Abstract
Total nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (ILA) of human plasma (measured by the adipose tissue assay) results from the additive effects of at least two distinct components. They differ in molecular size, solubility in acid-ethanol, and in thermostability. More than 90% of nonsuppressible ILA of human plasma is insoluble in acid-ethanol. Its molecular size of 100,000-150,000 remains unchanged by treatment with acid-ethanol, 5 M acetic acid-0.15 M NaCl, urea, and EDTA. It is inactivated by heat.
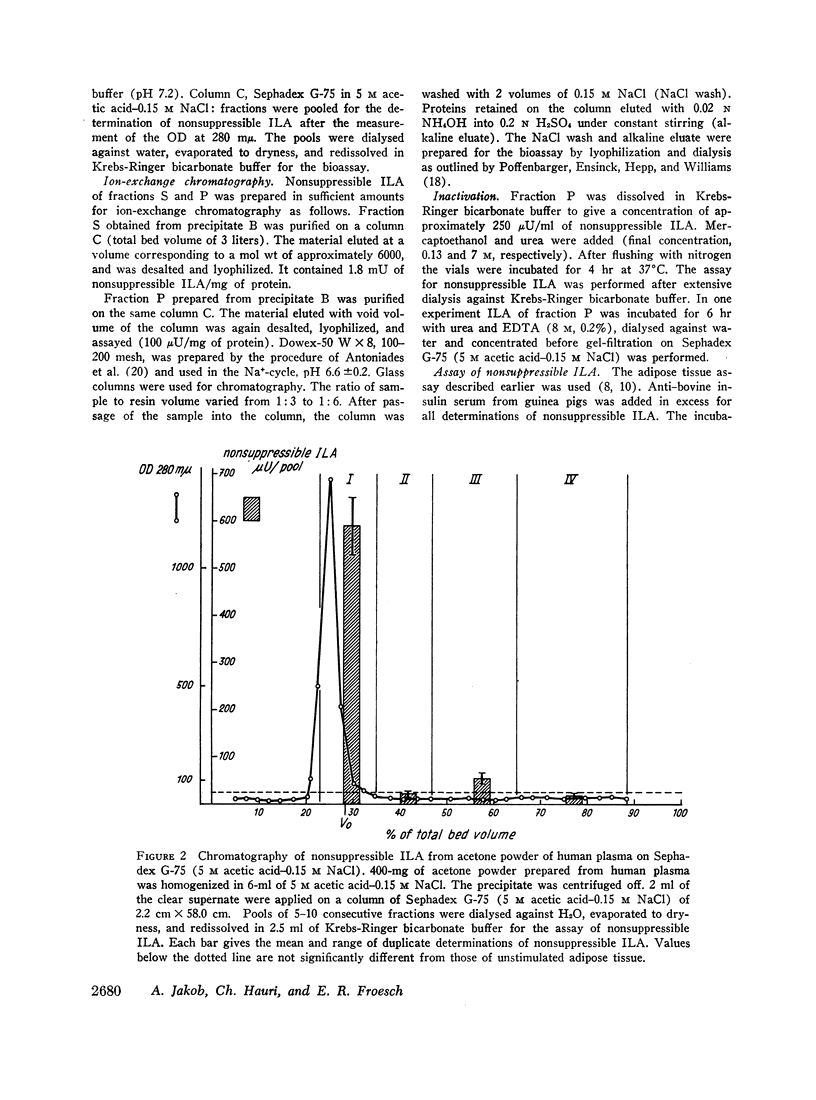
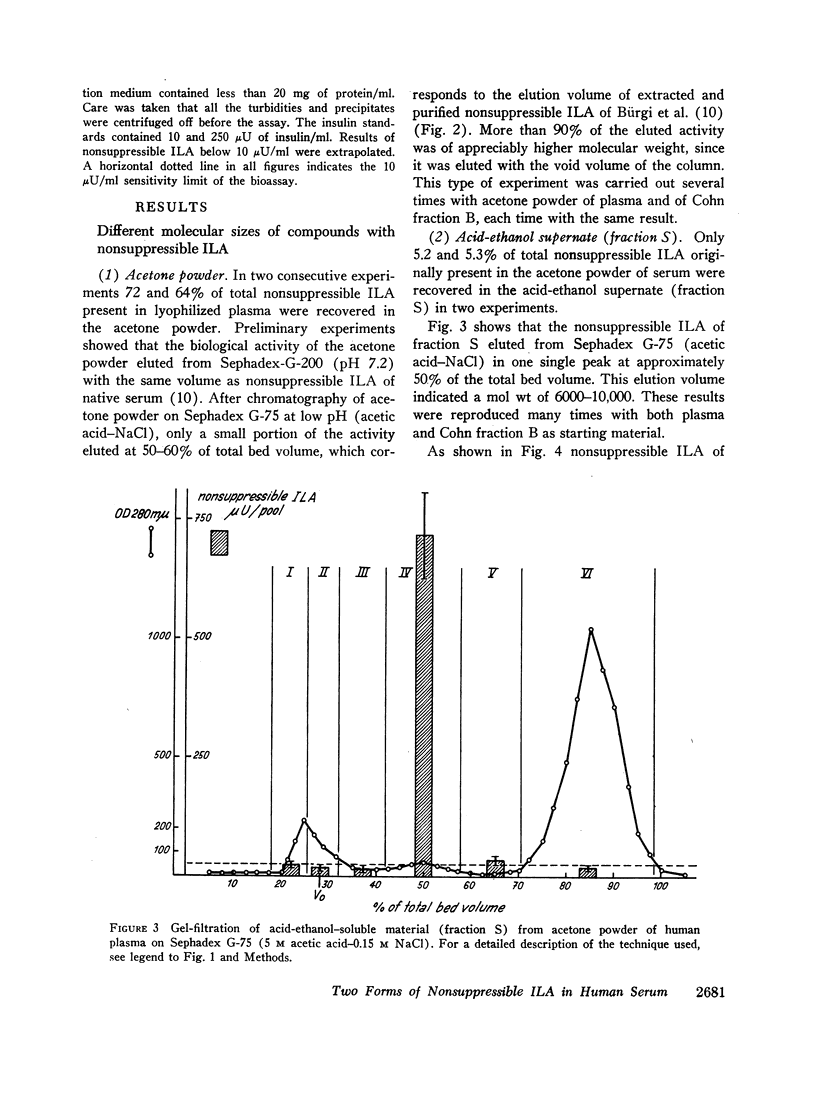
Approximately 5% of total nonsuppressible serum ILA is soluble in acid-ethanol. The molecular weight is 6000-10,000 after partial purification on Sepadex G-75 (acetic acid-NaCl). This molecule is thermostabile for 3 hr at 80°C.
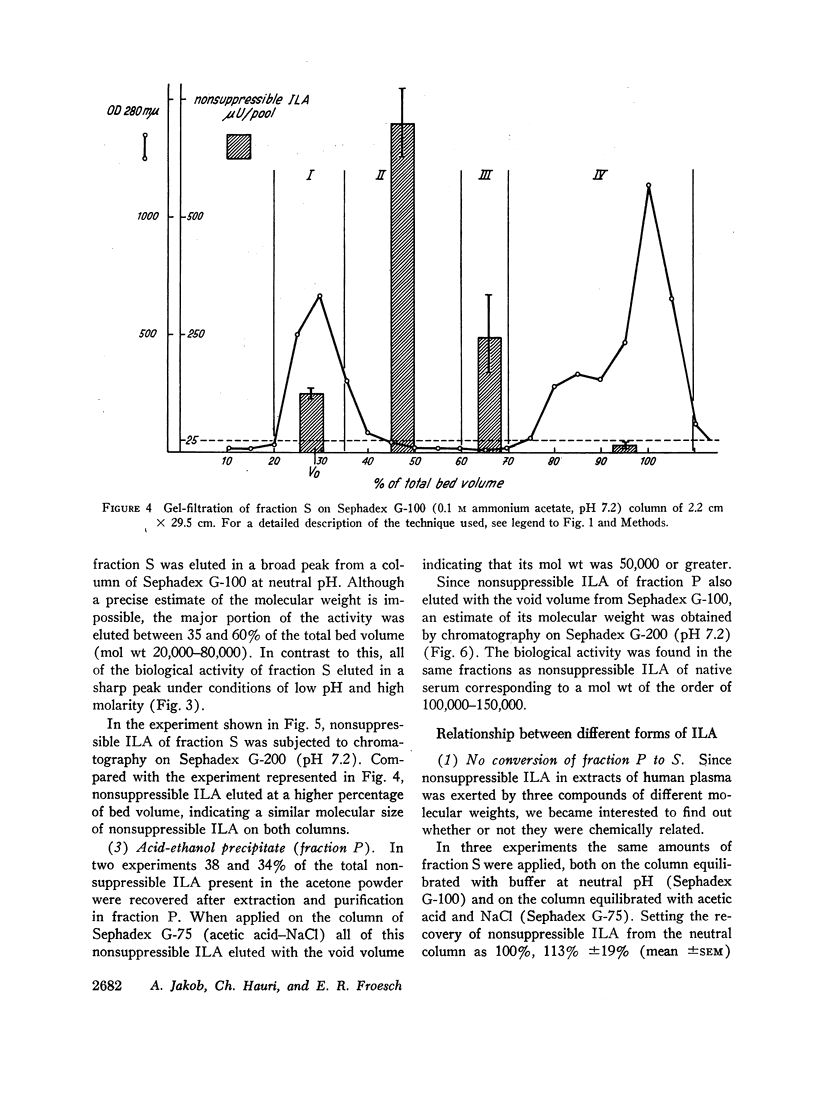
When the acid-ethanol soluble molecule with nonsuppressible ILA is chromatographed on Sephadex G-100 at neutral pH, it is eluted in a broad peak corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 50,000-70,000. When rechromatographed on Sephadex G-75 (acetic acid-NaCl) its mol wt is irreversibly converted from 70,000 to 6000.
