Abstract
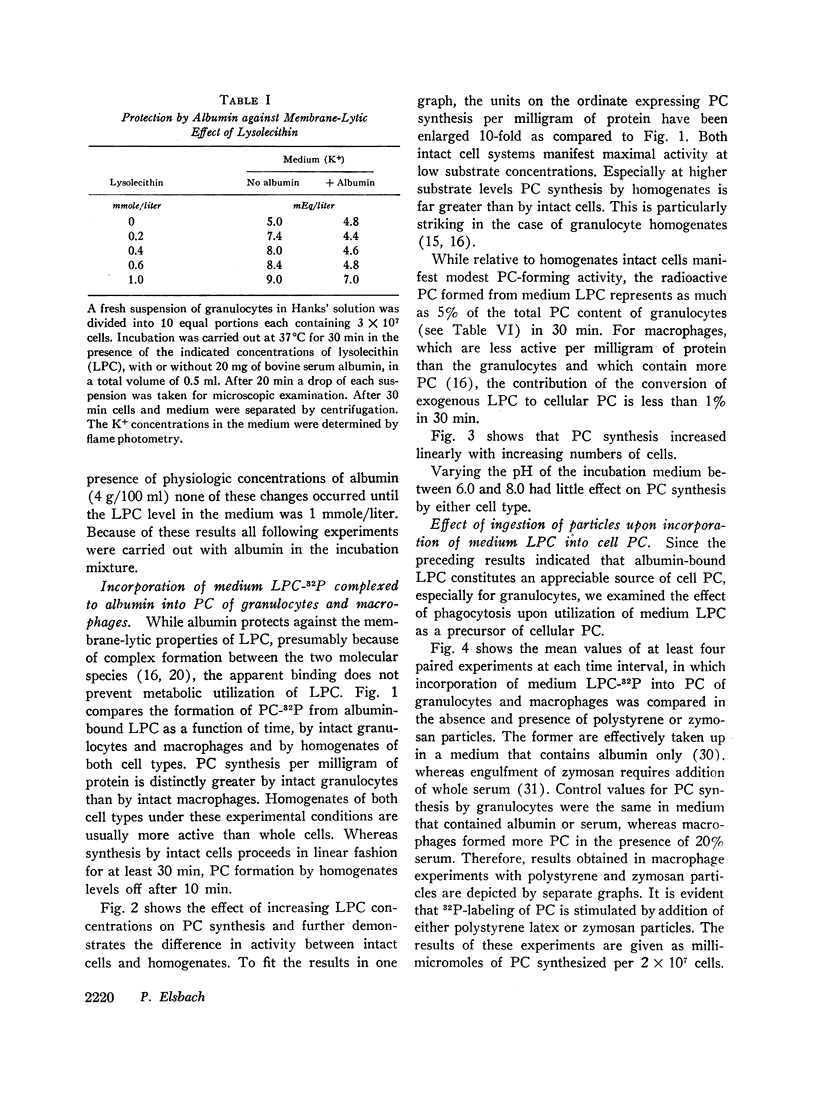
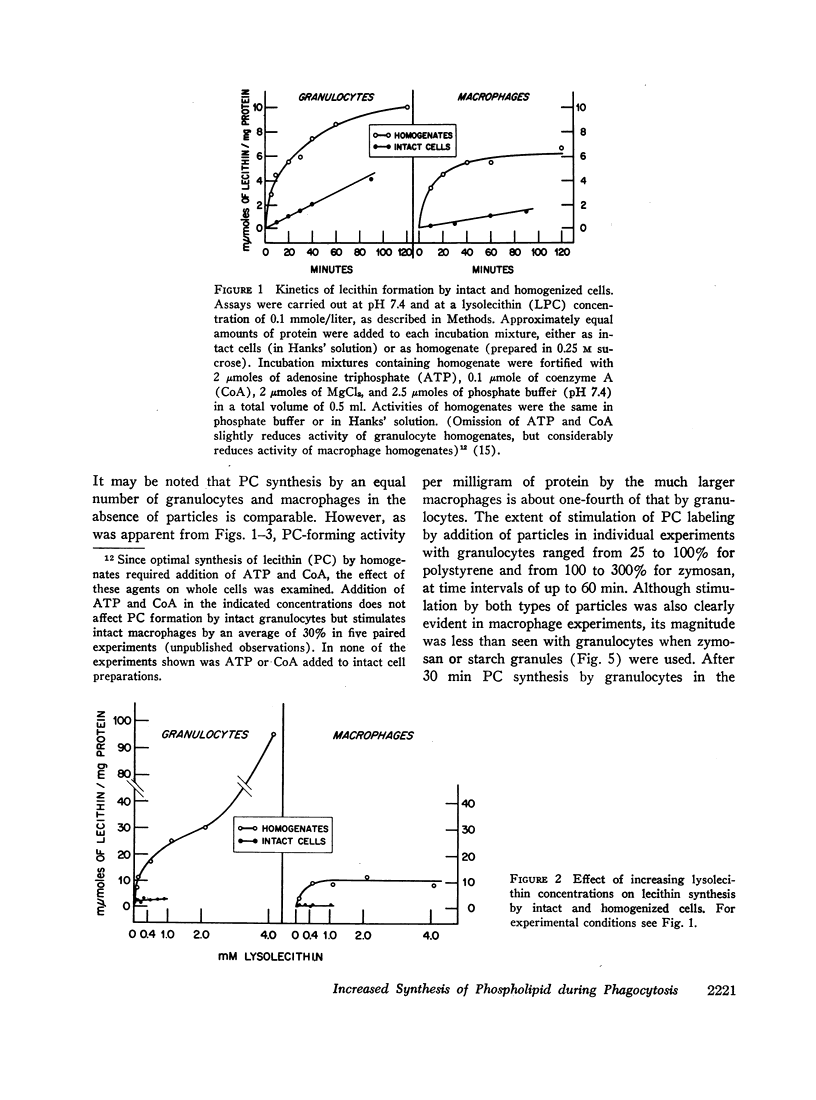
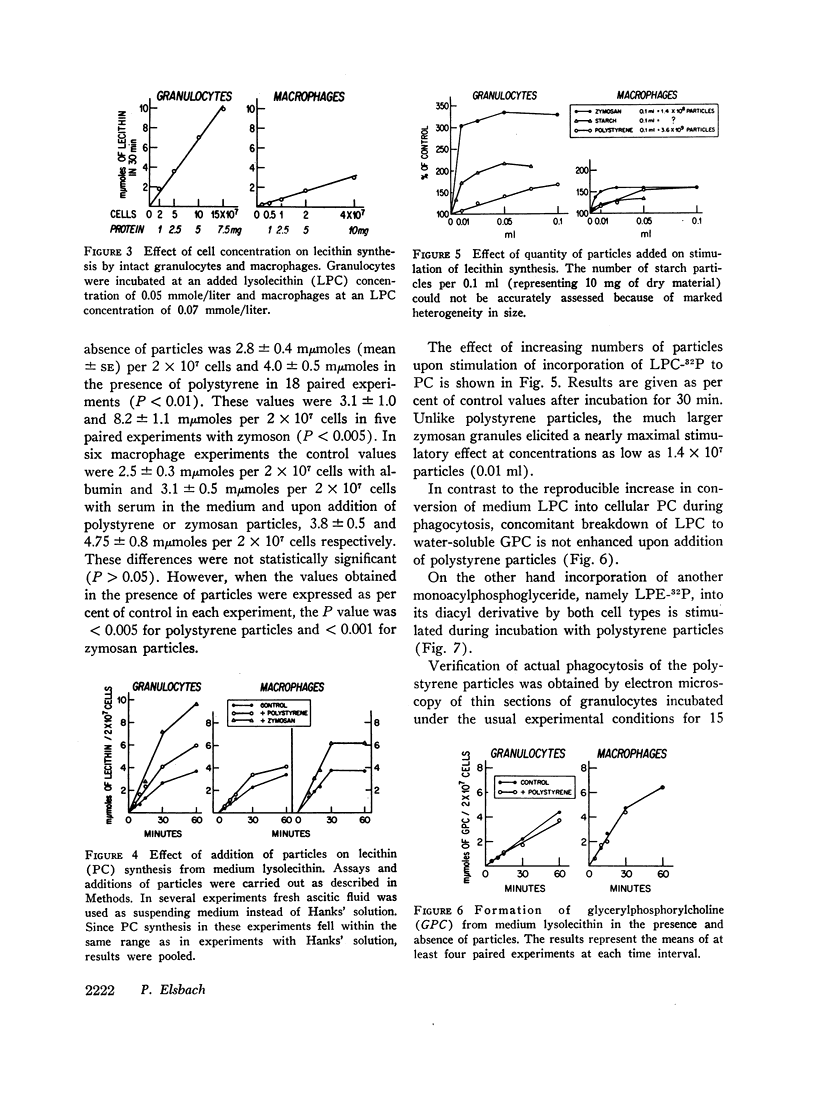
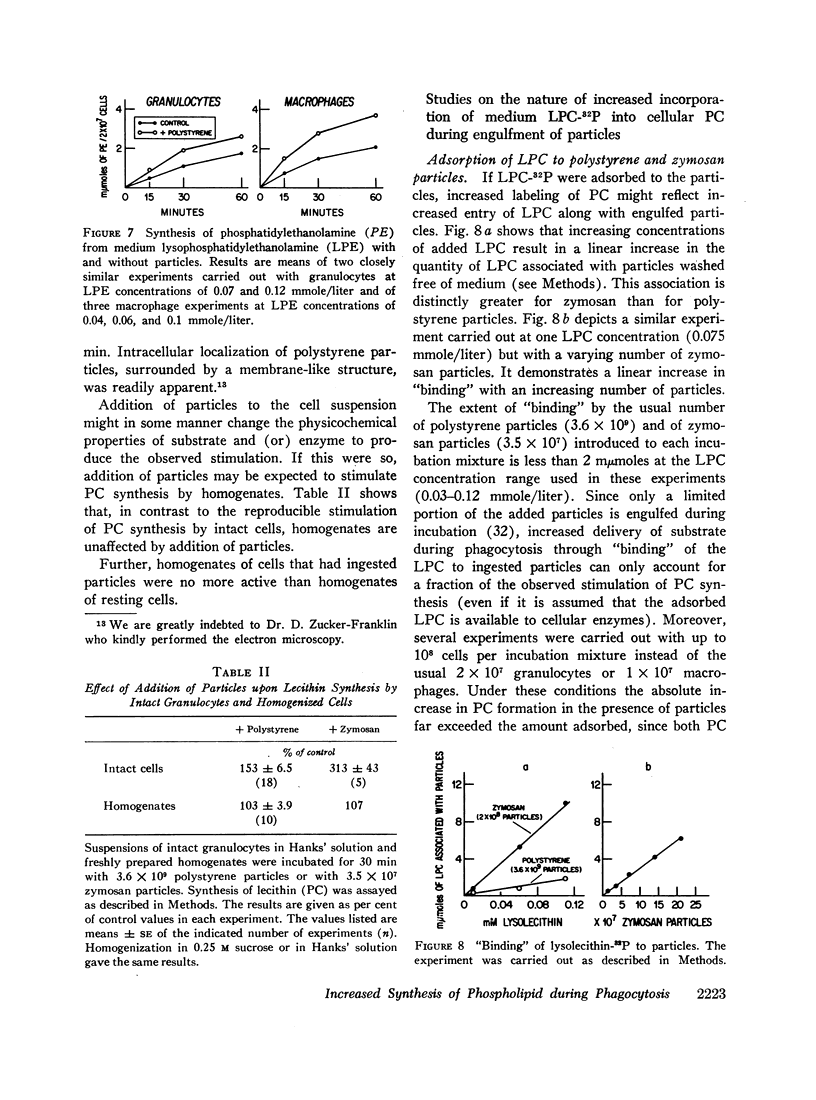
Incorporation in vitro of 32P-labeled lysolecithin (LPC) or lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) into respectively lecithin (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) of rabbit granulocytes and alveolar macrophages was compared in the absence and in the presence of ingestible particles. Maximal synthesis of PC by intact cells occurred at added LPC concentrations of less than 0.05 mmole/liter, i.e., at levels found in plasma. Accumulation of PC-32P proceeded linearly for at least 30 min and varied directly with cell concentration. While per cell granulocytes and macrophages converted comparable amounts of medium LPC to cellular PC, per milligram of protein, the granulocytes were approximately four times more active than the much larger macrophages. After 30 min newly synthesized PC-32P represented as much as 5% of total granulocyte PC. For macrophages this fraction did not exceed 1%. Addition of polystyrene or zymosan particles to the cell suspension resulted in up to 3-fold stimulation of incorporation of LPC-32P or LPE-32P into their respective diacyl derivatives. This stimulation did not occur when the cells were homogenized. Breakdown of LPC to water-soluble products during phagocytosis of polystyrene particles was the same as at rest. By use of doubly labeled LPC, the mechanism of PC synthesis by the two cell types has been identified as direct acylation of medium LPC, both at rest and during engulfment. Evidence presented in the case of granulocytes suggests that the increased translocation of medium LPC-32P during phagocytosis and its conversion to PC represents net synthesis.
