Abstract
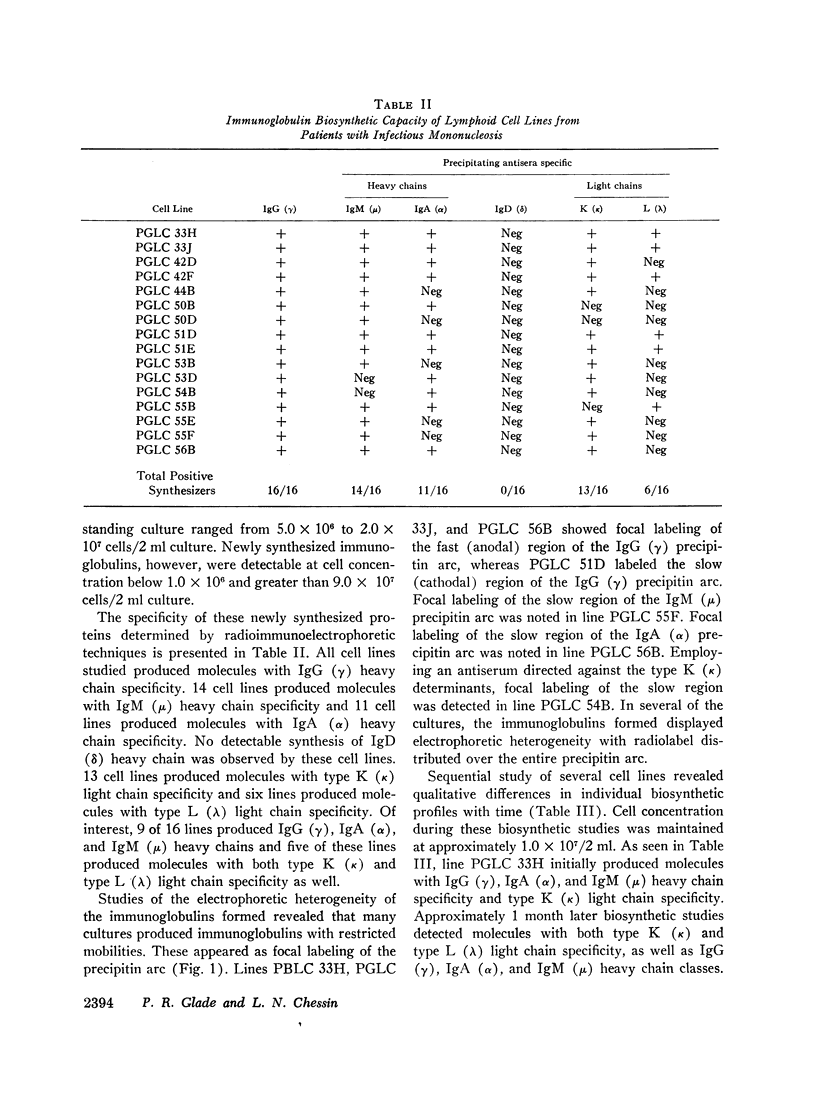
Immunoglobulin synthesis by 16 long-term suspension cultures of mononuclear cells derived from peripheral blood of nine patients with heterophile-positive infectious mononucleosis (IM) has been demonstrated by radioimmunoelectrophoretic techniques. All cell lines synthesized molecules with IgG (γ) heavy chain specificity. 14 cell lines produced molecules with IgM (μ) heavy chain specificity and 11 cell lines produced molecules with IgA (α) heavy chain specificity. No detectable synthesis of molecules with IgD (δ) heavy chain specificity was observed by these cell lines derived from peripheral blood of patients with IM. 13 cell lines produced molecules with type K (κ) light chain specificity and 6 cell lines produced molecules with type L (λ) light chain specificity. Of interest, 9 of 16 lines produced IgG (γ), IgA (α), and IgM (μ) heavy chain molecules and 5 of these cell lines produced molecules with type K (κ) and type L (λ) light chain specificity as well.
