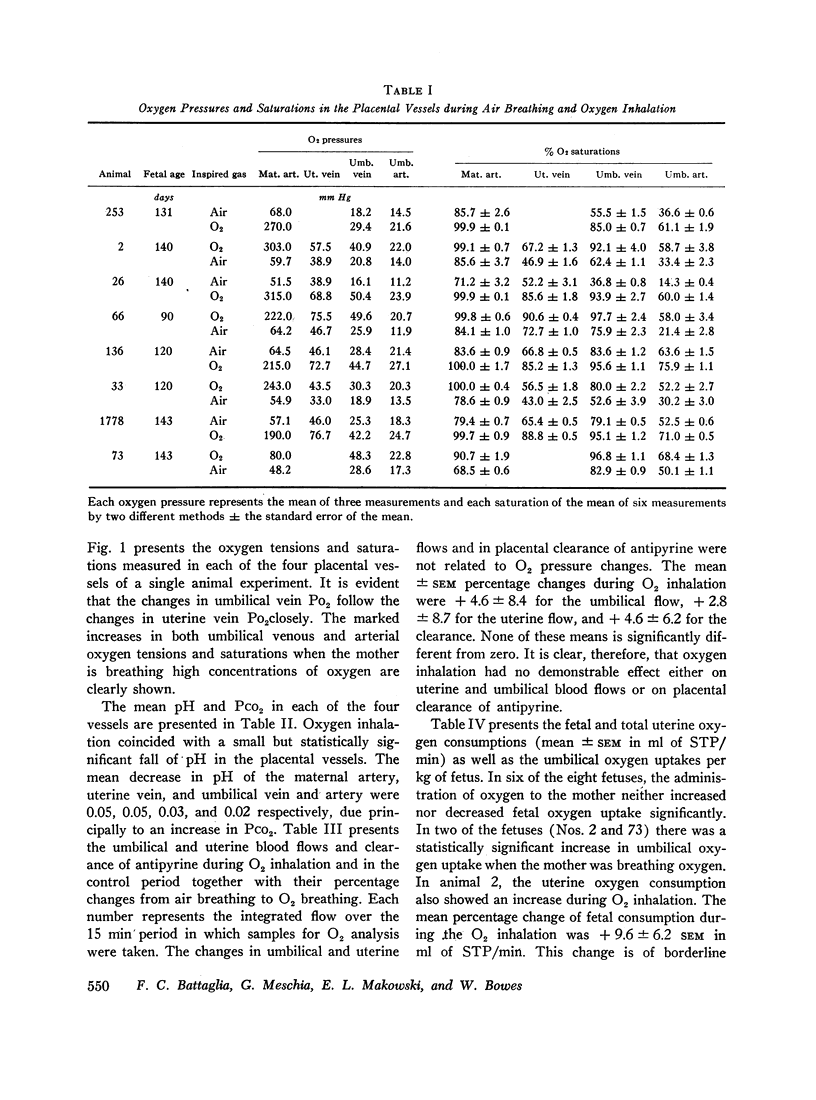
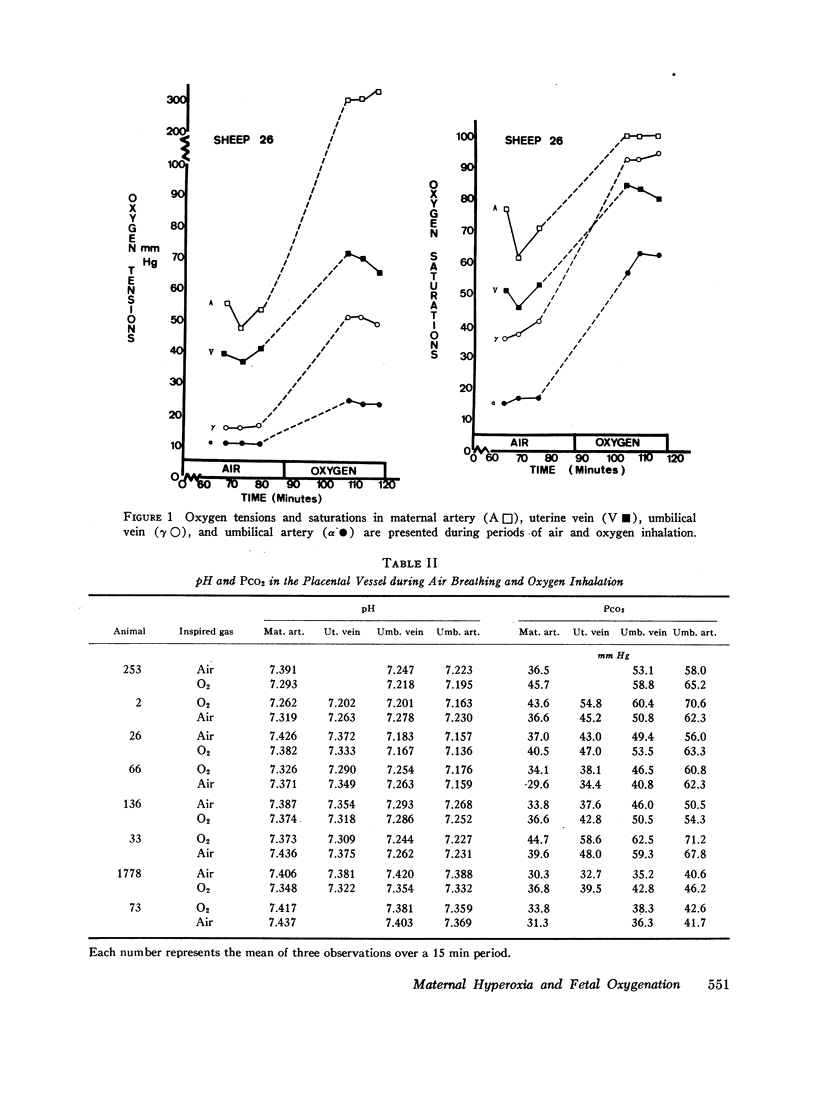
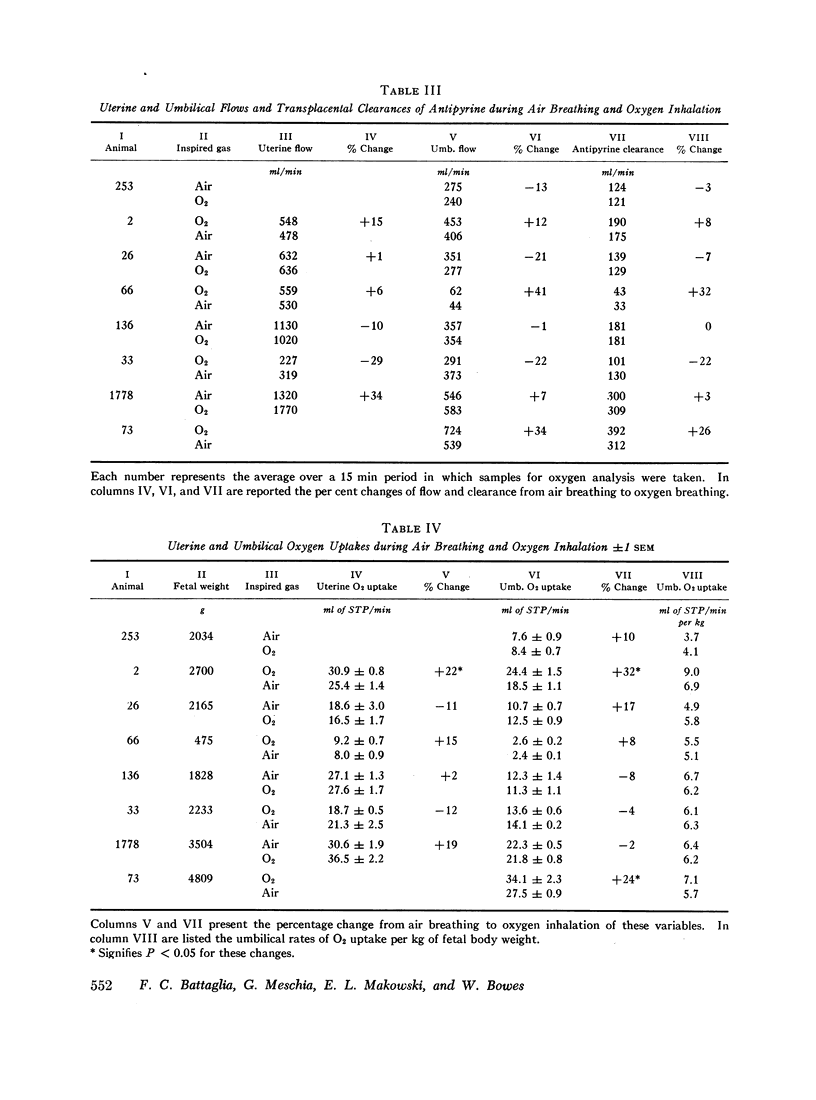
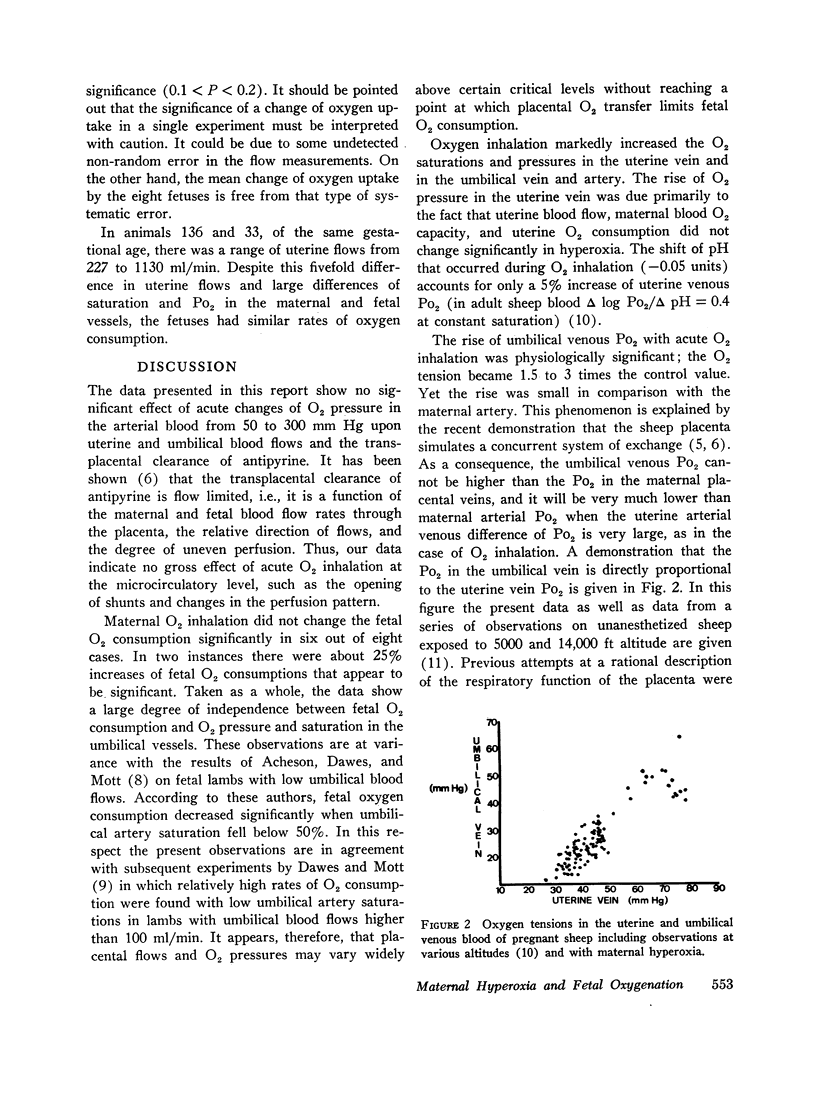
Abstract
In eight sheep, uterine and umbilical blood flows and oxygen uptakes, the transplacental flow-limited clearance of an inert molecule, pH values, and oxygen pressures, saturations, and capacities in the main placental vessels have been measured during maternal air breathing and oxygen inhalation. The mean ±SEM percentage changes during oxygen inhalation were +4.6 ±8.4 for the umbilical flow, +2.8 ±8.7 for the uterine flow, and +4.6 ±6.2 for the clearance. None of these changes are statistically significant. Oxygen uptake rose slightly in two cases and remained unchanged in the others. In all cases the oxygen pressures, saturations, and contents rose significantly in the uterine and umbilical vessels with oxygen inhalation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACHESON G. H., DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C. Oxygen consumption and the arterial oxygen saturation in foetal and new-born lambs. J Physiol. 1957 Mar 11;135(3):623–643. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C. CHANGES IN O2 DISTRIBUTION AND CONSUMPTION IN FOETAL LAMBS WITH VARIATIONS IN UMBILICAL BLOOD FLOW. J Physiol. 