The findings indicate that LPC, a normal constituent of plasma, can serve as substrate in PC synthesis by phagocytic cells. This mechanism of PC synthesis can account for appreciable addition of membrane PC, especially by granulocytes. It is proposed that stimulation of this pathway provides building blocks for increased membrane formation during phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., WIENER E. THE PARTICULATE HYDROLASES OF MACROPHAGES. I. COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY, ISOLATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Exp Med. 1963 Dec 1;118:991–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBACH P. Composition and synthesis of lipids in resting and phagocytizing leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1959 Dec 1;110:969–980. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.6.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSBACH P. COMPARISON OF UPTAKE OF PALMITIC, STEARIC, OLEIC AND LINOLEIC ACID BY POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 24;84:8–17. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSBACH P., RIZACK M. A. ACID LIPASE AND PHOSPHOLIPASE ACTIVITY IN HOMOGENATES OF RABBIT POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES. Am J Physiol. 1963 Dec;205:1154–1158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.6.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSBACH P., SCHWARTZ I. L. Studies on the sodium and potassium transport in rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1959 May 20;42(5):883–898. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Stein Y., Stein O. The role of lysolecithin in phospholipid metabolism of human umbilical and dog carotid arteries. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P. Metabolism of lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine and lysophosphatidyl choline by homogenates of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes and alveolar macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P. Phospholipid metabolism by phagocytic cells. I. A comparison of conversion of [32P]lysolecithin to lecithin and glycerylphosphorylcholine by homogenates of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes and alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):510–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., van den Berg J. W., van den Bosch H., van Deenen L. L. Metabolism of phospholipids by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):338–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbland J. F., Marinetti G. V. The enzymatic acylation and hydrolysis of lysolecithin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 7;106(1):128–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbland J. F., Marinetti G. V. The metabolism of lysolecithin in rat-liver particulate systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 7;106(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOMSET J. A. The mechanism of the plasma cholesterol esterification reaction: plasma fatty acid transferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 19;65:128–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., COHN Z. A. Degranulation of polymorphonuclear leucocytes following phagocytosis of microorganisms. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1005–1014. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. L., WALLACH D. F. The metabolic basis of phagocytosis. III. Incorporation of inorganic phosphate into various classes of phosphatides during phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:1895–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDS W. E. Metabolism of glycerolipids. 2. The enzymatic acylation of lysolecithin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2233–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q. N., LEAKE E. S., OSHIMA S. A study of macrophages and epitheloid-like cells from granulomatous (BCG-induced) lungs of rabbits. J Immunol. 1962 Nov;89:745–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Lastra R. Fatty acid biosynthesis in human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1596–1602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra U. K. Isolation of lysophosphatidylethanolamine from human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder E., van Deenen L. L. Metabolism of red-cell lipids. 3. Pathways for phospholipid renewal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):348–356. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder E., van den Berg J. W., van Deenen L. L. Metabolism of red-cell lipids. II. Conversions of lysophosphoglycerides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 7;106(1):118–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munder P. G., Ferber E., Fischer H. Untersuchungen uber die Abhangigkeit der cytolytischen Wirkung des Lysolecithins von Membranenzymen. Z Naturforsch B. 1965 Nov;20(11):1048–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVEIRA M. M., VAUGHAN M. INCORPORATION OF FATTY ACIDS INTO PHOSPHOLIPIDS OF ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES. J Lipid Res. 1964 Apr;5:156–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OREN R., FARNHAM A. E., SAITO K., MILOFSKY E., KARNOVSKY M. L. Metabolic patterns in three types of phagocytizing cells. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jun;17:487–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. B. THE ISOLATION OF LYSOLECITHIN FROM HUMAN SERUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jul 15;43(7):566–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.7.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS J., QUASTEL J. H. PARTICLE UPTAKE BY POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUCOCYTES AND EHRLICH ASCITES-CARCINOMA CELLS. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:150–156. doi: 10.1042/bj0890150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. 2. Incorporation of C14-labeled building blocks into lipid, protein, and glycogen of leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2224–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN Y., STEIN O., SHAPIRO B. Enzymic pathways of glyceride and phospholipid synthesis in aortic homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 19;70:33–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90716-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. S., Hokin L. E. Studies on the role of phospholipids in phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3354–3361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Stein Y., Stein O. Incorporation of dietary lecithin and lysolecithin into lymph chylomicrons in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4919–4924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Stein Y. Utilization of lysolecithin by Landschütz ascites tumor in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein Y., Stein O. Metabolism of labeled lysolecithin, lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine and lecithin in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 1;116(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer S., Eder H. A. Transport of lysolecithin by albumin in human and rat plasma. J Lipid Res. 1965 Oct;6(4):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster G. R. The acylation of lysophosphatides with long-chain fatty acids by rat brain and other tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 1;98(3):512–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKER-FRANKLIN D., HIRSCH J. G. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON THE DEGRANULATION OF RABBIT PERITONEAL LEUKOCYTES DURING PHAGOCYTOSIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:569–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


