Abstract
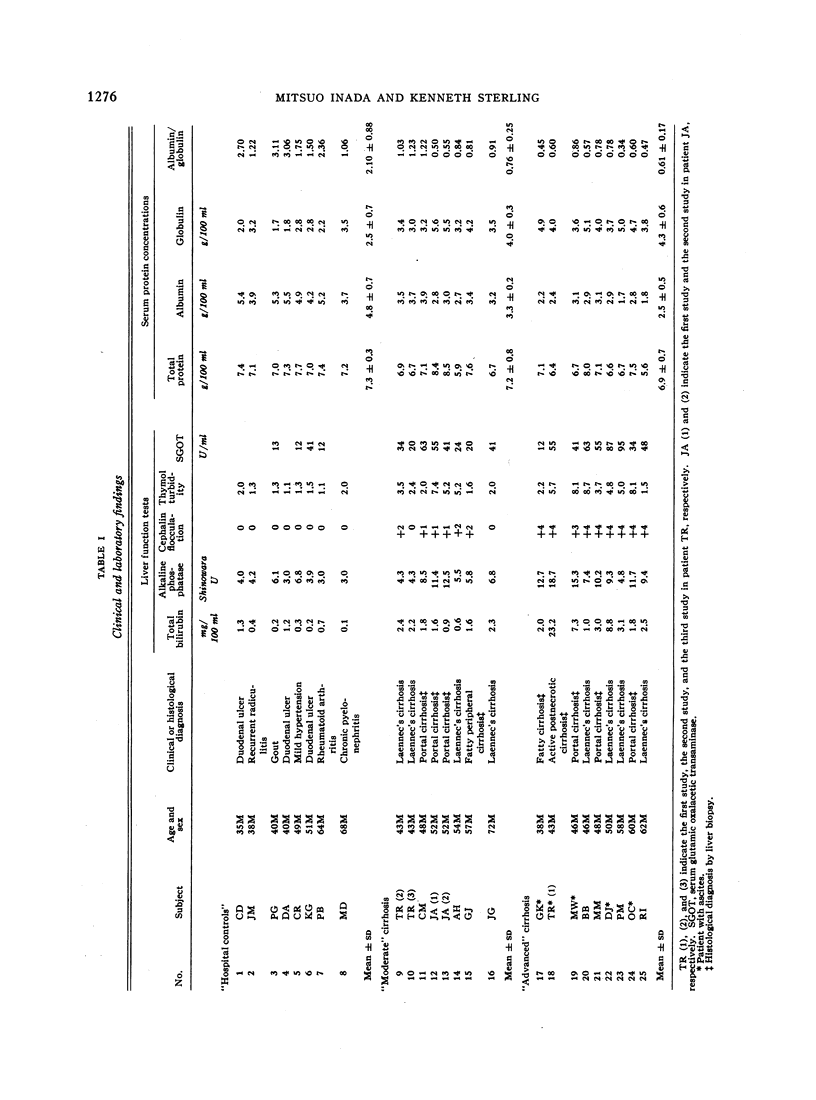
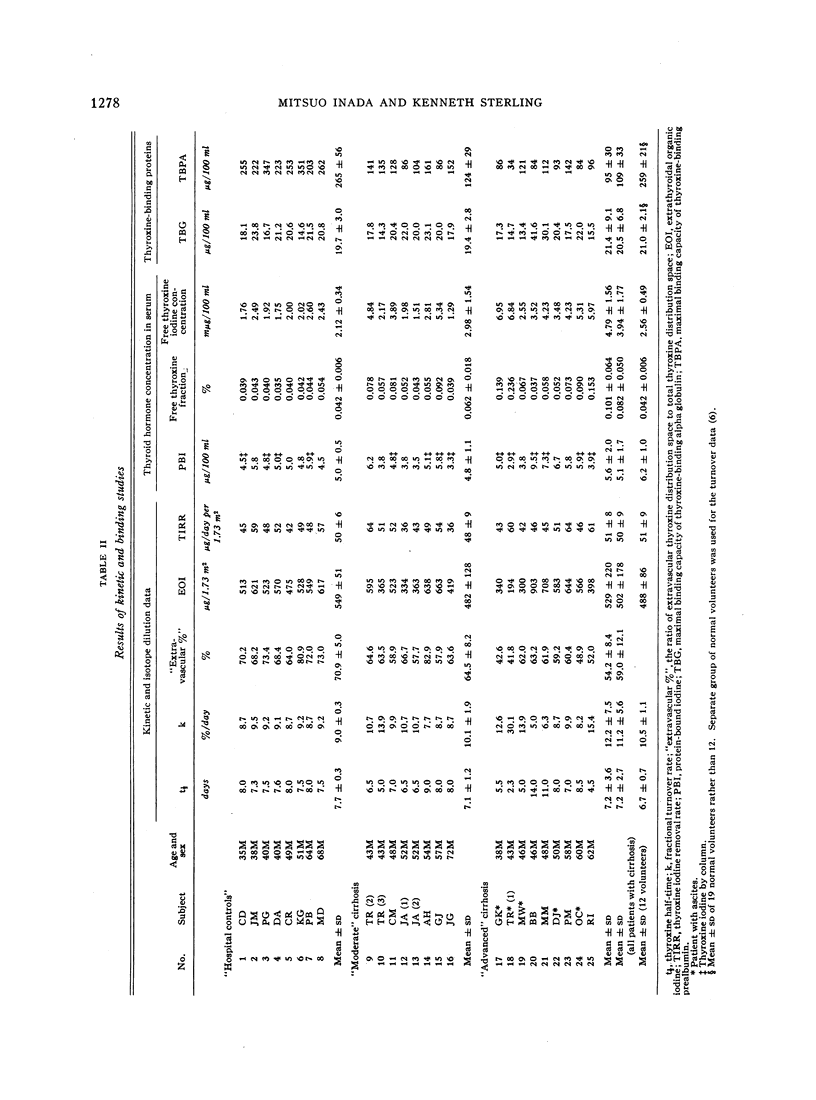
Studies of the metabolism of thyroxine in 14 cases of cirrhosis revealed a variety of deviations from normal. In addition to radiothyroxine turnover studies, determinations were made of the free thyroxine fractions and free thyroxine iodine concentrations in serum (magnesium precipitation method) as well as the maximal binding capacities of thyroxine-binding alpha globulin (TBG) and thyroxine-binding prealbumin (TBPA) by reverse flow paper electrophoresis in a glycine acetate system at pH 8.6.
All cases of cirrhosis exhibited diminutions in TBPA capacities but their TBG capacities showed a wide scatter (13.4 to 41.6 μg/100 ml). The free thyroxine fraction was quite variable, with distinct elevations in nine of the 17 sera.
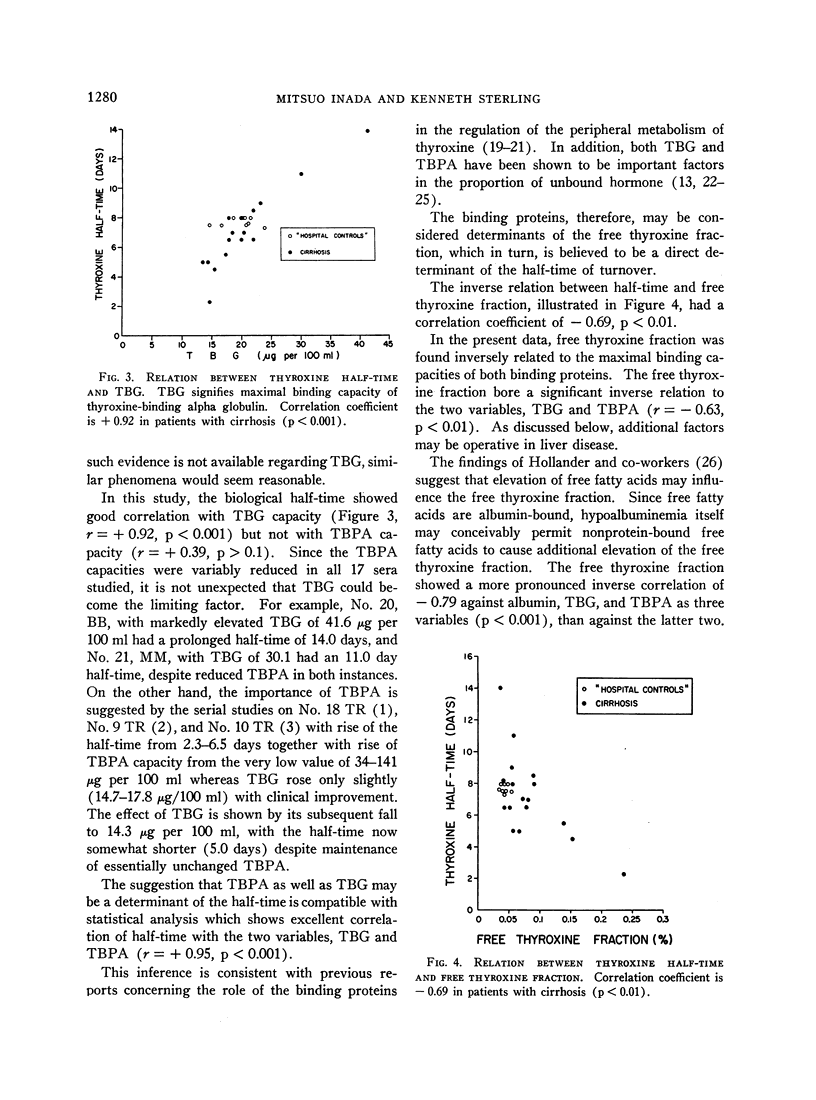
The binding proteins appeared to be determinants of the free thyroxine fraction, which in turn, appeared to be a direct determinant of the half-time of turnover. These inferences did not exclude other possible factors including diminished hepatic uptake and metabolism of the hormone in liver disease.
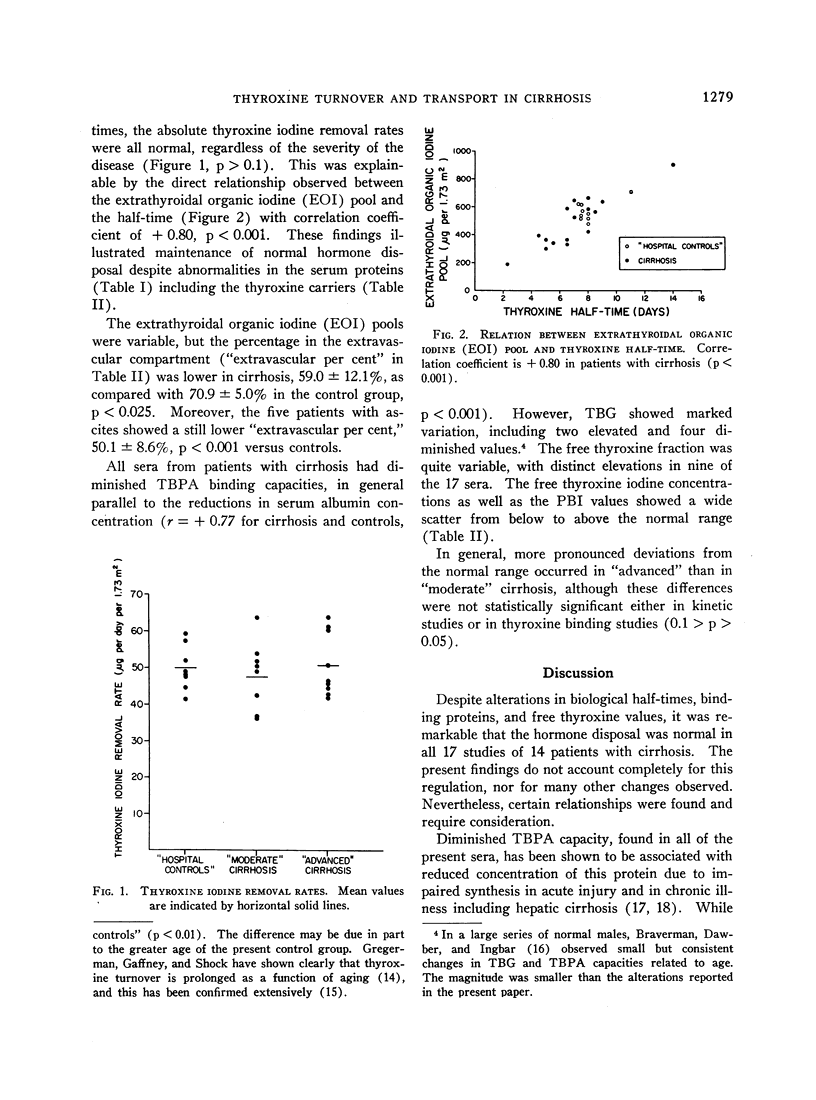
Despite considerable alterations in biological half-times, free thyroxine values, and binding proteins, it was remarkable that the absolute hormone disposal was normal in all 14 patients with cirrhosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein G., Oppenheimer J. H. Factors influencing the concentration of free and total thyroxine in patients with nonthyroidal disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Feb;26(2):195–201. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. W., Dawber N. A., Ingbar S. H. Observations concerning the binding of thyroid hormones in sera of normal subjects of varying ages. J Clin Invest. 