load CH2O attained maximal levels (up to 20% of the filtered load) and remained stable as V increased to 50% of the filtered load. It was concluded that saline loading progressively inhibits proximal sodium reabsorption. Initially, the distal tubule absorbes a large fraction of the proximal rejectate and sodium excretion rises slightly. Eventually, an alteration in distal sodium transport appears which culminates in a maximal rate or transport limit. This distal transport limit provoked by saline loading could not be characterized by a classical Tm as seen with glucose and does not seem to be consequent to high rates of flow through the distal tubule. Regardless of the precise nature of this limit, the major increment in sodium excretion develops during saline loading only after saline alters the capacity of the distal tubule to transport sodium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER E. L., GINN H. E. Free water excretion in normal dogs. Am J Physiol. 1962 Jun;202:1131–1135. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.6.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIRKS J. H., CIRKSENA W. J., BERLINER R. W. THE EFFECTS OF SALINE INFUSION ON SODIUM REABSORPTION BY THE PROXIMAL TUBULE OF THE DOG. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jul;44:1160–1170. doi: 10.1172/JCI105223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARLEY L. E., FRIEDLER R. M. RENAL TUBULAR EFFECTS OF ETHACRYNIC ACID. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1495–1506. doi: 10.1172/JCI105026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARLEY L. E., KAHN M., ORLOFF J. The effects of infusions of chlorothiazide on urinary dilution and concentration in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1961 May;40:857–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI104320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARLY L. E., FRIEDLER R. M. OBSERVATIONS ON THE MECHANISM OF DECREASED TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF SODIUM AND WATER DURING SALINE LOADING. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1928–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI105067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBISCH G., WINDHAGER E. E. RENAL TUBULAR TRANSFER OF SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND POTASSIUM. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:643–669. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG M., MCCURDY D. K., FOLTZ E. L., BLUEMLE L. W., Jr EFFECTS OF ETHACRYNIC ACID (A NEW SALURETIC AGENT) ON RENAL DILUTING AND CONCENTRATING MECHANISMS: EVIDENCE FOR SITE OF ACTION IN THE LOOP OF HENLE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:201–216. doi: 10.1172/JCI104905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG M., MCCURDY D. K., RAMIREZ M. A. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SALINE AND MANNITOL DIURESIS IN HYDROPENIC MAN. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44:182–192. doi: 10.1172/JCI105133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN M. H., LEVITT M. F., HAUSER A. D., POLIMEROS D. Effect of meralluride on solute and water excretion in hydrated man: comments on site of action. J Clin Invest. 1961 Apr;40:731–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI104307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINEMANN H. O., DEMARTINI F. E., LARAGH J. H. The effect of chlorothiazide on renal excretion of electrolytes and free water. Am J Med. 1959 Jun;26(6):853–861. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laragh J. H., Cannon P. J., Bentzel C. J., Sicinski A. M., Meltzer J. I. ANGIOTENSIN II, NOREPINEPHRINE, AND RENAL TRANSPORT OF ELECTROLYTES AND WATER IN NORMAL MAN AND IN CIRRHOSIS WITH ASCITES. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42(7):1179–1192. doi: 10.1172/JCI104803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., WAGNER H. N., Jr, DAVIDSON D. G. The effect of variations in solute excretion and vasopressin dosage on the excretion of water in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1958 Mar;37(3):458–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI103625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, VANGIESEN G., KIIL F., SELDIN D. W. INFLUENCE OF EXPANSION OF EXTRACELLULAR VOLUME ON TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF SODIUM INDEPENDENT OF CHANGES IN GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE AND ALDOSTERONE ACTIVITY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:341–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI104919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINMETZ P. R., EISINGER R. P., GOMBOS E. A., CHASIS H., BALDWIN D. S. EXCRETION OF FREE WATER AND SOLUTE DURING MAXIMAL WATER DIURESIS IN NORMAL AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Aug;64:238–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN R. M., BERCOVITCH D. D., LEVITT M. F. DUAL EFFECTS OF SALINE LOADING ON RENAL TUBULAR SODIUM REABSORPTION IN THE DOG. Am J Physiol. 1964 Oct;207:826–834. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.4.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldin D. W., Eknoyan G., Suki W. N., Rector F. C., Jr Localization of diuretic action from the pattern of water and electrolyte excretion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Nov 22;139(2):328–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. M., Abramson R. G., Bercovitch D. D., Levitt M. F. Effects of unilateral renal arterial constriction on tubular reabsorption of sodium and water during an osmotic diuresis. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1720–1729. doi: 10.1172/JCI105279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANGIESEN G., REESE M., KIIL F., RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF RENAL HYPOPERFUSION IN DOGS WITH ACUTE AND CHRONIC REDUCTIONS IN GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE AS DISCLOSED BY THE PATTERN OF WATER AND SOLUTE EXCRETION AFTER HYPOTONIC SALINE INFUSIONS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:416–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI104926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