1964 Apr;170:524–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum T. H., Lucas W. E., DeHaven J. C., Assali N. S. The dynamics of placental oxygen transfer. I. Effects of maternal hyperoxia in pregnant ewes and fetal lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967 Jun 1;98(3):429–443. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo L. D., Power G. G., Forster R. E., 2nd Respiratory function of the placenta as determined with carbon monoxide in sheep and dogs. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):812–828. doi: 10.1172/JCI105581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METCALFE J., MOLL W., BARTELS H., HILPERT P., PARER J. T. TRANSFER OF CARBON MONOXIDE AND NITROUS OXIDE IN THE ARTIFICIALLY PERFUSED SHEEP PLACENTA. Circ Res. 1965 Feb;16:95–101. doi: 10.1161/01.res.16.2.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meschia G., Battaglia F. C., Bruns P. D. Theoretical and experimental study of transplacental diffusion. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jun;22(6):1171–1178. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.6.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAUGHTON M. A., MESCHIA G., BATTAGLIA F. C., HELLEGERS A., HAGOPLAN H., BARRON D. H. HEMOGLOBIN CHARACTERISTICS AND THE OXYGEN AFFINITY OF THE BLOODS OF DORSET SHEEP. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1963 Oct;48:313–323. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1963.sp001674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYBERG R., WESTIN B. The influence of oxygen tension and some drugs on human placental vessels. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957 Jun 8;39(2-3):216–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRYSTOWSKY H. Fetal blood studies. XI. The effect of prophylactic oxygen on the oxygen pressure gradient between the maternal and fetal bloods of the human in normal and abnormal pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1959 Sep;78:483–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivard G., Motoyama E. K., Acheson F. M., Cook C. D., Reynolds E. O. The relation between maternal and fetal oxygen tensions in sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967 Apr 1;97(7):925–930. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90518-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towell M. E. The influence of labor on the fetus and the newborn. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1966 Aug;13(3):575–598. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)31870-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