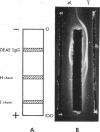
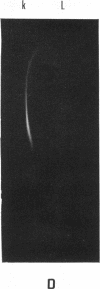
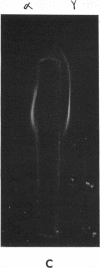
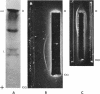
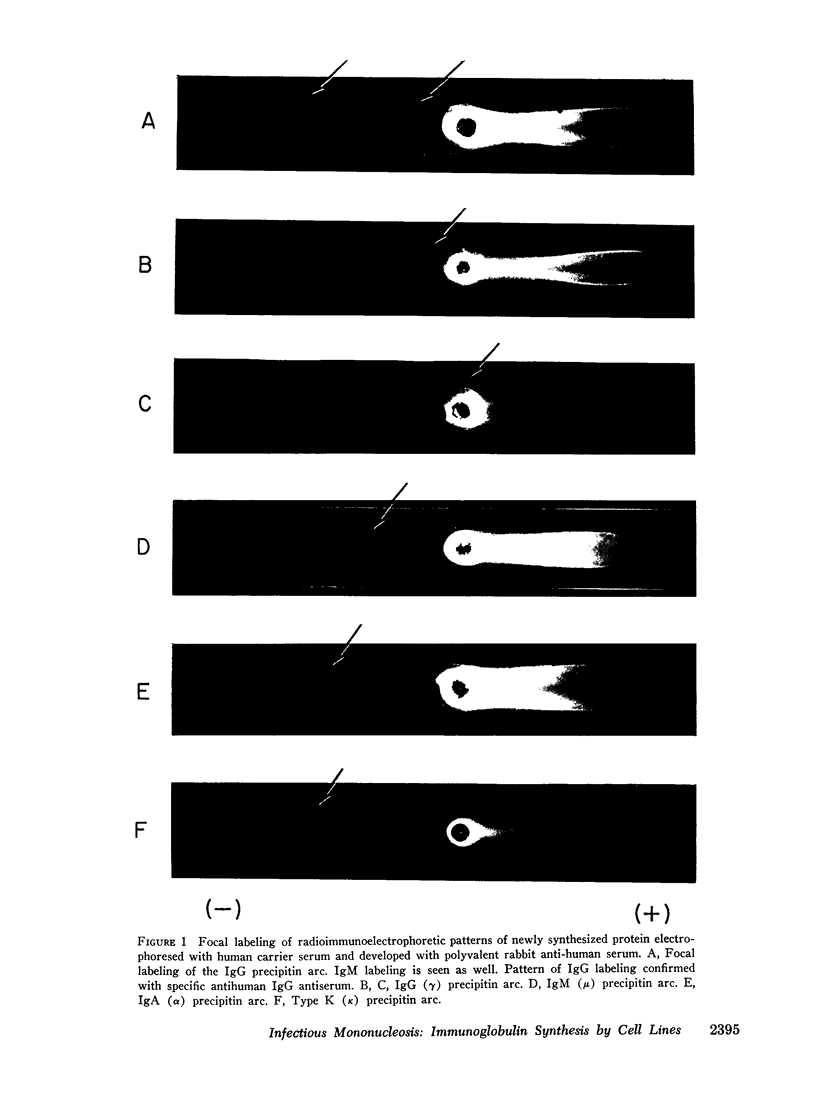
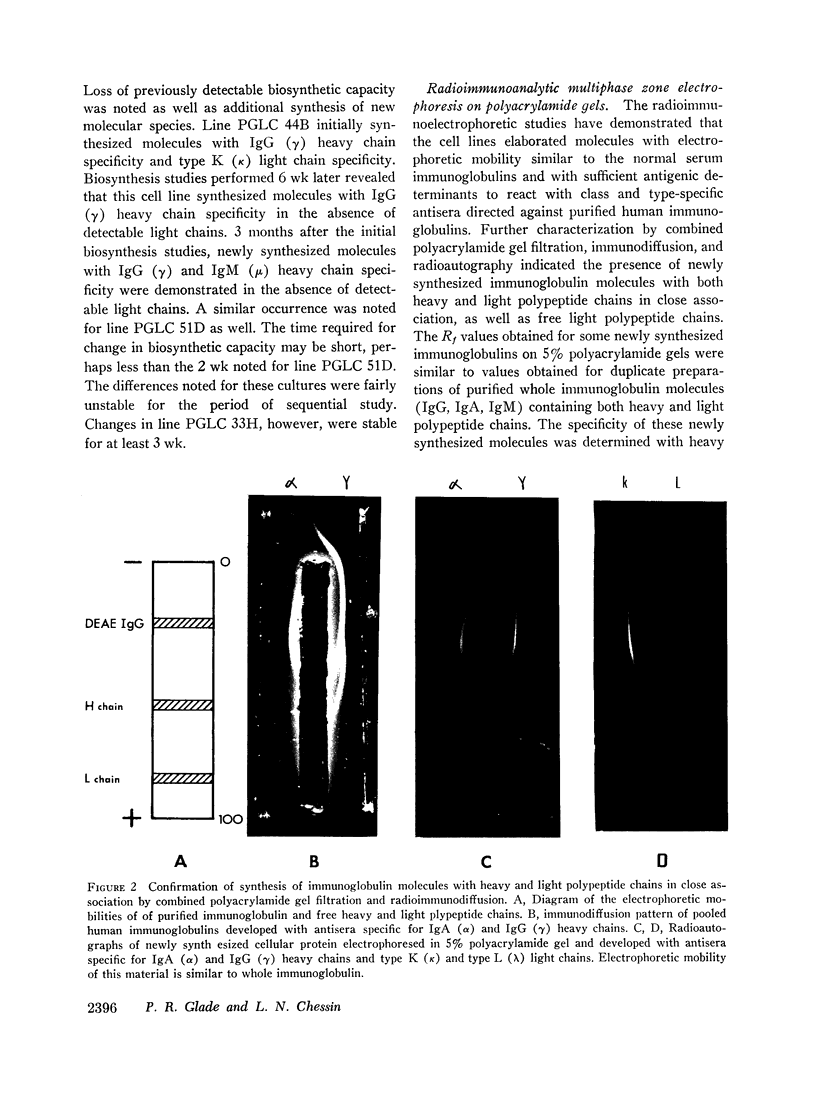
Further characterization by combined polyacrylamide gel filtration, immunodiffusion, and radioautography indicated the presence of newly synthesized immunoglobulin molecules with both heavy and light polypeptide chains in close association as well as free light polypeptide chain synthesis. Investigation of the localization of immunoglobulin in single cells by immunofluorescent techniques revealed that 5-22% of cells in these lines were strongly reactive with a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated rabbit antisera directed against the antigenic determinants of human IgG and cross-reactive with the determinants common to IgA and IgM. No heterophile antibody, heteroagglutinin, or hemolytic antibody could be demonstrated in these cell lines derived from peripheral blood of patients with heterophile-positive infectious mononucleosis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATTARDI G., COHN M., HORIBATA K., LENNOX E. S. ANTIBODY FORMATION BY RABBIT LYMPH NODE CELLS. II. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE BEHAVIOR OF SINGLE ANTIBODY-PRODUCING CELLS WITH RESPECT TO THEIR SYNTHETIC CAPACITY AND MORPHOLOGY. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:346–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. L. Antibody formation in infectious mononucleosis. II. Other 19S antibodies and false-positive serology. Br J Haematol. 1966 May;12(3):268–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb05633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. L. Review of some recent observations on 'glandular fever cells'. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Sep;19(5):448–455. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Borjeson J., Chessin L. N. Studies on human lymphocytes in vitro. IV. Comparative fine structural features of the established Burkitt lymphoma cell lines AL-1, EB-2 and phytomitogen-transformed lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):340–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN L. B., BRECHER G. DNA AND RNA SYNTHESIS OF CIRCULATING ATYPICAL LYMPHOCYTES IN INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS. Blood. 1965 Feb;25:197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCLAUGHLIN C. PREPARATION OF ANTISERA SPECIFIC FOR 6.6 S GAMMA-GLOBULINS, BETA 2A-GLOBULINS, GAMMA-1.-MACROGLOBULINS, AND FOR TYPE I AND II COMMON GAMMA-GLOBULIN DETERMINANTS. J Immunol. 1963 Oct;91:484–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L. TWO TYPES OF 6.6 S GAMMA-GLOBULINS, BETA-2A-GLOBULINS AND 18 S GAMMA 1-MACROGLOBULINS IN NORMAL SERUM AND GAMMA-MICROGLOBULINS IN NORMAL URINE. J Immunol. 