Abstract
Materials indistinguishable from authentic mono- and diiodotyrosines were identified in extracts of normal human serum as well as in extracts of purified human serum albumin. These materials were not found in association with the other serum proteins. Identification of MIT and DIT was made by a technique using rechromatography to constant specific activity, as well as by the Barker wet ash distillation method, which established the compounds in question as being iodinated ones. By two different extraction and chromatographic methods we estimated the amounts of both MIT and DIT present in normal human serum or albumin; the estimates were in good agreement. These compounds together constituted between 19% and 25% of the extractable serum iodine.
Full text
PDF

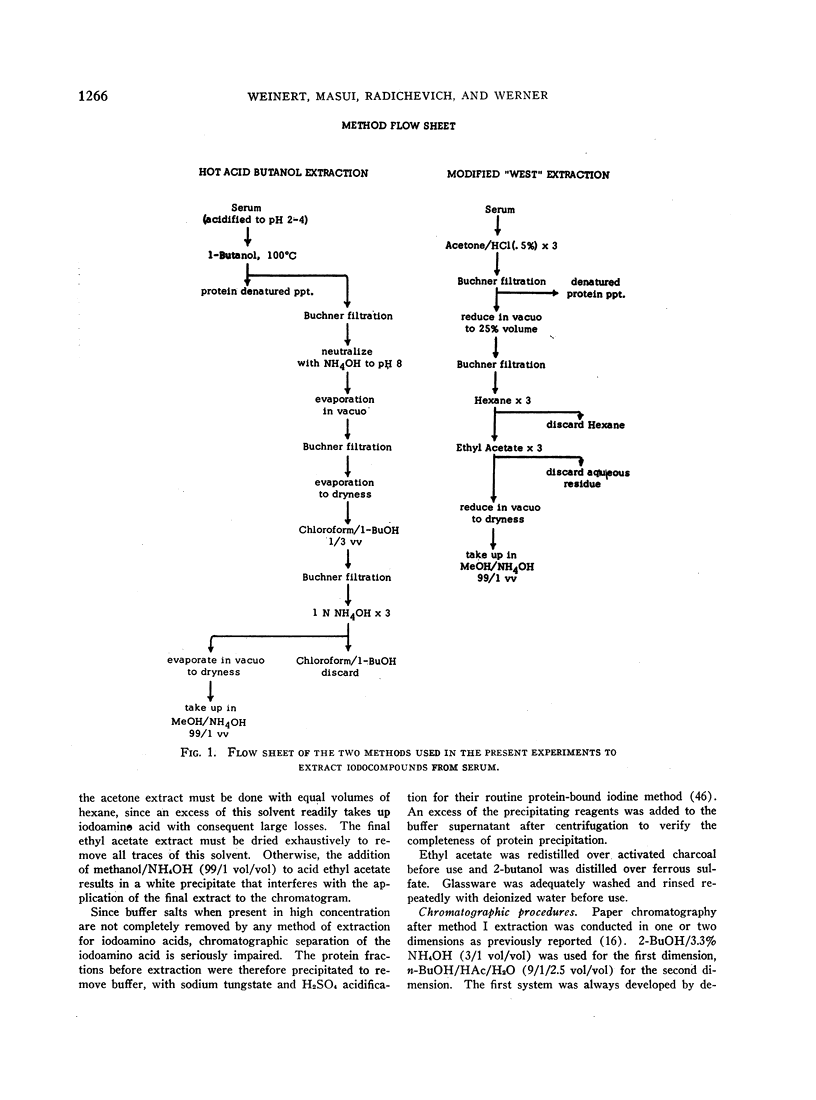
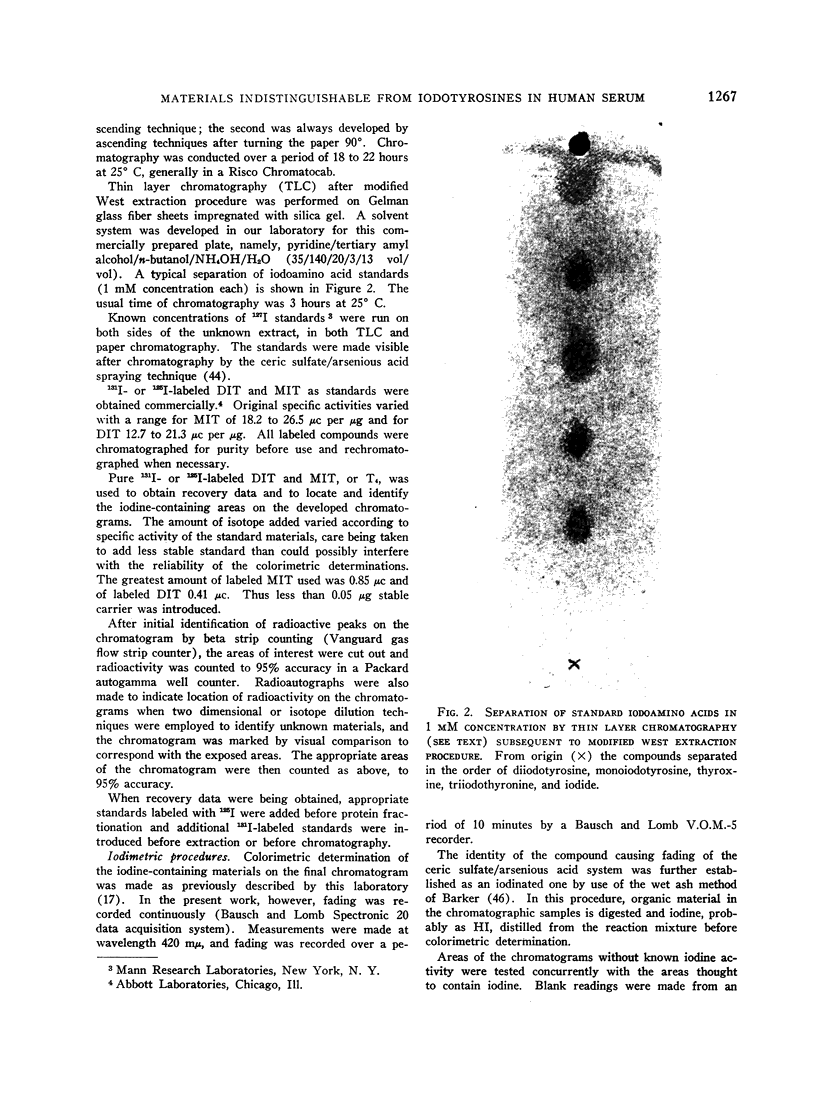
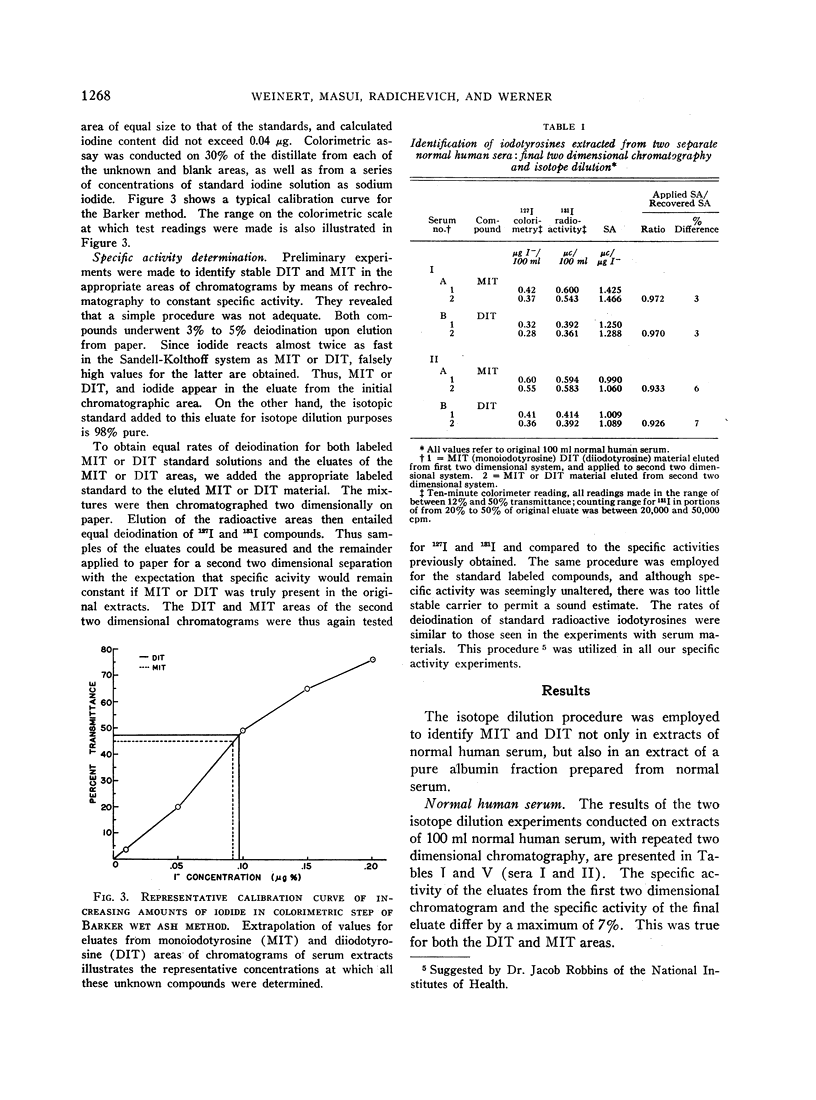

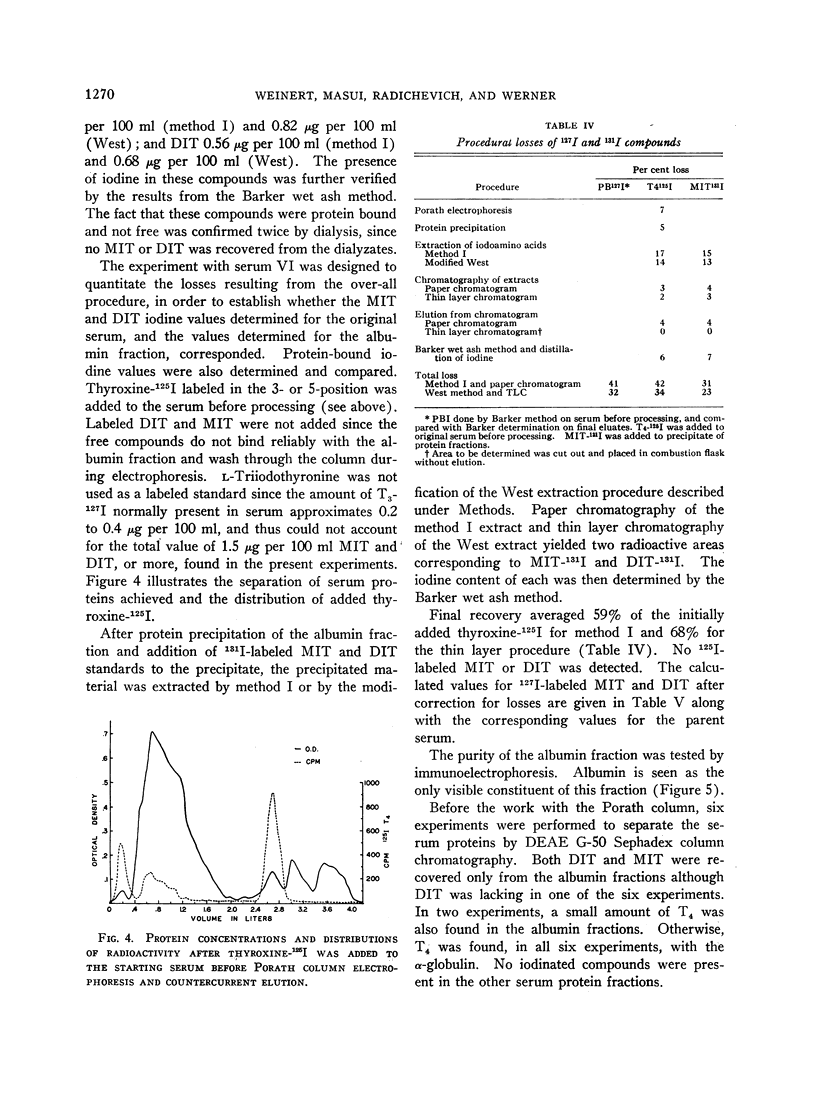



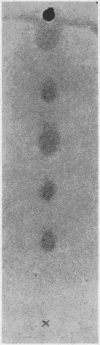
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AROSENIUS K. E. STUDIES ON THE IODO-AMINO ACIDS IN BLOOD SERUM. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1963;68:215–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRD R., FARRAN H. E. A sensitive method for the detection of iodinated compounds in human plasma, and its applications in the study of thyrotoxicosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Jan;20:81–88. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCK R. J., WERNER S. C., MANDL R. H. A method for the investigation of the distribution of radioiodine in the serum after small test doses of I 131. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Jan;73(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCK R. J., WERNER S. C., MANDL R. H., ROW V. V., RADICHEVICH I. The probable presence of diiodotyrosine and of monoiodotyrosine in human serum. A discrepancy between the distribution of iodo compounds when estimated by I 131 and by I 127. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 May;88:98–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIMITRIADOU A., FRASER R., TURNER P. C. IODOTYROSINE-LIKE SUBSTANCES IN HUMAN SERUM. Nature. 1964 Feb 8;201:575–578. doi: 10.1038/201575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIMITRIADOU A., RUSSELL FRASER T., SLATER J. D., TURNER P. C. Staining for iodine in chromatograms of human plasma: an artefact due to thiourea or thiouracils. Nature. 1960 Aug 20;187:691–693. doi: 10.1038/187691b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIMITRIADOU A., TURNER P. C., FRASER R. Activation analysis of paper chromatograms for iodine (iodine-127--iodine-128). Nature. 1963 May 11;198:576–577. doi: 10.1038/198576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN J. T., WERNER S. C. METABOLISM OF L-THYROXINE (3:5-131-I) IN MAN. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 May;24:460–466. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-5-460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER P. E., LITVAK J., STANBURY J. B. The capacity of normal man to deiodinate iodotyrosine. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1958 Oct;29(2):307–314. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0290307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALTON V. A., PITT-RIVERS R. A quantitative method for the separation of thyroid hormones and related compounds from serum and tissues with an anion-exchange resin. Biochem J. 1959 Jun;72(2):310–313. doi: 10.1042/bj0720310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A. Méthode permettant l'étude conjuguée des proprietés électrophorétiques et immunochimiques d'un mélange de protéines; application au sérum sanguin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., LEBLOND C. P., FRANKLIN A. E., QUASTEL J. H. Presence of iodinated amino acids in unhydrolyzed thyroid and plasma. Science. 1950 Jun 2;111(2892):605–608. doi: 10.1126/science.111.2892.