Most of the insulin-like activity retained on Dowex-50 (“bound insulin”) is eluted off Sephadex G-75 (acetic acid-NaCl) at the same column volume as the small molecular weight nonsuppressible ILA. The latter molecule is retained on Dowex-50, whereas big molecular weight nonsuppressible ILA is not.
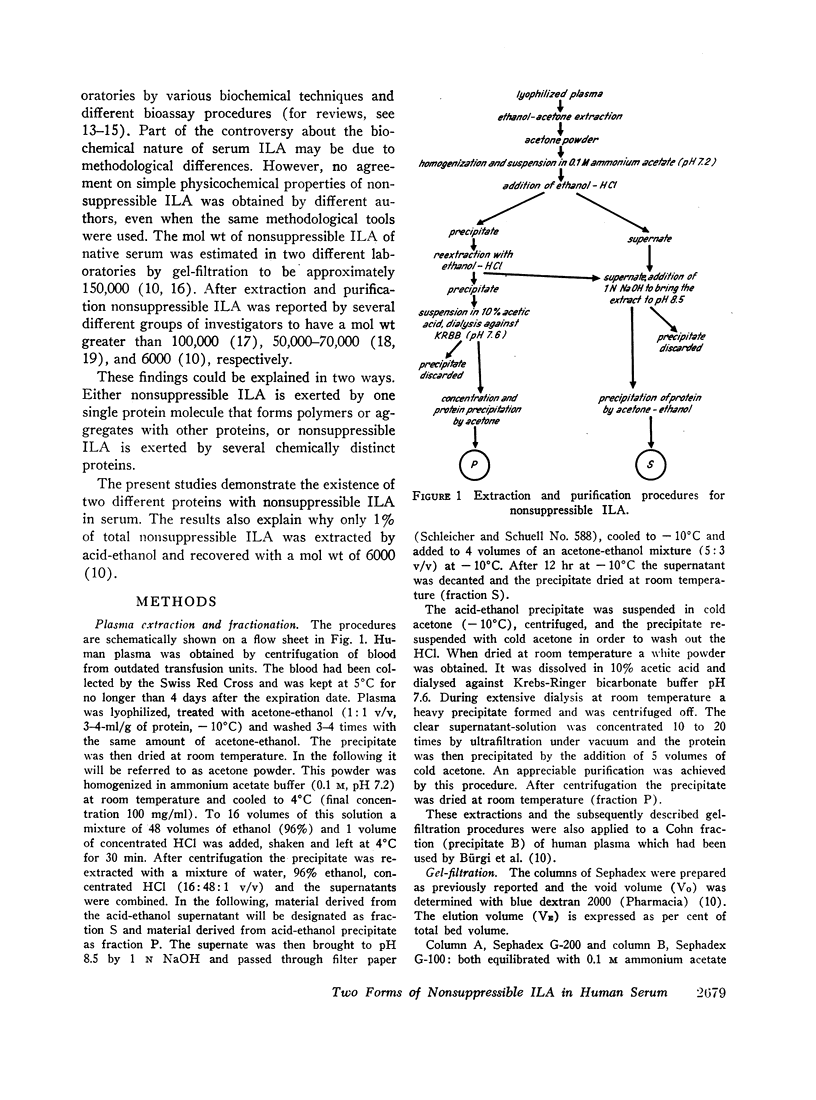
Full text
PDF
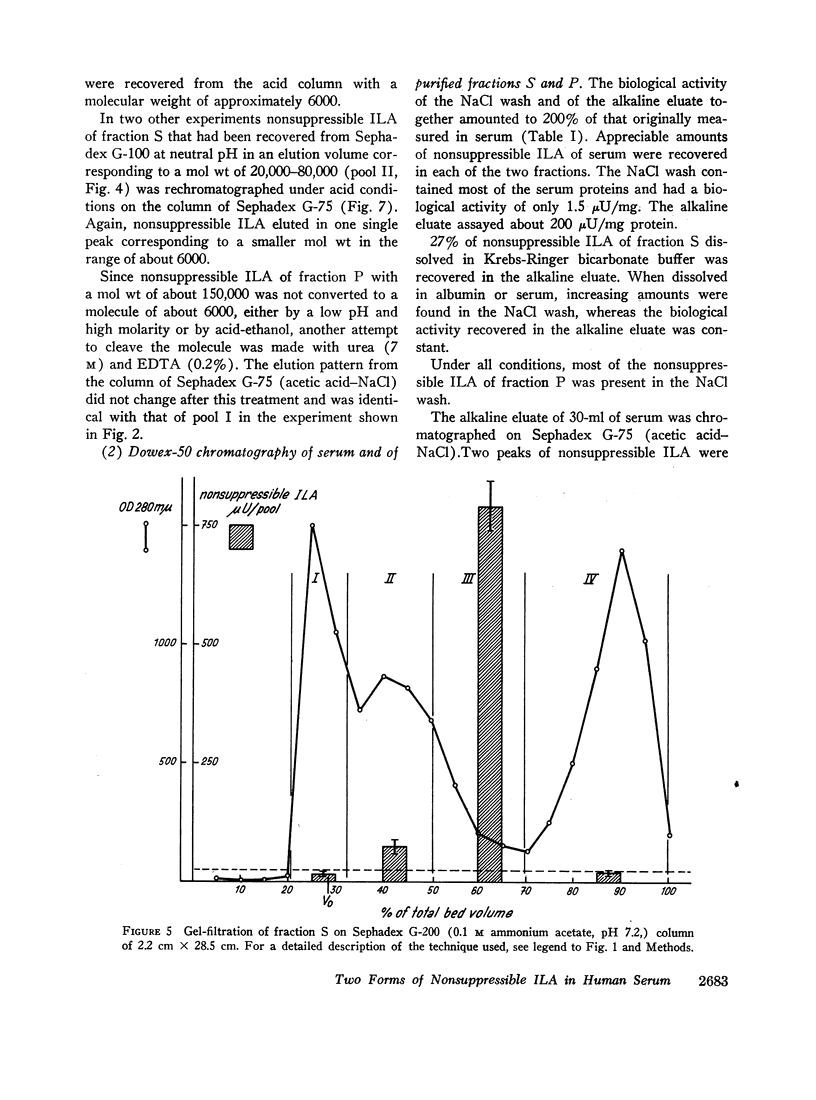
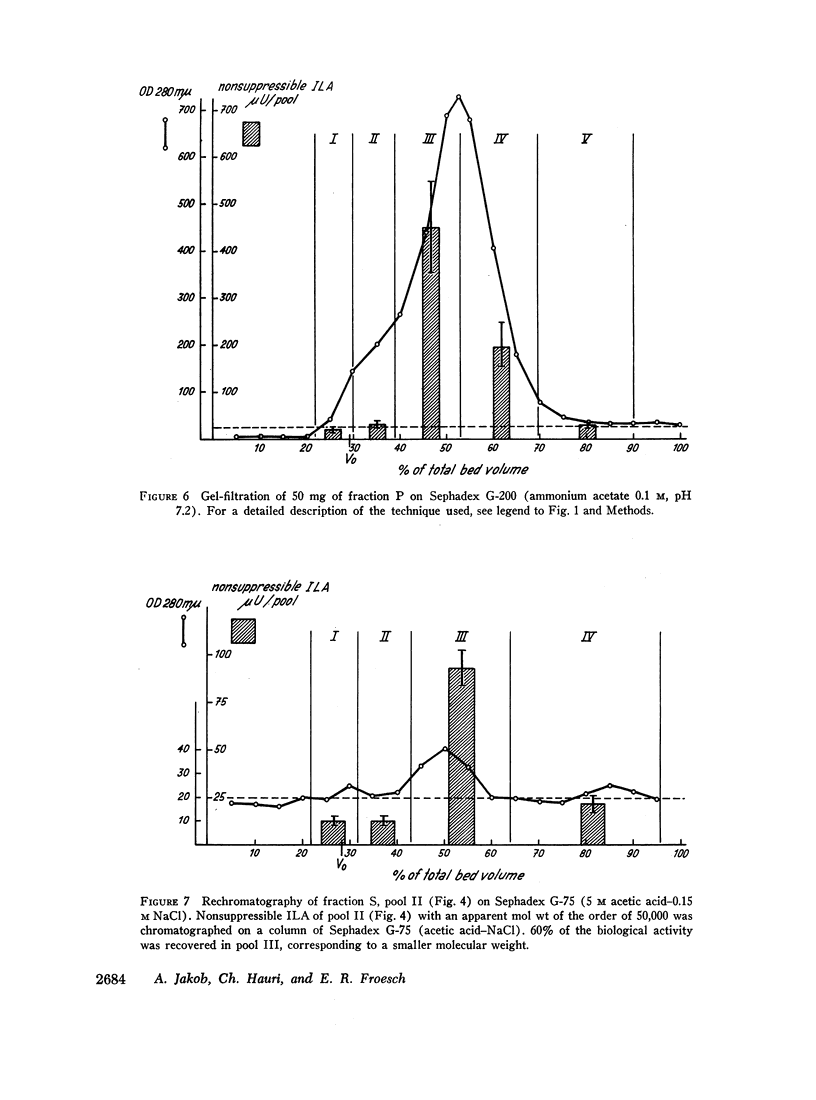
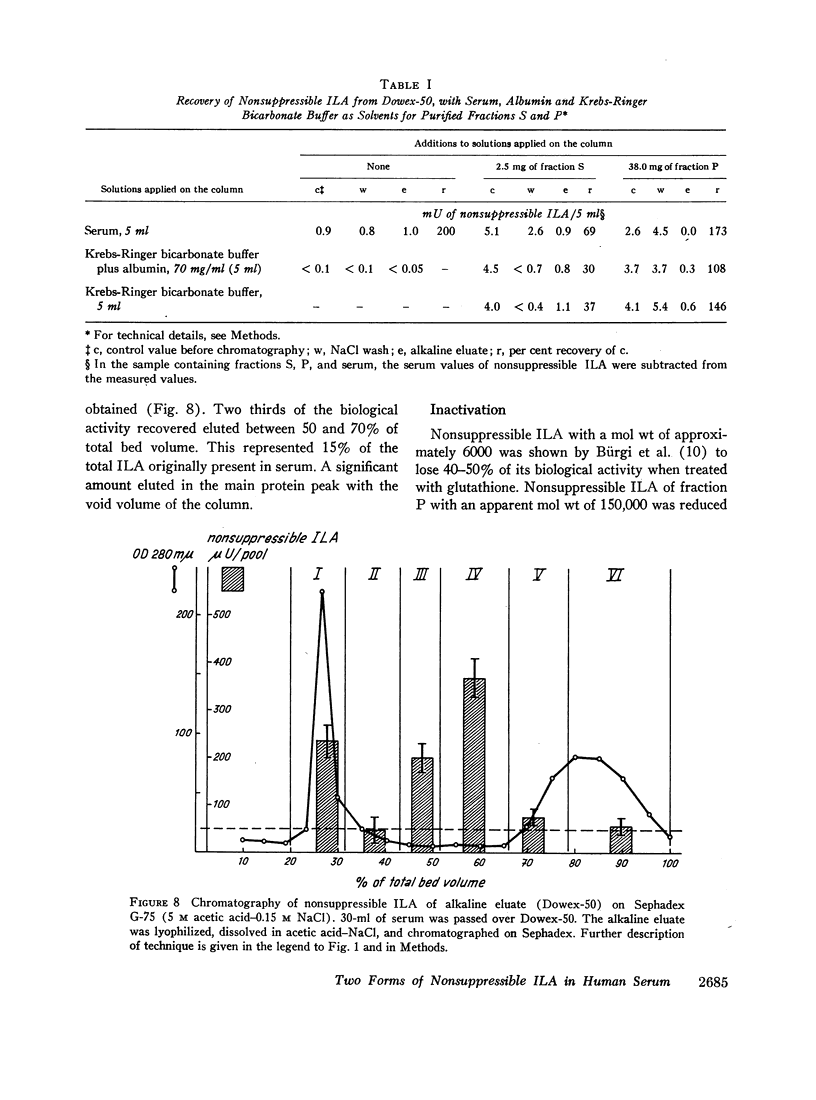



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONIADES H. N., HUBER A. M., BOSHELL B. R., SARAVIS C. A., GERSHOFF S. N. STUDIES ON THE STATE OF INSULIN IN BLOOD: PROPERTIES OF CIRCULATING "FREE" AND "BOUND" INSULIN. Endocrinology. 1965 Apr;76:709–721. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-4-709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor B. R. Insulin-like activity. Diabetes. 1967 Jun;16(6):418–434. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.6.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgi H., Müller W. A., Humbel R. E., Labhart A., Froesch E. R. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. I. Physicochemical properties, extraction and partial purification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., BUERGI H., RAMSEIER E. B., BALLY P., LABHART A. ANTIBODY-SUPPRESSIBLE AND NONSUPPRESSIBLE INSULIN-LIKE ACTIVITIES IN HUMAN SERUM AND THEIR PHYSIOLOGIC SIGNIFICANCE. AN INSULIN ASSAY WITH ADIPOSE TISSUE OF INCREASED PRECISION AND SPECIFICITY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1816–1834. doi: 10.1172/JCI104866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Bürgi H., Müller W. A., Humbel R. E., Jakob A., Labhart A. Nonsuppressible insulinlike activity of human serum: purification, physiochemical and biological properties and its relation to total serum ILA. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:565–616. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Müller W. A., Bürgi H., Waldvogel M., Labhart A. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. II. Biological properties of plasma extracts with non-suppressible insulin-like activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):360–374. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROEN J., KAMMINGA C. E., WILLEBRANDS A. F., BLICKMAN J. R. Evidence for the presence of insulin in blood serum; a method for an approximate determination of the insulin content of blood. J Clin Invest. 1952 Jan;31(1):97–106. doi: 10.1172/JCI102583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guevera L. B., Meek J. C., Bolinger R. E. Partial characterization of urine protein with insulin-like activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1049–1052. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARDS J. R., LANDAU B. R., BARTSCH G. Assay of insulin-like activity with rat epididymal fat pad. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Oct;60:552–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Quijada C., R-Candela J. L. Insulin and insulin-like activity in the bile of rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):209–212. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenbarger P. L., Ensinck J. W., Hepp D. K., Williams R. H. The nature of human serum insulin-like activity (ILA)P Characterization of ILA in serum and serum fractions obtained by acid-ethanol extraction and adsorption chromatography. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):301–320. doi: 10.1172/JCI105726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power L., Rojas G. R., Londono J. H. New evidence for islet-cell origin of insulin-like activity in serum. Lancet. 1967 May 27;1(7500):1123–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91705-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENOLD A. E., MARTIN D. B., DAGENAIS Y. M., STEINKE J., NICKERSON R. J., SHEPS M. C. Measurement of small quantities of insulin-like activity using rat adipose tissue. I. A proposed procedure. J Clin Invest. 1960 Sep;39:1487–1498. doi: 10.1172/JCI104168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E. A., Hampers C. L., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Diffusion of glucose, insulin, inulin, and Evans blue protein into thoracic duct lymph of man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):903–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI105596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMAAN N., FRASER R., DEMPSTER W. J. THE "TYPICAL" AND "ATYPICAL" FORMS OF SERUM INSULIN. Diabetes. 1963 Jul-Aug;12:339–348. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.4.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. S., Poffenbarger P. L., Hepp D. K., Fenster L. F., Ensinck J. W., Williams R. H. Quantitation and partial characterization of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in serum and tissue extracts of the rat. Endocrinology. 1967 Aug;81(2):213–225. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. H., Ensinck J. W. Secretion, fates and actions of insulin and related products. Diabetes. 1966 Sep;15(9):623–654. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.9.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