1966 Aug;45(8):1273–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI105434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS T. Thyroxine metabolism in man estimated by means of I 131-labelled L-thyroxine. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1958 Dec;29(4):587–601. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0290587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGERMAN R. I., GAFFNEY G. W., SHOCK N. W., CROWDER S. E. Thyroxine turnover in euthyroid man with special reference to changes with age. J Clin Invest. 1962 Nov;41:2065–2074. doi: 10.1172/JCI104664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INADA M., KOSHIYAMA K., TORIZUKA K., AKAGI H., MIYAKE T. CLINICAL STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF 131-I-LABELED L-THYROXINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Aug;24:775–784. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-8-775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Regulation of the peripheral metabolism of the thyroid hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:353–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E., Dawber N. A., Lee G. Y. A new method for measuring the free thyroid hormone in human serum and an analysis of the factors that influence its concentration. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1679–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND G. S., BUSTOS J. G., HAMOLSKY M. W., FREEDBERG A. S. Studies in nonmyxedematous hypometabolism. II. Turnover of I131-labeld thyroxine after intravenous infusion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Nov;17(11):1365–1372. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-11-1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNON E. J., ENGBRING N. H., ENGSTROM W. W. Studies of the rate of disappearance of labeled thyroxine from the intravascular compartment. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jun;40:996–1005. doi: 10.1172/JCI104339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPEHNEIMER J. H., SURKS M. I., BERNSTEIN G., SMITY J. C. METABOLISM OF IODINE-131--LABELED THYROXINE-BINDING PREALBUMIN IN MAN. Science. 1965 Aug 13;149(3685):748–750. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3685.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SQUEF R., SURKS M. I., HAUER H. BINDING OF THYROXINE BY SERUM PROTEINS EVALUATED BY EQUILIBRUM DIALYSIS AND ELECTROPHORETIC TECHNIQUES. ALTERATIONS IN NONTHYROIDAL ILLNESS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1769–1782. doi: 10.1172/JCI104862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oddie T. H., Meade J. H., Jr, Fisher D. A. An analysis of published data on thyroxine turnover in human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Apr;26(4):425–436. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-4-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Bernstein G., Hasen J. Estimation of rapidly exchangeable cellular thyroxine from the plasma disappearance curves of simultaneously administered thyroxine-131-I and albumin-125-I. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):762–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI105577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. Proteins associated with the thyroid hormones. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:415–489. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. Reverse-flow zone electrophoresis; a method for determining the thyroxine-binding capacity of serum protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Aug;63(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., CHODOS R. B. Radiothyroxine turnover studies in myxedema, thyrotoxicosis, and hypermetabolism without endocrine disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jul;35(7):806–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI103333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., LASHOF J. C., MAN E. B. Disappearance from serum of I131-labeled l-thyroxine and l-triiodothyronine in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Invest. 1954 Jul;33(7):1031–1035. doi: 10.1172/JCI102970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SURKS M. I., OPPENHEIMER J. H. POSTOPERATIVE CHANGES IN THE CONCENTRATION OF THYROXINE-BINDING PREALBUMIN AND SERUM FREE THYROXINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Aug;24:794–802. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-8-794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socolow E. L., Woeber K. A., Purdy R. H., Holloway M. T., Ingbar S. H. Preparation of I-131-labeled human serum prealbumin and its metabolism in normal and sick patients. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1600–1609. doi: 10.1172/JCI105266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANNOTTI A., BERAUD T. Functional relationships between the liver, the thyroxine-binding protein of serum, and the thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Apr;19(4):466–477. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-4-466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOEBER K. A., INGBAR S. H. THE EFFECTS OF NONCALORIGENIC CONGENERS OF SALICYLATE ON THE PERIPHERAL METABOLISM OF THYROXINE. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:931–942. doi: 10.1172/JCI104979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


