Abstract
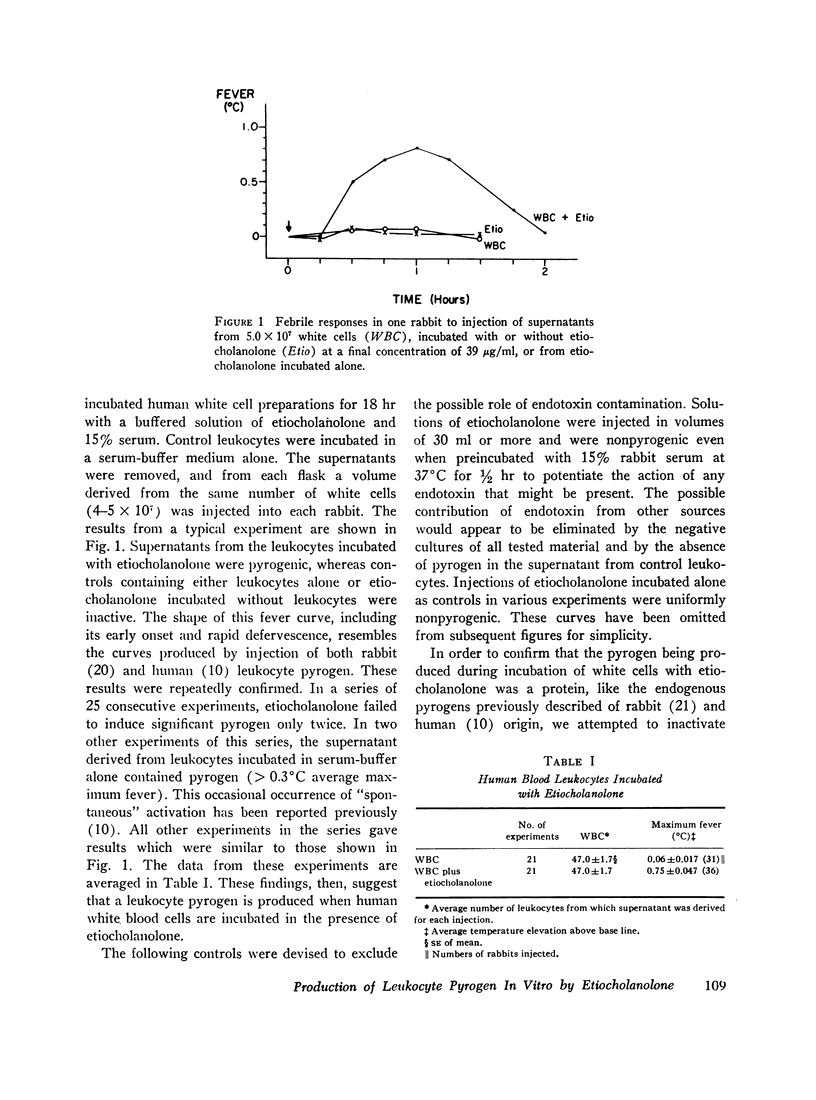
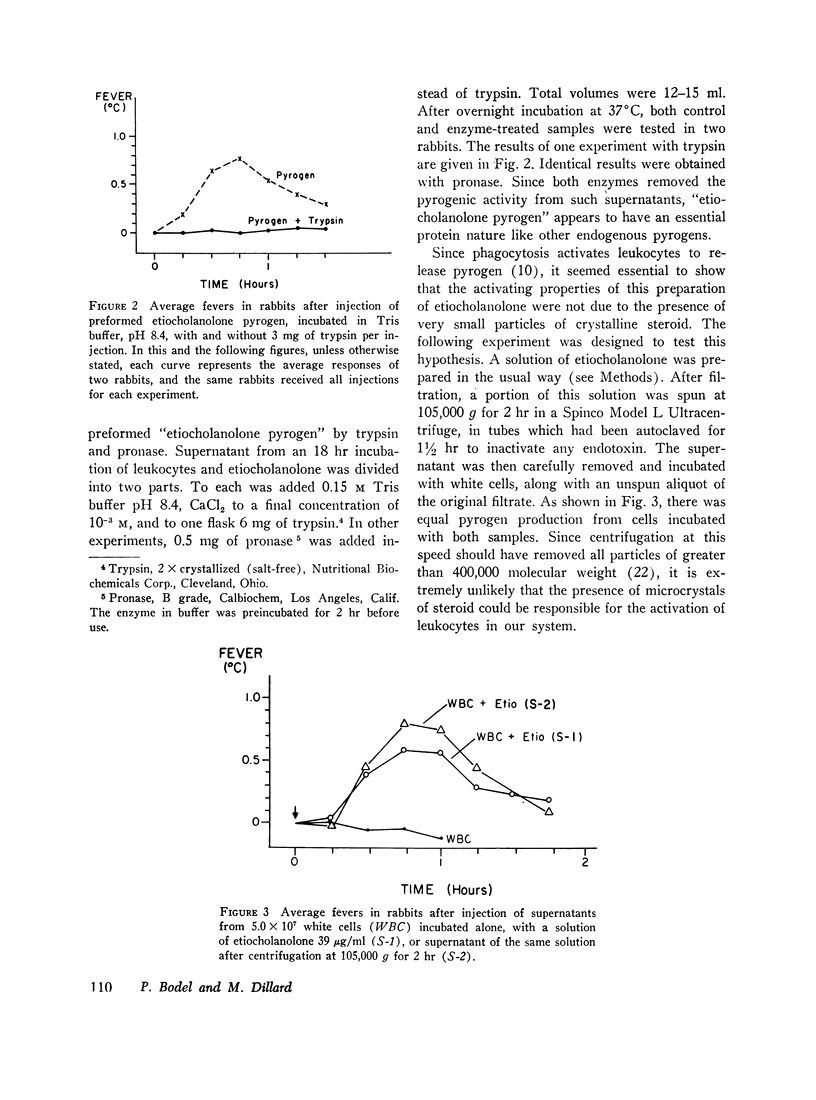
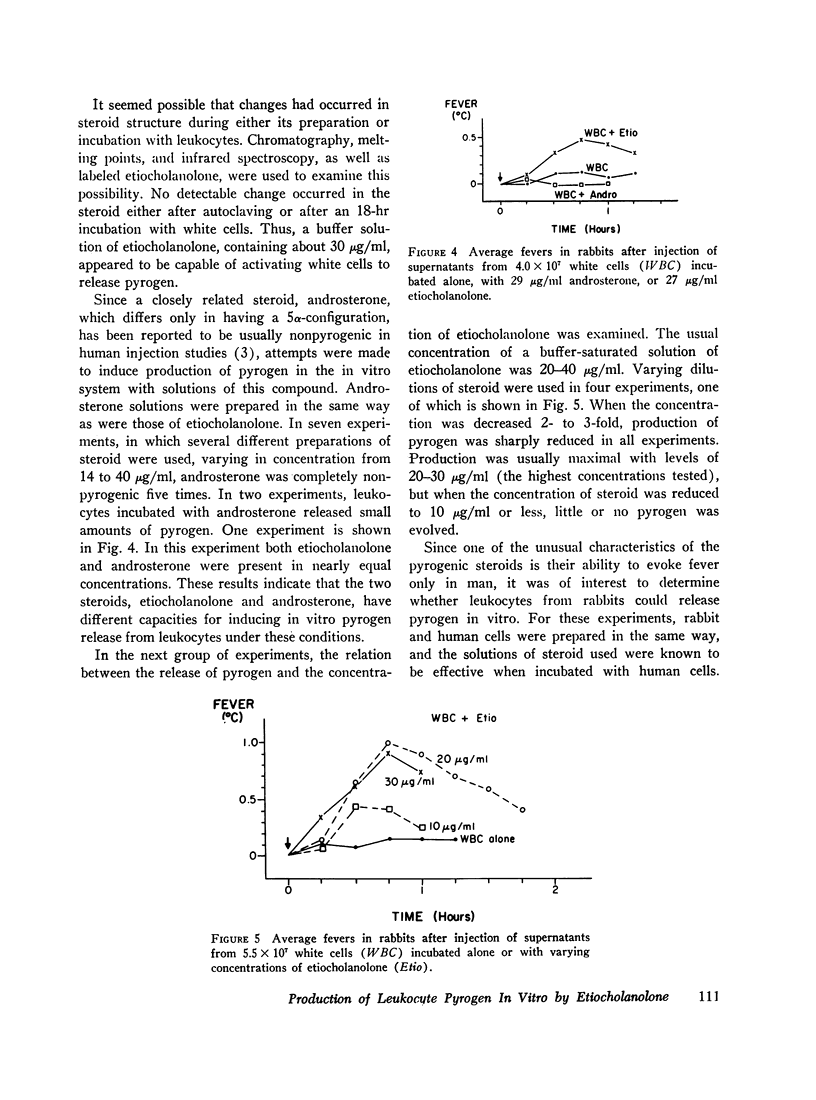
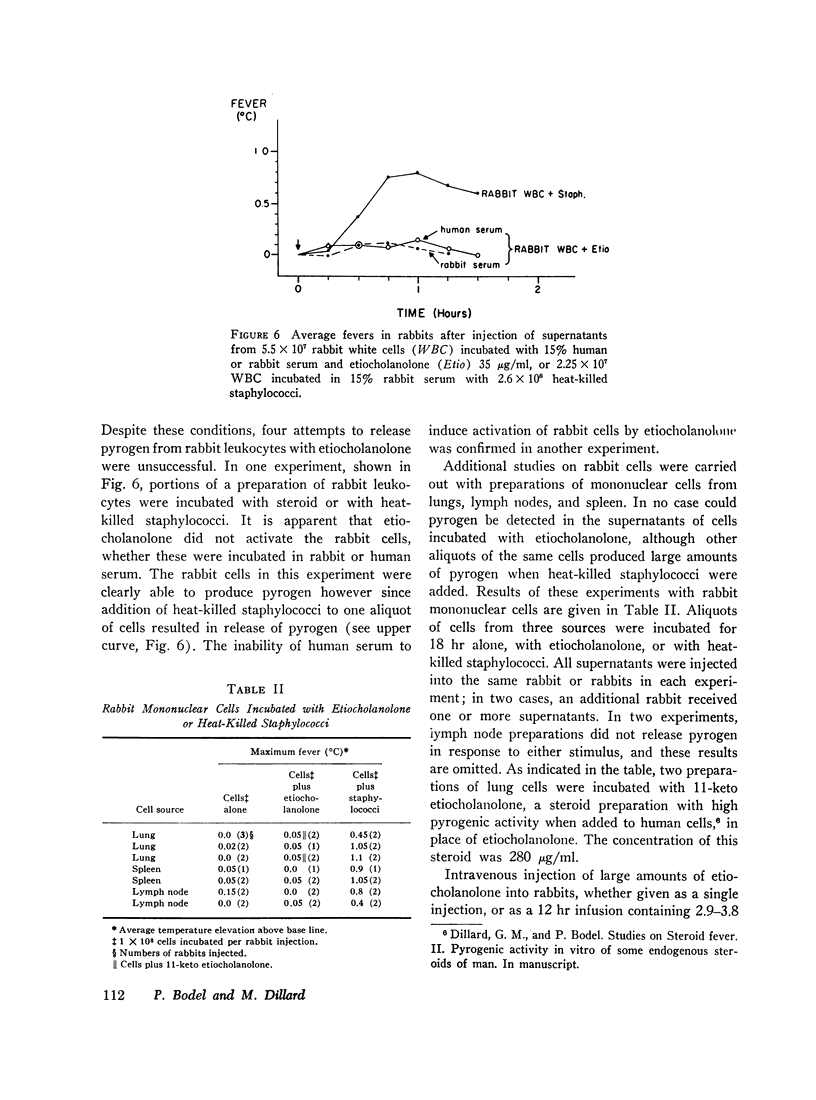
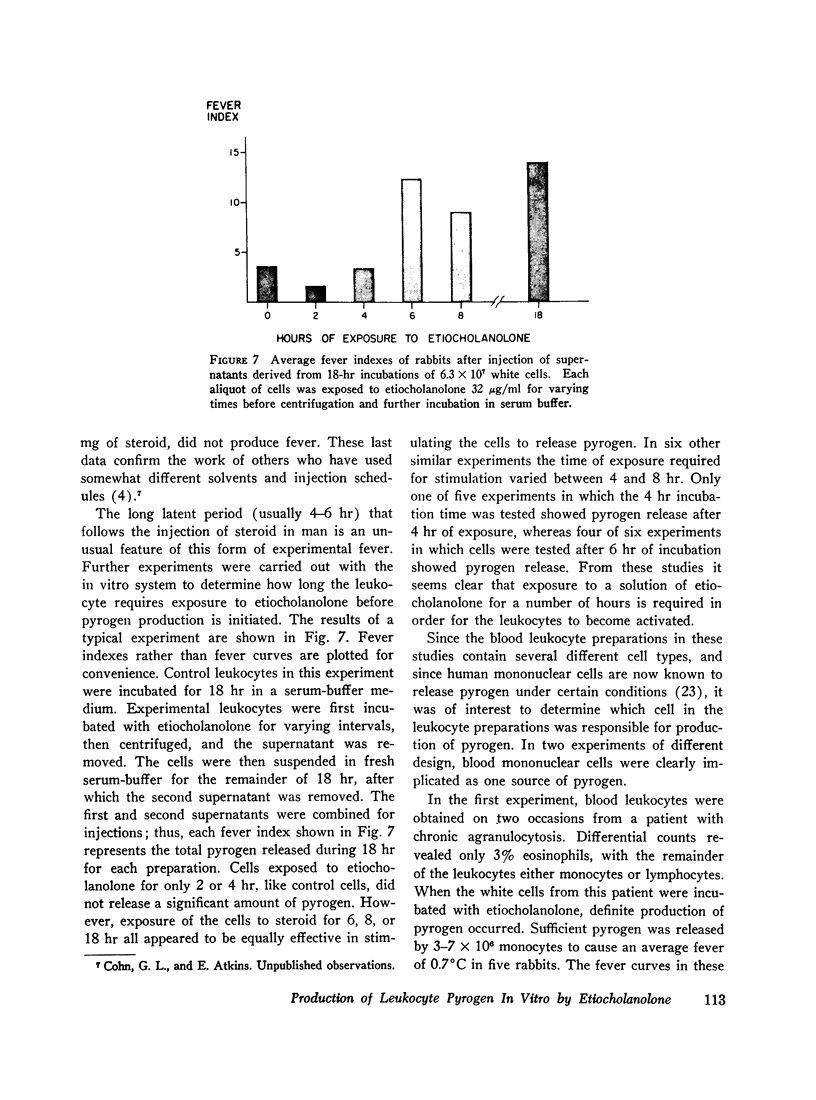
When a serum-buffer solution of etiocholanolone is incubated with human blood leukocytes in vitro, a pyrogen is released. Like endogenous pyrogen of leukocyte origin, this pyrogen produces prompt monophasic fevers in rabbits, does not induce fever tolerance when given daily, and is inactivated by trypsin. In many respects, the characteristics of the in vitro reaction resemble experimental steroid-induced fever. For example, release of pyrogen varies directly with the concentration of steroid. 4-8 hr of contact between steroid and leukocyte is required for activation of the cell. Rabbit leukocytes are not activated by etiocholanolone. Finally, androsterone, the 5α-isomer of etiocholanolone, does not induce pyrogen release in vitro. These studies suggest that experimental steroid fever in man may be mediated by an endogenous pyrogen released from leukocytes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINS E., HEIJN C., Jr STUDIES ON TUBERCULIN FEVER. 3. MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN THE RELEASE OF ENDOGENOUS PYROGEN IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:207–235. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins E., Bodel P., Francis L. Release of an endogenous pyrogen in vitro from rabbit mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):357–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT I. L., Jr, BEESON P. B. Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. II. Characterization of fever-producing substances from polymorphonuclear leukocytes and from the fluid of sterile exudates. J Exp Med. 1953 Nov;98(5):493–508. doi: 10.1084/jem.98.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONDY P. K., COHN G. L., GREGORY P. B. ETIOCHOLANOLONE FEVER. Medicine (Baltimore) 1965 May;44:249–262. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196505000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONDY P. K., COHN G. L., GREGORY P. B. ETIOCHOLANOLONE FEVER. Medicine (Baltimore) 1965 May;44:249–262. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196505000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. E., Cohn Z. A. The isolation and selected properties of blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):145–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodel P. T., Atkins E. Studies in staphylococcal fever. V. Staphlococcal filtrate pyrogen. Yale J Biol Med. 1965 Dec;38(3):282–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodel P., Atkins E. Human leukocyte pyrogen producing fever in rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Mar;121(3):943–946. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodel P., Atkins E. Release of endogenous pyrogen by human monocytes. N Engl J Med. 1967 May 4;276(18):1002–1008. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196705042761803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN G. L., BONDY P. K., CASTIGLIONE C. Studies on pyrogenic steroids. I. Separation, identification, and measurement of unconjugated dehydroepiandrosterone, etiocholanolone, and adrosterone in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:400–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI104267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALLON H. J., FREI E., 3rd, DAVIDSON J. D., TRIER J. S., BURK D. Leukocyte preparations from human blood: evaluation of their morphologic and metabolic state. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 May;59:779–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLICKMAN P. B., PALMER R. H., KAPPAS A. STEROID FEVER AND INFLAMMATION. STUDIES WITH 11-KETOPREGNANOLONE IN MAN. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Jul;114:46–58. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.03860070092009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. H., Char D. C., Postel W. B., Wood W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. XV. The production of endogenous pyrogen by peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):385–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPAS A., GLICKMAN P. B., PALMER R. H. Steroid fever studies: physiological differences between bacterial pyrogens and endogenous steroid pyrogens of man. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1960;73:176–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPAS A., HELLMAN L., FUKUSHIMA D. K., GALLAGHER T. F. The pyrogenic effect of etiocholanolone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Mar;17(3):451–453. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-3-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPAS A., HELLMAN L., FUKUSHIMA D. K., GALLAGHER T. F. The thermogenic effect and metabolic fate of etiocholanolone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Oct;18(10):1043–1055. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-10-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPAS A., PALMER R. H. Selected aspects of steroid pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1963 Mar;15:123–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPAS A., SOYBEL W., GLICKMAN P., FLUKUSHIMA D. K. Fever-producing steroids of endogenous origin in man. Arch Intern Med. 1960 May;105:701–708. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1960.00270170039005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKSHMANAN T. K., LIEBERMAN S. An improved method of gradient elution chromatography and its application to the separation of urinary ketosteroids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Nov;53(1):258–281. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q., LEAKE E. S., FARISS B. Studies on pulmonary alveolar macrophages from the normal rabbit: a technique to procure them in a high state of purity. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER R. H., RATKOVITS B., KAPPAS A. Steroid pyrogen studies in laboratory and domestic animals. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Mar;16:345–347. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSDORF R. G., BENNETT I. L., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. VII. Comparative observations on the production of fever by inflammatory exudates in rabbits and dogs. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Jun;100(6):277–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAFTER G. W., COLLINS R. D., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. VII. Preliminary chemical characterization of leucocytic pyrogen. J Exp Med. 1960 Jun 1;111:831–840. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.6.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN J. A., HERRMANN W. L., PETERSDORF R. G. EXPERIMENTAL ETIOCHOLANOLONE FEVER. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Nov;24:1136–1142. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-11-1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell E. S., Atkins E. Interactions of gram-negative bacterial endotoxin with rabbit blood in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1967 May;212(5):1103–1112. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.5.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G. STUDIES OF LYSOSOMES. VI. THE EFFECT OF NEUTRAL STEROIDS AND BILE ACIDS ON LYSOSOMES IN VITRO. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 Apr;14:525–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]