Abstract
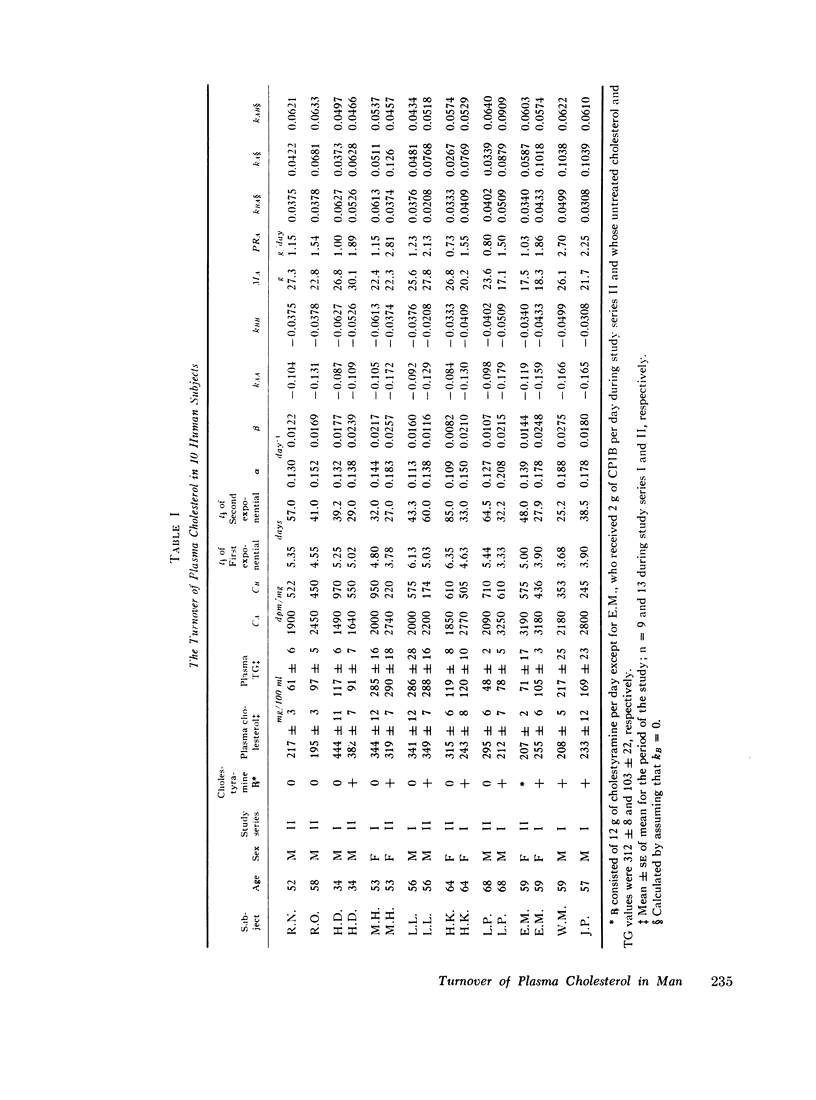
Cholesterol-4-14C was injected intravenously into a series of normal men, untreated hyperlipidemic patients, and hyperlipidemic patients being treated with cholestyramine. The specific radioactivity of plasma total cholesterol was measured during the ensuing 10 wk. 16 studies were carried out in 10 subjects. Analysis of the turnover curves of plasma cholesterol revealed that in every study the turnover of plasma cholesterol conformed to a two-pool model. Each turnover curve was analyzed in terms of this model, as expressed by the equation: specific activity = CAe-αt + CBe-βt. The parameters which were calculated included the constants CA, CB, α, and β; the size of the first pool (MA); the rate constants for the total rate of removal of cholesterol from each pool (kAA and kBB); and the production rate in pool A (PRA). In two normal men and five untreated patients the average size of pool A was 25g.
