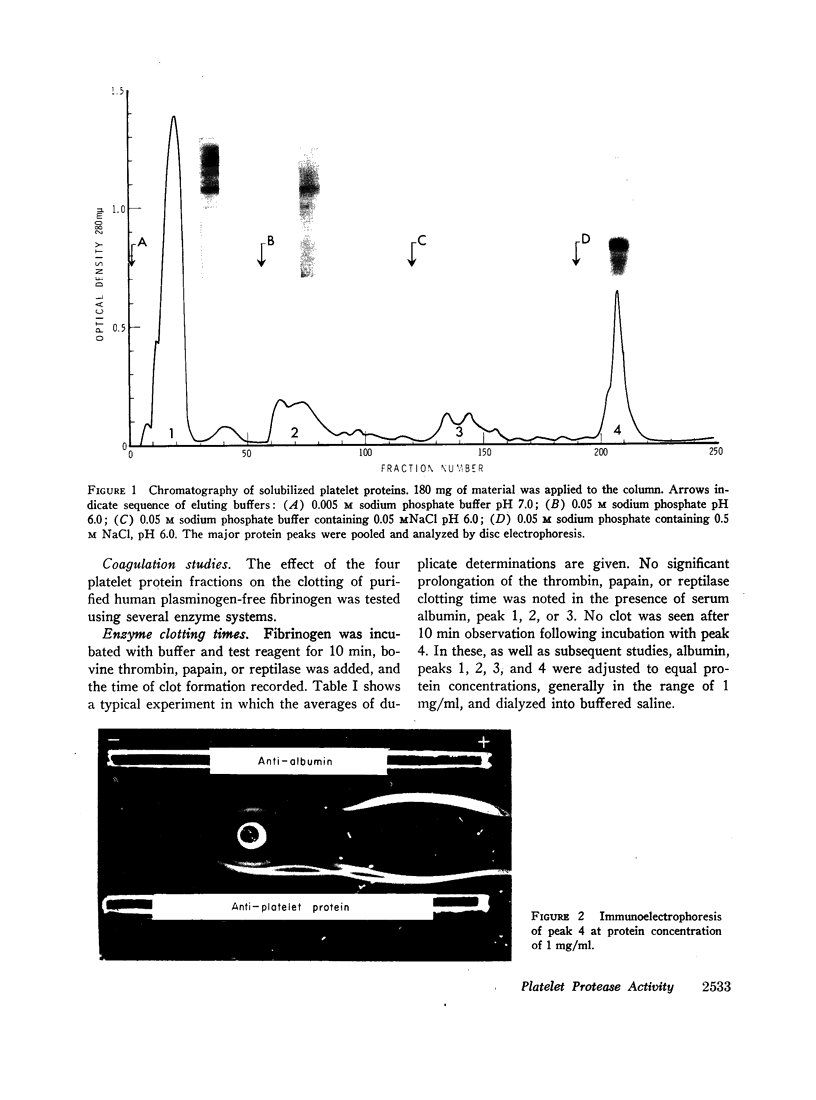
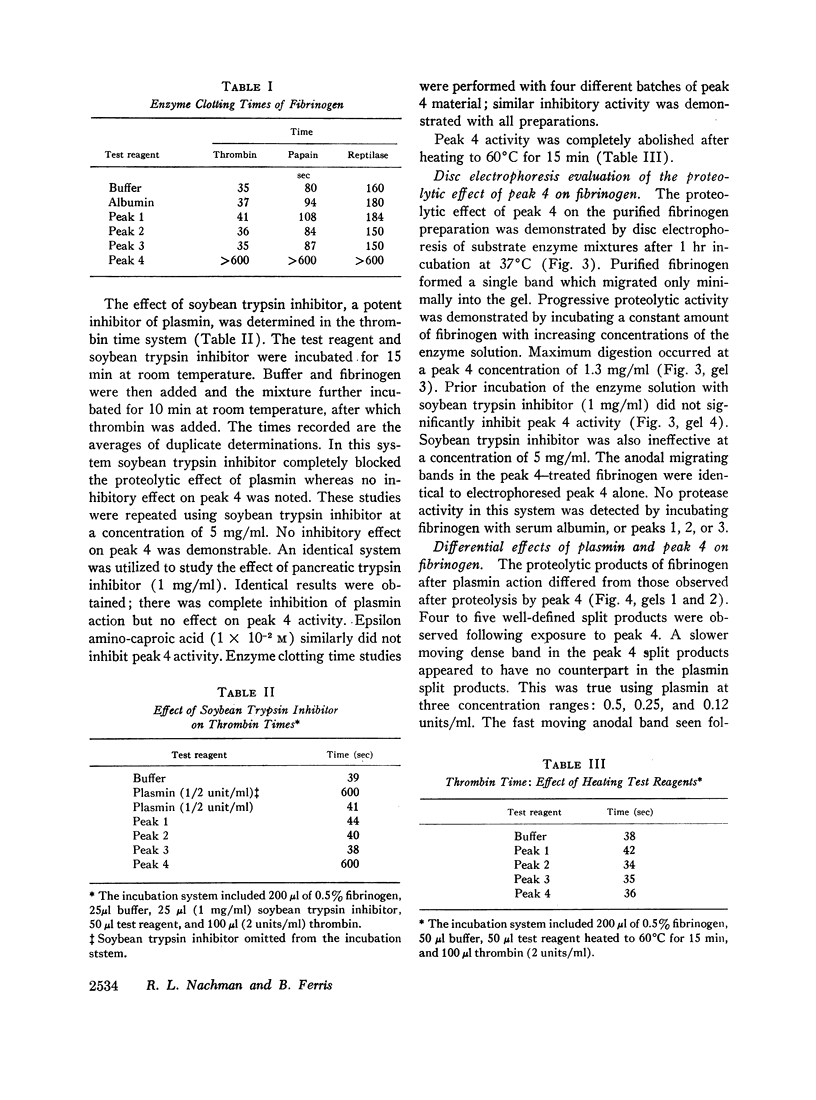
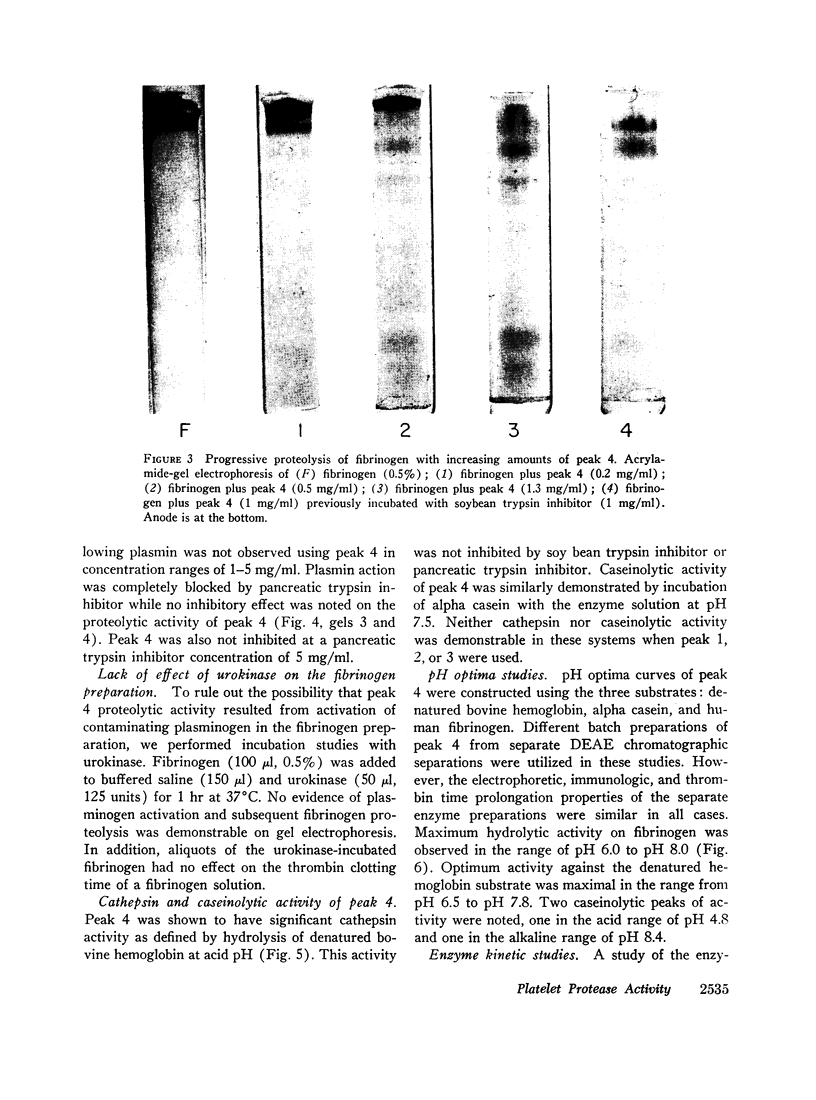
Abstract
Solubilized protein derived from human platelets was fractionated by DEAE cellulose column chromatography and analyzed for protease activity using three substrates: denatured bovine hemoglobin, alpha casein, and purified plasminogen-free human fibrinogen. A protein fraction was found with proteolytic activity which was heat labile and not attributable to plasmin. The activity was not potentiated by cysteine or inhibited by iodoacetamide. Studies of pH optima indicated a broad range of enzyme activity with peaks in both the acid and alkaline region. Cathepsin A activity was detected in the platelet protease fraction by hydrolysis of the synthetic substrate N-carbobenzoxy-α-L-glutamyl-L-tyrosine. Similar proteolytic activity was found when the proteins derived from isolated platelet granules were examined. The results indicate that human platelets possess potent intracellular proteolytic enzymes. The relationship of this proteolytic activity to the hemostatic process is discussed.