1963 Oct;91:438–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN J. D. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF IMMUNOLOGIC PROCESSES. Adv Immunol. 1964;27:175–248. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Finegold I., Rabson A. S., Manaker R. A. Immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro by established human cell lines. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1259–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold I., Fahey J. L., Granger H. Synthesis of immunoglobulins by human cell lines in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):839–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALBRAITH P., MITUS W. J., GOLLERKERI M., DAMESHEK W. THE "INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS CELL". A CYTOCHEMICAL STUDY. Blood. 1963 Nov;22:630–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG G. M. A study of malignant lymphomas and leukemias. V. Lymphogenous leukemia and infectious mononucleosis: the lymphatics in benign and malignant lymphoproliferative diseases. Cancer. 1962 Sep-Oct;15:869–881. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196209/10)15:5<869::aid-cncr2820150502>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Monroe J. H. Studies on leukocytes growing in continuous culture derived from normal human donors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Apr;40(4):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. P. Antibody synthesis in vitro by human peripheral lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1967;32(3):294–307. doi: 10.1159/000229940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glade P. R., Kasel J. A., Moses H. L., Whang-Peng J., Hoffman P. F., Kammermeyer J. K., Chessin L. N. Infectious mononucleosis: continuous suspension culture of peripheral blood leucocytes. Nature. 1968 Feb 10;217(5128):564–565. doi: 10.1038/217564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND R. J. Diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. Blood. 1960 Jul;16:1045–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Grace J. T., Jr Cloning of immunoglobulin-producing human leukemic and lymphoma cells in long-term cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):107–111. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulliger L., Sorkin E. Formation of specific antibody by circulating cells. Immunology. 1965 Oct;9(4):391–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamei H., Moore G. E. Production of phage-neutralizing activity in vitro by cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. Nature. 1967 Aug 19;215(5103):860–861. doi: 10.1038/215860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., SANDERSON R. P., BERNSTEIN M. T., JACKSON A. L. ANTIBODY PRODUCTION BY LEUCOCYTES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD. Nature. 