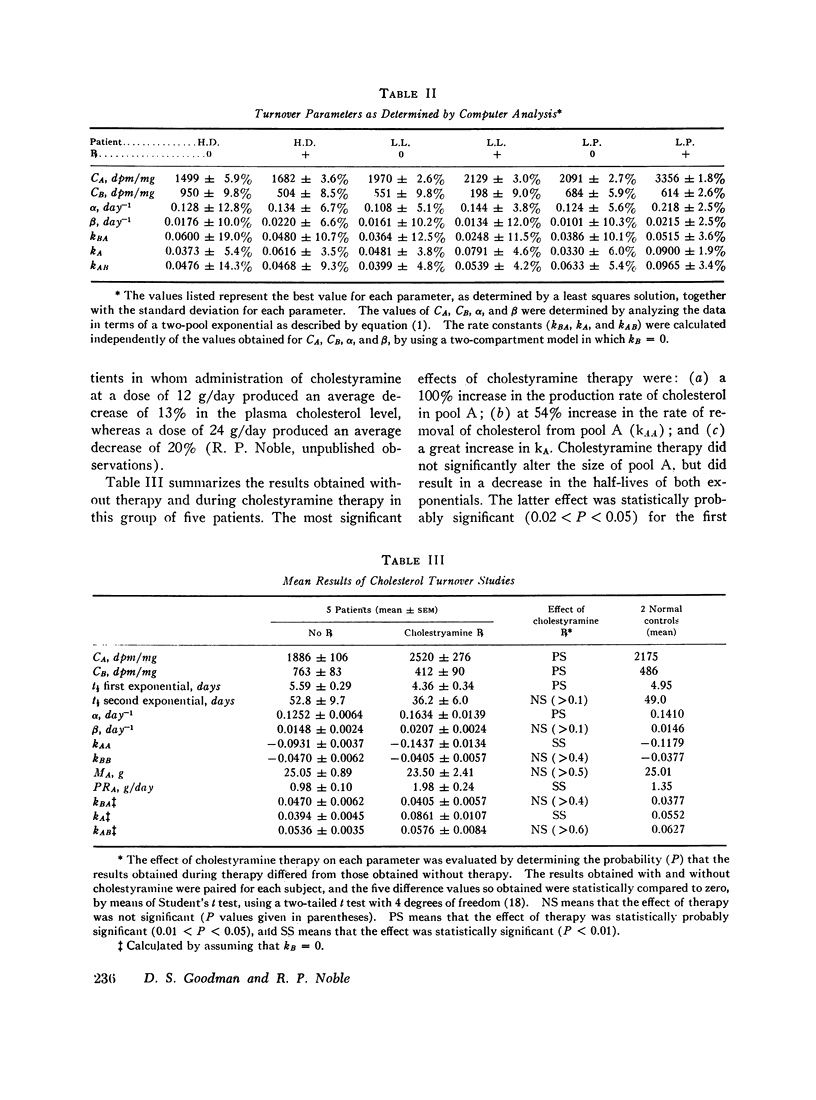
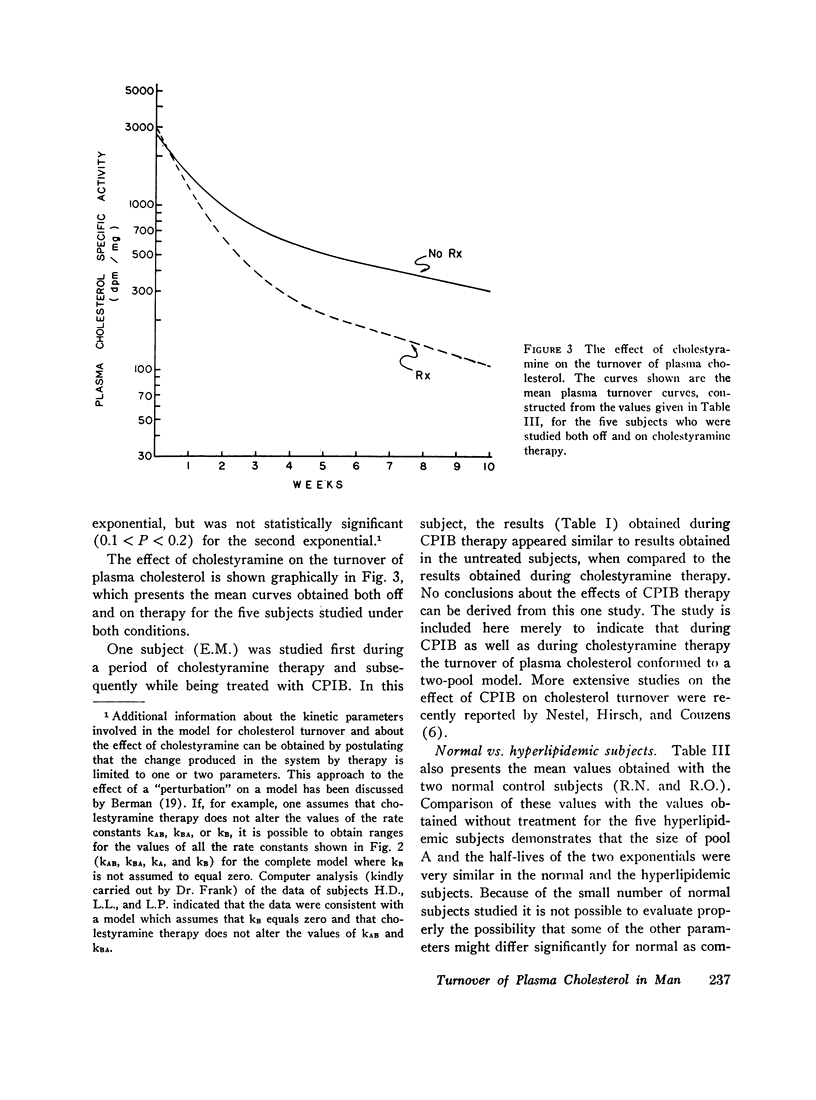
The effect of cholestyramine was assessed by comparing the results obtained without therapy with those obtained during therapy in five subjects studied under both conditions. Cholestyramine therapy produced a large increase in PRA (from 0.98 to 1.98 g/day) and in the rate of removal of cholesterol from pool A. Cholestyramine did not significantly alter the size of pool A.