Full text
PDF


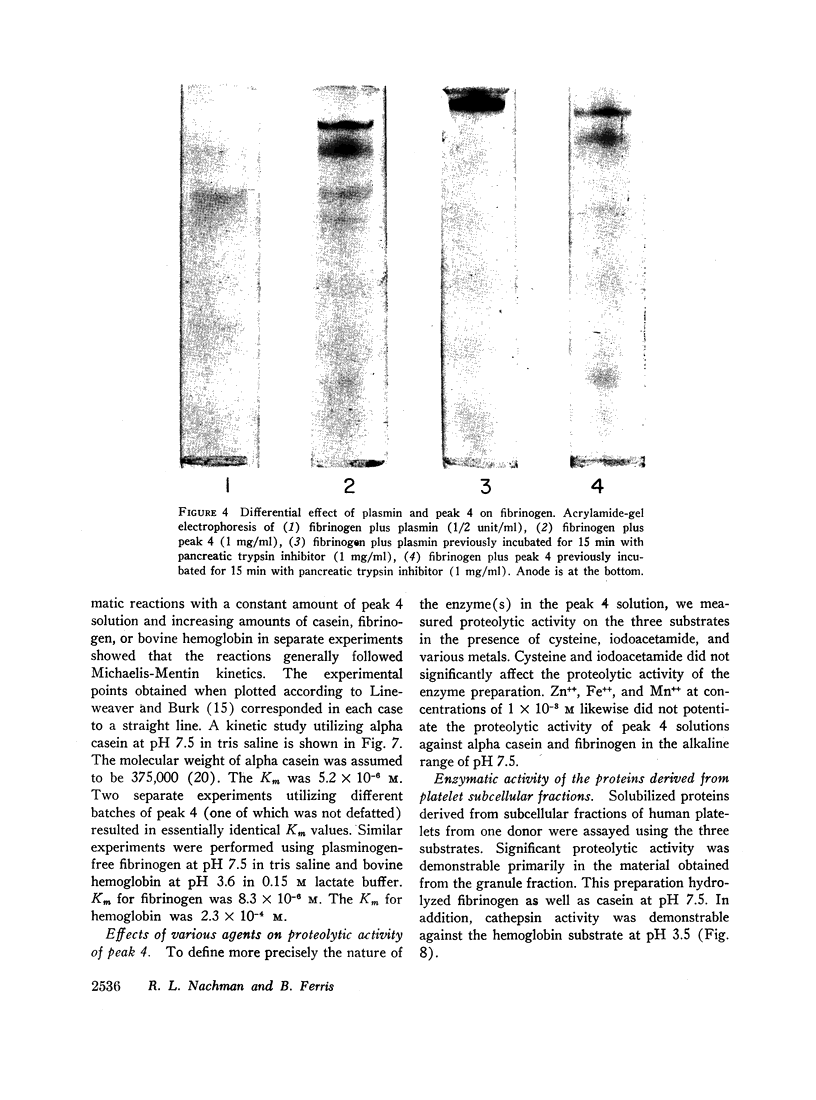
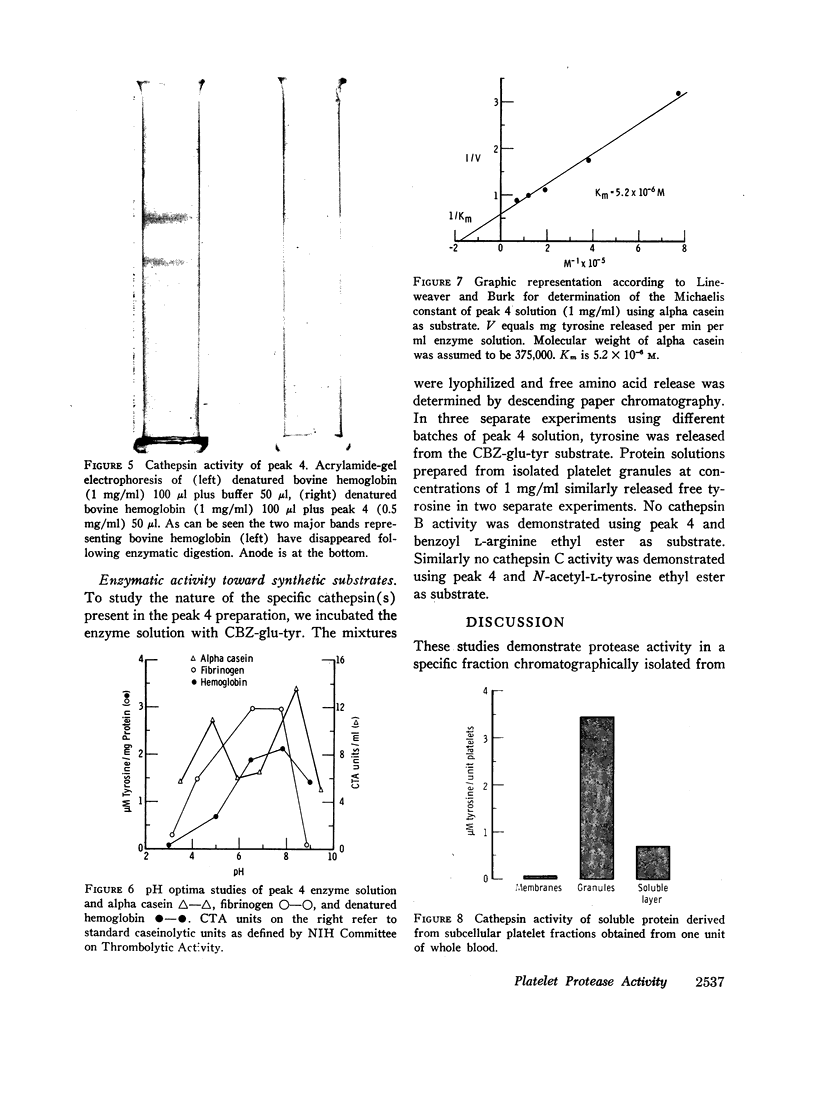



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. An inhibitor of liver alcohol dehydrogenase in preparations of reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide. Nature. 1961 Sep 9;191:1098–1099. doi: 10.1038/1911098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., COHN Z. A. Degranulation of polymorphonuclear leucocytes following phagocytosis of microorganisms. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1005–1014. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLEMANS R., GROSS R. Fibrinolytic activities present in human blood platelets. Nature. 1961 Jan 21;189:238–239. doi: 10.1038/189238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNGOLD L. The distribution and immunochemical properties of human tissue and tumor antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Dec 16;69(4):681–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb49709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPRESLE C., WEBB T. The purification and properties of a proteolytic enzyme, rabbit cathepsin E, and further studies on rabbit cathepsin D. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj0840455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. L., NEURATH H. Proteolytic enzymes of the formed elements of human blood. I. Erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L. Studies on human platelet granules and membranes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):14–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI105318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHMAN R. L. IMMUNOLOGIC STUDIES OF PLATELET PROTEIN. Blood. 1965 May;25:703–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Safier L. B. Platelet thrombosthenin: subcellular localization and function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1380–1389. doi: 10.1172/JCI105630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D. Immunologic studies of proteins associated with subcellular fractions of normal human platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):651–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L. Thrombasthenia: immunologic evidence of a platelet protein abnormality. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Mar;67(3):411–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESS E. M., PORTER R. R., CEBRA J. The isolation and properties of a proteolytic enzyme, cathepsin D, from bovine spleen. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:501–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0740501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman N. F., Mason R. G. Platelet-platelet interaction: relationship to hemostasis and thrombosis. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLAN H. H., JONES M. E., FRUTON J. S. On the proteolytic enzymes of animal tissues. X. Beef spleen cathepsin C. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):793–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasi S., Murray R. K., Macmorine D. R., Movat H. Z. The role of PMN-leucocyte lysosomes in tissue injury, inflammation and hypersensitivity. II. Studies on the proteolytic activity of PMN-leucocyte lysosomes of the rabbit. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Aug;47(4):411–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]