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., LEBLOND C. P. Metabolites of thyroxine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Apr;76(4):686–689. doi: 10.3181/00379727-76-18595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., LEBLOND C. P. The presence of free iodinated compounds in the thyroid and their passage into the circulation. Endocrinology. 1951 Jun;48(6):714–725. doi: 10.1210/endo-48-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R. The identification of 3:5:3'-L-triiodothyronine in human plasma. Lancet. 1952 Mar 1;1(6705):439–441. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)91952-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLERSHOHN C., COMAR D., LE POEC C. [Determination of blood iodine by activation analysis]. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1961 Dec;12:87–103. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(61)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONO T., VAN MIDDLESWORTH L., ASTWOOD E. B. Chemical identification of iodine-containing compounds in human serum. Endocrinology. 1960 Jun;6:845–850. doi: 10.1210/endo-66-6-845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J. C. Nature of the circulating thyroid hormone. Nature. 1949 Nov 26;164(4178):927–927. doi: 10.1038/164927a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISSITZKY S., BISMUTH J., SIMON C. ABSENCE OF FREE IODOTYROSINES FROM THE PLASMA OF THE RAT. Nature. 1963 Sep 7;199:1002–1003. doi: 10.1038/1991002a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDL R. H., BLOCK R. J. Methods for the qualitative, semiquantitative and quantitative determination of iodoamino acids and of inorganic iodide in iodoprotein digests and in human serum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Mar;81(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette R. P., Balcius J. F., Zuppinger K. The determination of iodine-containing compounds by neutron activation of I-129. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1966 Dec;17(11):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(66)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILEGGI V. J., SEGAL H. A., GOLUB O. J. DETERMINATION OF ORGANIC IODINE COMPOUNDS IN SERUM. III. IODOTYROSINES IN NORMAL HUMAN SERUM. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Mar;24:273–280. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-3-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITT-RIVERS R., RALL J. E. Radioiodine equilibrium studies of thyroid and blood. Endocrinology. 1961 Feb;68:309–316. doi: 10.1210/endo-68-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSTIMES T. J. DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN IODINE AND NON-IODINE SPOTS ON PAPER CHROMATOGRAMS DURING THE MICROQUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF THE IODINATED AMINO ACIDS OF HUMAN SERUM. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Dec;10:581–583. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL J. E. Iodine compounds in the blood and urine of man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1950 Sep;10(9):996–1006. doi: 10.1210/jcem-10-9-996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHE J., MICHEL R. Nature, biosynthesis and metabolism of thyroid hormones. Physiol Rev. 1955 Jul;35(3):583–610. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1955.35.3.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG I. N. The nature of the circulating thyroid hormone in Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1951 Jan;30(1):1–10. doi: 10.1172/JCI102409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoes B. A., Wagner H. N., Jr Are iodotyrosines normal constitutents of plasma? Nature. 1966 May 7;210(5036):647–648. doi: 10.1038/210647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Row V. V., Volpe R., Ezrin C. 127-I-iodotyrosine-like compounds in normal human serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 May;13(5):666–668. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY J. B., KASSENAAR A. A., MEIJER J. W. The metabolism of iodotyrosines. I. The fate of mono- and di-iodotyrosine in normal subjects and in patients with various diseases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Jun;16(6):735–746. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-6-735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUROG A., CHAIKOFF I. L., TONG W. The nature of plasma iodine as revealed by filter paper partition chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):99–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONG W., TAUROG A., CHAIKOFF I. L. The metabolism of I131-labeled diiodotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):59–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLBY M. L., HETZEL B. S. Demonstration of iodotyrosines in human plasma in response to thyroid stimulation. Nature. 1962 Feb 24;193:752–754. doi: 10.1038/193752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERNER S. C., BLOCK R. J. Discrepancy between the distributions of iodine in human serum when estimated by iodine-131 and iodine-127. Nature. 1959 Feb 7;183(4658):406–407. doi: 10.1038/183406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERNER S. C., RADICHEVICH I. Presence of iodine-127 iodotyrosines in extracts of normal human serum. Nature. 1963 Mar 2;197:877–878. doi: 10.1038/197877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNN J. Organic iodine constituents in human serum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Mar;87:120–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. D., Chavré V. J., Wolfe M. A serum thyroxine method: application in thyroid disease and iodine-treated patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Sep;25(9):1189–1195. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-9-1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]