It is not possible to calculate the size of the total body exchangeable pool of cholesterol from the turnover curve of plasma cholesterol. It is also not possible to calculate the metabolic turnover rate, i.e., the rate of cholesterol degradation and excretion, in the whole body. This parameter can, however, be estimated by assuming that cholesterol is removed from the body only by way of the tissue pools that comprise pool A. Under these conditions the metabolic turnover rate is equal to the production rate in pool A.
Full text
PDF

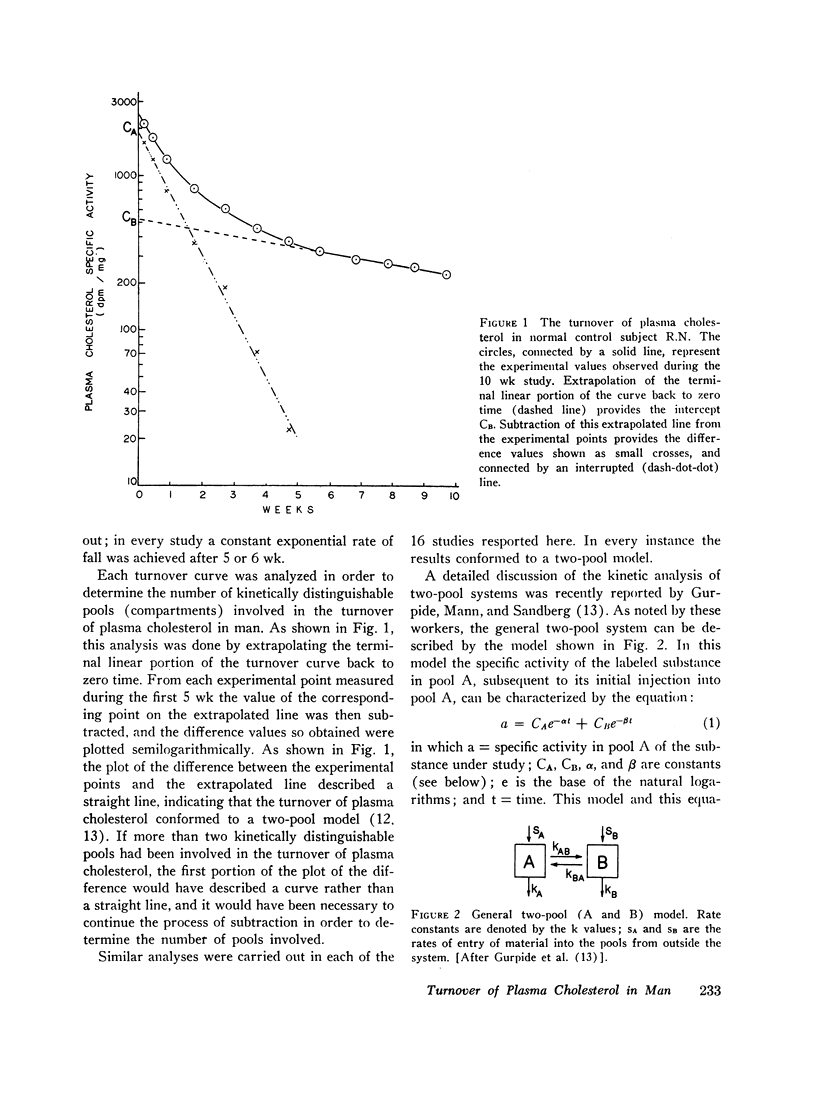





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avigan J., Steinberg D. Sterol and bile acid excretion in man and the effects of dietary fat. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1845–1856. doi: 10.1172/JCI105292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN M., SHAHN E., WEISS M. F. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models: a mathematical formalism for digital computers. Biophys J. 1962 May;2:275–287. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86855-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN M. The formulation and testing of models. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 10;108:182–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN M., WEISS M. F., SHAHN E. Some formal approaches to the analysis of kinetic data in terms of linear compartmental systems. Biophys J. 1962 May;2:289–316. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86856-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. A postulate to aid in model building. J Theor Biol. 1963 May;4(3):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASDORPH H. R., JUERGENS J. L., ORVIS A. L., OWEN C. A., Jr Rate of disappearance of cholesterol-C-14 from the bloodstream of dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jan;112:191–194. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-27989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOBANIAN A. V., BURROWS B. A., HOLLANDER W. Body cholesterol metabolism in man. II. Measurement of the body cholesterol miscible pool and turnover rate. J Clin Invest. 1962 Sep;41:1738–1744. doi: 10.1172/JCI104632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOBANIAN A. V., HOLLANDER W. Body cholesterol metabolism in man. I. The equilibration of serum and tissue cholesterol. J Clin Invest. 1962 Sep;41:1732–1737. doi: 10.1172/JCI104631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX G. E., TAYLOR C. B., PATTON D., DAVIS C., Jr, BLANDIN N. Origin of plasma cholesterol in man. Arch Pathol. 1963 Jul;76:60–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Siperstein M. D. Effect of cholesterol feeding and fasting on sterol synthesis in seventeen tissues of the rat. J Lipid Res. 1967 Mar;8(2):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECKLES N. E., TAYLOR C. B., CAMPBELL D. J., GOULD R. G. The origin of plasma cholesterol and the rates of equilibration of liver, plasma, and erythrocyte cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Sep;46(3):359–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD H., Jr, SWELL L., SCHOOLS P. E., Jr, TREADWELL C. R. Dynamic aspects of cholesterol metabolism in different areas of the aorta and other tissues in man and their relationship to atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1960 Oct;22:547–558. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.22.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. THE IN VIVO TURNOVER OF INDIVIDUAL CHOLESTEROL ESTERS IN HUMAN PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2026–2036. doi: 10.1172/JCI105077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD R. G., LEROY G. V., OKITA G. T., KABARA J. J., KEEGAN P., BERGENSTAL D. M. The use of C14-labeled acetate to study cholesterol metabolism in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Sep;46(3):372–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURPIDE E., MANN J., LIEBERMAN S. ANALYSIS OF OPEN SYSTEMS OF MULTIPLE POOLS BY ADMINISTRATION OF TRACERS AT A CONSTANT RATE OR AS A SINGLE DOSE AS ILLUSTRATED BY PROBLEMS INVOLVING STEROID HORMONES. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Nov;23:1155–1176. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-11-1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURPIDE E., MANN J., SANDBERG E. DETERMINATION OF KINETIC PARAMETERS INA TWO-POOL SYSTEM BY ADMINISTRATION OF ONE OR MORE TRACERS. Biochemistry. 1964 Sep;3:1250–1255. doi: 10.1021/bi00897a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Cholesterol ester metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1965 Oct;45(4):747–839. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr An evaluation of the relative merits of two methods for measuring the balance of sterols in man: isotopic balance versus chromatographic analysis. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1503–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI105457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLMAN L., ROSENFELD R. S., GALLAGHER T. F. Cholesterol synthesis from C14-acetate in man. J Clin Invest. 1954 Feb;33(2):142–149. doi: 10.1172/JCI102881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND G. S., LUCAS J. L., FREEDBERG A. S. The metabolism of intravenously infused C14-labeled cholesterol in euthyroidism and myxedema. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Apr;57:574–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTEL P. J., HIRSCH E. Z., COUZENS E. A. THE EFFECT OF CHLOROPHENOXYISOBUTYRIC ACID AND ETHINYL ESTRADIOL ON CHOLESTEROL TURNOVER. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jun;44:891–896. doi: 10.1172/JCI105205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRITZ N., AHRENS E. H., Jr, GRUNDY S. STEROL BALANCE IN MAN AS PLASMA CHOLESTEROL CONCENTRATIONS ARE ALTERED BY EXCHANGES OF DIETARY FATS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Sep;44:1482–1493. doi: 10.1172/JCI105255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAIT J. F., TAIT S. A., LITTLE B., LAUMAS K. R. The disappearance of 7-H-3-d-aldosterone in the plasma of normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:72–80. doi: 10.1172/JCI104239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HANDEL E., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Micromethod for the direct determination of serum triglycerides. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jul;50(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D., Lindsey C. A., Jr Studies on the influence of dietary cholesterol on cholesterol metabolism in the isotopic steady state in man. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1805–1814. doi: 10.1172/JCI105288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