1964 Dec 26;204:1320–1321. doi: 10.1038/2041320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITWINS J., LEIBOWITZ S. Abnormal lymphocytes (virocytes) in virus diseases other than infectious mononucleosis. Acta Haematol. 1951 Apr;5(4):223–231. doi: 10.1159/000203827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAELIDES M. C., COONS A. H. Studies on antibody production. V. The secondary response in vitro. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:1035–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of normal mouse spleen cell suspensions in vitro. Science. 1966 Aug 26;153(3739):1004–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3739.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Gerner R. E., Franklin H. A. Culture of normal human leukocytes. JAMA. 1967 Feb 20;199(8):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOSSAL G. J., SZENBERG A., ADA G. L., AUSTIN C. M. SINGLE CELL STUDIES ON 19S ANTIBODY PRODUCTION. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:485–502. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Small P. A., Jr Electrophoretic heterogeneity of polypeptide chains of specific antibodies. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki N., Yagi Y., Moore G. E., Pressman D. Immunoglobulin production in human leukemia cell lines. J Immunol. 1966 Nov;97(5):634–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T. W., Uhr J. W. Primary-type antibody response in vitro. Science. 1966 Mar 4;151(3714):1096–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3714.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield J. D., Thorbecke G. J., Old L. J., Boyse E. A. Production of immunoglobulins and their subunits by human tissue culture cell lines. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):308–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A., Williams R. C., Jr Studies on the macroglobulins of human serum. I. Polyclonal immunoglobulin class M (IgM) increase in infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jan 13;274(2):61–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196601132740202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood B. T., Thompson S. H., Goldstein G. Fluorescent antibody staining. 3. Preparation of fluorescein-isothiocyanate-labeled antibodies. J Immunol. 1965 Aug;95(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. A., Frenkel E. P. The atypical lymphocyte. Am J Med. 1967 Jun;42(6):923–936. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The formation of immunoglobulins by human tissues in vitro. IV. Circulating lymphocytes in normal and pathological conditions. Immunology. 1966 Jul;11(1):29–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]